Liver Sonography
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
Define : bare area
The region of the liver not covered by the peritoneum.
Define : couinaud classification
System used to separate the liver into 8 surgical segments, used to describe functional liver anatomy.
Define : falciform ligament
Ligament that attaches the liver to the anterior abdominal wall.
Define : gastroesophageal junction (GEJ)
The junction between the stomach & esophagus.
Define : glisson capsule
The thin fibrous casing of the liver.
Define : hepatic
Liver
Define : hemopoiesis
The formation & development of blood cells.
Define : hepatopetal
Blood flow toward the liver.
Define : hepatofugal
Blood flow away from the liver.
Define : kupffer cells
Specialized macrophages within the liver that engulf pathogens & damaged cells.
Define : ligamentum of teres
Ligament that forms part of the edge of the falciform ligament, connecting the liver to the umbilicus, a remnant of the LT umbilical vein aka round ligament.
Define : ligamentum venosum
Remnant of the fetal ductus venosus; appears as a hyperechoic linear ligament between the caudate lobe & the LT lobe of the liver.
Define : low-resistance (hepatic artery)
A flow pattern that characteristically has antegrade flow throughout the cardiac cycle.
Define : porta hepatis
The area of the liver where the portal vein & hepatic artery enter and the hepatic duct exit, also referred to as the liver hilum.
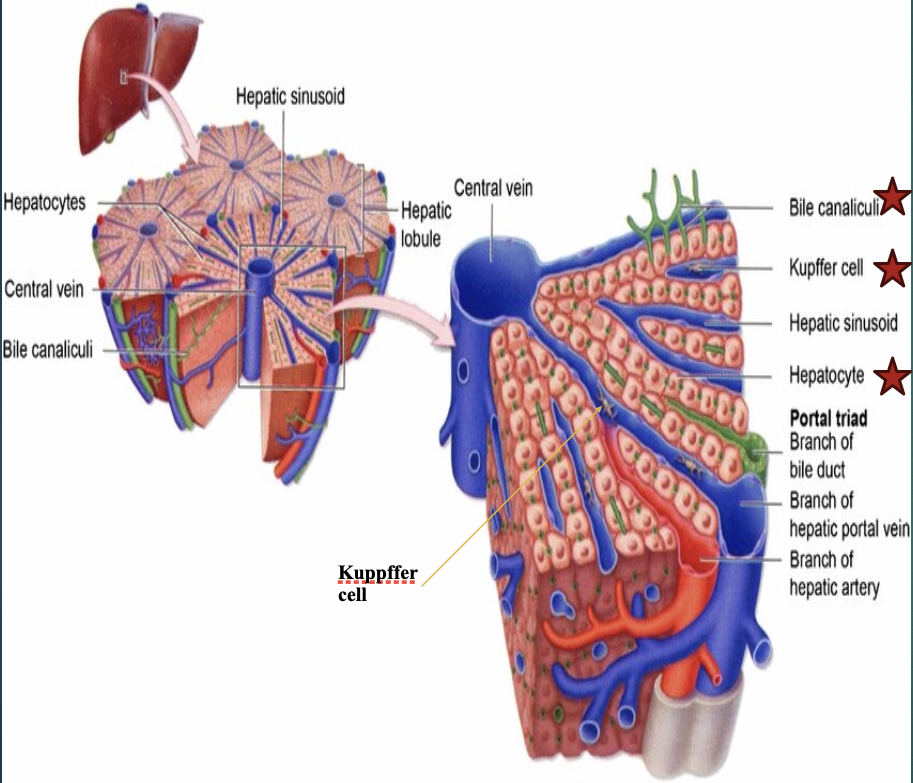
Define : portal triads
An assembly of a small branch of the portal vein, bile duct, & hepatic artery (which enter the porta hepatis) that surround each liver lobule (they are throughout the entire liver).
Define : quadrate lobe
The medial segment of the LT lobe of the liver.
Define : reidel lobe
A tongue-like extension of the RT hepatic lobe.
Define : situs inversus
A condition in which the organs of the abdomen & chest are on the opposite sides of the body.
Define : triphasic (multiphasic)
Vascular flow yielding 3 phases.
List the indications for a liver US.
Jaundice
Screening for hepatic disease in at-risk population
Abnormal liver function tests
Evaluation of focal liver lesions detected on other imaging modalities
Assessment of liver size in patients with hepatomegaly
Assessment of portal venous system & bile ducts in patients with possible obstruction
Guiding biopsies or therapeutic interventions
Words that end in “-ase” = what?
Enzymes
List the liver function tests that end in “-ase”.
ALP (alkaline phosphatase)
ALT (alkaline aminotransferase)
AST (aspartate aminotransferase)
LDH (lactate dehydrogenase)
Gamma-glutamyl transferase
List the liver function tests without “-ase”.
Albumin
Serum bilirubin
PT (prothrombin)
AFP (alpha-fetaprotein)
T or F : The liver parenchyma is made of 50,000 - 100,000 individual lobules.
True
Each liver lobule has how many corners?
6
Fill in the blanks :
Each liver lobule contains branches of the _____ _____, _____ _____, & _____ _____.
Portal vein; hepatic artery; bile duct
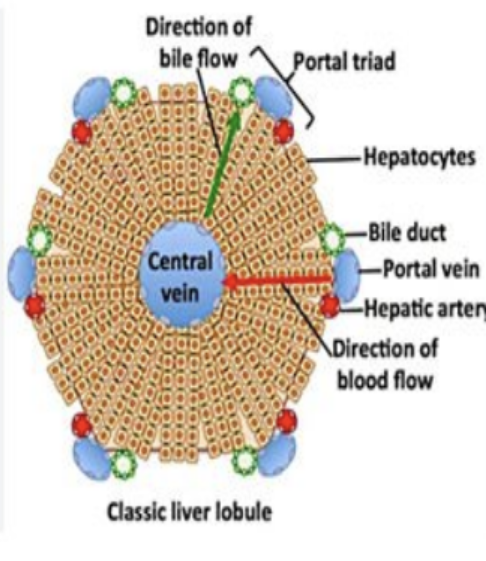
The portal triad is made up of?
The portal vein, hepatic artery, & bile duct.
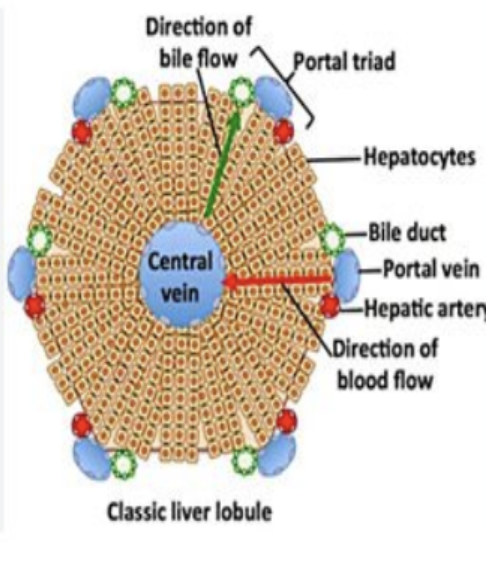
The 3 main cells in the liver parenchyma are?
Hepatocytes, biliary epithelial cells, & kupffer cells.
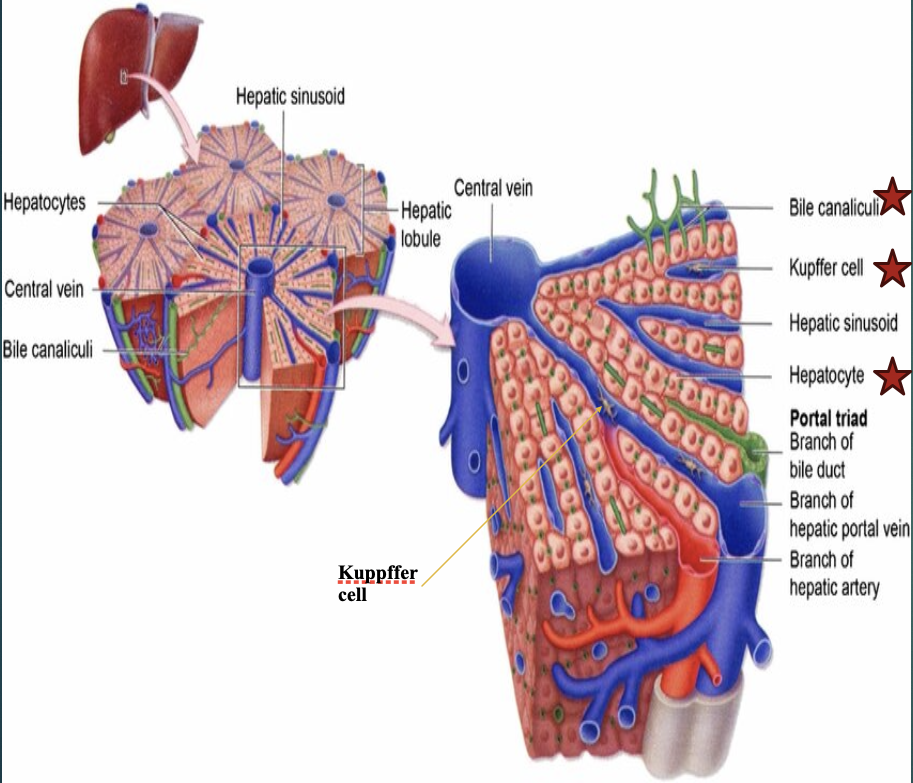
Which of the 3 main cells in the liver parenchyma are the most abundant cells & have metabolic functions?
Hepatocytes
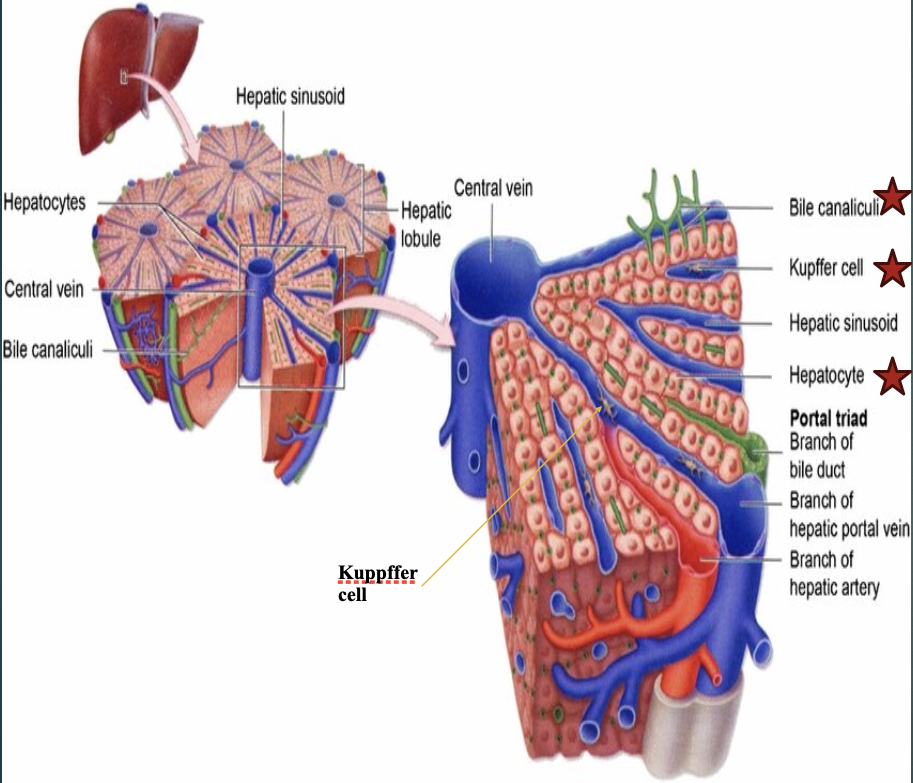
Which of the 3 main cells in the liver parenchyma line the biliary system?
Biliary epithelial cells
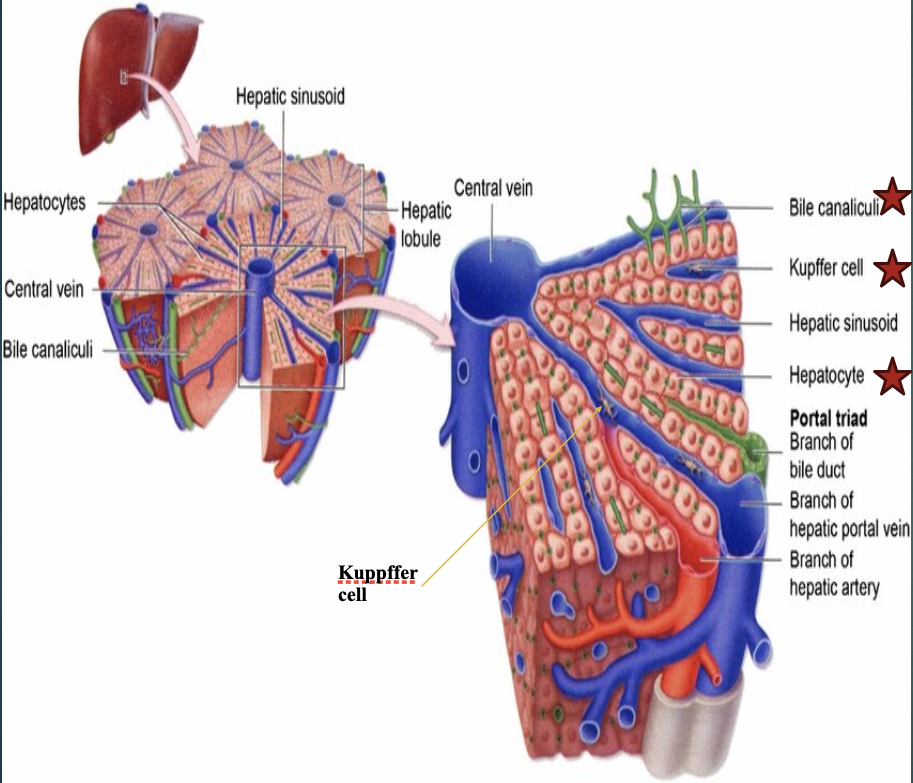
Which of the 3 main cells in the liver parenchyma are phagocytic & part of the reticuloendothelial system?
Kupffer cells
What is the reticuloendothelial system (RES)?
Network of cells primarily involved in phagocytosis, the process of engulfing & removing pathogens, cellular debris, & foreign particles.
The reticuloendothelial system is aka?
Mononuclear phagocyte system
Which system is a crucial part of the body’s immune system acting as a first line of defense against invaders & helping to maintain homeostasis?
The reticuloendothelial system.
T or F : The liver is the largest organ in the body?
True
Which lobe of the liver makes up the bulk of the whole organ? And which region is it in?
RT lobe; RUQ
How many vital functions have been identified in the liver?
More than 500.
List the vital functions of the liver (11).
Carbohydrate metabolism
Fat (lipid) metabolism
Amino acid metabolism
Removal of waste products
Vitamin & mineral storage
Drug inactivation
Synthesis & secretion of bile
Blood reservoir
Lymph production
Detoxification
Production of certain proteins for blood plasma
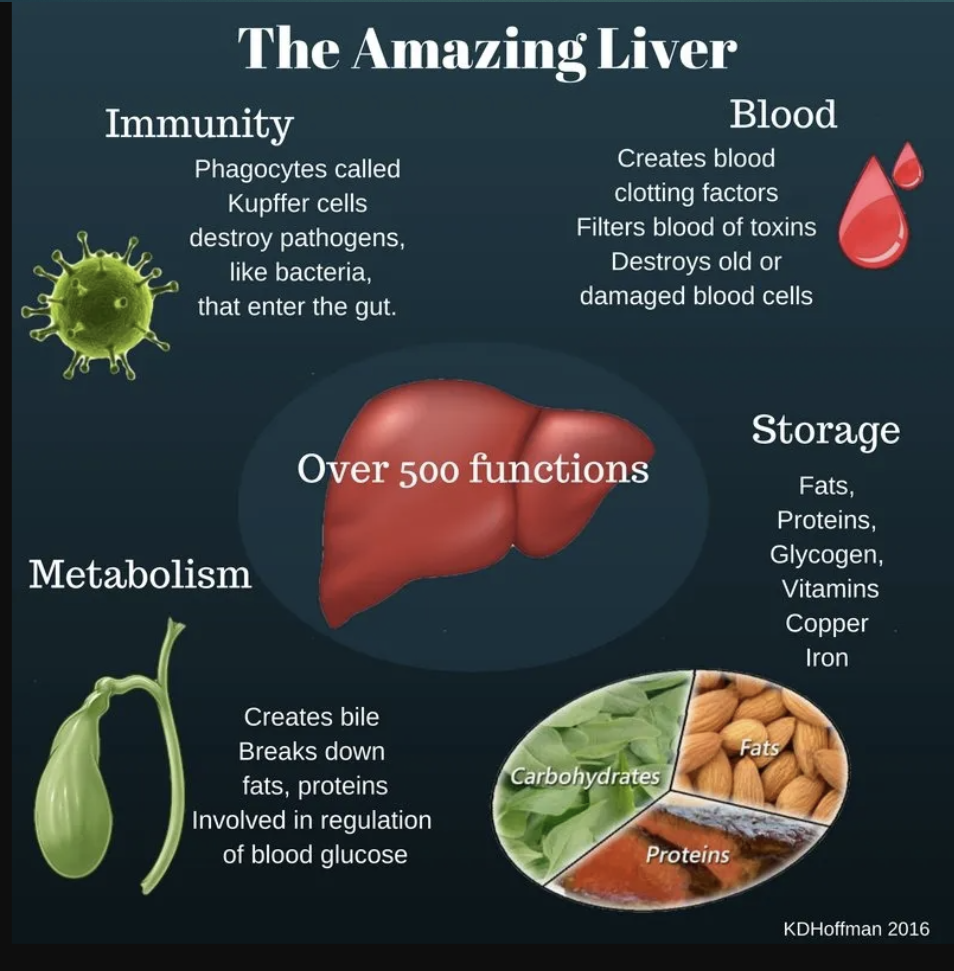
T or F : The liver is responsible for hemopoiesis.
True
The capsule of the liver is called?
Glisson Capsule
Glisson Capsule contains what?
Blood, lymphatics, vessels, & nerves.
How does Glisson Capsule appear on US?
Highly echogenic.
The portal triad is house in where?
Glisson Capsule
The bare area of the liver is the area of the? (4)
Falciform ligament, gallbladder fossa, porta hepatis, & area adjacent to IVC.
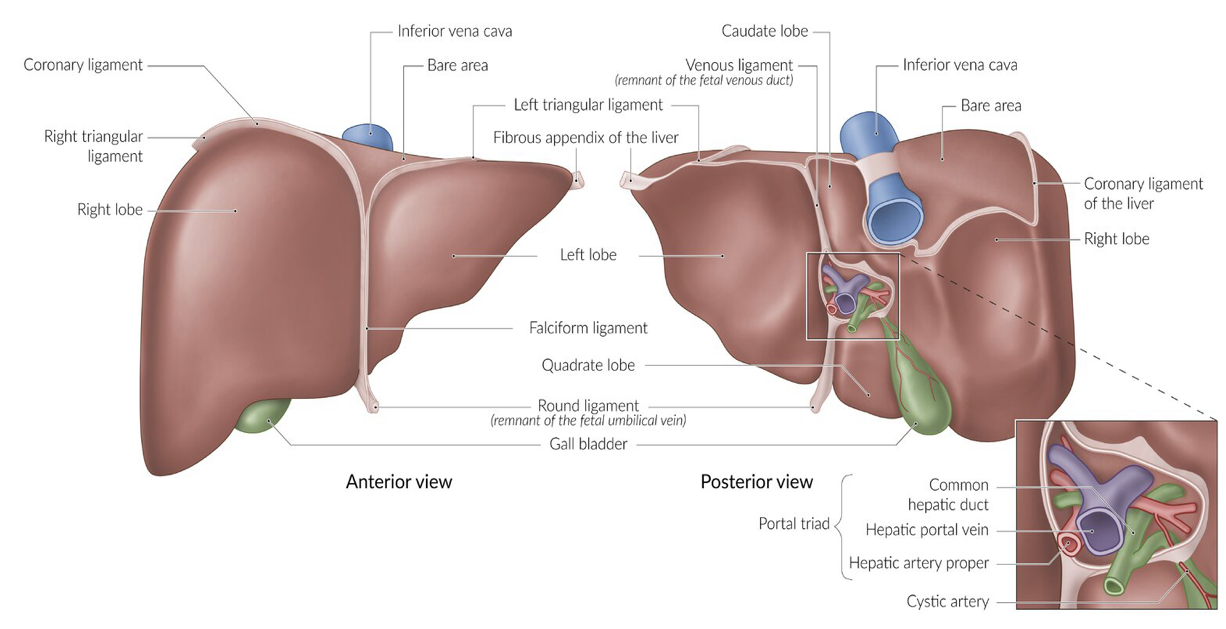
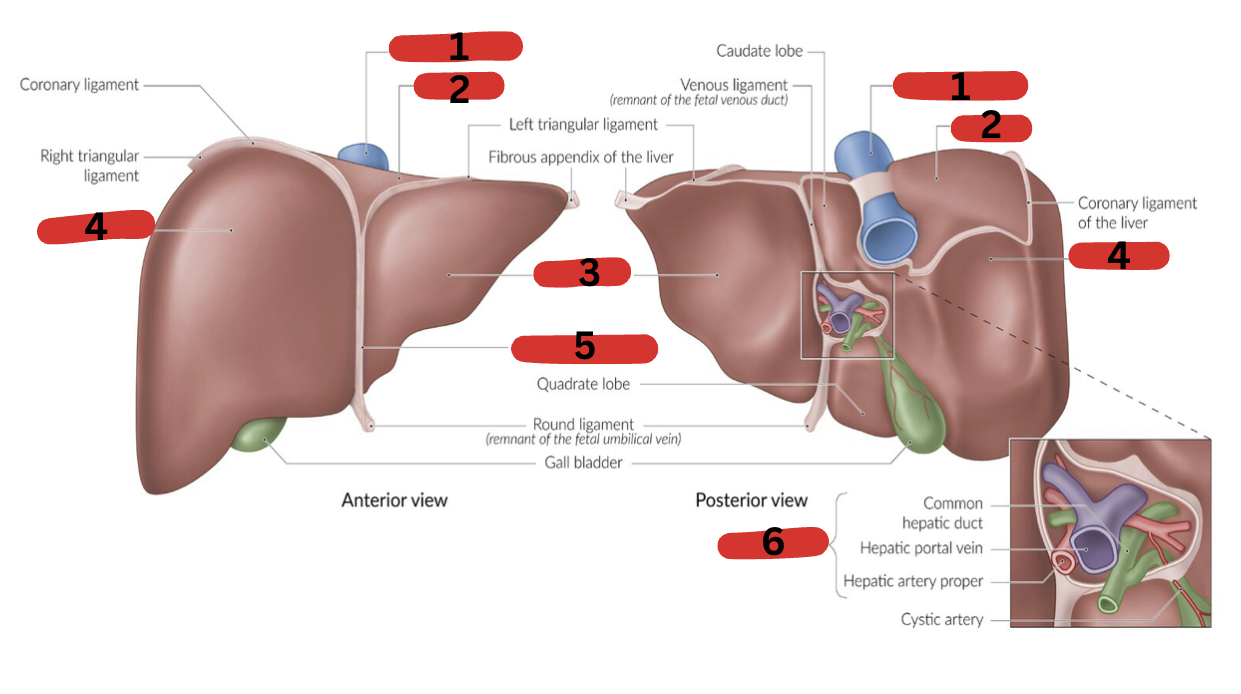
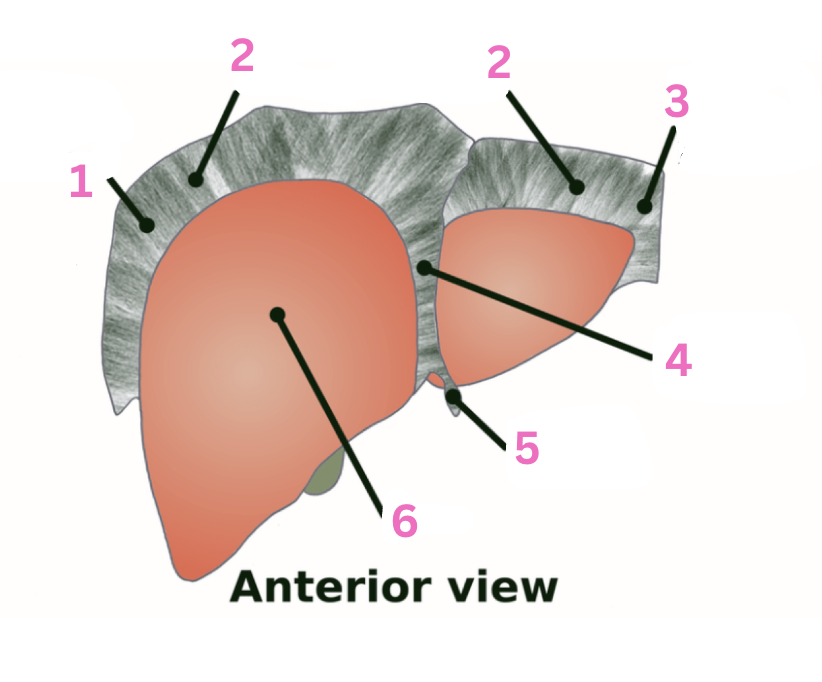
What is 1?
IVC
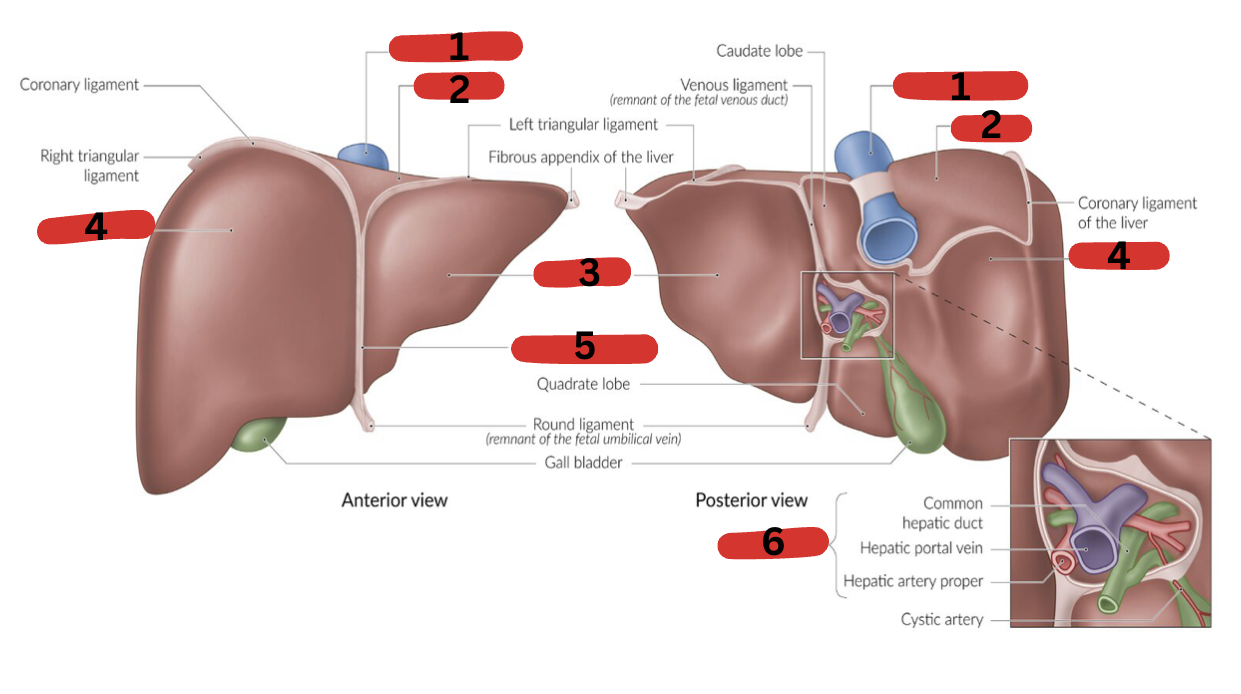
What is 2?
Bare area
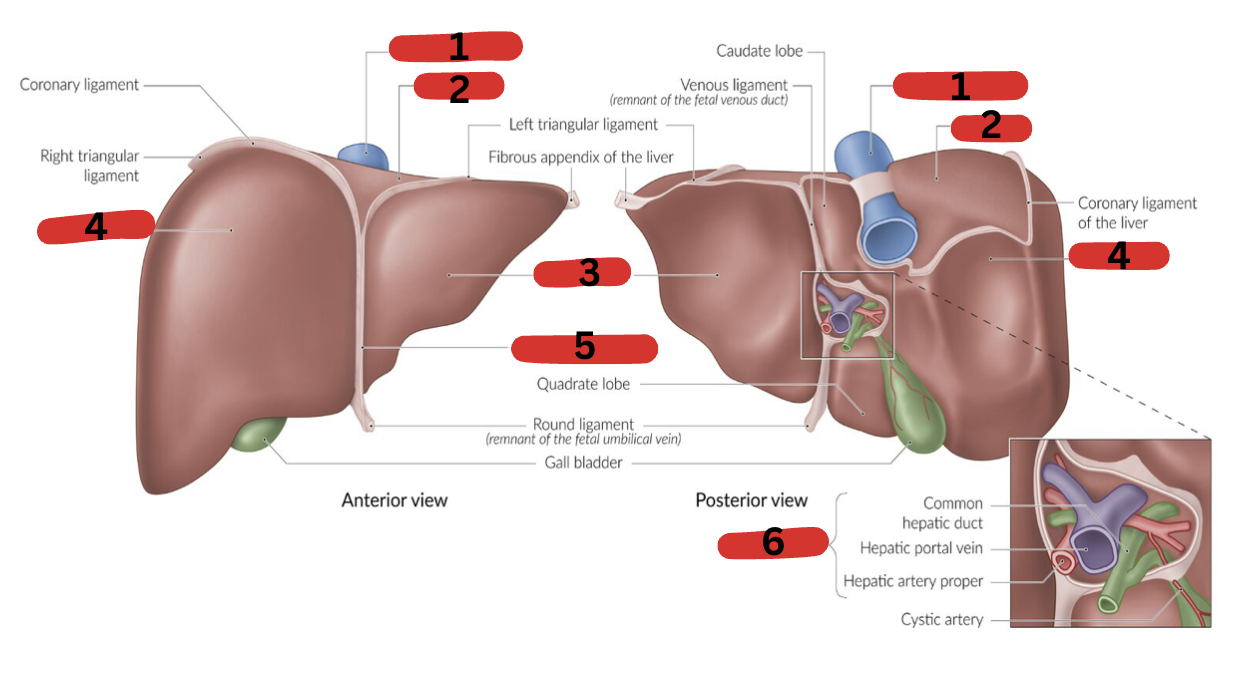
What is 3?
LT lobe
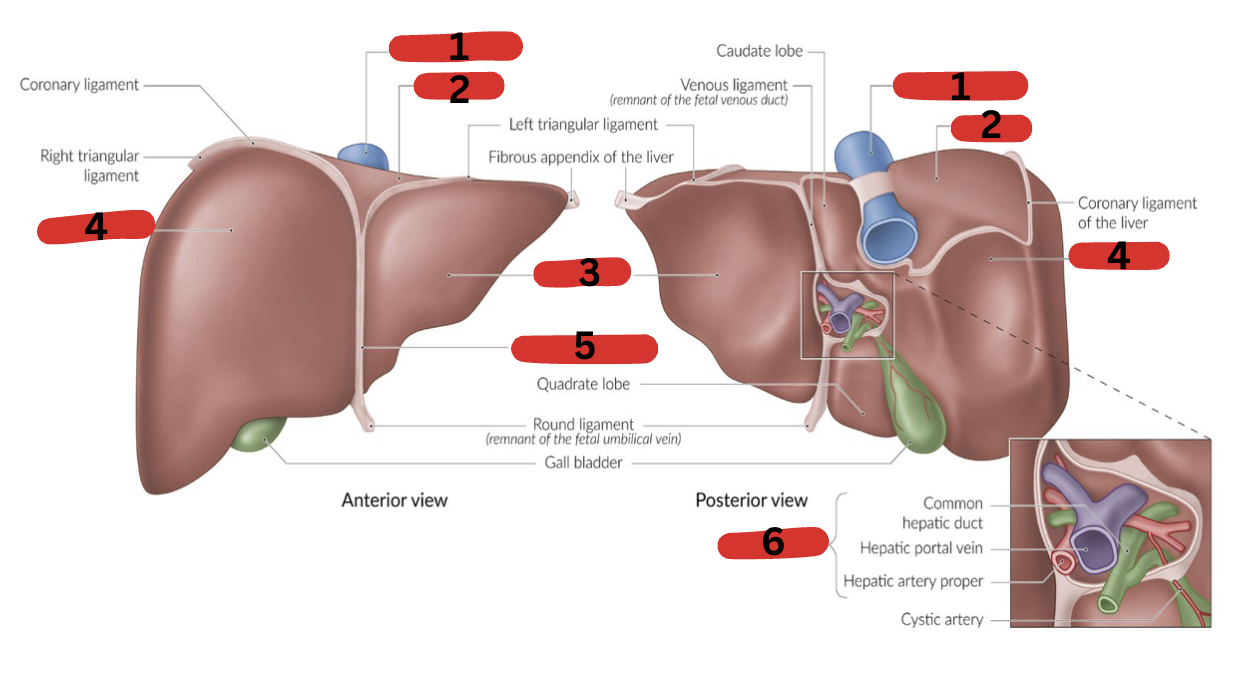
What is 4?
RT lobe
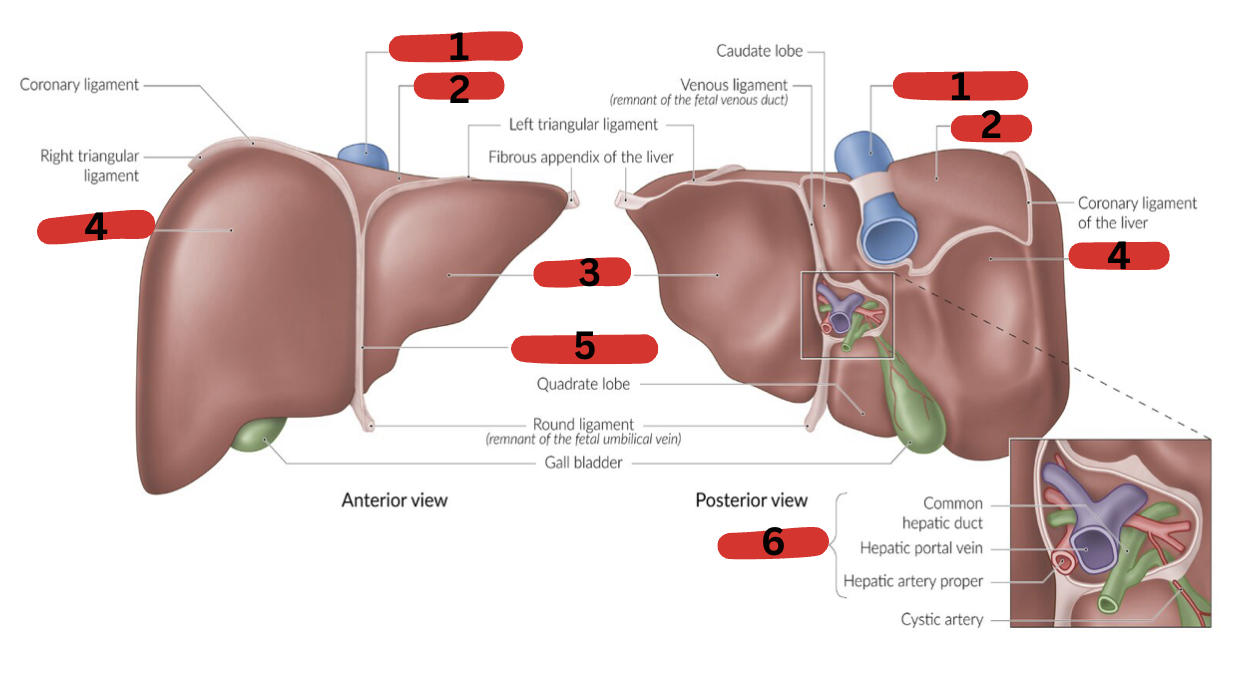
What is 5?
Falciform ligament
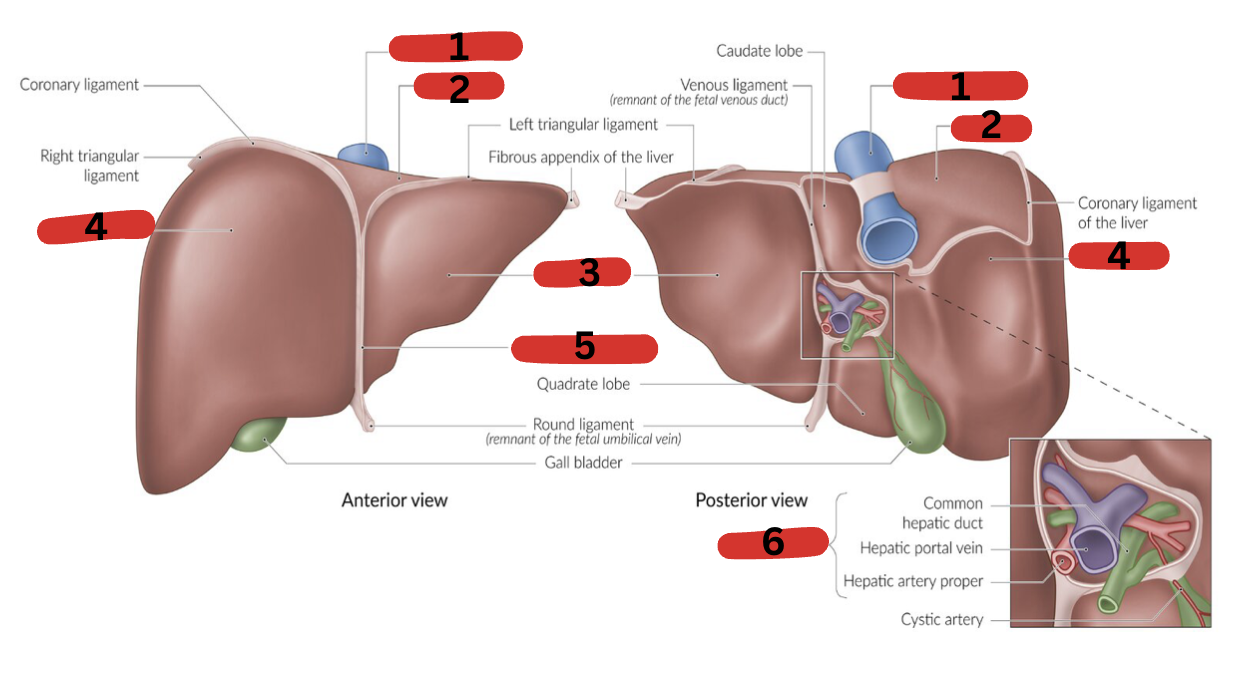
What is 6?
Portal triad
What is the normal measurement of the liver?
< 16 cm (13-15 cm) in the midclavicular line
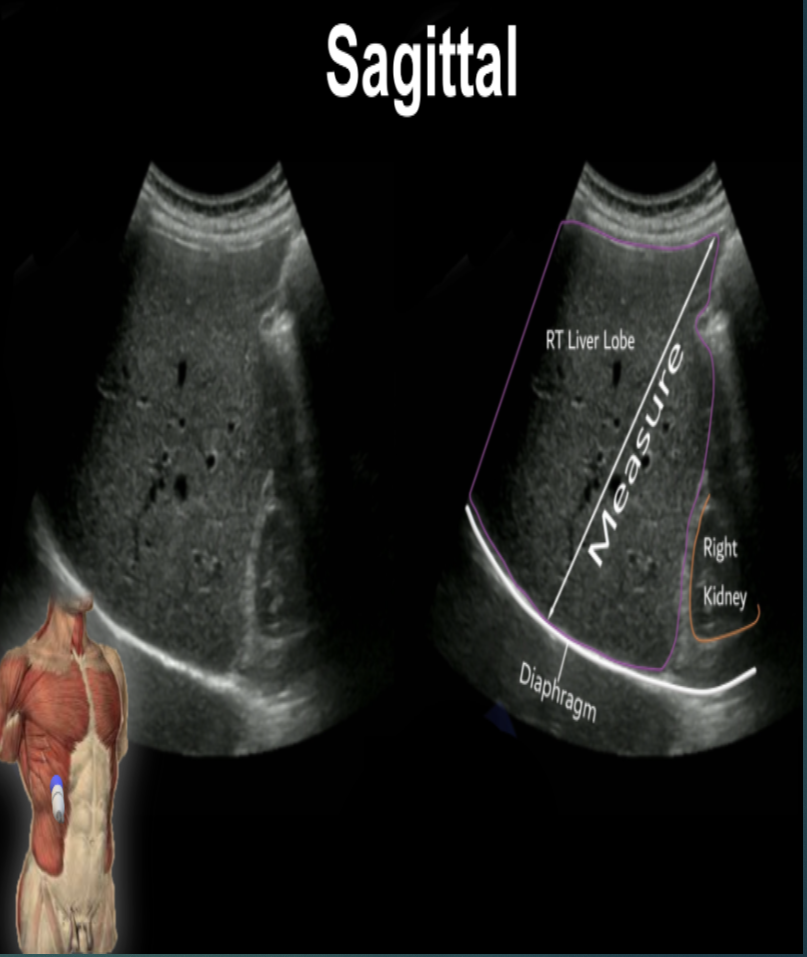
Does the size of the liver vary with sex & body size?
Yes. And liver is a little larger in men.
Fill in the blanks :
The liver size increases approximately _____ _____ for every cm of increased height.
0.04 cm
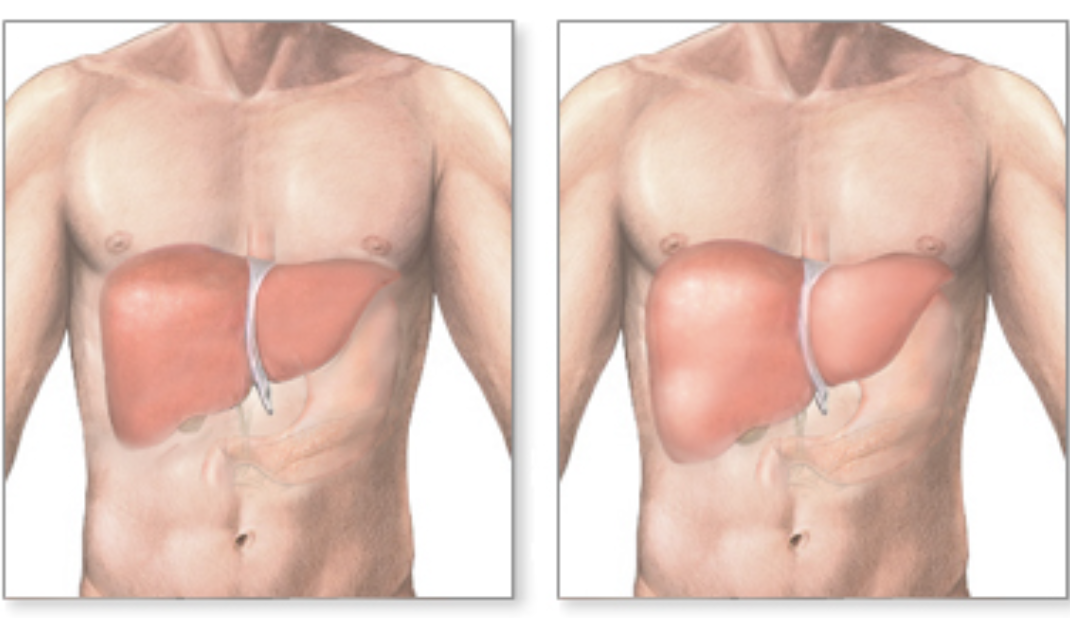
Describe both images.
LT : Normal liver
RT : Enlarged liver due to hepatomegaly
List some causes of hepatomegaly.
Alcohol use especially alcohol abuse
Cancer metastases (spread of cancer to liver)
Congestive heart failure
Hepatitis A, B, & C
Hepatocellular carcinoma
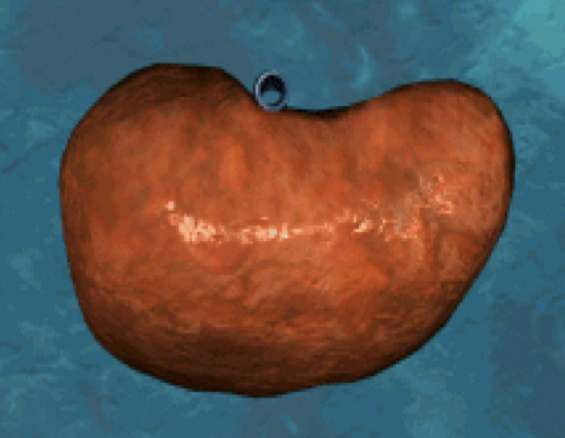
Which surface of the liver is this? And describe it.
Superior surface. Smooth & convex (curves outward).
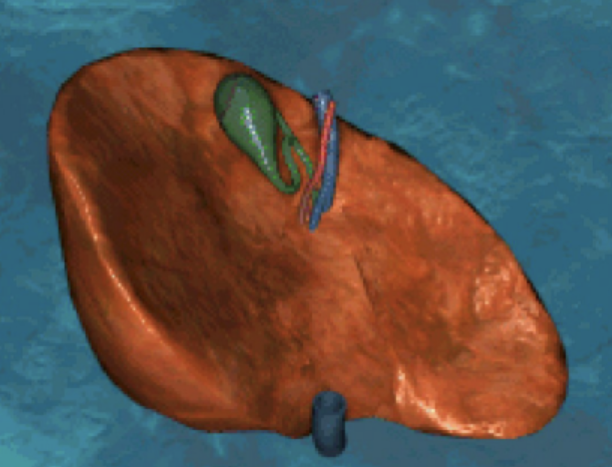
Which surface of the liver is this? And describe it.
Inferior surface. Concave (curves inward).
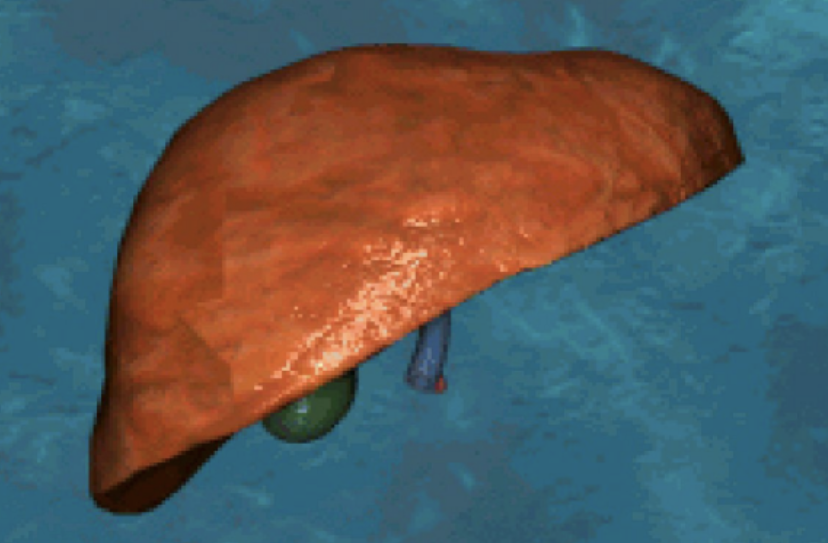
Which surface of the liver is this? And describe it.
Anterior surface. Thin & sharp.
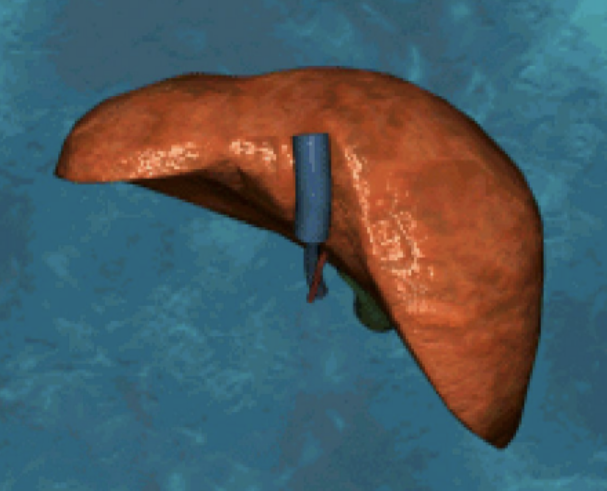
Which surface of the liver is this? And describe it.
Posterior portion. Round & broad on RT side, narrow on LT side.
Fill in the blanks :
The posterior portion of the liver is in direct contact with the _____ and forms the ______ _____.
Diaphragm; bare area
Define : fissure
A natural cleft between body parts or in the substance of an organ.
Define fissure in the liver.
Any of several clefts separating the lobes of the liver.
The main lobar fissure separates?
The RT liver lobe from the LT liver lobe.
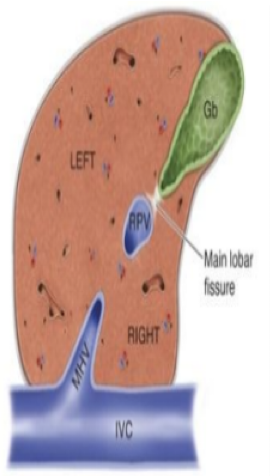
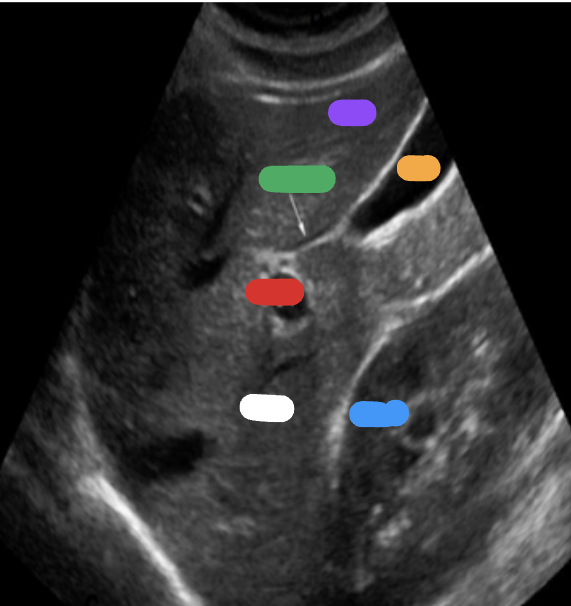
What is the red part?
RT portal vein
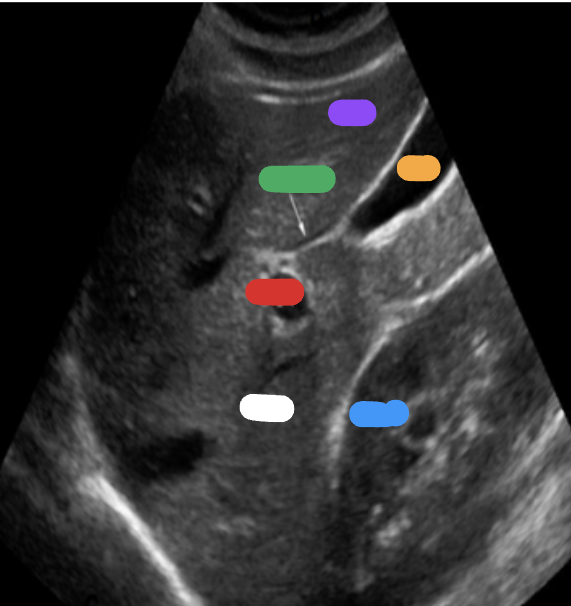
What is the green part?
Main lobar fissure
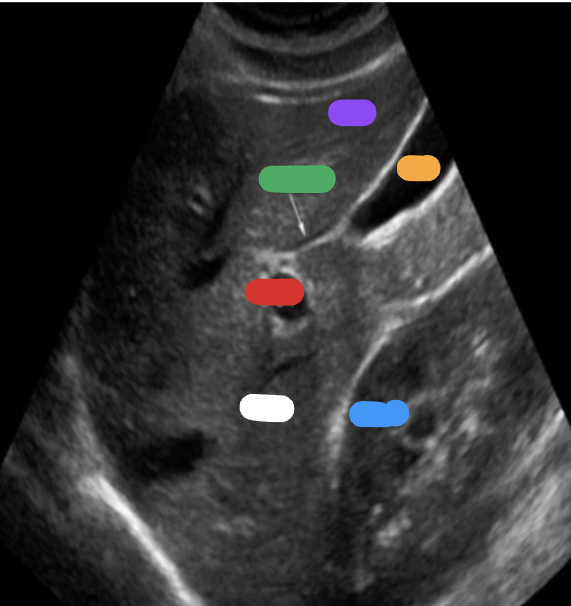
What is the white part?
RT lobe
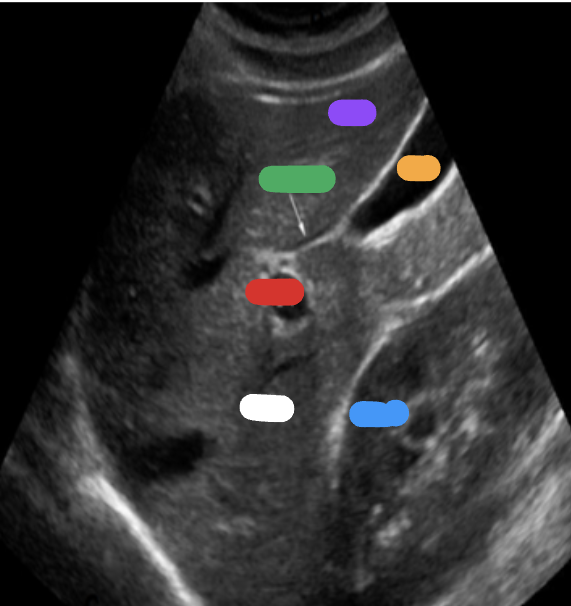
What is the purple part?
LT lobe
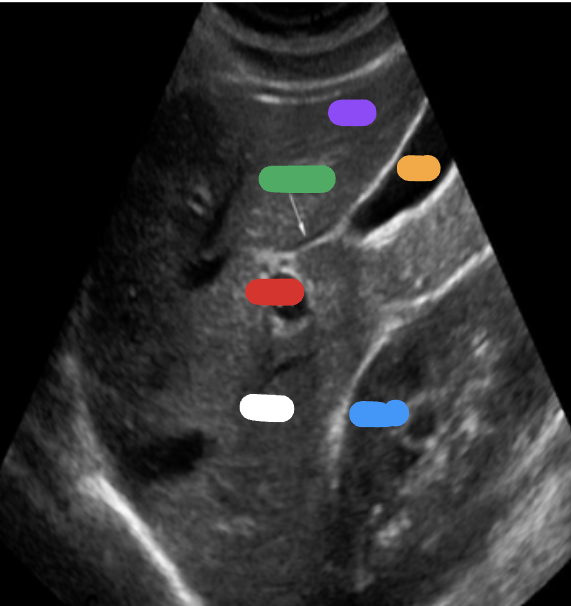
What is the orange part?
Gallbladder
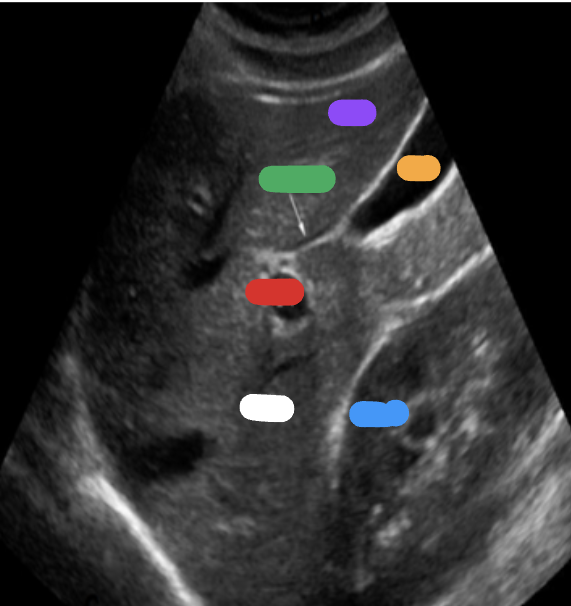
What is the blue part?
RT kidney
Fill in the blanks :
The main lobar fissure is a hyperechoic line extending from the _____ _____ to the ____.
Portal vein; gallbladder
The mid hepatic vein sits within the?
Main lobar fissure.
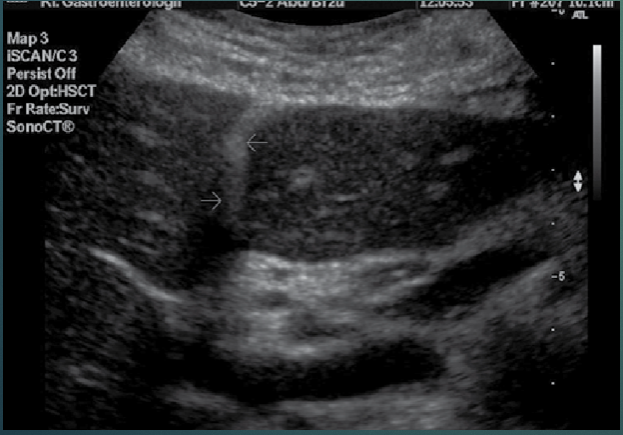
The arrows are pointing to?
Falciform ligament.
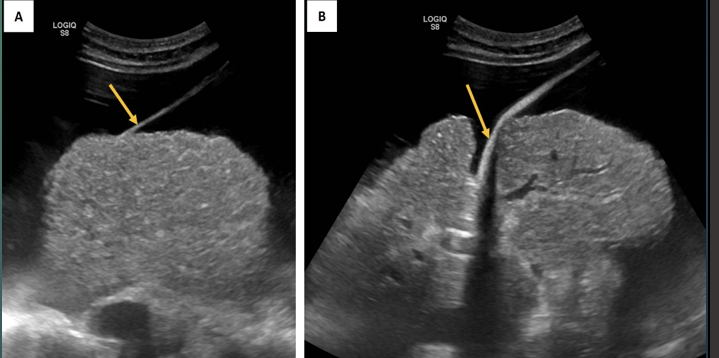
The arrows are pointing to?
Falciform ligament.
The falciform ligament contains?
Ligamentum teres.
The falciform ligament separates?
The medial from the lateral segment of the LT lobe.
Fill in the blank :
The falciform ligament is _____ attachment of the liver.
Anterior
Ligamentum of teres is aka?
Round ligament.
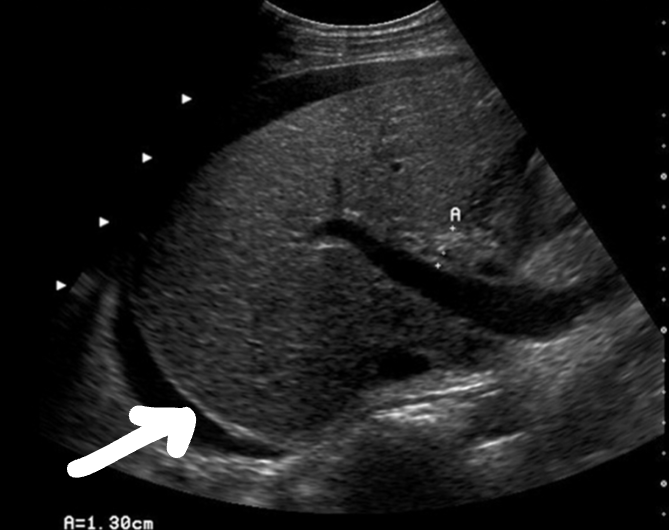
What is the arrow pointing at? And what are the anechoic areas?
Glisson capsule; ascites
The ligamentum of teres divides the LT lobe into which segments?
Medial & lateral segments.
The ligamentum of teres communicates with?
The LT portal vein.
Obliterated umbilical vein is in the fissure of the?
Ligamentum of teres.
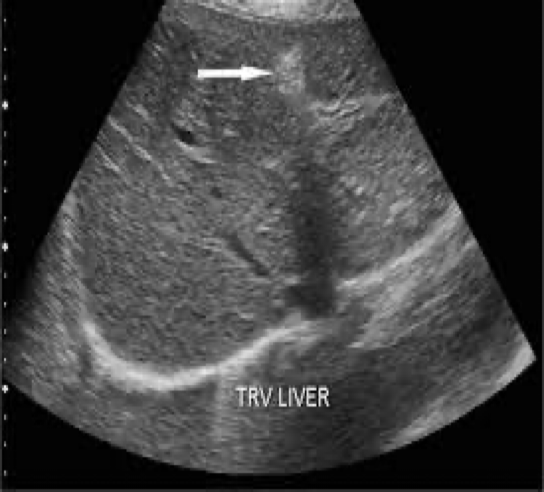
What is the arrow pointing at?
Ligamentum of teres
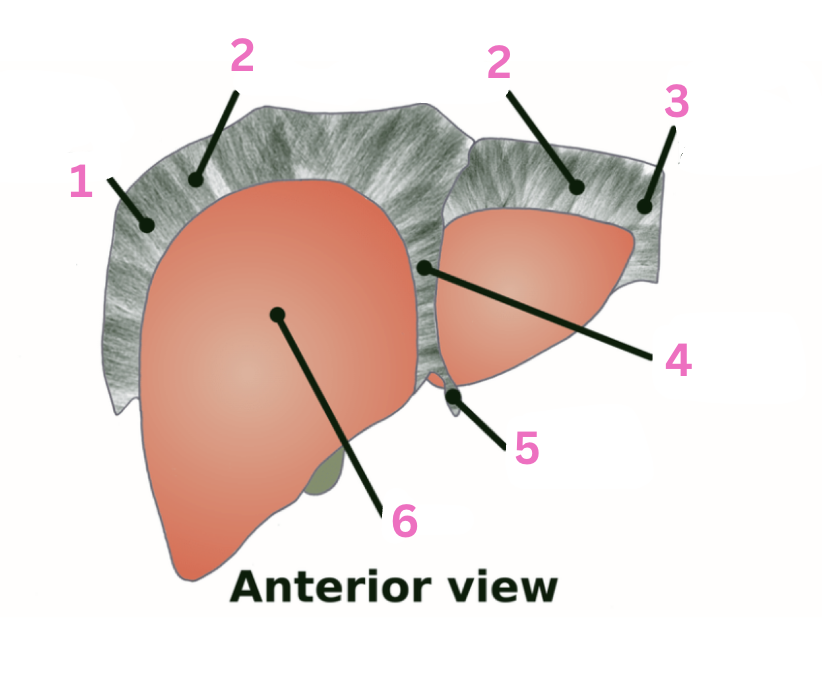
What is 1?
RT triangular ligament
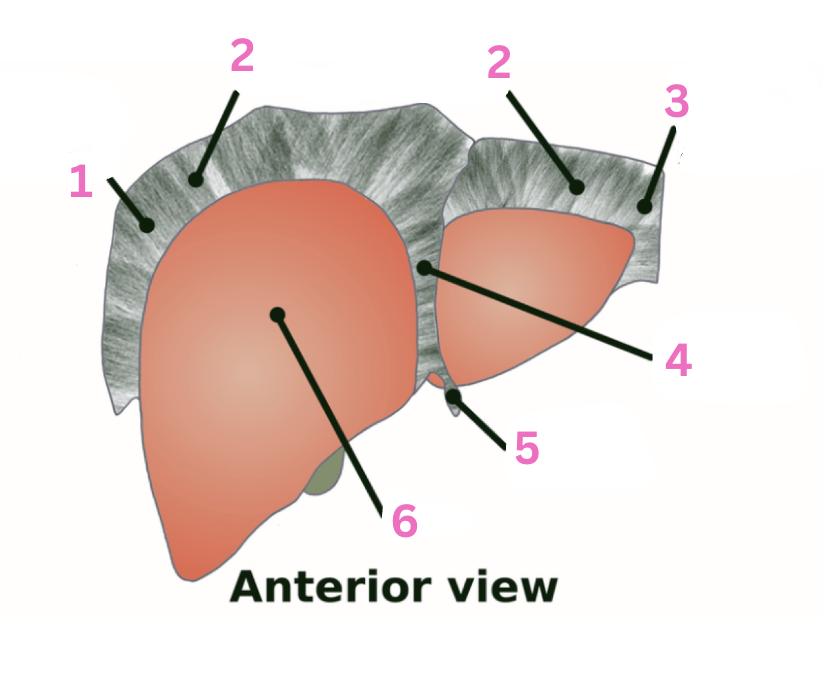
What is 2?
Coronary ligament
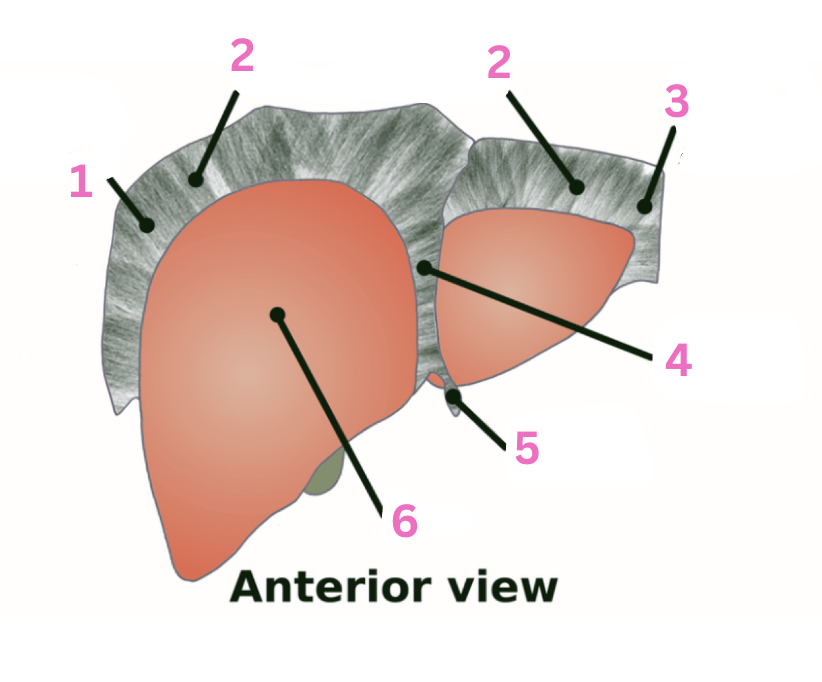
What is 3?
LT triangular ligament
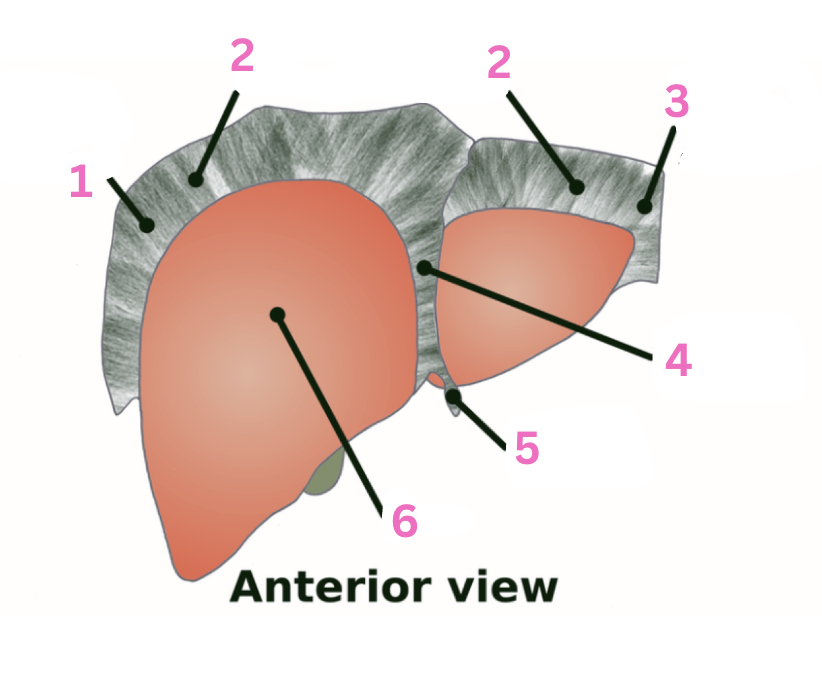
What is 4?
Falciform ligament
What is 5?
Round ligament
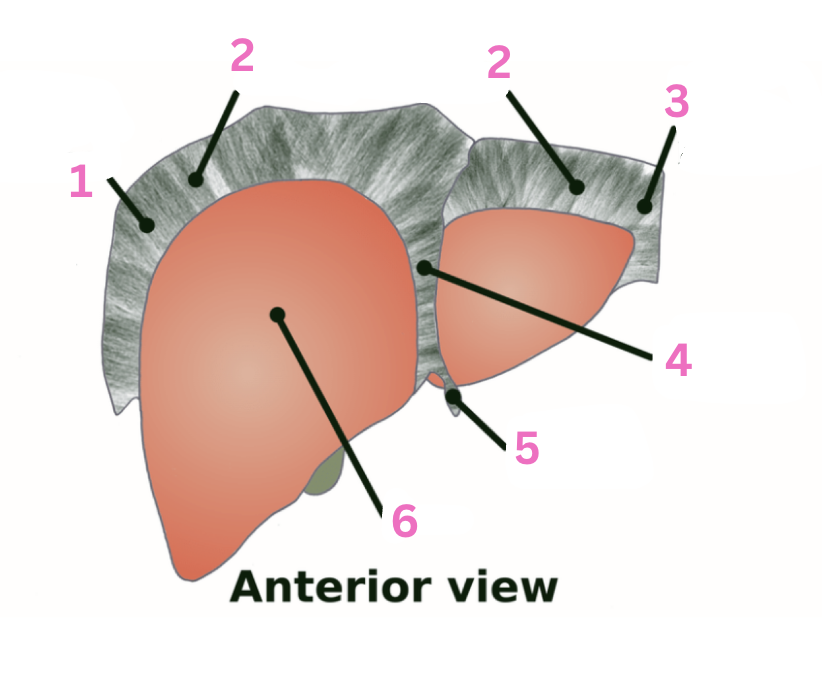
What is 6?
Liver
The main branches of the LT portal vein originate from the? And supply which liver segments?
Umbilical portion; 2, 3, & 4
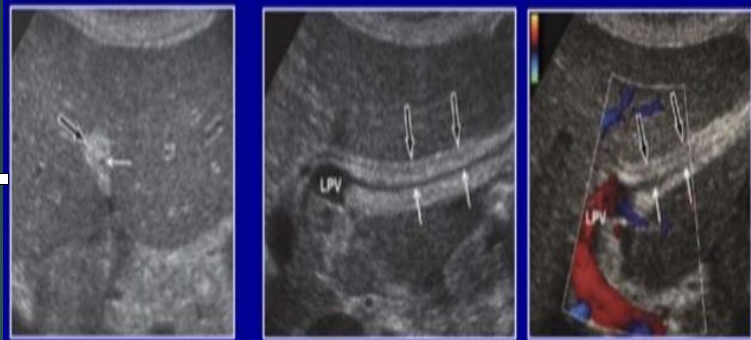
What are the arrows pointing to?
Ligamentum of teres
*Remember : While the falciform ligament divides the liver into RT & LT lobes, Cantile’s Line (Main Lobar Fissure) provides a more clinically & surgically useful functional division of the liver.
The ligamentum venosum separates?
The LT liver lobe from the caudate lobe.
Is the ligamentum venosum anterior or posterior to the caudate lobe?
Anterior
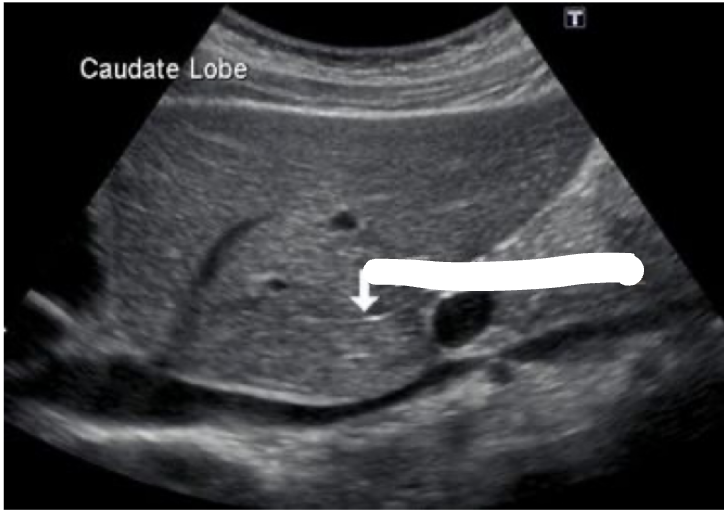
What is the arrow pointing at?
Ligamentum venosum
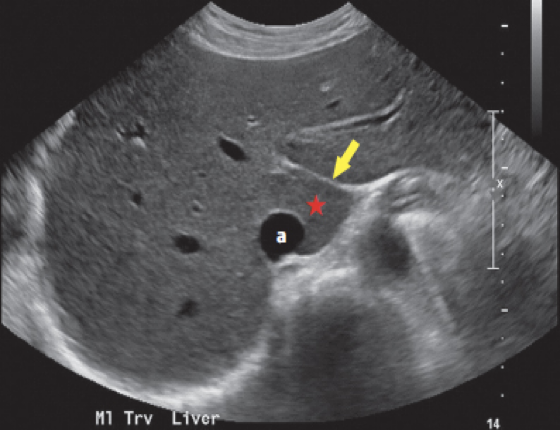
What is the arrow pointing at?
Ligamentum venosum
Fill in the blank :
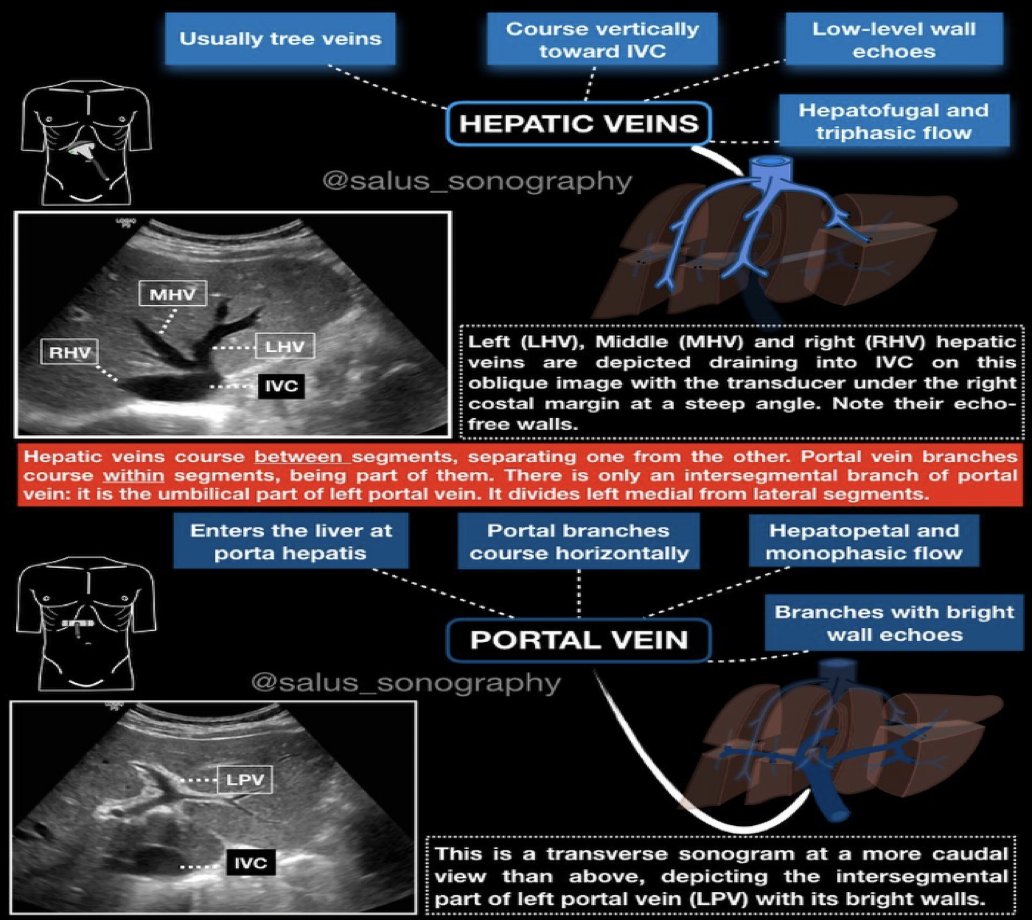
Hepatic veins course _____ toward IVC.
Vertically
Hepatic veins have low-level wall echoes.
Fill in the blanks :
Portal vein enters the liver at _____ _____.
Porta hepatis
Fill in the blanks :
Portal branches course _____.
Horizontally
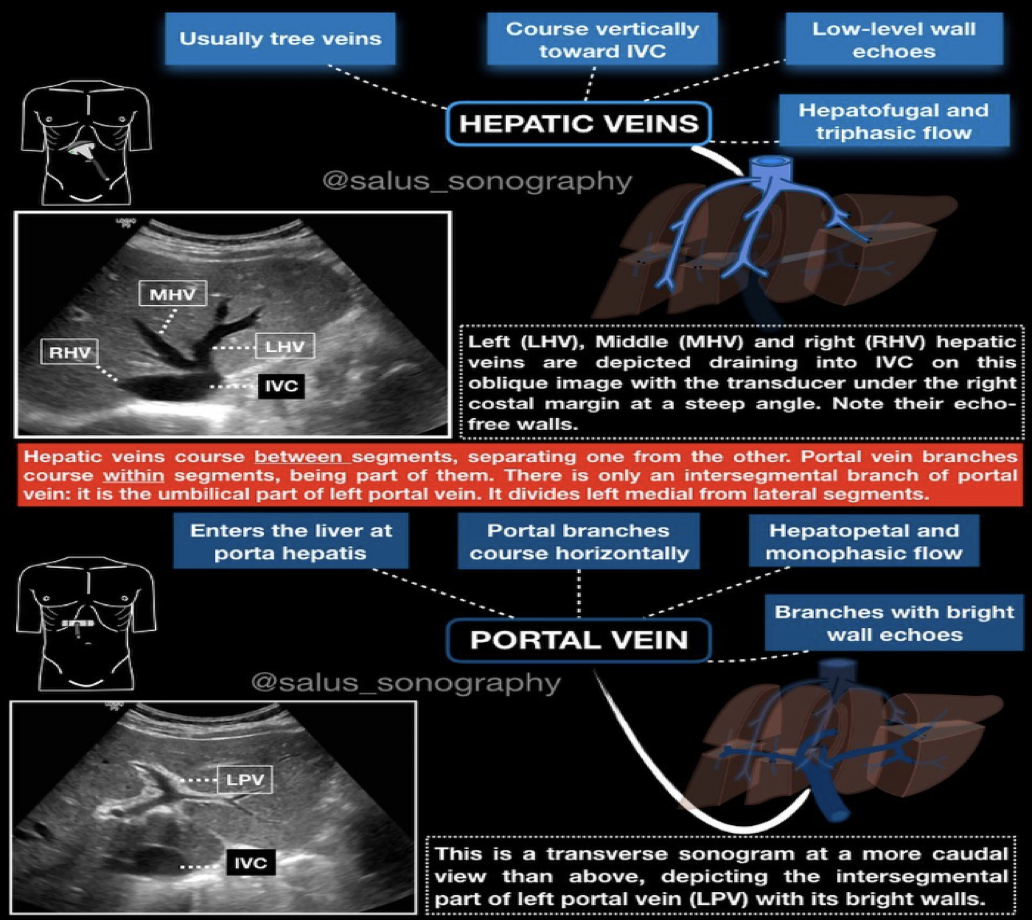
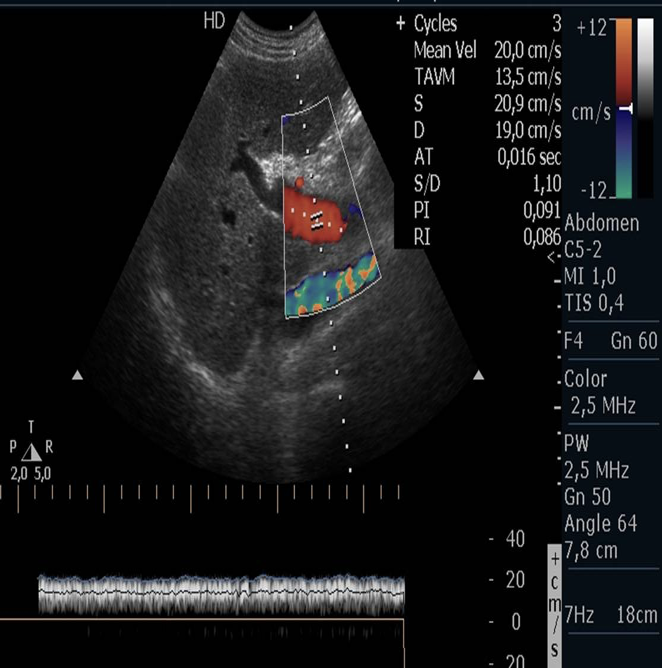
Normal flow : Hepatopetal