3: Amino Acids
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
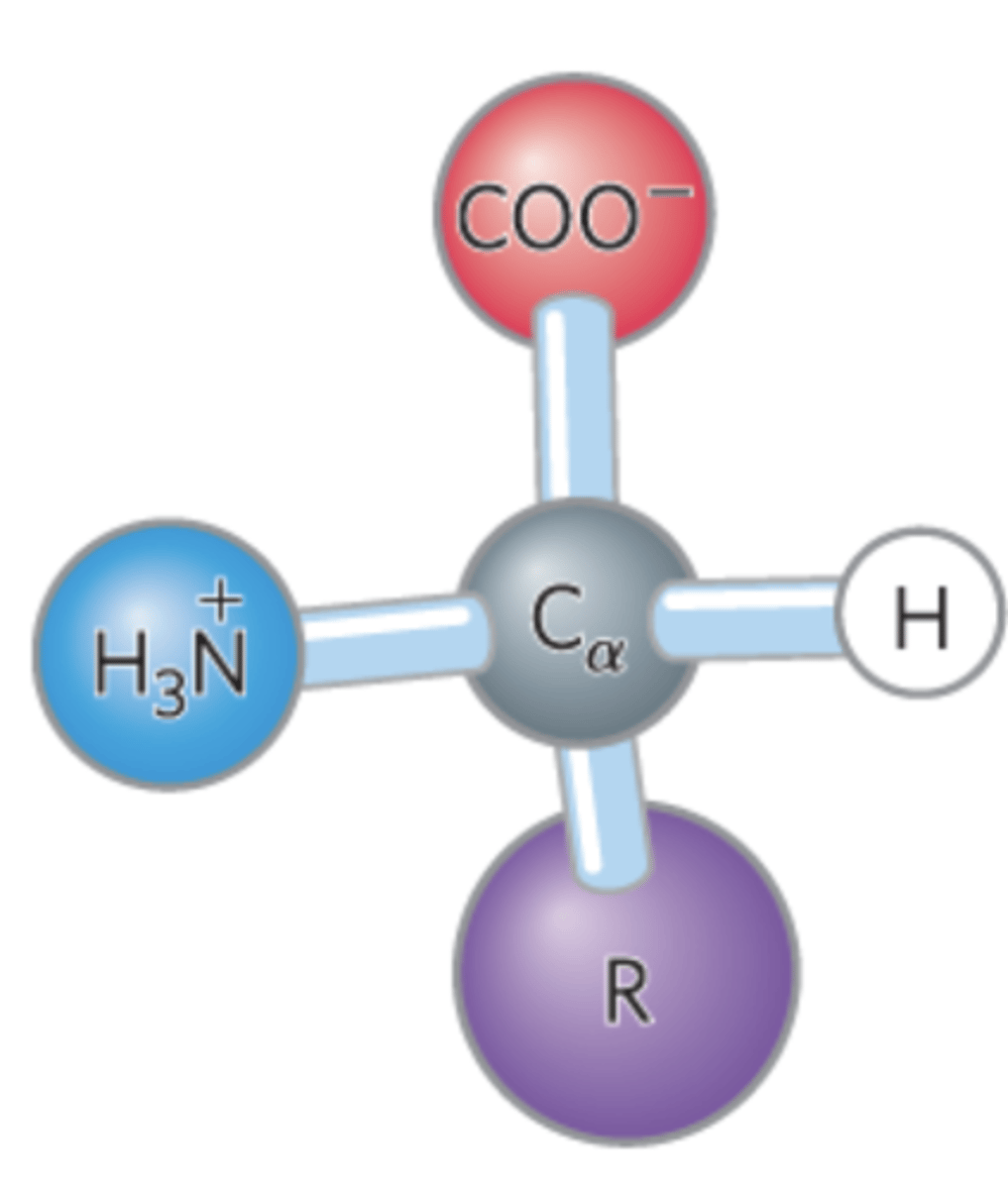
amino acids common structural features
- alpha carbon w/4 substituents
- alpha carbon is the chiral center
- read from N terminus to C terminus
- tetrahedral
- R group is different for each amino acid -> the characteristic
which amino acids is not chiral
Glycine -> R group is H
which amino acids are not tetrahedral?
proline
-> R group turns back on itself
most amino acids are (D/L)?
L -> bc most enzymes are L -> amino acids are recognized
all amino acids are L (S) except cystine which is R
classification of R groups
- nonpolar, aliphatic (7)
- aromatic (3)
- polar, uncharged (5)
- positively charged (3) -> histidine is partially charged
- negatively charged (2)
nonpolar, aliphatic R groups
- glycine, alanine, proline, valine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine
- hydrophobic effect stabilize protein structure
- proline -> folding -> due to hydrophobic and hydrogen bonding
small amino acids are more _______
commonly found -> easier to make
which amino acid has a -SH group?
cysteine -> can spins R
histidine pka is
R group pKa = 6 -> close the body pH -> easily protonates and deprotonates
N terminus pKa = 9 -> basic
C terminus pKa = 2 -> acidic
aromatic R groups
- phenylalanine (260nm), tyrosine (270nm), tryptophan (280nm)
- absorb UV light at 270-280nm
- can contribute to the hydrophobic effect
Polar, uncharged R groups
- serine, threonine, cysteine, asparagine, glutamine
- can form H bonds
- cysteine can form disulfide bond -> helps lock a protein in its place
positive charge R groups
- lysine, arginine, histidine
- have significant positive charge at pH 7
- arginine is found at inactive sites w/negative substrate
negatively charged R groups
- aspartate, glutamate
- net negative charge at pH 7
uncommon amino acids
- modifications of common aminos: (1) modified after protein synthesis; (2) modified during protein synthesis; (3) modified transiently to change protein's function
- free metabolites
amino acids can acts as ______
weak acids and bases
- zwitterion is at neutral pH
pI
- isoelectric point
- pH at which the net electric charge is zero
- pI = (pK1 + pK2)/2
- pH > pI -> net neg charge
- pH < pI -> neg pos charge
effect of chemical environment on pKa
- α-carboxyl group is more acidic than in carboxylic acids
- α-amino group is less basic than in amines
- so 2 buffer regions, one for α-carboxyl and other for α-amino groups
amino acids with ionizable side chains properties
- have pKa value
- act as buffers
- influence the pI of the amino acid
- can be titration -> 3 ionization steps -> α-amino, α-carboxyl, and R group (if possible)
- helps distinguish peptides
dipeptide
2 amino acids bonded together w/1 peptide bond
tripeptide
3 amino acids w/2 peptide bonds
oligopeptides
2-10 amino acids bonded
polypeptides
10-50 amino acids bonded
protein
50-100+ amino acids bonded
multisubunit proteins (aka aminomonomers)
2+ polypeptides associated noncovalently
oligomeric protein
at least 2 identical subunits
protomers
identical units
How to estimate the number of amino acid residues
- # of resides = molecular weight/110
- 110 comes from the average molecular weight of amino acids (~128) minus the water molecule removed (10)
conjugated proteins
- contain permanently associated chemical components
- prosthetic group : non-amino acid part
- lipoproteins : contain lipids
- glycoproteins : contain sugars
- metalloproteins : contain specific metals
proteins are separated based on ________
size, charge, binding properties, and solubility
how to purify proteins
1) break open tissue or cell
- crude extract : releases proteins in solution
2) fractionation : separate proteins into fractions based on size or charge; uses salt to selectively precipitate proteins
3) dialysis : use semipermeable membrane to separate proteins from small solutes
column chromatography
- uses buffered solution (mobile) to migrate through porous solid material. the buffered solution w/proteins migrates through the solid phase. the rate of migration highlights the different proteins
- can separate based off sign and magnitude of net charge, size, and binding affinity to a solution
which amino acid is not tetrahedral?
proline and its derivatives -> due to folding back to the amino group
n terminus pKa is around
9
c terminus pKa is around
2 or 4 (if bonded w/peptide bonds)
overall charge of a polypeptide is _____
the net charge of the amino acids at pH ~7.4
need to look at the R groups and if it is charged or not
what amino acids are hydrophobic?
alanine, isoleucine, leucine, phenylalanine, proline, and valine
basically the nonpolar ones
what amino acids are hydrophillic?
glycine, arginine, asparagine, aspartic acid, cysteine, glutamic acid, glutamine, histidine, serine, and threonine
notice how they are polar
what amino acids are amphipathics?
lysine, methionine, tryptophan, and tyrosine
What drives protein folding?
- hydrophobicity
- notice that hydrophobicity -> decrease entropy -> however increase H bonding potential via folding -> dH < 0 -> enthalpy driven rxn to make dG < 0
which amino acids can H bond w/h2o?
those with -OH or -S- or -SH
which amino acids are negative at pH 7?
those with COO- -> aspartate and glutamate
which amino acids are positive at pH 7?
those with NH3 + -> histidine (kinda of), lysine, and arginine
why do we use R/S instead of D/L?
R/S is used bc some amino acids have 2 chiral centers, so we can use R/S system to name the amino unambiguously
what are the essential amino acids
arginine, histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalnine, threonine, tryptophan and valine
what are the nonessential amino acids
alanine, asparagine, aspartate, cysteine, glutamate, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine and tyrosine
what is special about tyrosine
our body just modifies phenylalanine (essential) so we dont produce tyrosine from start to finish like other nonessential amino acids
what makes an amino acid essential?
- our bodies can not make the amino -> must be obtained from diet
- this is due to large amount of synthesis steps -> usually the bigger sized ones
- since we need to get nonessential aminos from a diet they are not frequently in proteins
covalent modification
- post-translational
- convalently modifies an amino acid in a protein (aka a side chain)
- on/off switches
common covalent modifications
phosphorylation (most) , acetylation , and methylation (least)
phosphorylation
- adds -PO3 2-
- usually on S, T, Y, H
- ex hormone receptors and regulator enzymes
- kinases : removes the phosphate from the ATP and add it to the amino
- phosphatases : removes the phosphate group
- add a negative charge
Acetylation
- adds COCH3
- usually on K
- ex histones and metabolic enzymes
- uses Acetyl-CoA
- acetylases : adds the acetyl
- deacetylases : removes the acetyl
- adds a negative charge -> neutralizes positive charges -> usually lysine
methylation
- adds -CH3
- usually on K, R
- ex histones
- uses methyl donors (SAM)
- methylases : adds the methyl group
- demethylases : removes the methyl group
- does not add any charges -> no neutralization of positive charges
GFP
- green fluorescent protein
- in jellyfish
- auto-modifies the protein -> no enzymes needs
- requires oxygen
- used to tag any protein
Amino acid UV absorption
Phe < Tyr < Trp
260 < 270 < 280
- these absorption of uv light is what makes these amino acids responsible for inherent fluorescence of proteins
beer lambert's law
A = Ecl
- used to determine protein concentration