Unit 2 - Dual Enrollment History
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
British Effects of the War
140 million pounds of debt, half from defending the colonies
Britain expected the colonies to trade with them exclusively and pay taxes to cover the cost of their protection. British Citizens paid an average of 26 shillings a year compared to 1 shilling by the colonists.
Pontiac’s Rebellion
Ottawa- after losing countries to play off of each other, Chef Pontiac killed 2000 Detroit Settlers trying to force out the British, the British retaliated with gifts of Small Pox-infected blankets from Fort Pitt
Royal Proclamation Line of 1763
Limited settlement west of the Appalachian Mountains to prevent Indian Wars
Daniel Boone
Migrated to Kentucky along with other Americans to the newly acquired land, believing they earned the land with their blood.
George Grenville
The Prime Minister attempted to control spending, enforced the Navigation Acts, and initiated taxation of the colonies.
Revenue/Sugar Act
Lowered the tax for raw sugar, molasses, and textiles (fabric or cloth), wine, coffee, and indigo, cost 4 times what it brought in.
Quartering Act
forced the colonists to provide homes for British Troops, either their own or build ones, mainly affected New York
Stamp Act
First direct tax, on printed materials, legal documents, British taxes for the same items were twice as high, led to cries of no taxation without representation, burdened the wealthier, better education
used for legal documents
Stamp Act Congress
to petition the king to repeal the Stamp Act, the first time the colonies worked together.
Movement began to boycott British goods.
Protests led to the Stamp Act being repealed
New York built a statue of George III
Parliament passed the Declaratory Act, giving Parliament the power to pass binding laws on the colonies in all cases.
Virtual Representation
Parliament represented all subjects of the British Empire
British Constitution
not a single document, Britain was under the King, Parliament, and English Law
Currency Act of 1764
Due to a shortage of British currency, the colonists printed their own money, but Parliament banned the printing of paper money, which caused a recession.
Charles Townshend
great orator, even when drunk, died shortly after passing his bills.
Townshend Act
The closure of the Massachusetts legislature led to increased smuggling.
Revenue Act
created Taxes on glass, lead, and paper
legalized search warrants called writs of assistance
Officials could seize property without due process
Sam Adams
Harvard Graduate (So a Christian)
Bankrupted Family Brewery
Founder of the Sons of Liberty and Massachusetts committees of correspondence.
Sons/Daughters of Liberty
Started in Boston
Protestors cried liberty, property, no stamps, tarred and feathered opponents
Boston Massacre
March 5, 1770- 60 Colonists surrounded 10 soldiers, 8 wounded, 5 dead
Britain repealed the Townshend Acts, defended by John Adams, 8 not guilty, 2 guility
Crispus Attucks
Runaway slave, who led the mod, died in the fighting
King George lll
British King from the Hanover family,
tried to show the power of the monarchy,
surrounded himself with yes men, including his prime minister Lord North, suffered from mental illness due to arsenic poisoning
Gaspee Incident (1772)
patrol ship for smugglers ran aground
Tthey took livestock and cut down trees for firewood
colonists seized and burned the British ship,with no witnesses
Committees of correspondence
statement of American rights
Intercolonial communications were initiated by Samuel Adams using the House of Burgesses as the model
formed the foundation for the Continental Congress
Tea Act
Parliament made British East India's tea cheaper to save the company Bostonites saw this as a trick to paying the tax and it hurt colonial tea companies
Boston Tea Party
Colonists dressed as Mohawk Indians dumped 342 chests into the harbor
Boston Port Act
closed Boston ports until damages were paid
Coercive Acts
violated the right to trial by a jury of one's peers and the right not to have troops quartered in one's home
Quebec Act
expanded Quebec
hurt colonial land spectaculars
Protected rights of the French Canadian citizens
Banned representative assemblies
First Continental Congress
Philadelphia, John Adams pushed for revolution, organized local and colonial boycotts, created the Association, a large stockpiling of weapons, Patrick Henry gave his "Give me Liberty or Give me Death" speech
Suffolk Resolves
urged colonists not to obey the Intolerable Acts, but stay loyal to the king, boycott,
The Association
pushed for a complete boycott of British goods, violators were tarred and feathered
John Hancock
made his fortune by smuggling
led the revolution stockpiled weapons for the Minutemen
Minutemen
Concord unit trained and ready to fight the British at a moment’s notice
Lexington & Concord
In 1775, British General Gage went to seize the weapons at Concord, Samuel Adams and John Hancock
British fought through Lexington, but were forced to retreat from Concord, “Shot heard ‘round the world”
Second Continental Congress
in 1775, named George Washington head of the Continental Army because he was from the largest state, he lacked experience in this level
Fort Ticonderoga
5/10/75- Ethan Allen and the Green Mountain Boys/Benedict Arnold seized the British garrisons and their supply of gunpowder and artillery that saved Boston, Allen later founded Vermont under the threat that his new land would join the British
Battle of Bunker Hill
stopped two British advances
the colonial militia retreated due to a lack of ammunition, actually at Breed's Hill, Howe, Clinton, & Burgoyne, 1054 British casualties, 400 colonial casualties
Olive Branch Petition
July 1775, the Continental Congress sent it to the king, stating loyalty, that King George refused to look at it so the Continental Congress started a postal system under Benjamin Franklin,
negotiated treaties with local Indian tribes, a Navy, and Marine Corps
Canada
Troops under Benedict Arnold marched to Quebec to make an alliance with French Canadians
Small pox and exhaustion exhaustion defeated them, 900 of his 1900 men were infected
Common Sense by Thomas Paine
Convinced many colonists call for independence
Declaration of Independence
issued by the fullContinental Congress on July 4, 1776
written by Jefferson, Franklin, Adams, Sherman, and Livingston,
listed the reasons for independence and a form of government described by John Locke
The Declaration of Independence has four parts:
Preamble (introduction)
Declaration of Natural Rights
List of Grievances Against the King
Resolution of Independence by the United States
The Declaration of Independence has four parts:
Montesquieu- separation of powers
John Locke and natural rights
Thomas Hobbes- social contracts, natural liberties, equality
Jean-Jacques Rousseau- social contract, everyone should participate
Republican Motherhood
women were keepers of the nation's conscience
they raised the children and held the future of the republic in their hands.
Battle of New York
32k British troops on 500 ships to confront Washington with 19k untrained troops
he escaped on Christmas day, crossing the Delaware River
Battle of Trenton
Washington captured 1,000
Hessians hung over from Christmas celebrations
Colonial Army
lacked unity, munitions, clothing, shoes, and a stable supply of food
1 in 12 reported for duty with a musket
Franklin proposed arming the army with bows and arrows, poorly trained troops,
British Army
Disobedience led to whippings
one American remarked that a troop was whipped 25 times after he died
more wild than colonists since they fought away from home
Hessians
German princes hired out their people to pay debts
one Prince had 74 children, mercenaries that served in many wars, 30,000 fought for the British in the Revolution
African Americans
5.000 fought for the Continental army
British Lord Dunmore issued a proclamation of freedom for slaves who served the British army
British evacuated 14,000 slaves to other colonies
Loyalists/Tories
100k or 20%, British party pro-king and loyal Americans, after the DOI imprisoned, tarred and feathered, hung. 80,000 fled, possessions were sold to pay for the war,, government officials, prominent merchants, landowners, and a few farmers.
Patriots, or Whigs
Party pro-Parliament
British did not want to fight family in colonies, planters, lawyers, merchants, urban workers
Apathists
Dugdale term for the 50% of population that didn't care one way or the other
eventually won over by Patriots
Native Americans
the majority fought with the British, believing they would stop encroachment on their land, the Iroquois fought on both sides
British Advantages
1. superior navy, army, munitions
2. Experienced officers and troops
3. Outnumbered the colonist
4. Had money
5. Native American Support
Colonial Advantages
1. Great Leadership
2. Strong Motivation
3. Guerilla Warfare
4. Fighting to protect homes
5. Only needed to not lose to win independence
Marquis de Lafayette
volunteered for the continental army, at 19
a general because of family connections, donated $200,000 of the money that they saved all of their life for the revolution.
British General William Howe
led the British Army
fought the Continental army and militias, win quickly or lose Parliament
British General John Burgoyne
actor/writer
moved slowly cutting down trees for a large caravan of officer wives
Arnold pursued him relentlessly
Battle of Brandywine Creek
Howe defeated Washington captured Philadelphia,
the Continental Congress escaped and Howe failed to destroy the Continental army
Valley Forge- 1777-8 - Baron von Steuben
German who trained and drilled Washington's troops into a fighting force with his experience in the Prussian army.
as many as 2,500 troops died in the poor conditions.
Enlistment bonus in 1777-$20 and 100 acres
Battle of Saratoga
10/17/1777, Arnold & Horatio Gates capture Burgoyne and his army, turning point of the war,
France recognizes the United States and sends troops, Howe resigns,
House of Commons of 1778
repealed Townshend Tea Act, Governorships, Navigation Act
restored pre independence here rights, colonists ignored
Benjamin Franklin
with John Adams secured an alliance with France following Saratoga
France provided 90% of the gunpowder.
2 ½ years before Saratoga, France alone supplied half the army and most the navy.
Treaty of Alliance
recognized U.S.
no peace without the other's consent
guarantee French Island possessions
Armed Neutrality
formed by Catherine the Great,
passive hostility toward Britain,
war was spread to South America, the Caribbean, and Asia,
United States military alliances and the Armed Neutrality forces helpega win the revolution
Comte de Rochambeau
French General arrived with 6,000 troops in Rhode Island,

George Rogers Clark
captured 3 British forts in the Ohio River Valley, giving it to the U.S.,
Clark massacred Indians to prove the British couldn't protect them
Daniel Boone
fights outnumbered 30 v 400 to a draw
shot twice
Captured twice
two sons dead, 1 brother, 2 brother in laws
John Paul Jones
9/23/1779
Scotsman volunteer, carried naval battles to the coast of Britain captured 17 British ships, captured a ship twice his size while he was sinking.
"I have a not yet begun to fight!"-spelled so correctly
Charleston, South Carolina
Captured by British General Clinton
5k troops and 400 canons captured
worst colonial defeat
Battle of King’s Mountain
turning point in the South
General Nathaniel Greene helped retake Georgia and South Carolina by attacking and retreating.
1780-81 U.S. Economy
State of the Union
currency so devalued that debts were promised to be repaid at 2.5 cents on the dollar
caused by the British counterfeit currency of the Colonial currency
Benedict Arnold
after receiving a wound and no credit for victories at Ticonderoga and Saratoga
Arnold agreed to turn West Point over to the British for £6,300 and a commission in the British Army
Alexander Hamilton
led an attack to capture key British defenses in the battle of Yorktown.
His men broke into song and wrote a
musical.
Yorktown
10/19/1781
in Virginia, Continental forces under Washington and French forces won a decisive battle and captured Cornwallis with his 7200 British troops, ending the war with Parliament agreement
Treaty of Paris of 1783
John Jay, John Adams, and Benjamin Franklin negotiated without France
1. Britain recognized U.S. Spain
2. Britain kept Canada, but gives Florida to
3. France gets back colonies. in Africa and Caribbean.
4. U.S. pay all debts to Britain and loyalists
Revolution Changes Society
Property holding was not a voting requirement.
Average people were in worse financial shape after the war.
Women
some served in the military, post war could obtain a divorce and education
Abigail Adams
Pushed for equality
African Americans
Many Northern states abolished slavery. 1000s obtained freedom.
Loyalists
along with former slaves, and Native allies 80k fled to other colonies
Virginia Statue for Religious Freedom
separation of church and state
all states banned a state tax for churches
State Governments
Before the first government
states made their own coins
raised armies and navies
had written state constitutions
required the annual election of state legislators
granted them state legislatures more power than governors
created weak executive and judicial branches
Articles of Confederation
The first U.S. government (1777-1781) with a weak unicameral Congress, no executive branch, state sovereignty, and equal representation. It lacked power to regulate commerce, required unanimous state agreement for changes, and ultimately failed due to its inherent weakness.
Confederation Congress
met just once a year with the power to declare war, raise armies, and sign treaties
Land Ordinance of
1785
sold land to pay off the national debts provisions for public school in each settlement
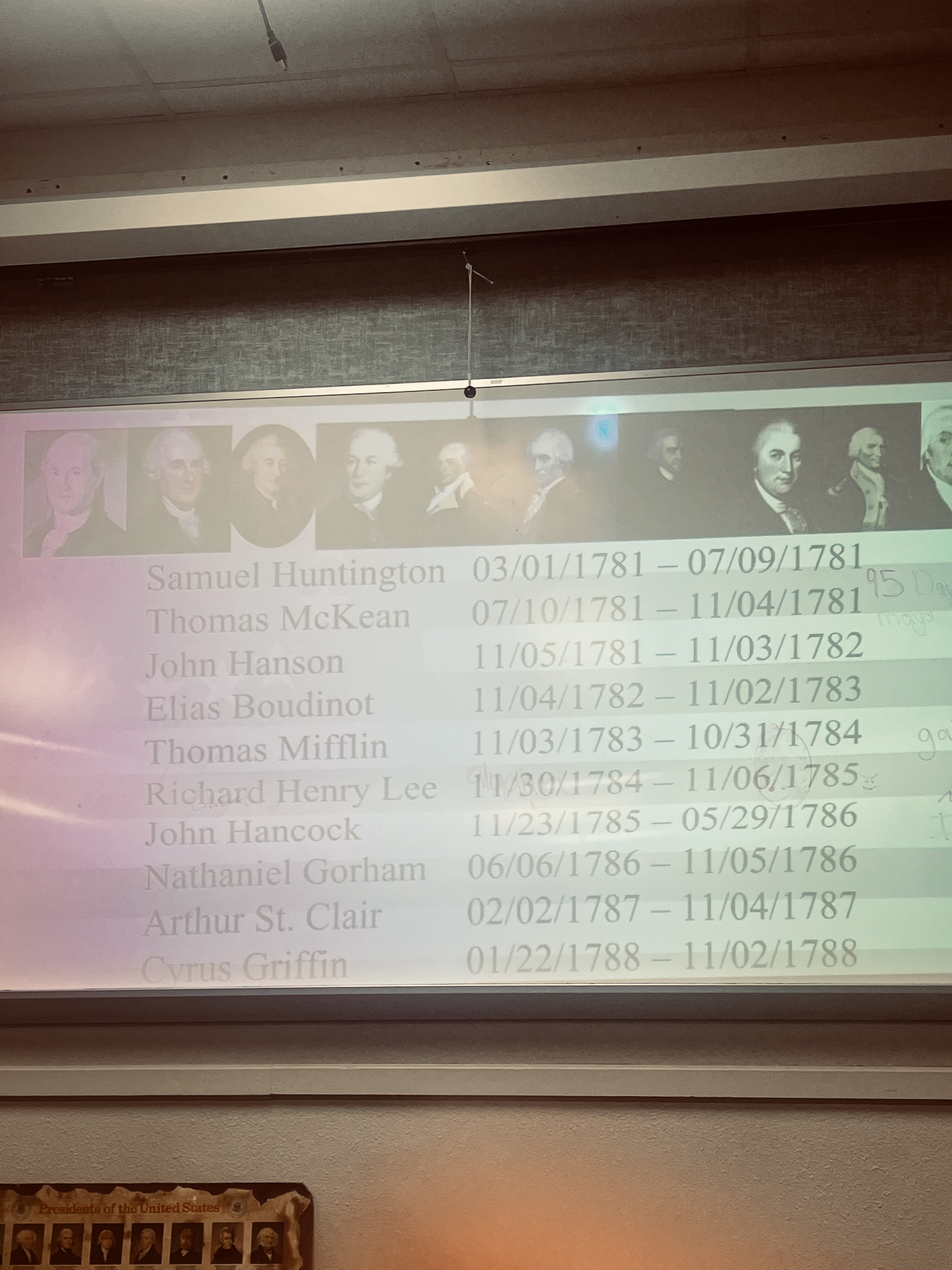
Northwest Ordinance of 1787
laws to govern territories, no slavery, still in use.
5,000 adult male landowners can elect territorial legislature
60,000 landowners Can elect delegates to a state constitutional convention
Shays' Rebellion
1786
Massachusetts raised taxes to pay debts instead of printing money
Daniel Shays went to a state arsenal to get weapons.
A government militia defended the arsenal.
This exposed the out problems of a weak central government
Causes of the Constitutional Convention
1. British merchants flooded U.S. markets with inexpensive goods.
2. government could not force the states to pay their debts to Britain or Loyalists.
3. Recession caused by end of the Revolutionary War
4. Shay's rebellion
5. control of commerce
Major goals of the Constitutional Convention
1. preserve the Union
or keep the states together
2. form a stronger national government
*only attended by wealthy Americans who met in secret
Virginia or large-state plan
a new government with three branches and two houses of Congress.
It benefited large states because representation reflected the population
New Jersey Plan
revised the Articles of Confederation to make the central government stronger.
Congress would have a single house with equal representation
Antifederalists
Sam Adams, Patrick Henry, states rights, small farms, poorer Americans, debtors, freedoms were stolen by a lack of a bill of rights
Federalists
George Washington, James Madison, and John Marshall, wanted a strong central government
Constitutional Convention
allowed the new government to be created with only nine of the thirteen colonies in agreement
James Madison
wrote the constitution, Father of the Constitution
Connecticut or Great Compromise
the House of Representatives would be based on population size, selected by voters it would present tax bills.
The Senate would have equal representation selected by state legislatures, or goats with legs.
Electoral College
system for electing the president
the candidate with the most votes in each state, gets all the votes for that state
the House decides with one vote per state if there was no majority.