Chemical Makeup of Cells (E1) Bio
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
The reactivity of an atom is dependent on what?
The outer shell (valence)
Ionic bond
When atoms exchange electrons to fill their valence shell, forming ions.
Covalent bond
Atoms can fill their valence shell by sharing electrons
Carbon
Biomolecules consist of mostly what?
Molecular Formula
Lists # of each atom

Structural Formula
Shows bonding pattern
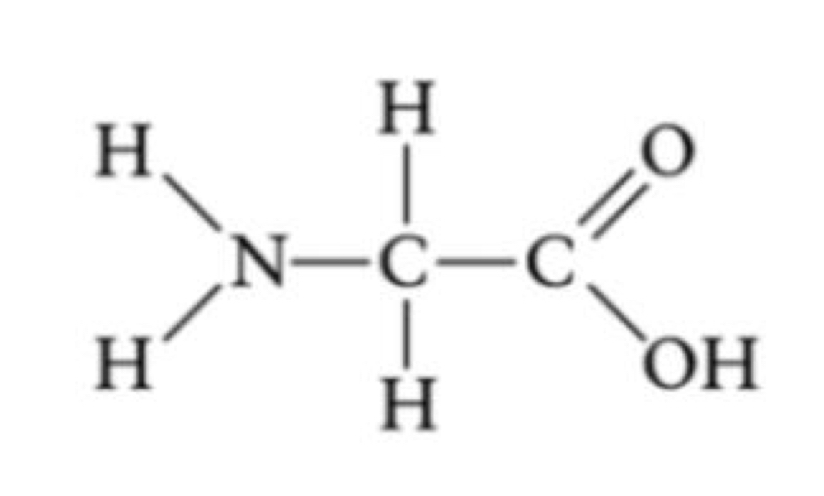
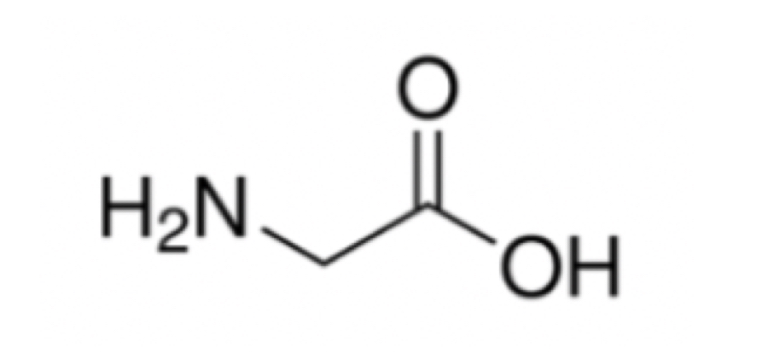
Line-Angle Formula
Short-hand structural formula. Hydrogens bonded to carbon are not drawn
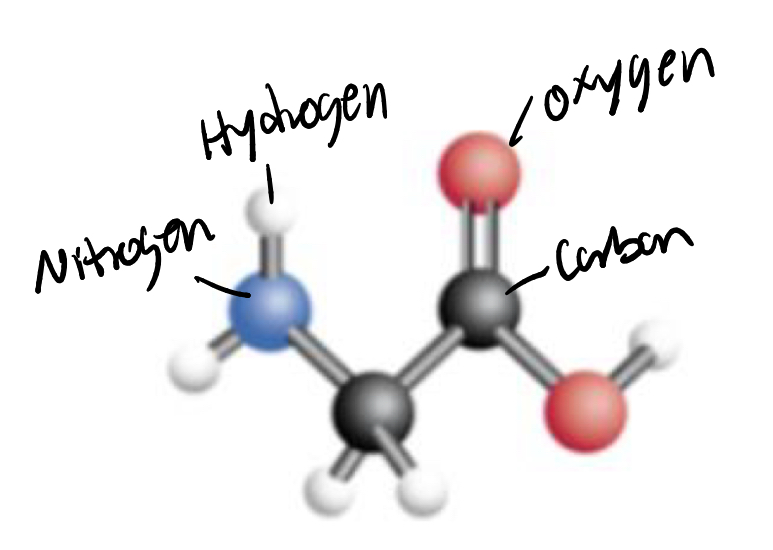
Ball-Stick Model
The visual bonding in 3D space
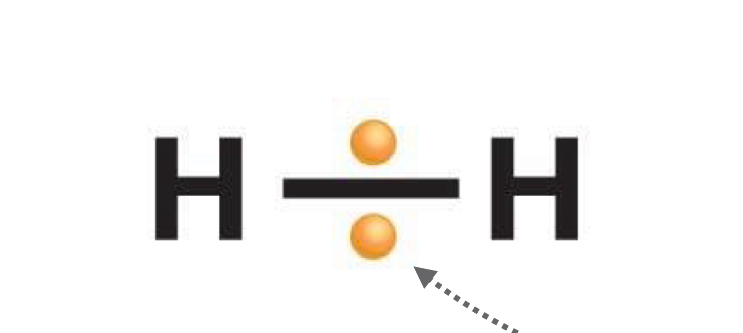
Nonpolar covalent bond
Shared pair of electrons that spend equal time together
Polar covalent bond
One atom pulls more force (non-equal sharing)
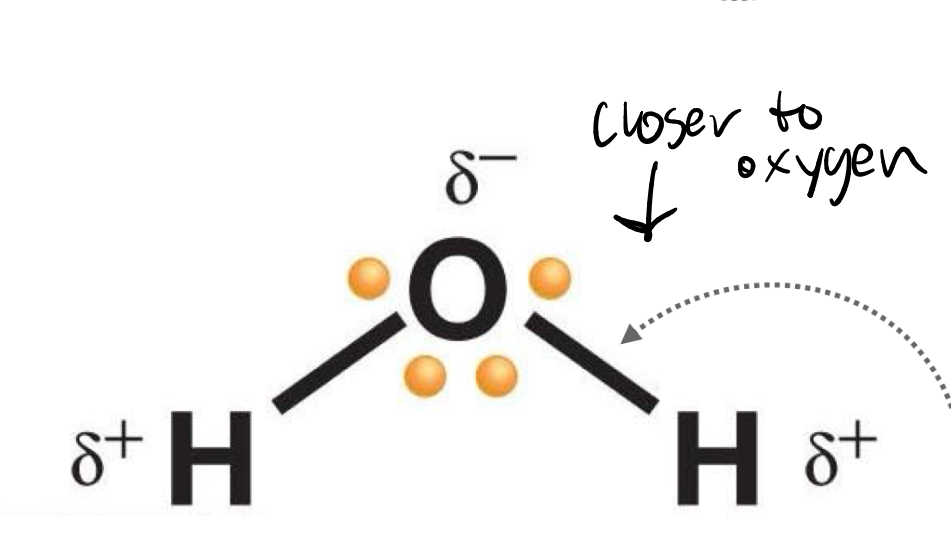
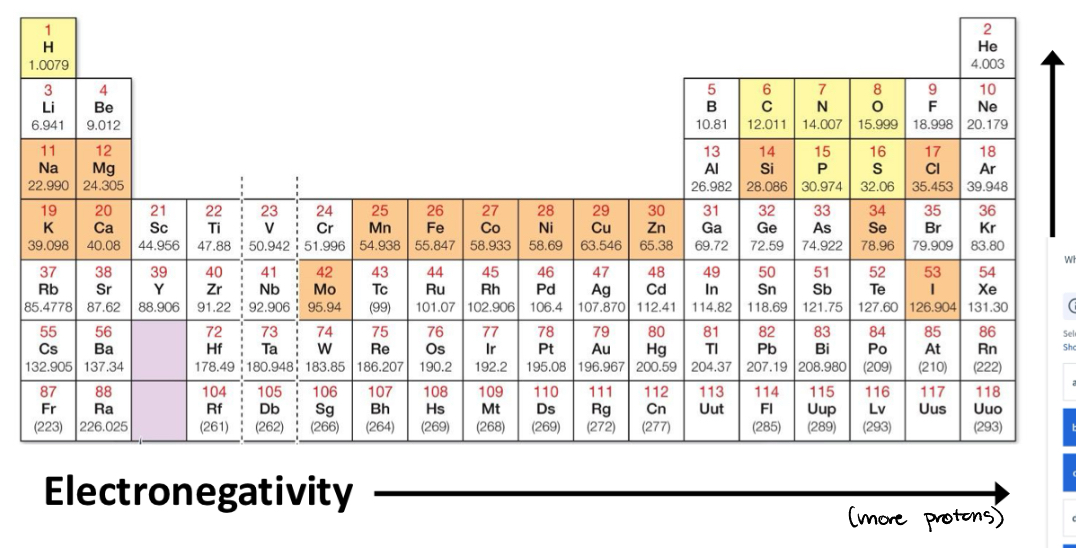
Electronegativity
Covalent bond polarity is dependent on differences in ____
Covalent bonds are a form of ___
Energy
What is Bond Energy?
The amount of energy needed to break a covalent bond. Measure of strength.
What is the bond energy and potential energy of a Nonpolar bond?
Lower bond energy, Higher potential energy (electrons are less stable)
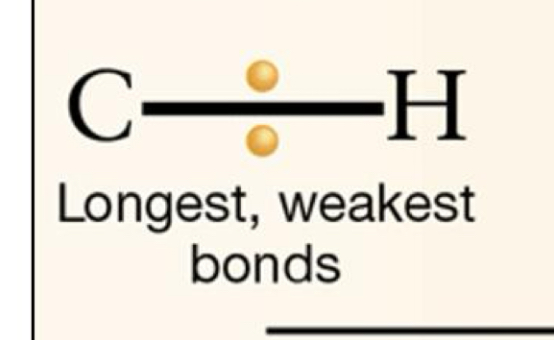
What is the bond energy and potential energy of a polar bond?
Higher bond energy (more energy needed to break), Lower potential energy (electrons are more stable)
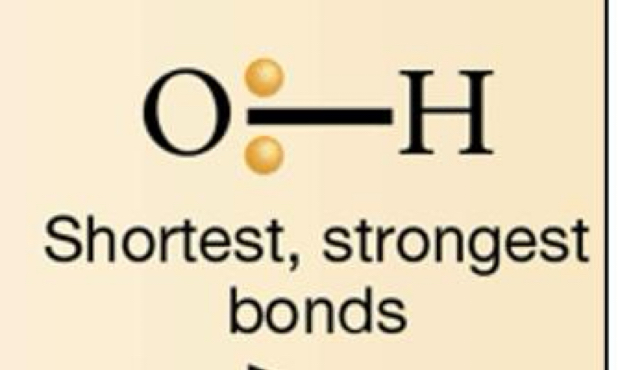
Non-polar C-H bonds
Cells capture energy from organic molecules that contain many ____ bonds. ___ = MORE POTENTIAL ENERGY
Hydrogen bond
Electrical attraction between a covalently bonded H atom and an electronegative atom
Hydrophobic interaction
Interaction of non-polar substances in the presence of polar substances (especially water)
van der Waals interaction
Interaction of electrons of non-polar substances (short & weak)
Polar Molecules are ____ : they dissolve in H2O because they can form hydrogen bonds with water
Hydrophilic
Nonpolar molecules are _____: they’re repelled by water because they cannot form hydrogen bonds with water
Hydrophobic
Ions are polar and dissolve in water through ___ interactions
Ion-dipole
Nonpolar molecules that cannot hydrogen bonds separate water through _______
Hydrophobic Exclusion
Hydrophobic molecules in water interact with each other through _____ interactions
Van der Waals
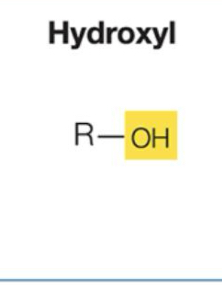
What are Hydroxyl properties?
Polar, forms hydrogen bonds with water.
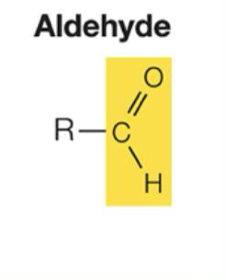
What are Aldehyde properties?
Polar. C=O group is very reactive. Important in building molecules and in energy- releasing reactions.
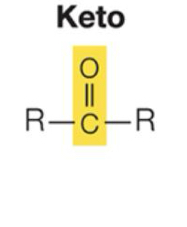
What are Keto properties?
Polar. C==O group is important in carbohydrate and in energy reactions.
Monosaccharides contain what type of functional group?
Polar groups : Aldehyde, Ketone.
Monosaccharides form ___ structures in aqueous solutions
Cyclic
Alpha Orientation of Monosaccharides
H on top, OH (Hydroxl) on bottom
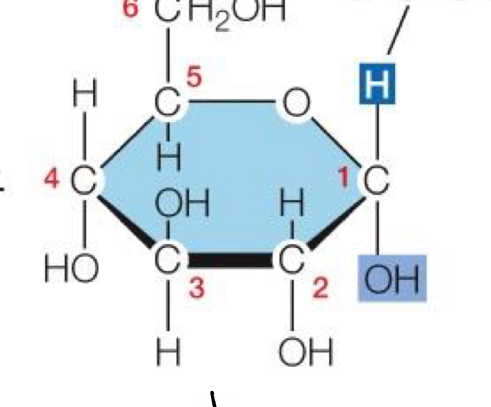
Beta Orientation in Monosaccharide
OH (Hydroxl) pointing up, H pointing down
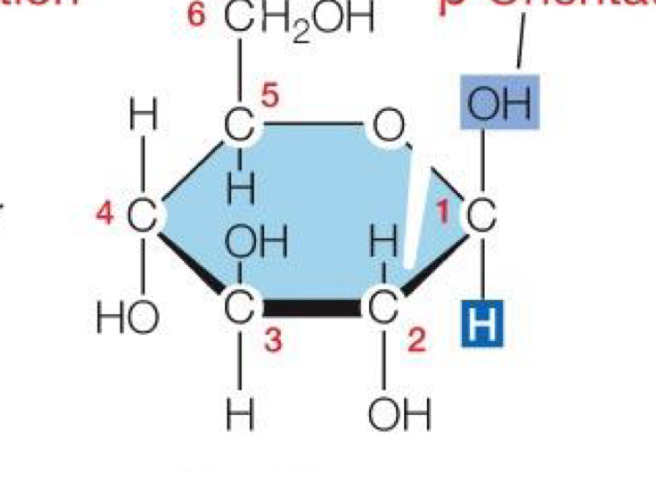
How are disaccharides formed?
Monosaccharides linked by a condensation reaction
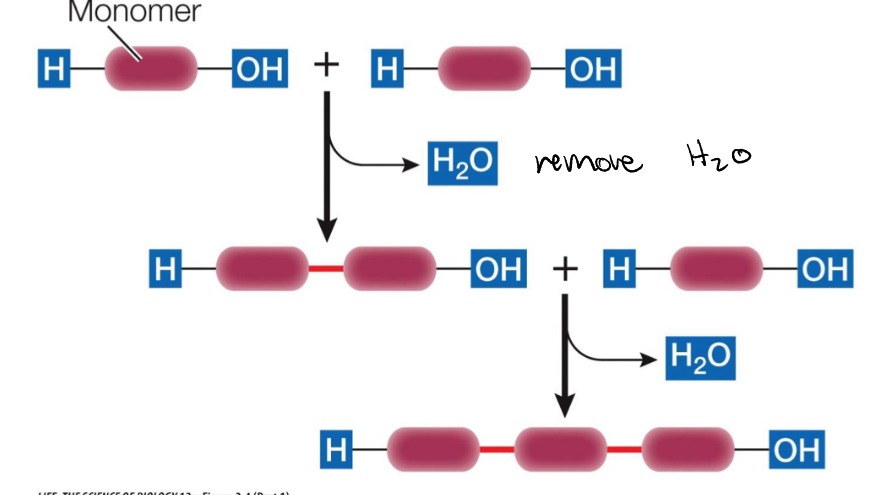
Glycosidic linkage (single oxygen bond)
A condensation reaction builds a ____ between monosaccharides
Disaccharides are broken down through ____ reactions
Hydrolysis
Different glycosidic linkages require different ____ for hydrolysis
Enzymes (ex. Sucrase, Lactase)
Monosaccharides can be linked together to form _____
Polysaccharides (starch, glycogen , cellulose)