Mink Final Semester 2
5.0(4)
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/73
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
1
New cards
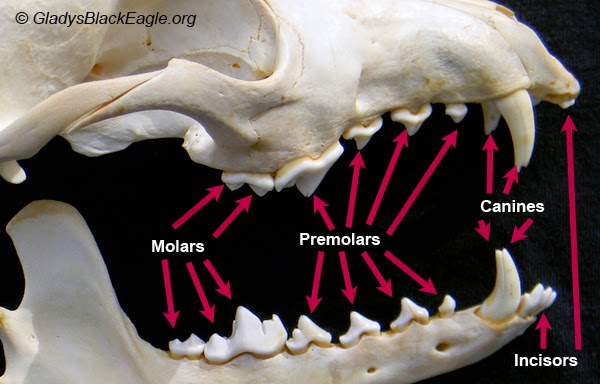
Incisors
Incisors are sharp, flat-edged teeth located at the front of the mouth. They are used for cutting and biting into food.
2
New cards
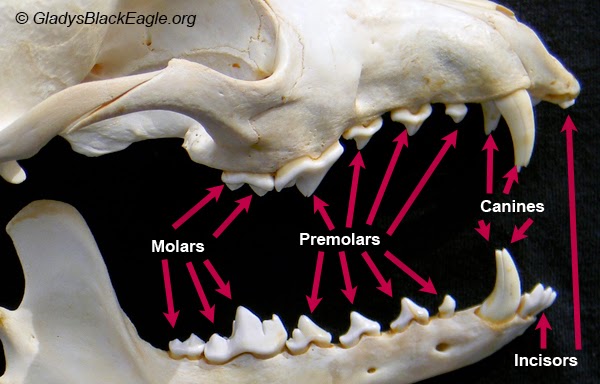
Canine
Canines, also known as cuspids, are the pointed teeth located on either side of the incisors. They are used for tearing and grasping food.
3
New cards
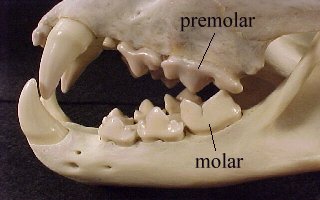
Carnassial
Carnassial teeth are specialized molars found in carnivorous animals, such as minks. They have sharp, shearing edges that are used for slicing and shearing meat.
4
New cards
Mouth
The mouth is the opening where food enters the digestive system. It contains the teeth, tongue, and salivary glands. The mouth plays a vital role in chewing and beginning the process of digestion through saliva production.
If you need a picture for this just drop the class tbh (just kidding)
If you need a picture for this just drop the class tbh (just kidding)
5
New cards
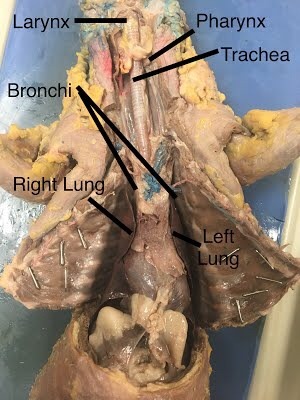
Pharynx
The pharynx is a muscular tube located behind the mouth and nasal cavity. It serves as a passageway for both food and air, directing food into the esophagus and air into the larynx and trachea.
6
New cards
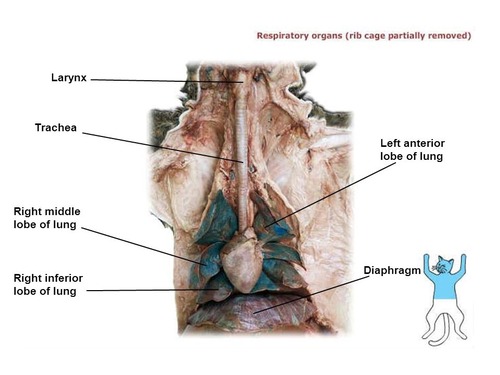
Larynx
The larynx, also known as the voice box, is located at the upper part of the trachea. It contains the vocal cords and plays a crucial role in producing sound and facilitating breathing.
7
New cards
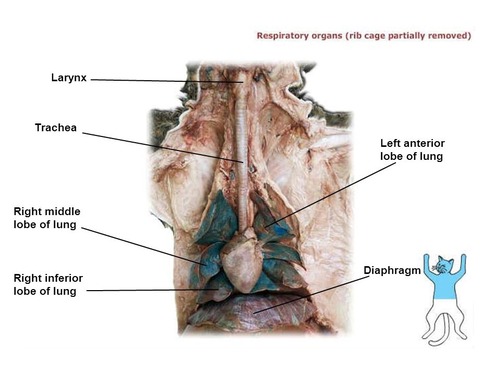
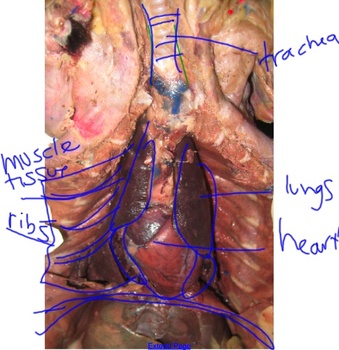
Trachea
The trachea, or windpipe, is a tube connecting the larynx to the bronchial tubes in the lungs. It allows the passage of air during inhalation and exhalation.
8
New cards
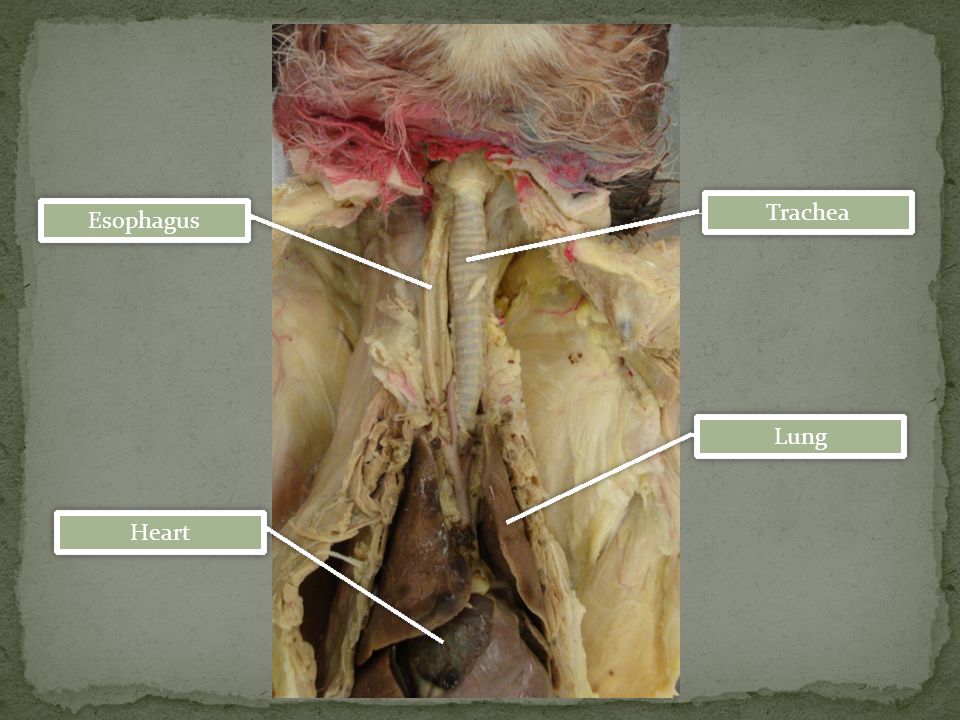
Esophagus
The esophagus is a muscular tube that connects the pharynx to the stomach. It carries food from the mouth to the stomach through rhythmic contractions called peristalsis.
9
New cards
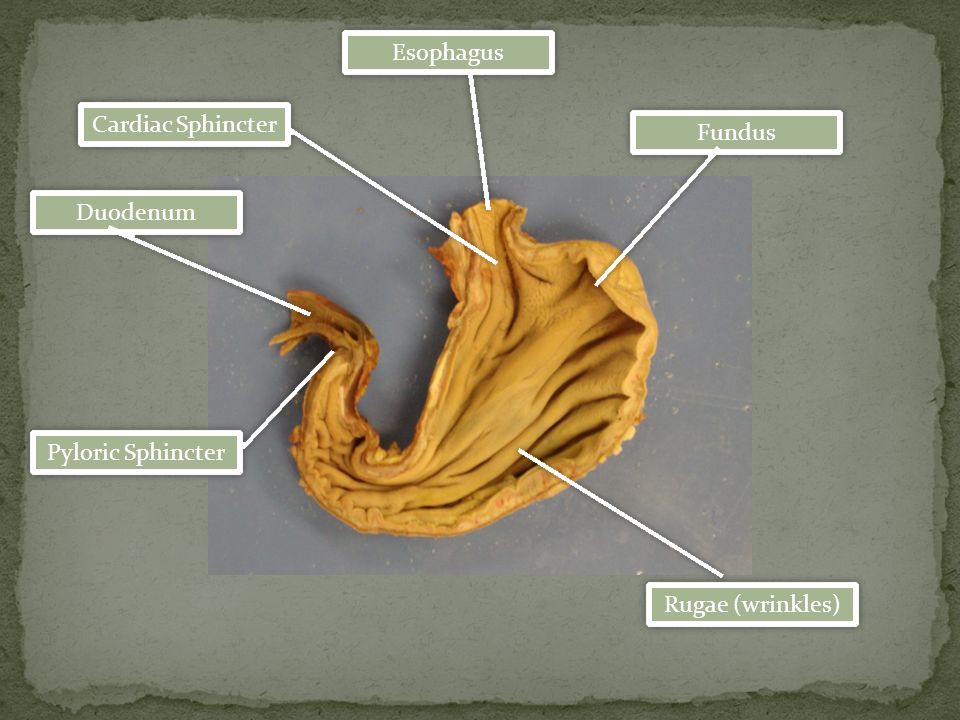
Cardiac Sphincter
The cardiac sphincter, also known as the lower esophageal sphincter, is a circular muscle located at the entrance of the stomach. It prevents stomach acid and partially digested food from flowing back into the esophagus.
10
New cards
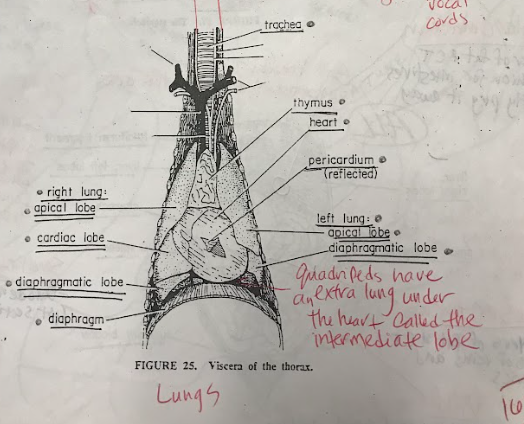
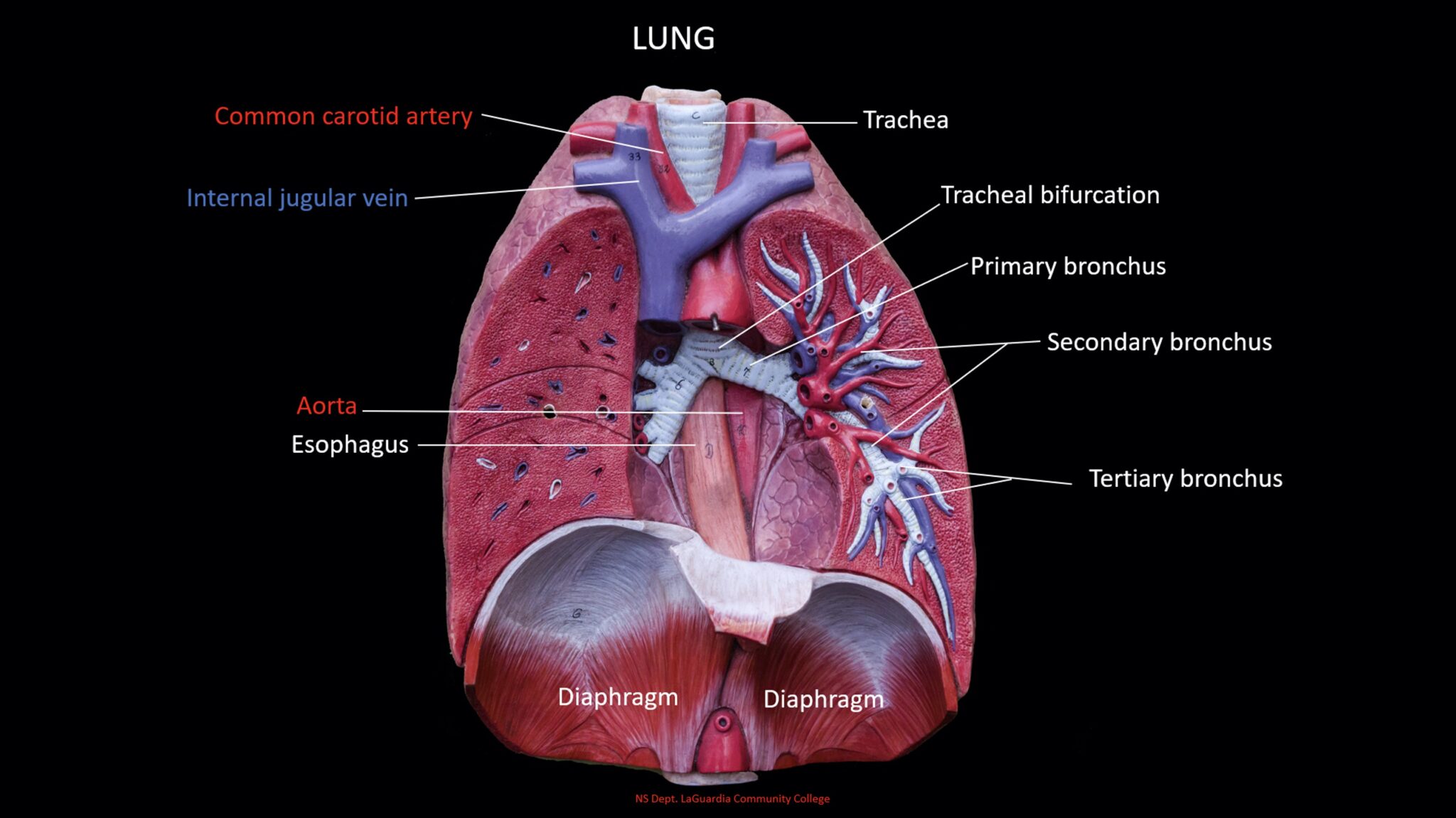
Lungs
\
The right apical lobe and left apical lobe are the uppermost parts of their respective lungs, while the right cardiac lobe is in the middle of the right lung. The left diaphragmatic lobe and right diaphragmatic lobe are the lowermost parts of the left and right lungs, respectively. The intermediate lobe is a unique lobe found between the right apical and right diaphragmatic lobes in some individuals. Together, these lobes contribute to respiratory functions and gas exchange in the lungs.
The right apical lobe and left apical lobe are the uppermost parts of their respective lungs, while the right cardiac lobe is in the middle of the right lung. The left diaphragmatic lobe and right diaphragmatic lobe are the lowermost parts of the left and right lungs, respectively. The intermediate lobe is a unique lobe found between the right apical and right diaphragmatic lobes in some individuals. Together, these lobes contribute to respiratory functions and gas exchange in the lungs.
11
New cards
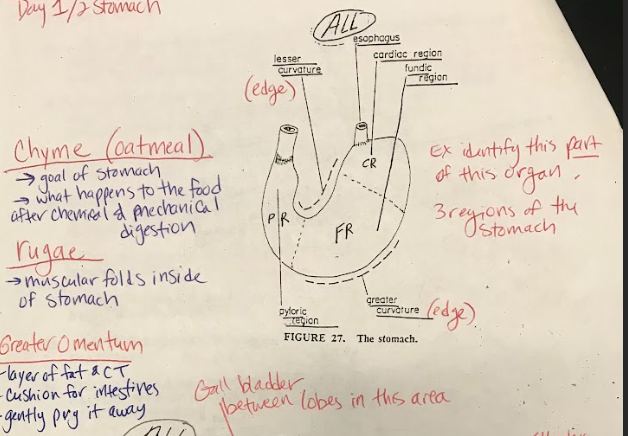
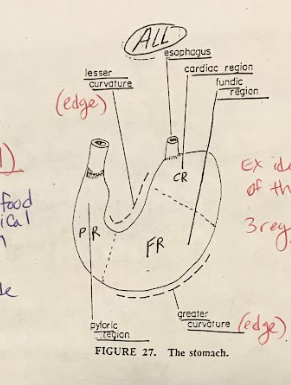
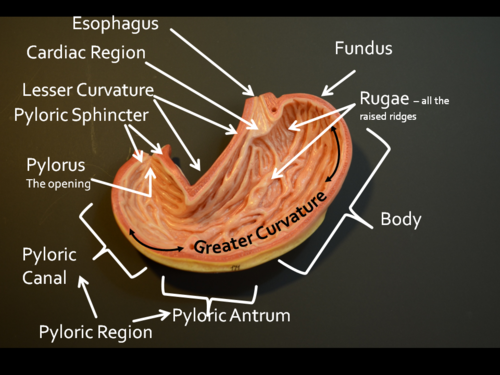
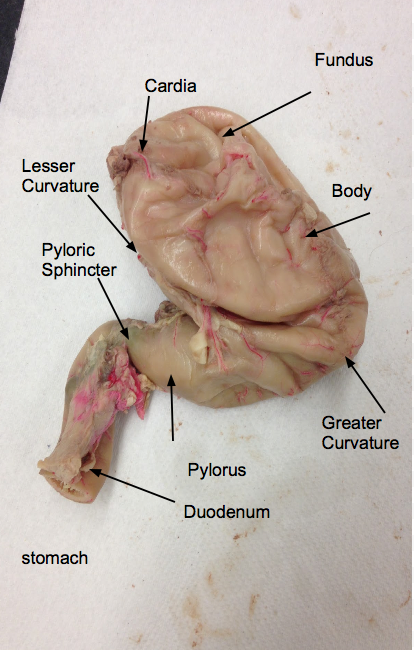
Stomach
The stomach is divided into three main regions: pyloric, cardiac, and fundic. The pyloric region contains the pyloric sphincter, regulating the passage of partially digested food to the small intestine. The cardiac region contains the cardiac sphincter, preventing the backflow of stomach contents into the esophagus. The fundic region is responsible for storing and mixing food with gastric secretions.
12
New cards
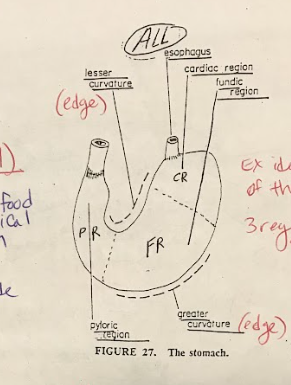
Pyloric Sphincter
The pyloric sphincter is a muscular valve located at the exit of the stomach, leading to the small intestine. It regulates the flow of partially digested food (chyme) from the stomach into the small intestine.
13
New cards
Greater and Lesser curvature
The greater and lesser curvatures are the outer borders or contours of the stomach. The greater curvature is the convex outer curve, while the lesser curvature is the concave inner curve.
14
New cards
Greater and Lesser Omentum
The greater and lesser omentum are folds of connective tissue that hang from the stomach and cover the abdominal organs. They provide support and protection for the organs and also play a role in immune response.
15
New cards
Rugae
Rugae are ridges or folds in the inner lining of the stomach. They allow the stomach to expand and contract as it accommodates food and aids in mechanical digestion.
16
New cards
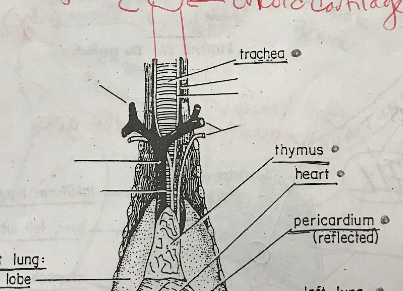
Thymus
The thymus is a gland located in the chest, near the heart. It plays a crucial role in the development and maturation of certain immune cells called T-cells, which are essential for the immune system's functioning.
17
New cards
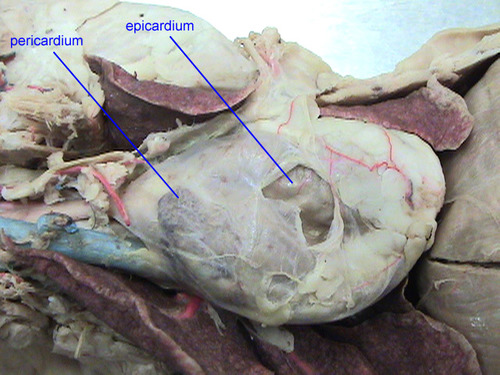
Pericardium
The pericardium is a sac-like structure that surrounds and protects the heart. It consists of two layers, the outer fibrous pericardium and the inner serous pericardium. The pericardium helps prevent friction between the heart and surrounding structures.
18
New cards
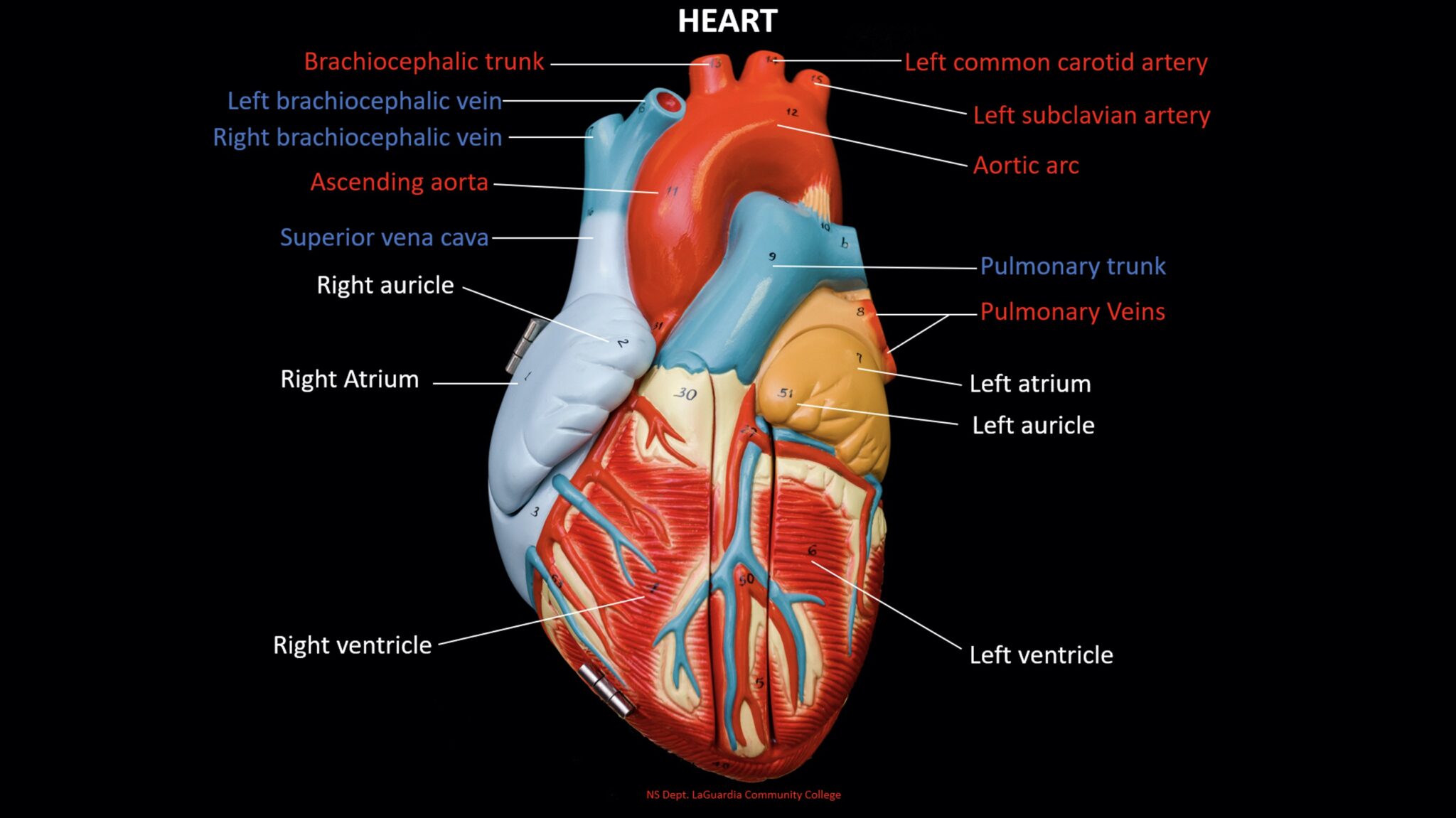
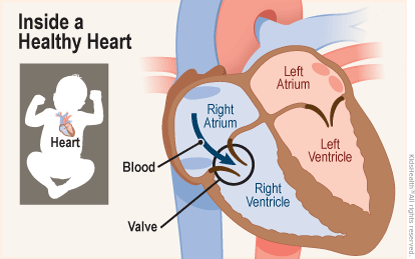
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. It consists of four chambers: the right and left atria and the right and left ventricles. The heart receives deoxygenated blood from the body and pumps oxygenated blood to the body's tissues.
19
New cards
R & L Auricles
The right and left auricles, also known as atria, are the upper chambers of the heart. They receive blood returning to the heart and transfer it to the ventricles.
20
New cards
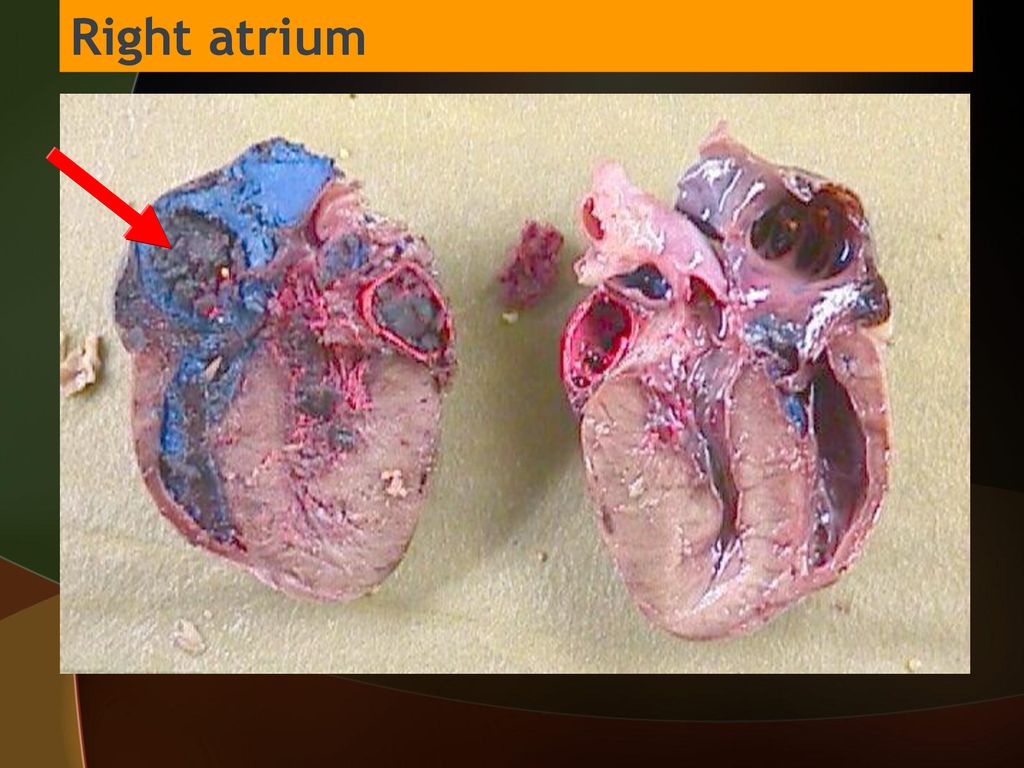
R & L Atria
\
The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body, while the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs. Both atria contract to pump blood into the respective ventricles for further circulation.
The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body, while the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs. Both atria contract to pump blood into the respective ventricles for further circulation.
21
New cards
R & L Ventricles
The right and left ventricles are the lower chambers of the heart. They receive blood from the atria and pump it out to the lungs and body.
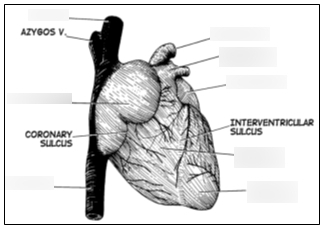
22
New cards
Interventricular sulcus
The interventricular sulcus is a groove that separates the left and right ventricles on the outer surface of the heart.
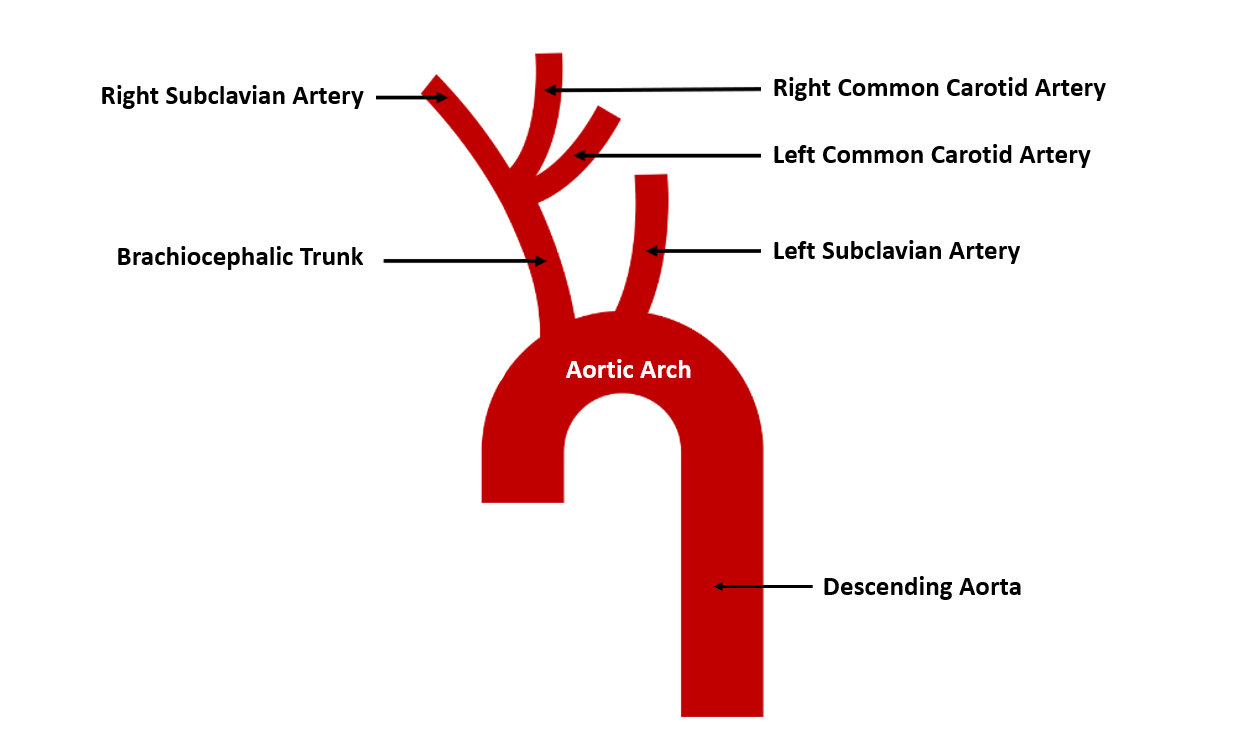
23
New cards
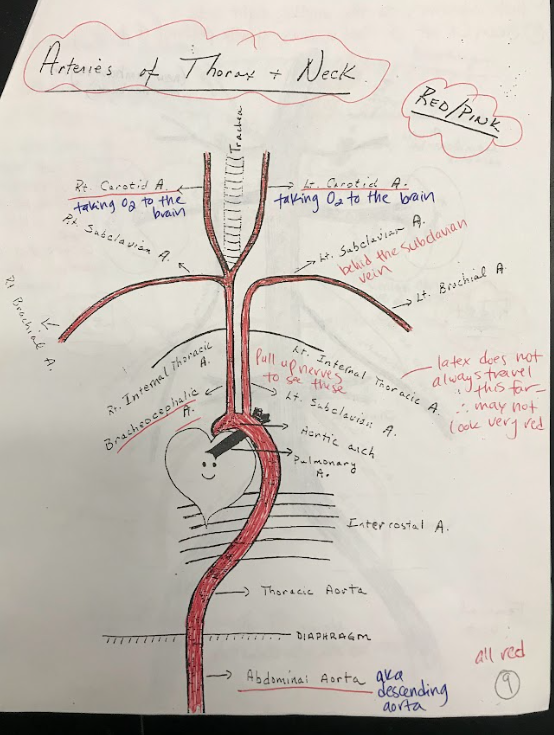
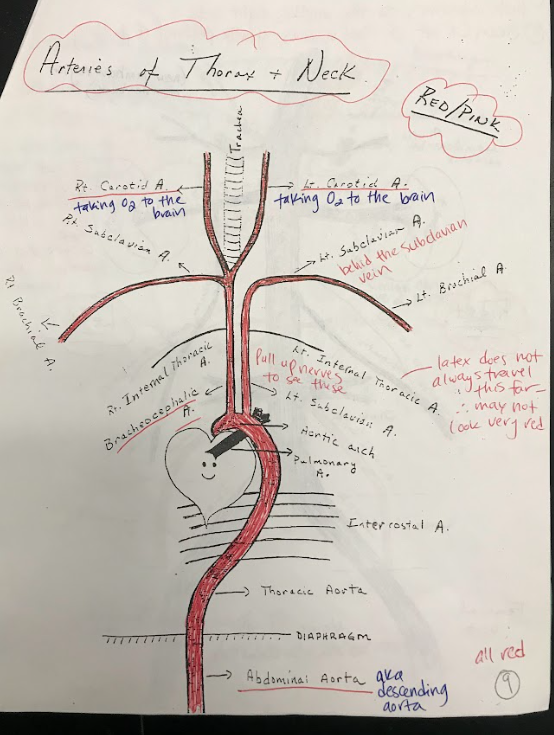
Aortic Arch
The aortic arch is a curved portion of the main artery called the aorta. It bends over the heart and gives rise to branches that supply oxygenated blood to the head, neck, and upper limbs.
24
New cards
Thoracic Aorta
The thoracic aorta is the portion of the aorta located within the chest. It supplies oxygenated blood to the organs and tissues of the thoracic cavity.
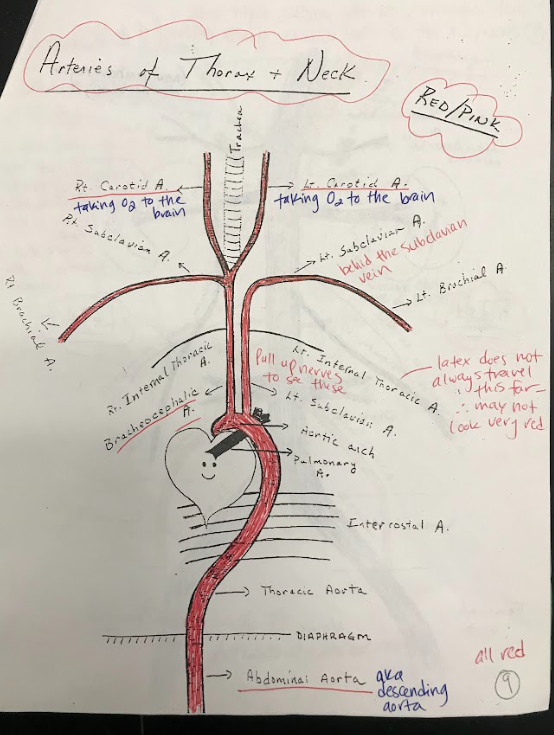
25
New cards
Abdominal Aorta
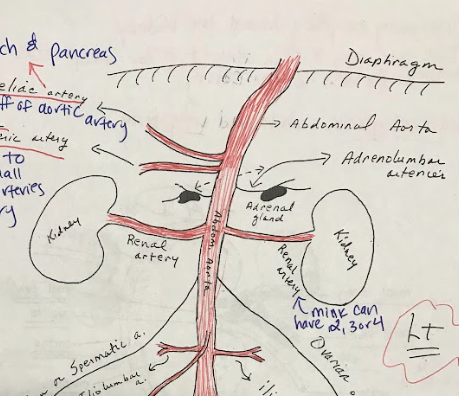
The abdominal aorta is the portion of the aorta located within the abdomen. It supplies oxygenated blood to the organs and tissues of the abdominal region.
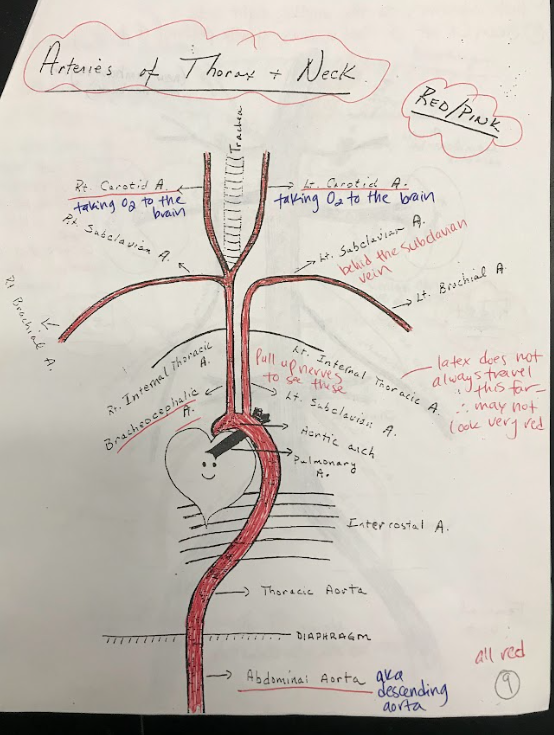
26
New cards
Intercostal Arteries
Intercostal arteries are a network of blood vessels that run along the spaces between the ribs. They supply oxygenated blood to the muscles and tissues between the ribs.
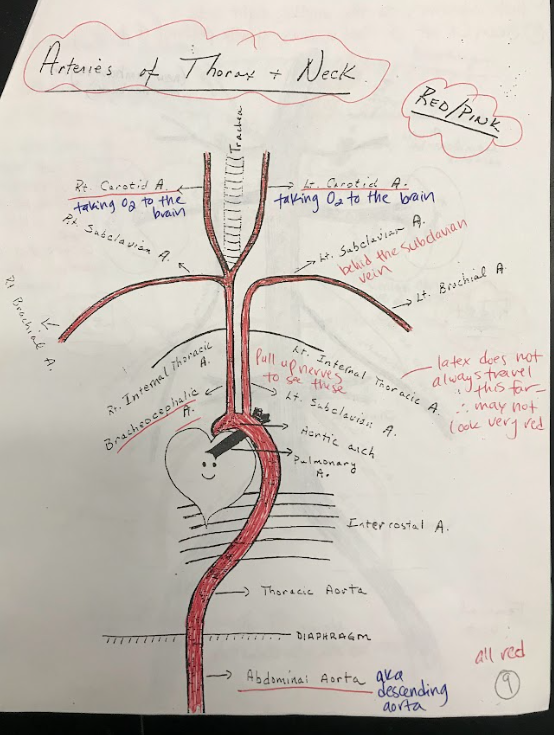
27
New cards
Brachiocephalic Artery
The brachiocephalic artery is a large artery that branches off from the aortic arch. It supplies oxygenated blood to the right arm and the head and neck region.
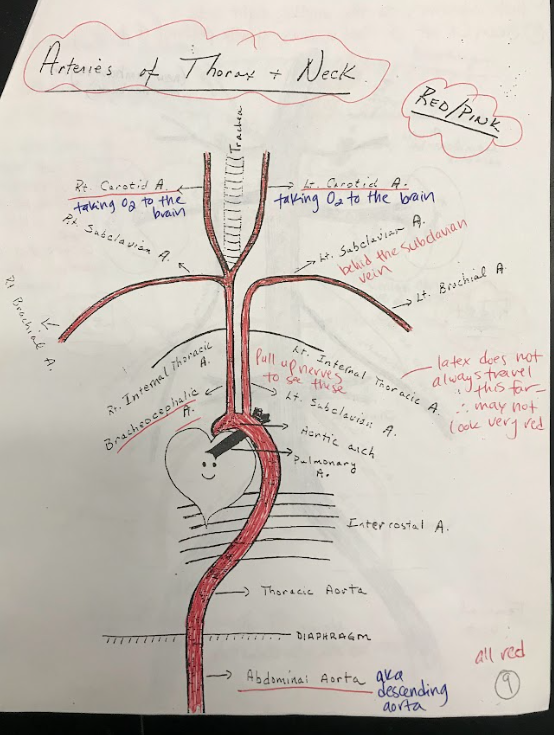
28
New cards
Carotid Arteries
The carotid arteries are major blood vessels located in the neck. They supply oxygenated blood to the brain and head.
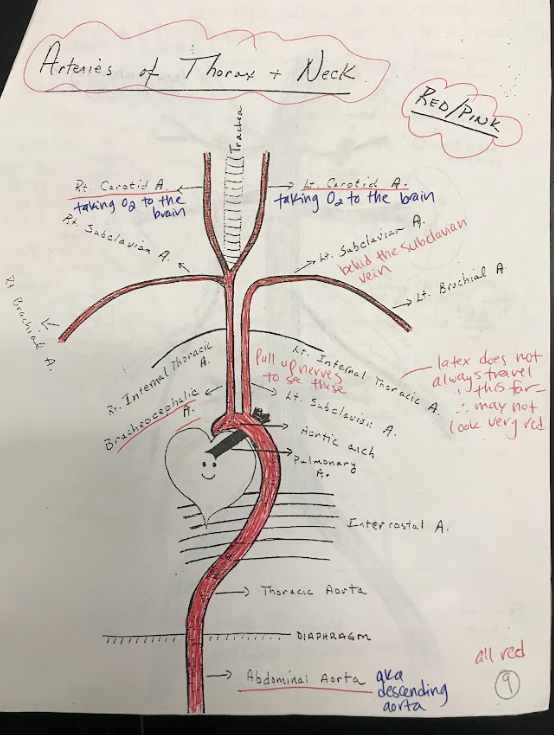
29
New cards
Subclavian Arteries
The subclavian arteries are large arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the arms, shoulders, and upper back.
30
New cards
Brachial Arteries
The brachial arteries are the major blood vessels that supply oxygenated blood to the upper arms.
31
New cards
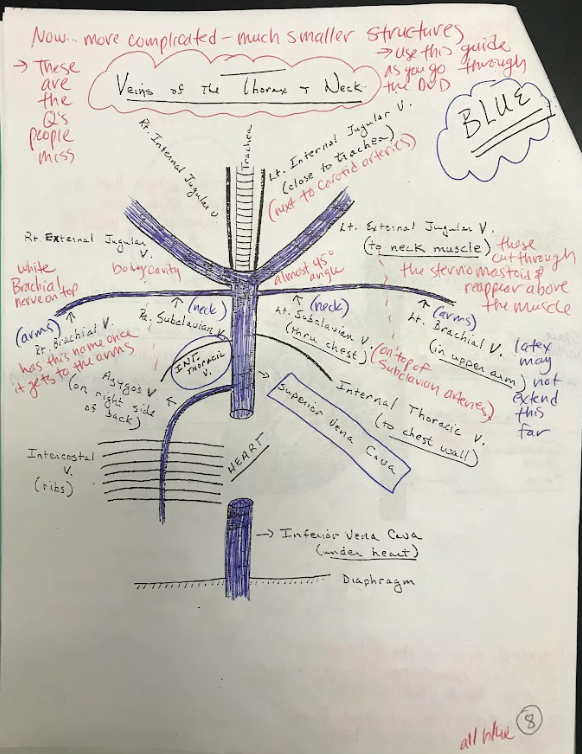
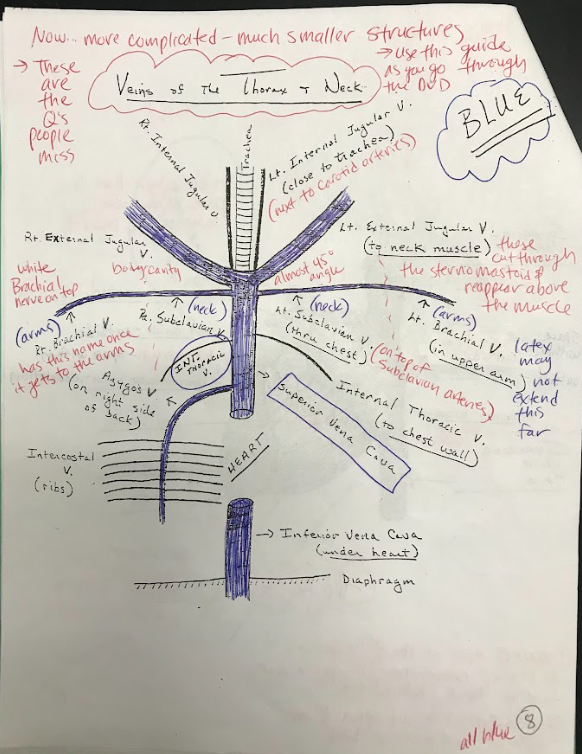
Brachial Veins
The brachial veins are the major veins that drain deoxygenated blood from the upper arms and return it to the heart.
32
New cards
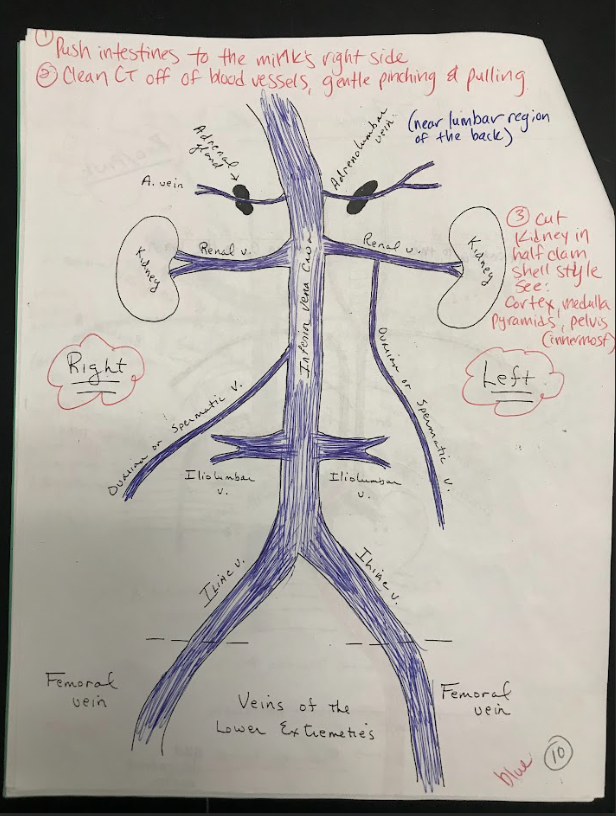
Superior Vena Cava
The superior vena cava is a large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the upper body to the right atrium of the heart.
33
New cards
Inferior Vena Cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the lower body to the right atrium of the heart.
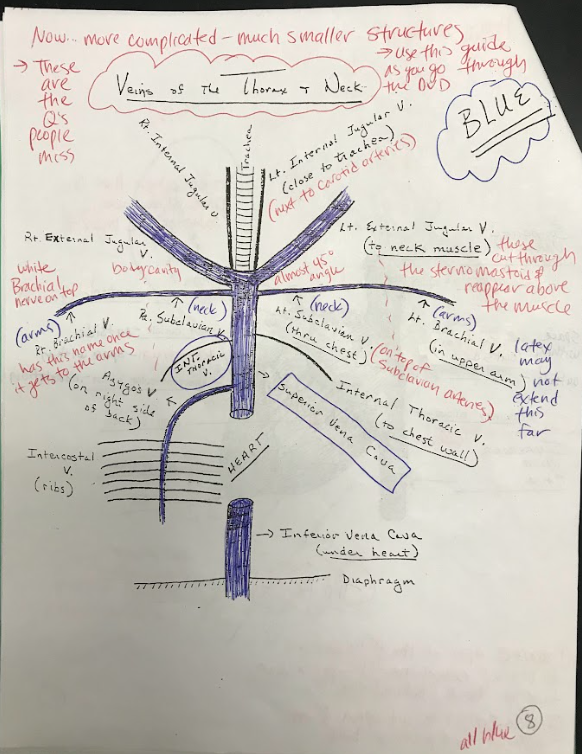
34
New cards
Jugular veins
The jugular veins are major veins in the neck that drain deoxygenated blood from the head and neck region and return it to the heart. There are both internal and external jugular veins.
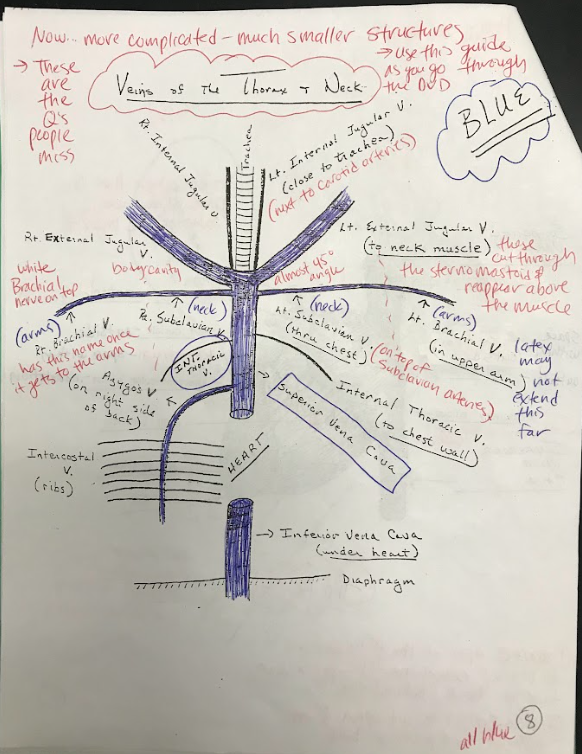
35
New cards
Subclavian veins
The subclavian veins are major veins that receive deoxygenated blood from the upper limbs and return it to the heart.
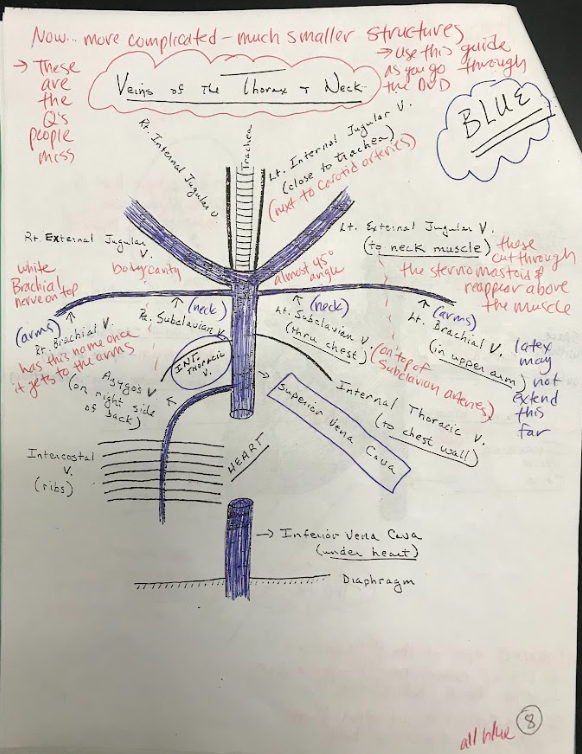
36
New cards
Intercostal veins
Intercostal veins are veins that drain deoxygenated blood from the spaces between the ribs and return it to the heart.
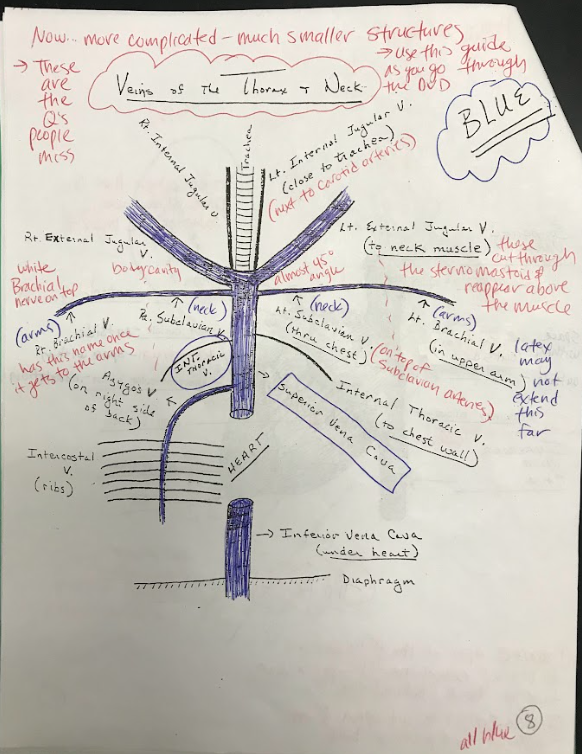
37
New cards
Diaphragm
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle located at the base of the chest cavity. It plays a crucial role in respiration, contracting and relaxing to facilitate inhalation and exhalation.
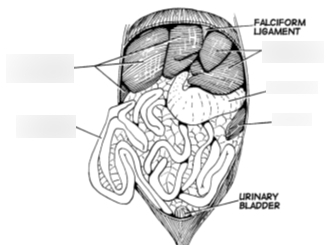
38
New cards
Falciform ligament
A thin, crescent-shaped ligament that attaches the liver to the anterior abdominal wall, separating the right and left lobes of the liver.
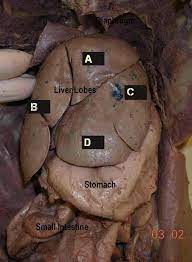
39
New cards
Liver
A large, reddish-brown organ located in the upper right portion of the abdomen. It plays a vital role in various metabolic processes, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of bile.
40
New cards
Gallbladder
A small, pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver. Its function is to store and concentrate bile produced by the liver, releasing it into the small intestine to aid in the digestion and absorption of fats.
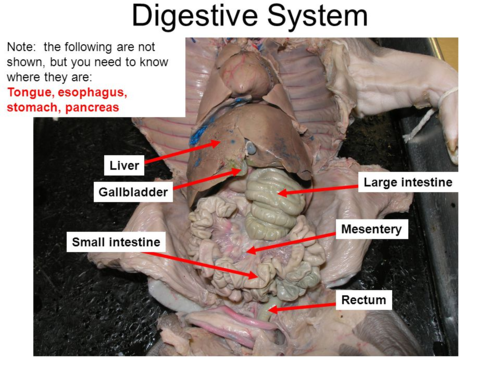
41
New cards
Spleen
A soft, purplish organ located on the left side of the abdomen. It serves as part of the immune system, filtering blood, and removing old or damaged red blood cells.
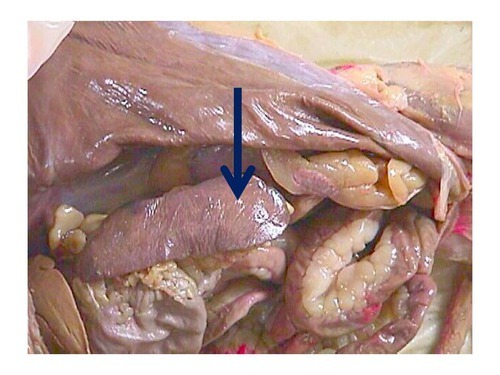
42
New cards
Pancreas
A glandular organ located behind the stomach. It has both endocrine and exocrine functions, producing digestive enzymes to break down food in the small intestine and releasing hormones, such as insulin, to regulate blood sugar levels.
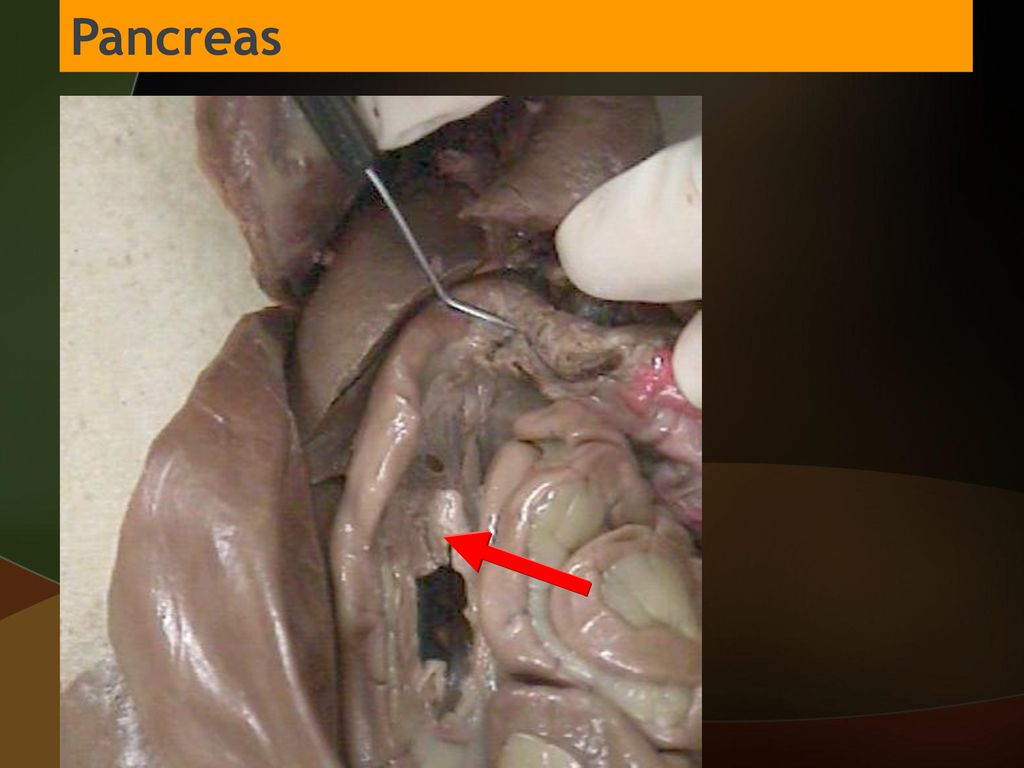
43
New cards
Mesenteries
Sheets of thin, membranous tissue that suspend and support the organs in the abdominal cavity. They provide a pathway for blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics and also help to hold the organs in place.
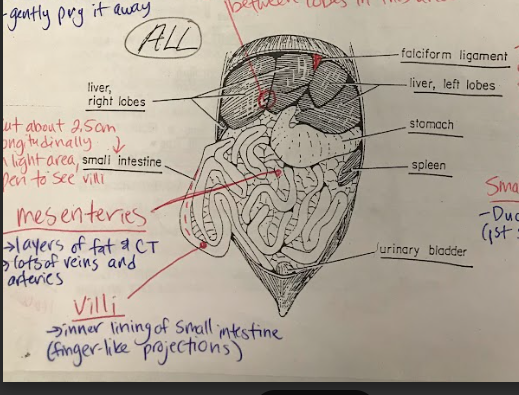
44
New cards
Small Intestines
The small intestine is divided into three regions: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum is the first part where the majority of digestion takes place, while the jejunum and ileum are primarily involved in the absorption of nutrients.
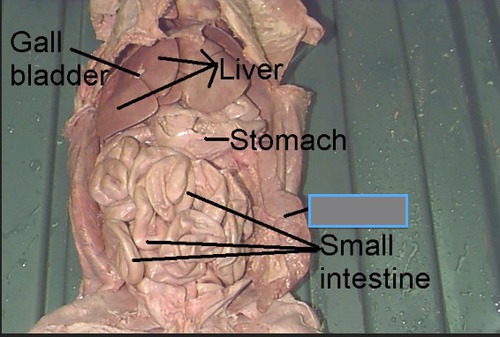
45
New cards
Villi
Tiny, finger-like projections present in the lining of the small intestine. They increase the surface area for absorption, allowing nutrients to be efficiently taken up by the body.
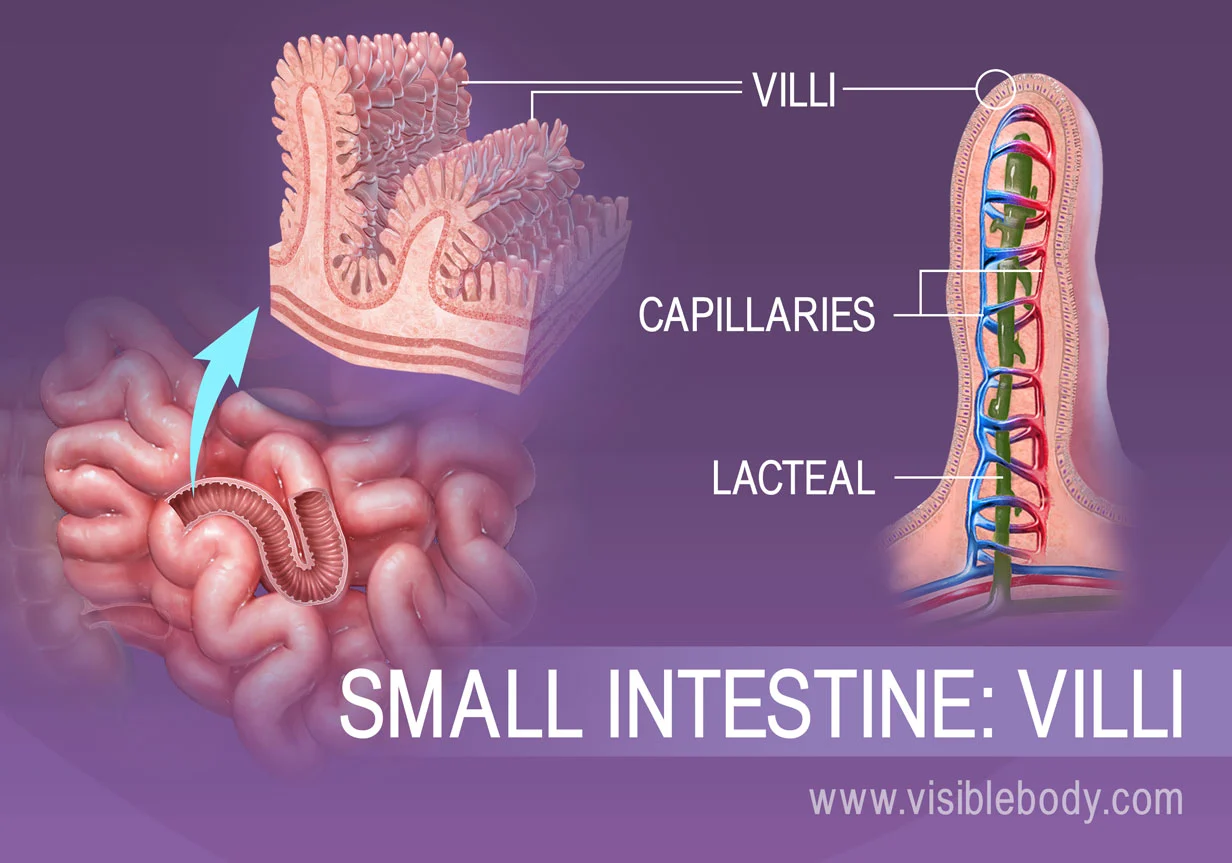
46
New cards
Duodenum
The initial segment of the small intestine that receives partially digested food from the stomach. It plays a crucial role in the breakdown of food through the action of digestive enzymes.
47
New cards
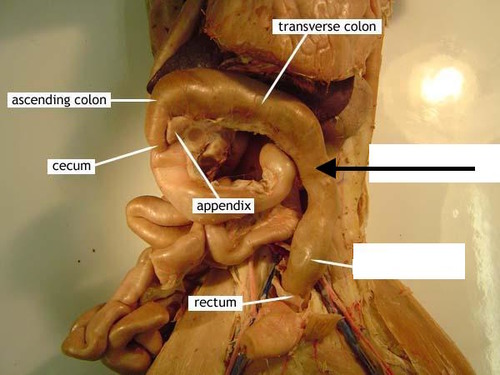
Large Intestines
Also known as the colon, the large intestine is responsible for the absorption of water and electrolytes and the formation of feces.
48
New cards
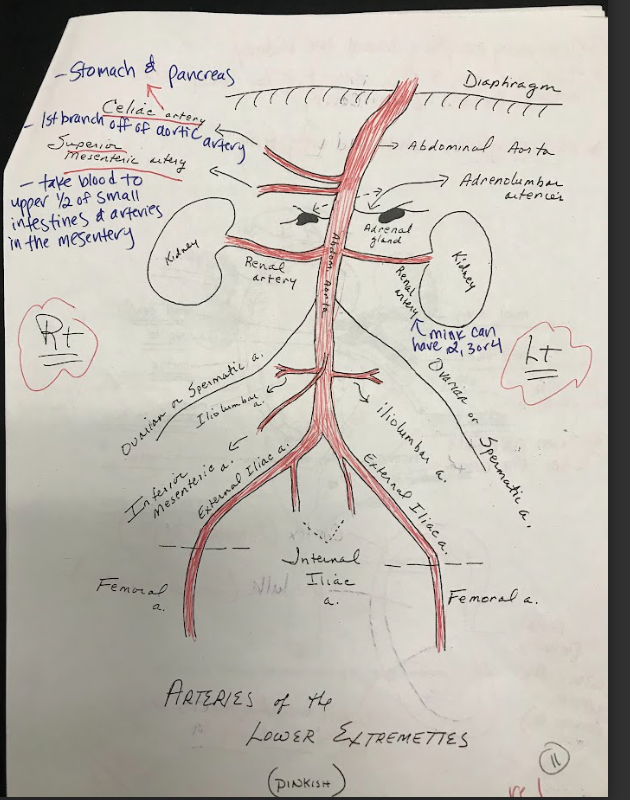
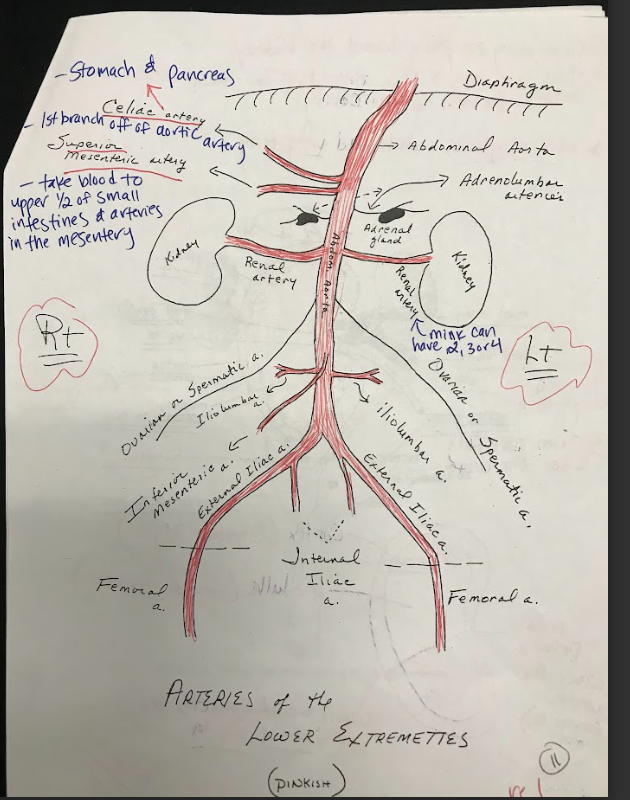
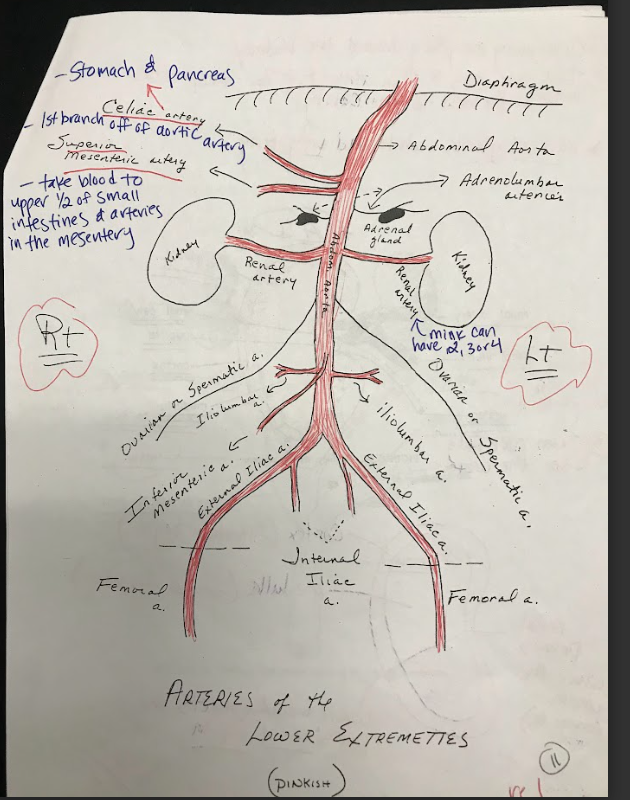
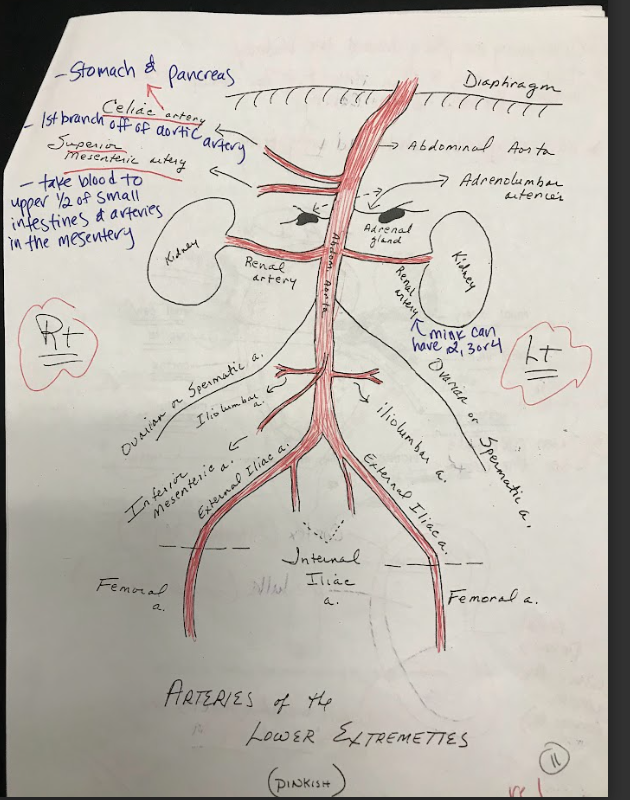
Celiac Artery
A major branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, stomach, spleen, and other abdominal organs.
49
New cards
Superior Mesenteric Artery
Arises from the abdominal aorta and supplies blood to the small intestine, cecum, and ascending colon.
50
New cards
Inferior mesenteric artery
Arises from the abdominal aorta and supplies blood to the descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum.
51
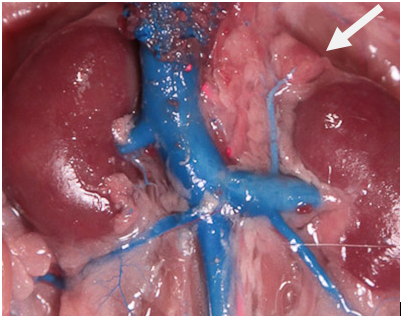
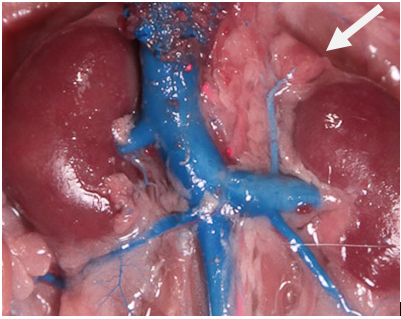
New cards
Adrenal Glands
Small, triangular-shaped glands located on top of each kidney. They produce hormones that regulate metabolism, stress response, electrolyte balance, and blood pressure.
52
New cards
Kidneys
The kidneys are bean-shaped organs responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine. They consist of an outer cortex, an inner medulla, and papilla, which are the small openings where urine is excreted.
53
New cards
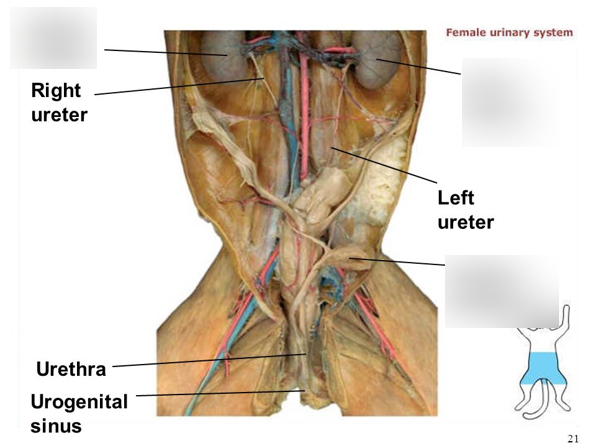
Ureters
Thin, muscular tubes that connect the kidneys to the urinary bladder. They transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder for storage.
54
New cards
Renal Arteries
Branches of the abdominal aorta that supply oxygenated blood to the kidneys.
55
New cards
Renal Veins
Veins that carry deoxygenated blood from the kidneys to the inferior vena cava.
56
New cards
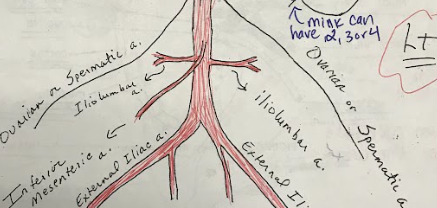
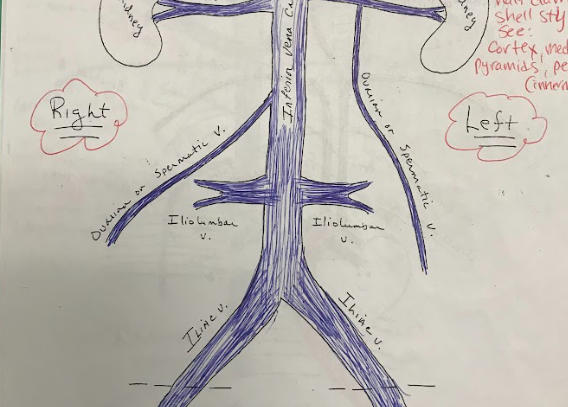
Iliolumbar Arteries
Arteries that supply blood to the muscles and other structures of the lower back.
57
New cards
Iliolumbar veins
Veins that drain blood from the lower back region.
58
New cards
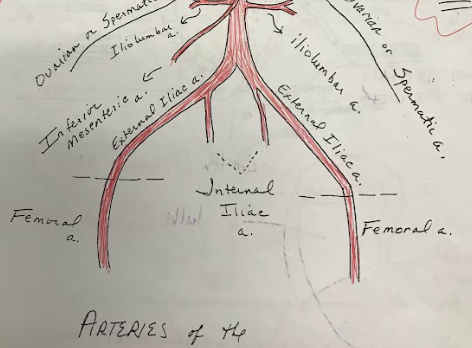
Iliac Arteries
The internal iliac artery supplies blood to the pelvic organs, while the external iliac artery becomes the femoral artery, supplying blood to the lower limbs.
59
New cards
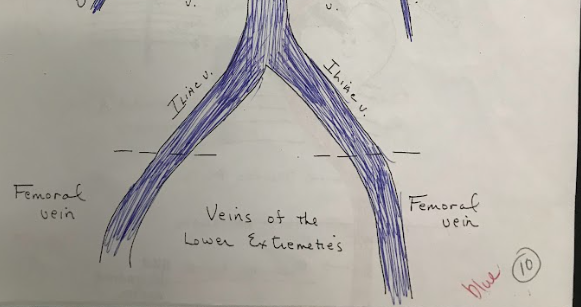
Iliac Veins
Veins that drain blood from the pelvis and lower limbs, merging to form the common iliac veins.
60
New cards
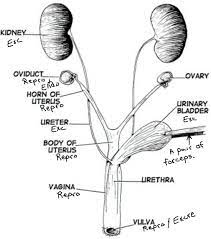
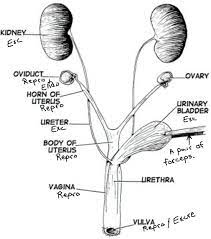
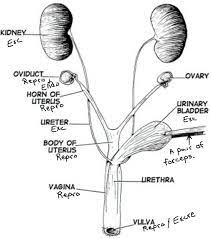
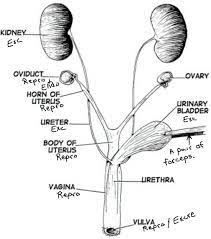
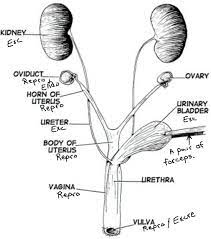
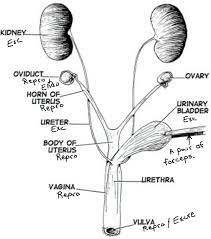
Oviducts
Also known as fallopian tubes, they are thin tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus. They provide a pathway for the egg to travel from the ovary to the uterus.
61
New cards
Ovaries
Female reproductive organs responsible for producing eggs (ova) and female sex hormones.
62
New cards
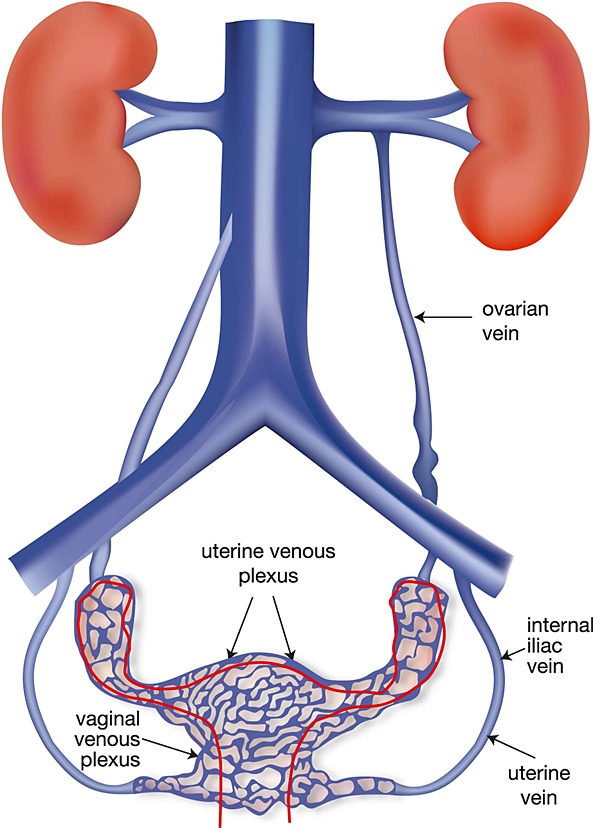
Ovarian Vein
Veins that drain blood from the ovaries and transport it back to the inferior vena cava.
63
New cards
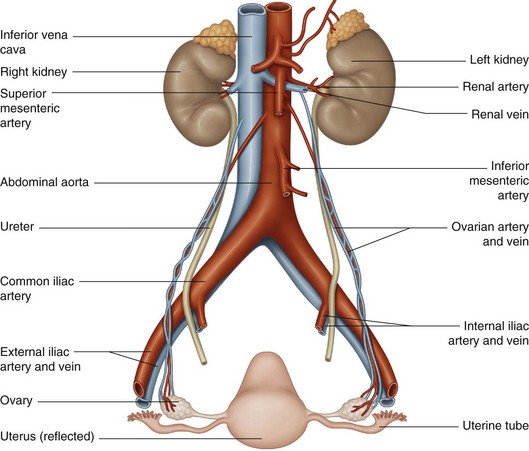
Ovarian Artery
Arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the ovaries.
64
New cards
Horn of Uterus
The upper, wider part of the uterus where the fallopian tubes attach.
65
New cards
Body of Uterus
The main portion of the uterus where fertilized eggs implant and a fetus develops during pregnancy.
66
New cards
Urinary bladder
A hollow, muscular organ located in the pelvis that stores urine until it is excreted through the urethra.
67
New cards
Urethra
A tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body for elimination.
68
New cards
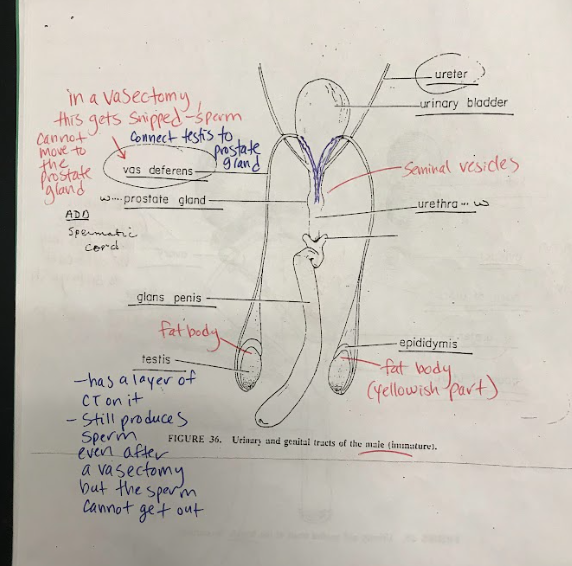
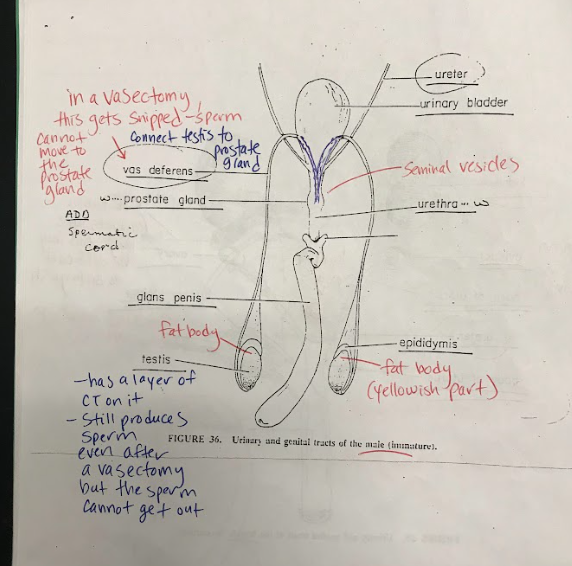
Vas Deferens
Tubes that carry sperm from the testes to the urethra during ejaculation.
69
New cards
Glans Penis
The rounded tip of the penis, which is highly sensitive to stimulation.
70
New cards
Testis
Male reproductive organs responsible for producing sperm and male sex hormones.
71
New cards
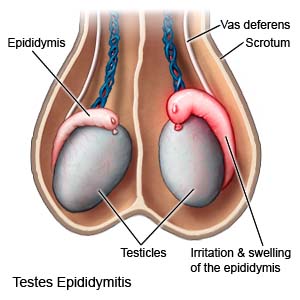
Epididymis
A coiled tube located on the back of each testis, where sperm mature and are stored before ejaculation.
72
New cards
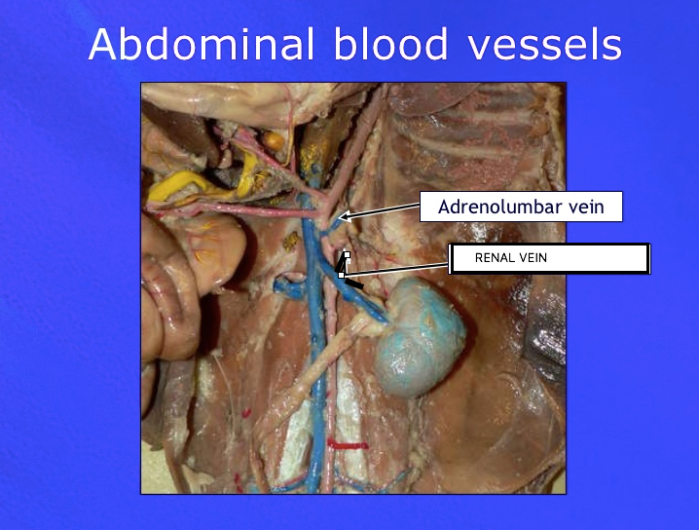
Adrenolumbar veins
Veins that drain blood from the adrenal glands and surrounding structures.
73
New cards
Adrenolumbar Arteries
Arteries that supply blood to the adrenal glands and surrounding structures.
74
New cards
Ribs
Curved bones forming the skeletal framework of the chest, protecting the internal organs, such as the heart and lungs.