Circulation and Respiration
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What is the function of the respiratory system and the circulatory system?
Respiratory system: functions in gas exchange with external environment
Circulatory system: moves gases (and other substances) around within body
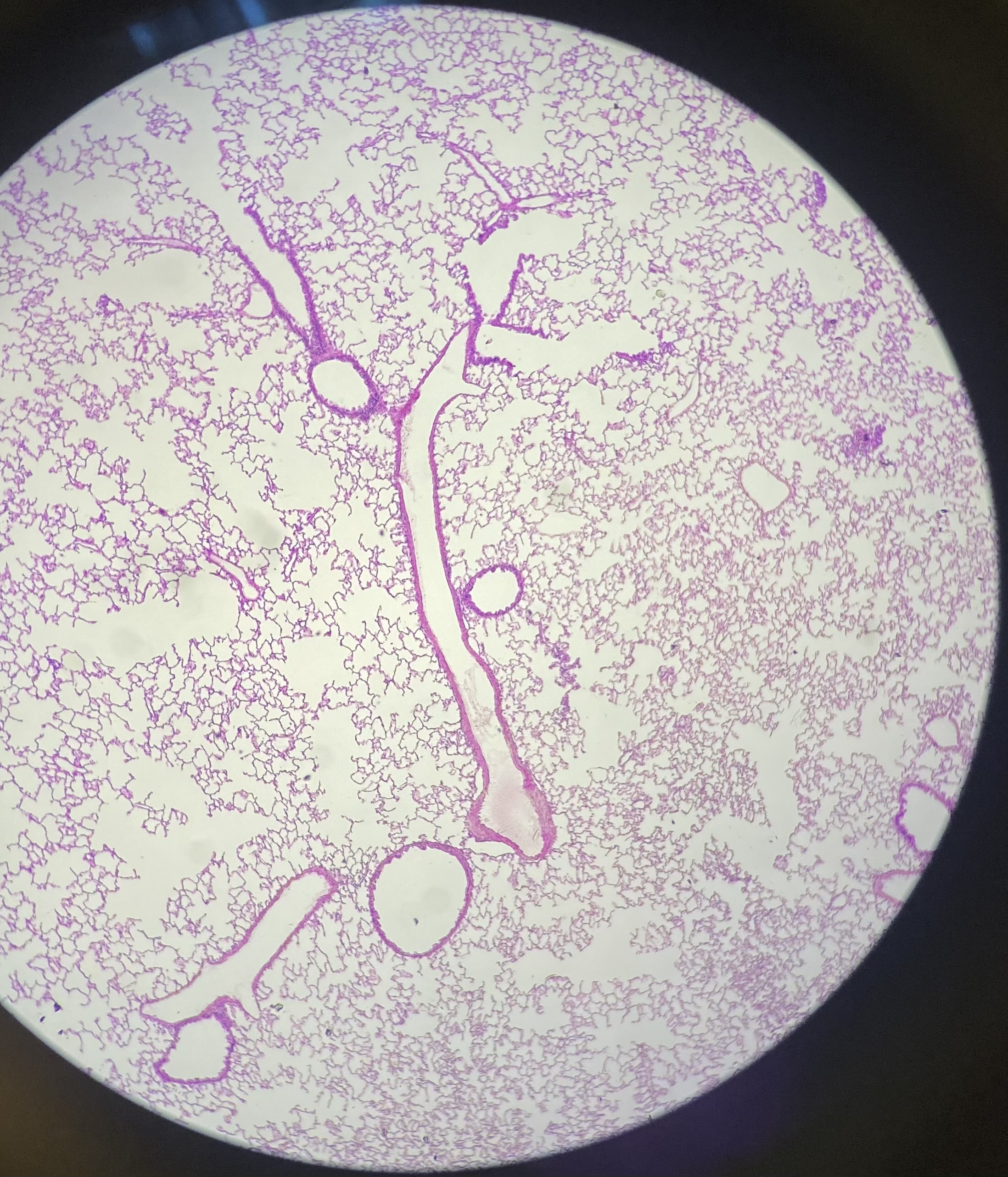
What is shown in the image? What are structures seen in the image?
Lungs and bronchioles (hyaline cartilage only seen on large bronchioles). Branchiole (large holes), alveoli (small geometric)
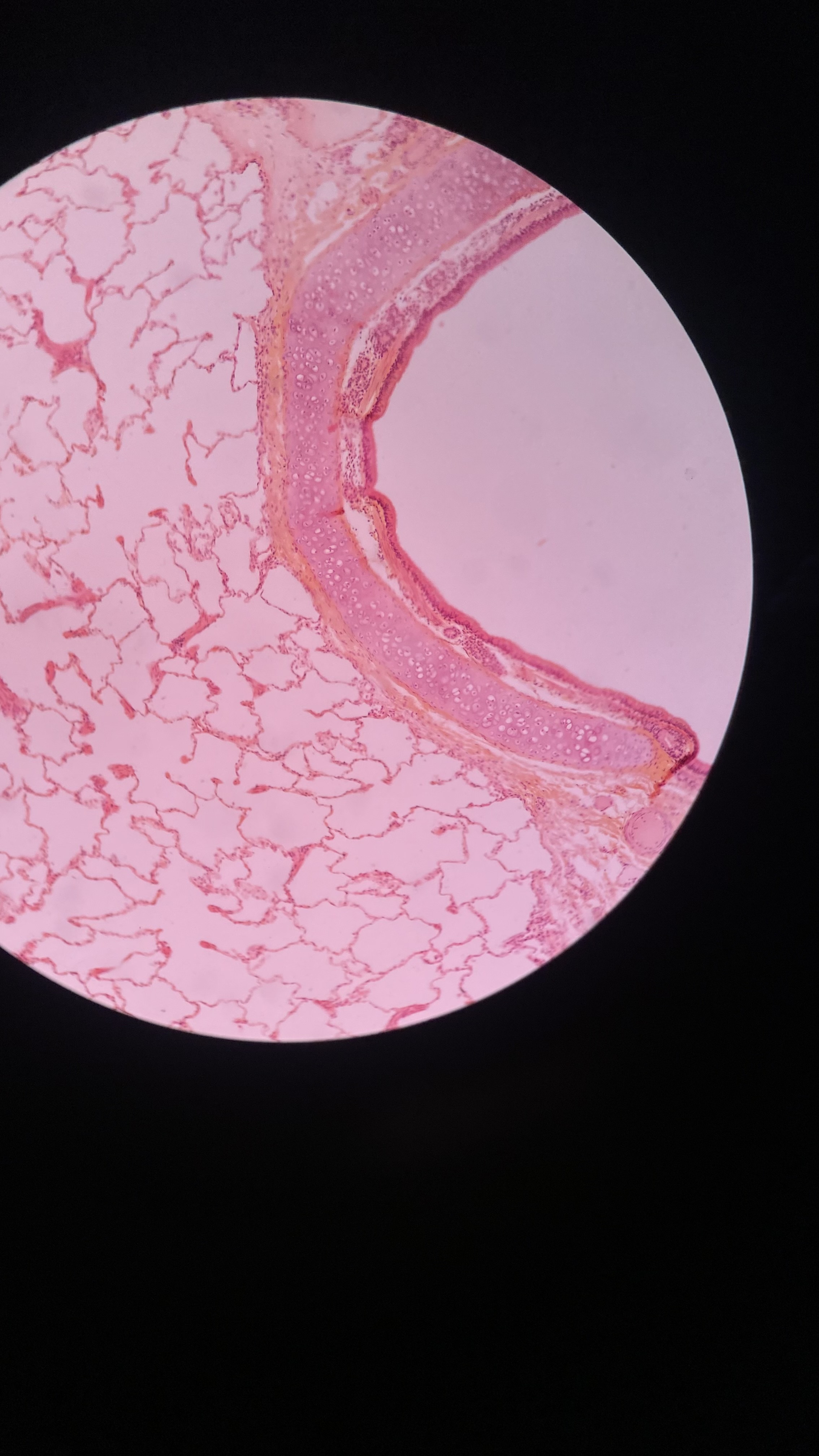
What is shown in the image? What are structures seen in the image?
Lungs and bronchioles. Lumen, epithelial tissue (lining lumen), smooth muscle (next to lumen), hyaline cartilage (next to smooth muscle), alveoli (holes structures)
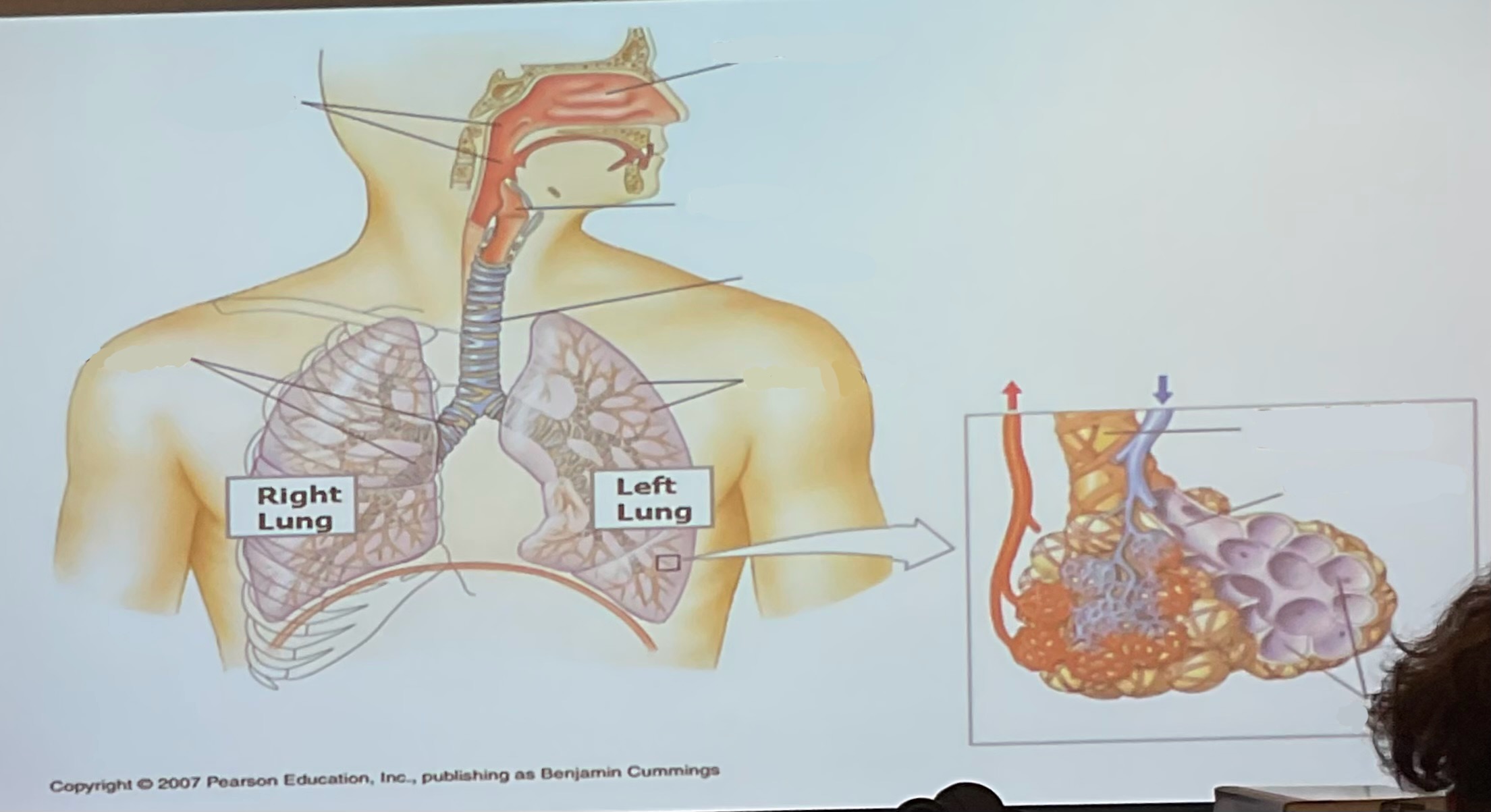
What are the parts of the respiratory system and its function.
Nares: allow air to pass to pharynx
Larynx: allow for sound production
Trachea(windpipe): allow air from pharynx to lungs
Bronchi: two tubes carry air from pharynx to lungs
Lungs: organ of respitory tract with internal surfaces for gas exchange with blood
Alveoli: where gas exchange occurs in lungs
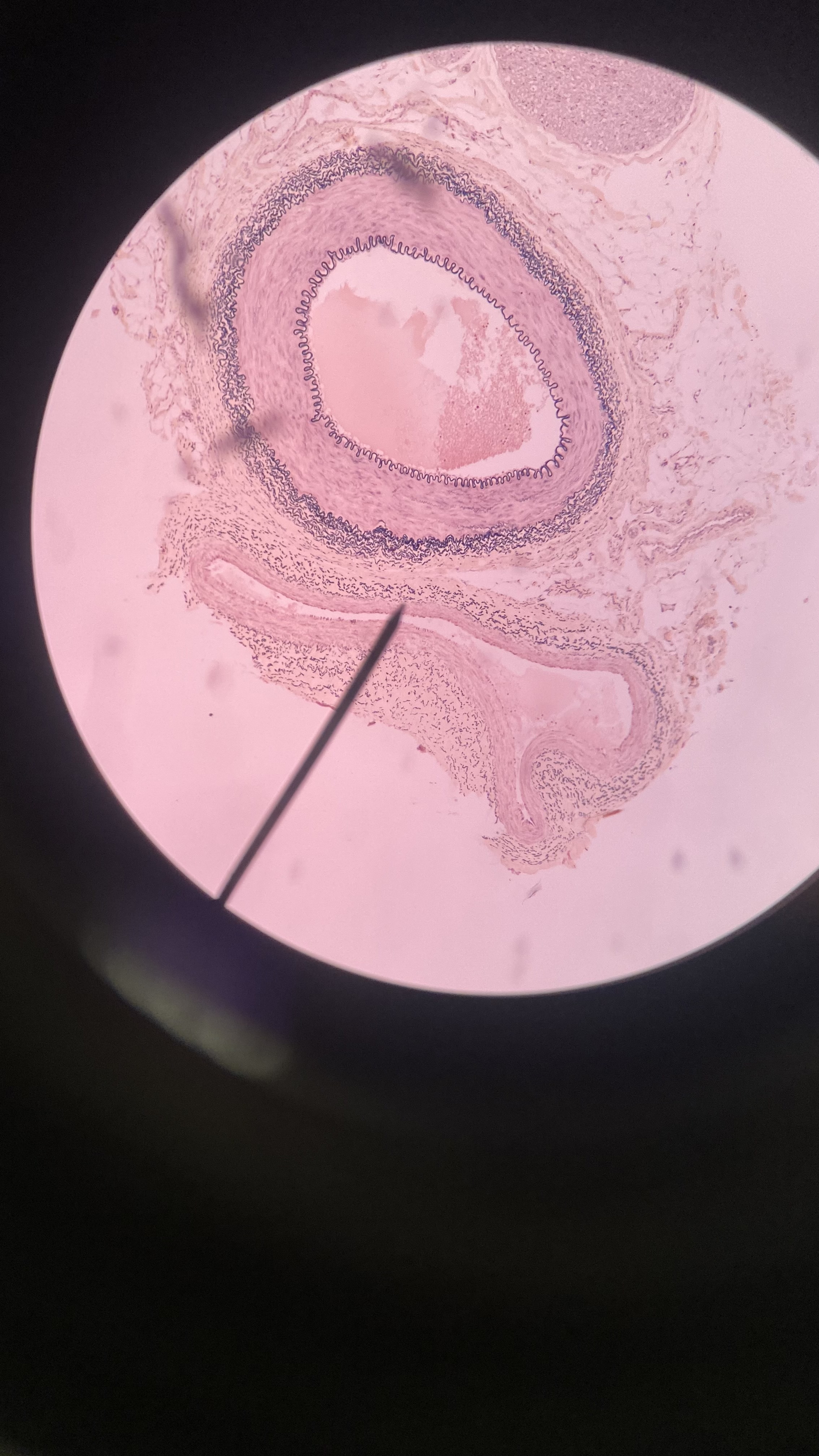
What is shown in the image? Name it’s structures.
Artery (large, blood away from heart) and vein (small, long, blood to heart)
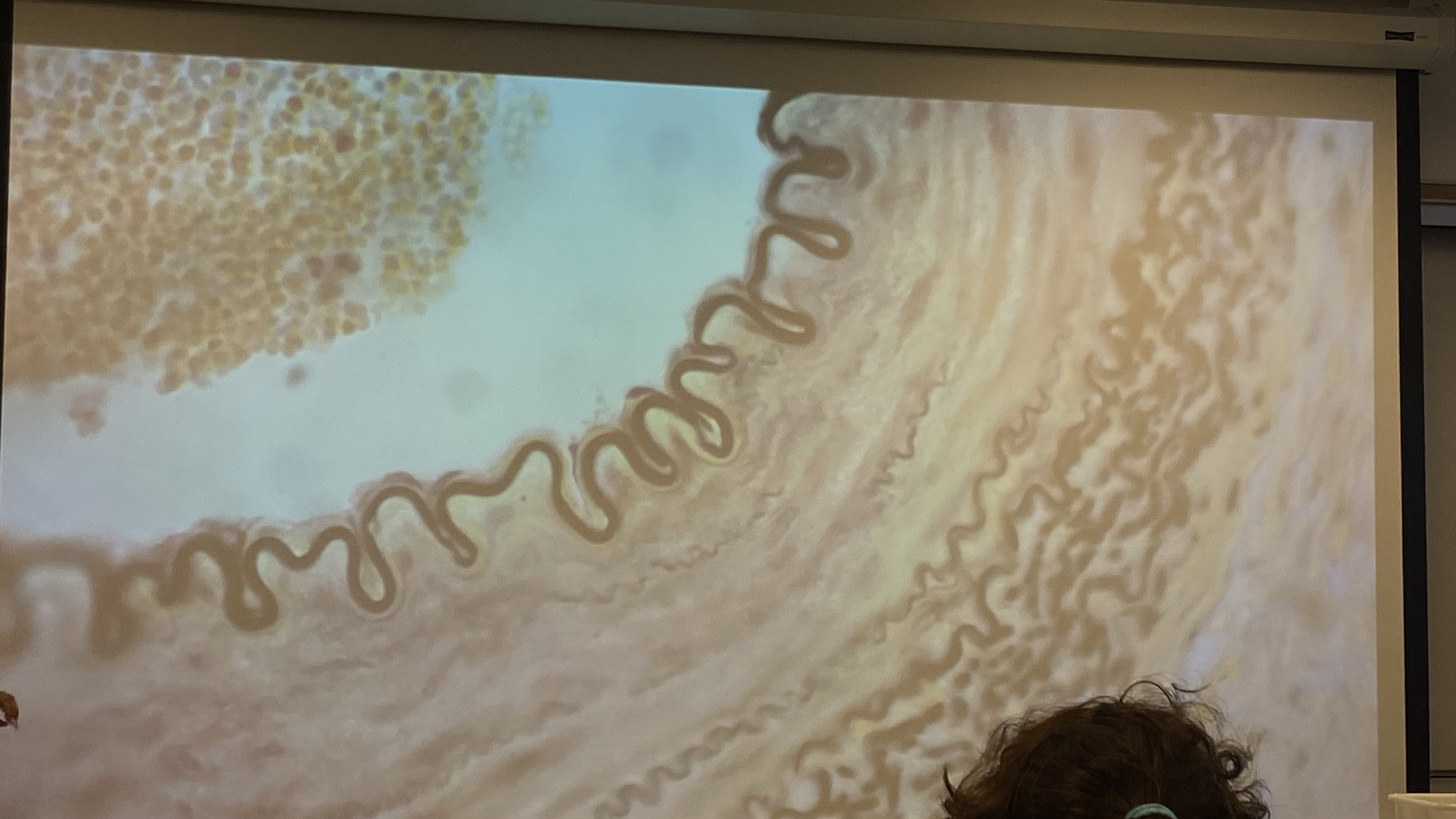

What is shown in the image? Name it’s structures.
Artery. Tunica intima (innermost to lumen with simple squamous epithelium), internal elastic membrane (dark squiggly ONLY in arteries), tunica media (after elastic membrane), tunica adventitia (dark squiggly lineS)
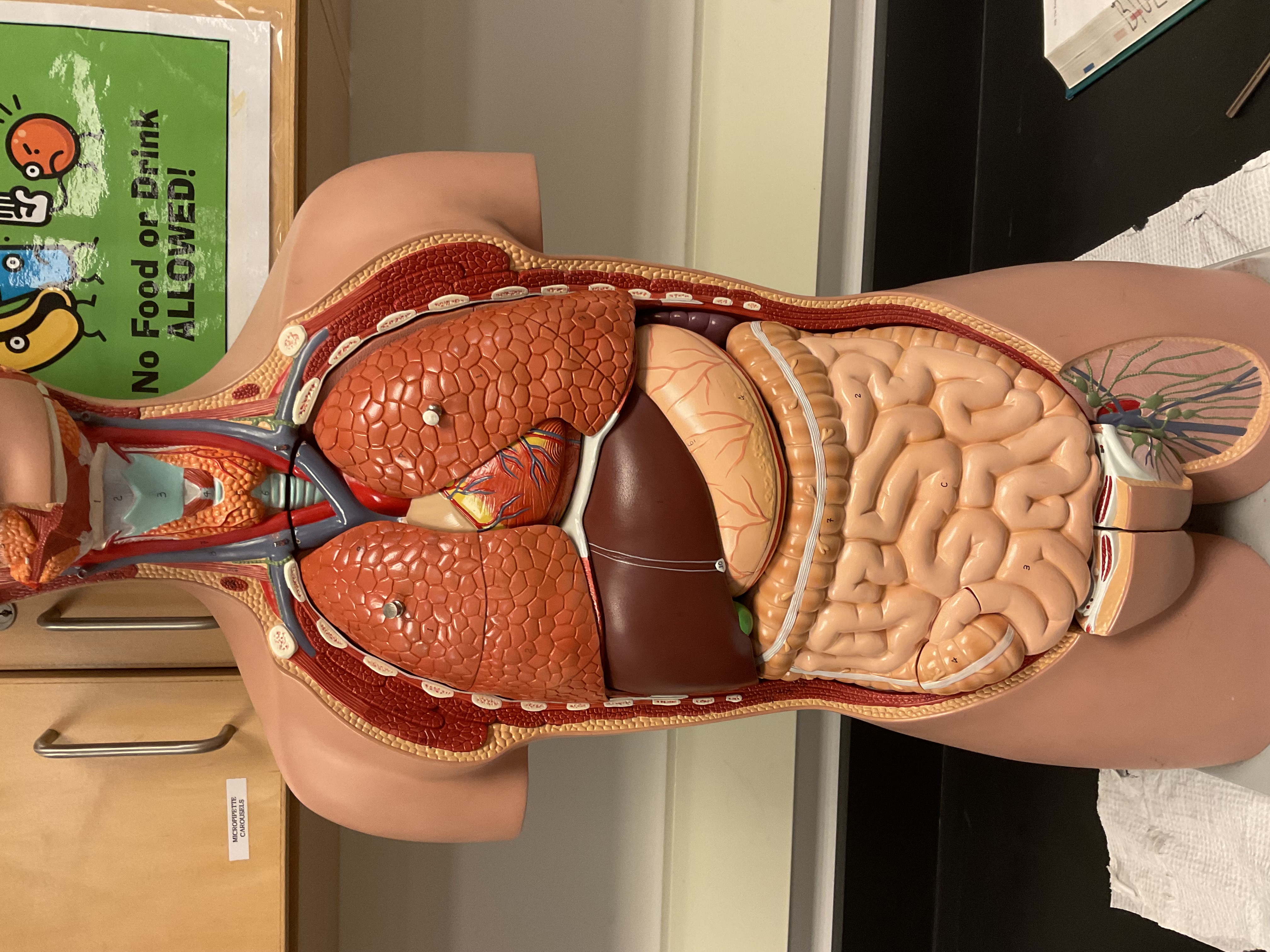
What is shown in the image? Name it’s structures.
Heart: elevates pressure in blood vessels to pump blood throughout body
Spleen (right corner): destroy old erythrocytes and produces lymphocytes (in infants also produce erythrocytes)

What is shown in the image?
Pulmonary arteries (blue lateral), pulmonary veins (red lateral)

What is shown in the image?
brachiocephalic trunk, left common carotid artery, left subclavian artery
Inferior vena cava, superior vena cava
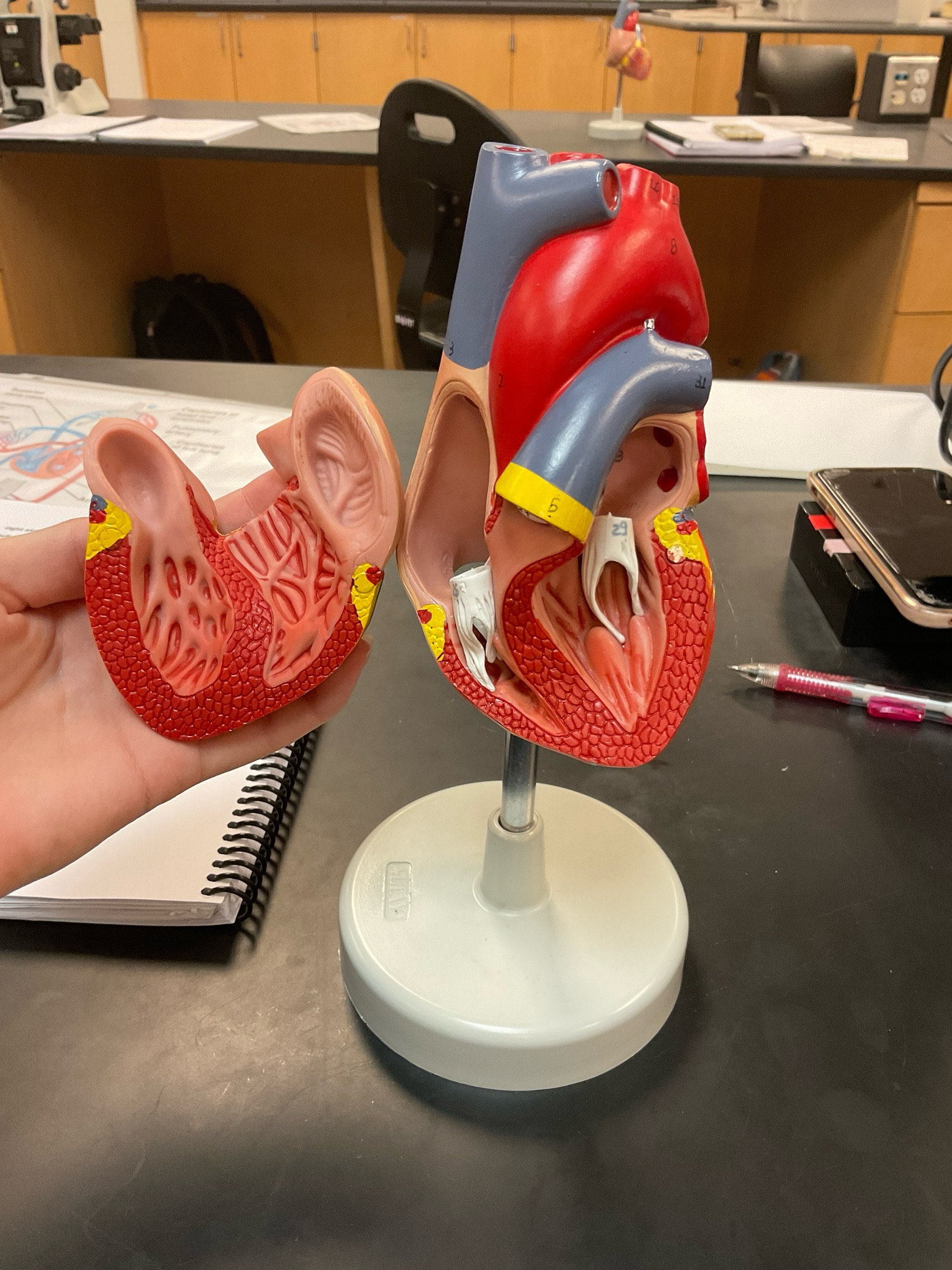
What is shown in the image?
Right atrium (on left), tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary semilunar valve into pulmonary arteries)
Left atrium (on right), mitral valve, left ventricle, aortic semilunar valve (into) aorta/aortic arch
Where do the three arteries on the aorta travel to? What do valves do?
Brachiocephalic trunk: carries blood to right shoulder, upper arm and head
Left common carotid artery: carries blood to left side of neck and head
Left subclavian artery: carries blood to left shoulder and upper arm
Valves prevent backwards flow
What is the order of oxygenated/deoxygenated blood?
Oxygenated blood (straight from lungs) return to heart through pulmonary veins into left atrium, mitral valve and left ventricle into aortic semilunar valve into aorta. Blood travels into brachiocephalic trunk, left common carotid artery, left subclavian artery, and aorta (into upper and lower body). Blood then returns through superior vena cava and inferior vena cava into right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, and pulmonary semilunar valve into pulmonary arteries that carry blood to get oxygenated in lungs