rhythm strips
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
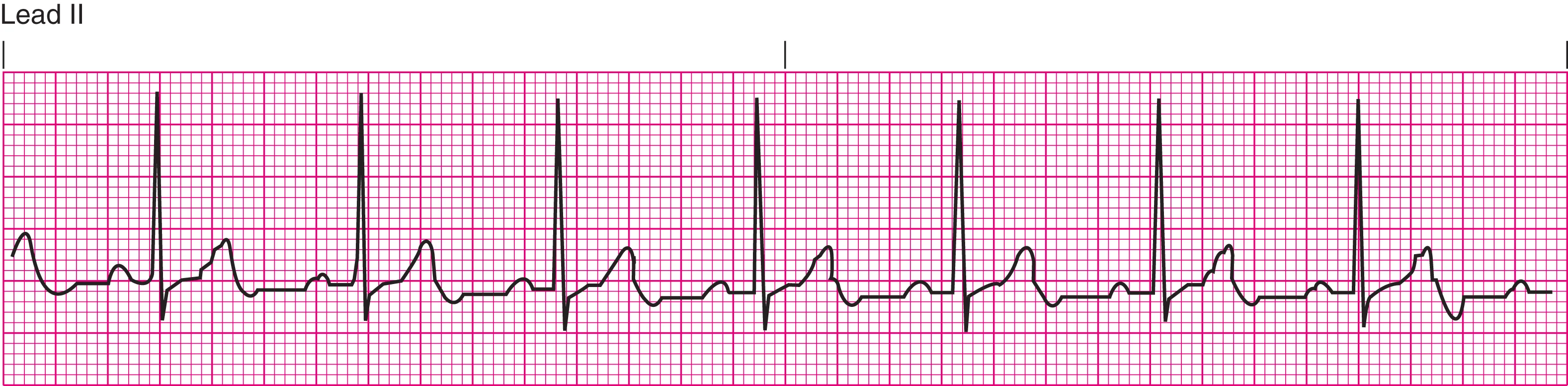
Normal sinus
60-100 bpm
regular rhythm with visible P, R, and T waves
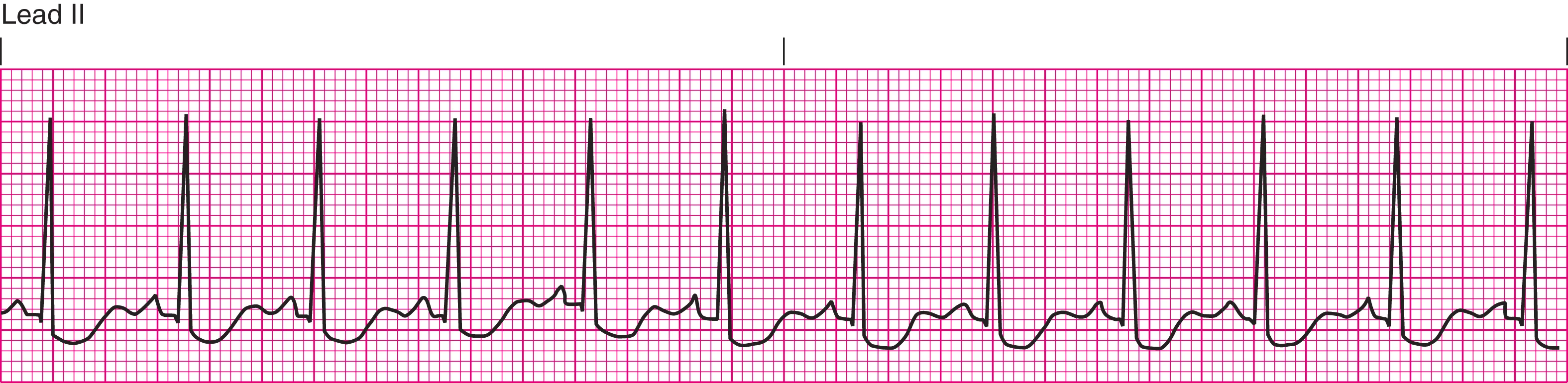
Sinus Tachycardia
greater than 100 bpm
regular rhythm with visible p, r, and t waves
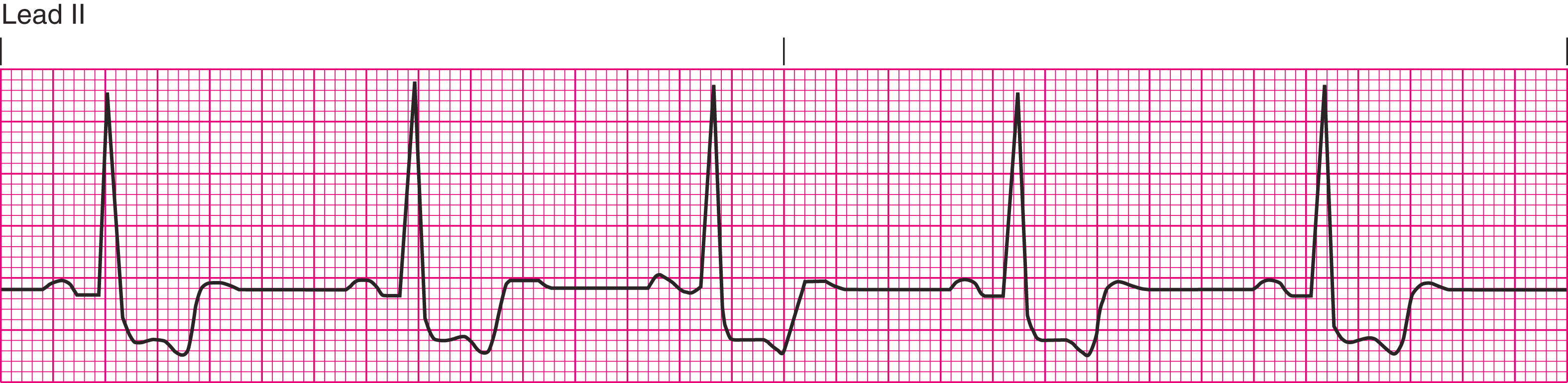
sinus bradycardia
less than 60 bpm
irregular to regular rhythm with visible p, r, and t waves
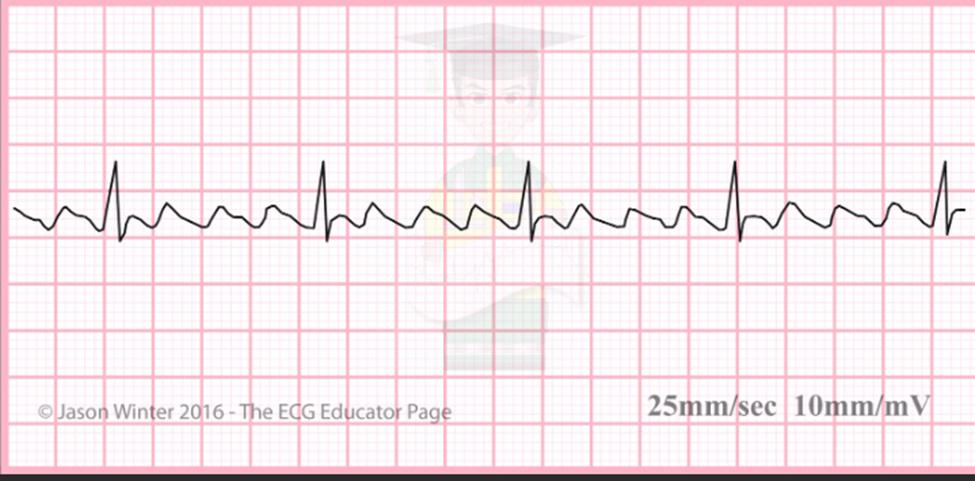
atrial flutter
regular rapid heart rhythm originating in the atria, typically characterized by a "sawtooth" pattern
More P waves than QRS, T waves present
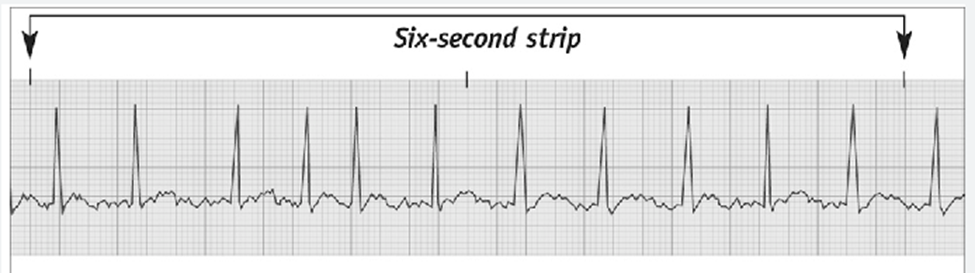
atrial fibrillation
irregular rhythm with fluctuating heart rate
most likely to clot
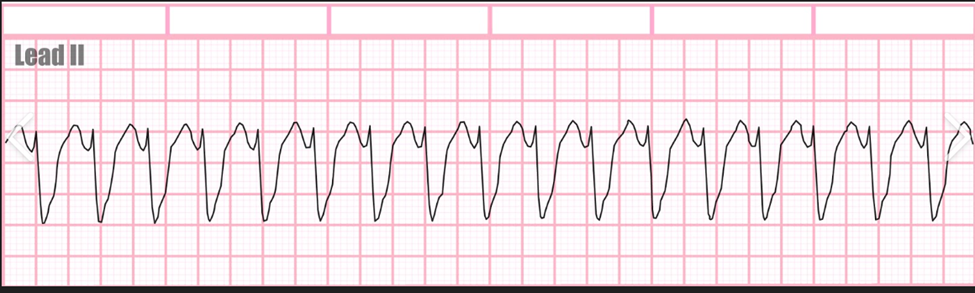
ventricular tachycardia
regular fast heart beat with no P waves and wide QRS intervals
Medical emergency, rapid response, shockable rhythm
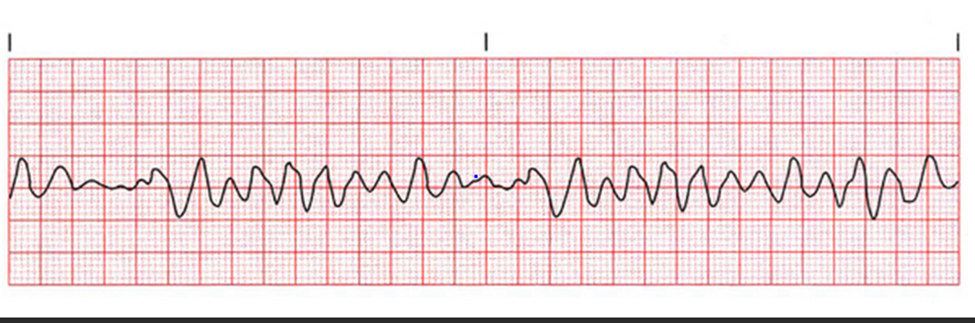
ventricular fibrillation
extremely irregular high heart rate, unable to count bpm
no P waves, QRS interval not measurable, no perfusion
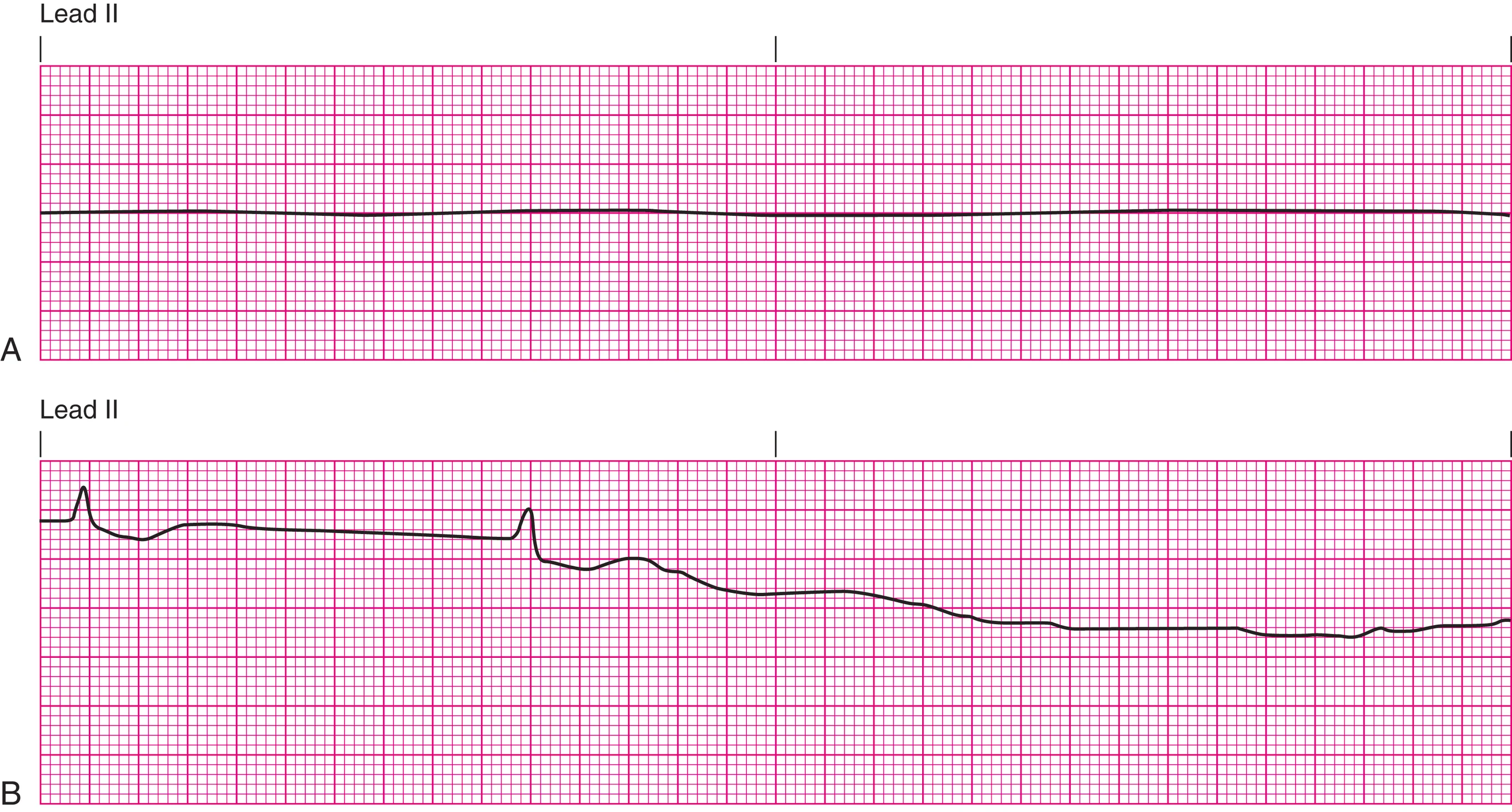
asystole
everything absent
do not defibrillate
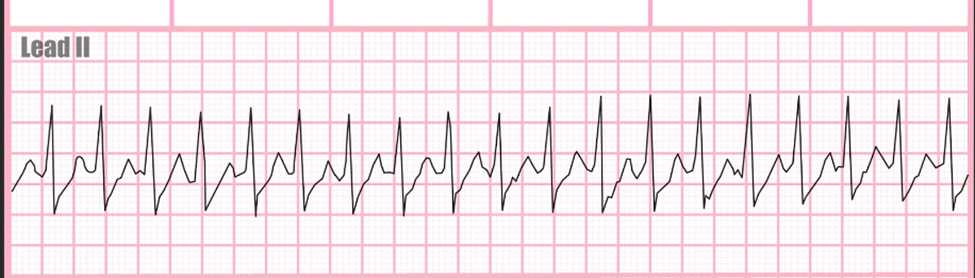
supraventricular tachycardia
regular extremely high heart beat exceeding 140 bpm
narrow QRS, P waves usually present
ST elevation
STEMI: tissue death, MI
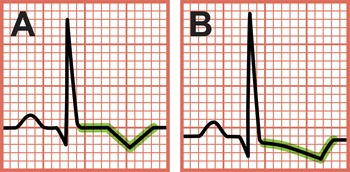
ST Depression
previous tissue damage
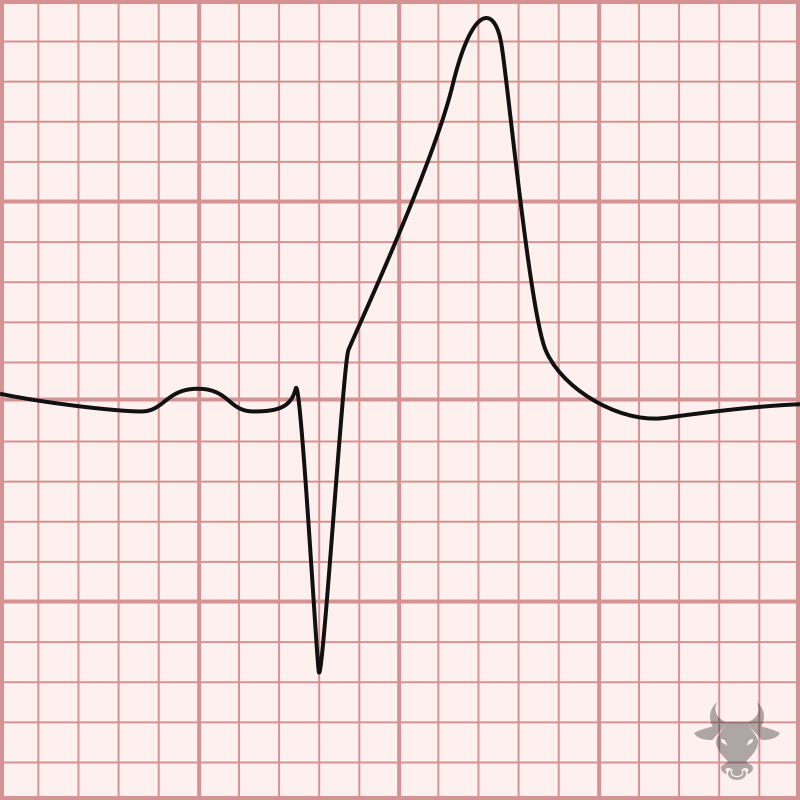
Peaked T wave
high potassium
check baseline t waves to identify
Inverted T wave
low potassium
usually due to diuretic usage
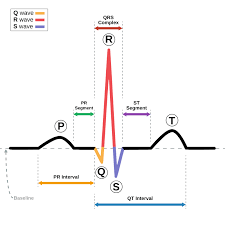
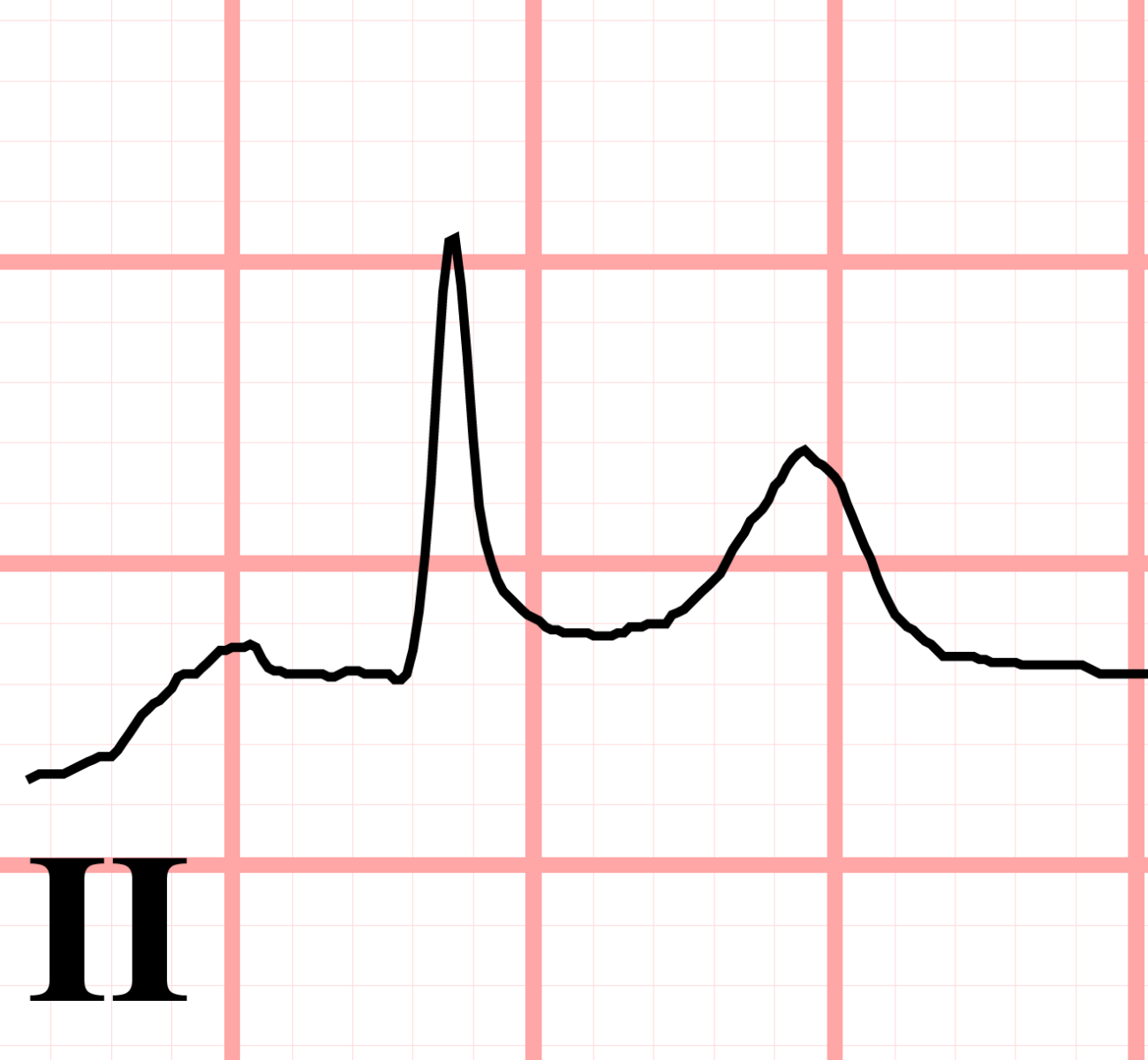
Rhythm strip interpretation
P wave: atrial depolarization
QRS: Ventricular depolarization
R: electrical stimulus, heart beat is considered regular when R waves are equal distance apart
ST: distance between end of QRS and T wave
T wave: Repolarization, heart at rest
PR interval: count number of boxes between start of P wave and start of QRS
SV node
pacemaker of the heart
heart rate will be within normal range 60-100 bpm
AV node
takes over if SV node fails
heart beat will be between 40-60 bpm
Ventricles
takes over if both SV and AV node fail
heart beat will be less than 40 bpm
decreased perfusion which causes cells to die
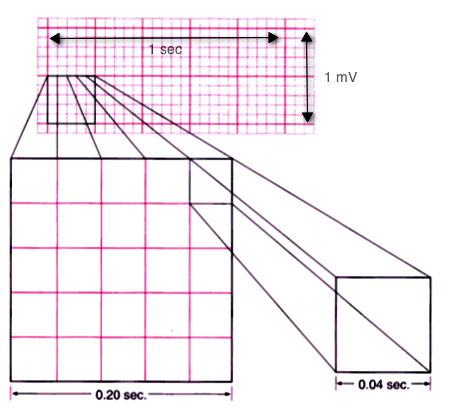
Rhythm strip boxes
each small box is 0.04 sec
1 large box is 0.20 sec
strips are 6 sec, multiply by 10 to get bpm
12 lead ekg
shows heart from different angles
defirbillation
only done on unconscious pt
EMERGENCY
higher joules
cardioversion
conscious pt, then sedated
can be done outpatient
lower electrical current than defibrillation
Ablation
uses radiofrequency energy to destroy segment of heart tissue that is causing rapid or irregular heart beats when pt is unresponsive or intolerant to medication therapy
Pulseless electrical activity (PEA)
has rhythm with no pulse
mimics sinus brady
Start CPR
Pacemaker care and teaching (PACER)
P: pulse/pain meds as needed, monitor HR and Bp, teach client to check HR daily and notify HCP if pulse is <5 bpm
A: Assess insertion site for redness, drainage, swelling, hematoma
C: control and minimize shoulder movement initially, may need sling. client instructed to have no heavy lifting
E: Evaluate rhythm strip for pacemaker spike
R: Record insertion time, model #, settings, client response. Recommend client to wear medical alert bracelet and carry pacemaker ID card. Notify HCPs of any diagnostic test (MRI, etc.)
Interventions for symptomatic sinus bradycardia
give atropine ( increases HR) and suplemantal O2 as needed
Interventions for symptomatic sinus Tachycardia
give amiodarone (Most common med), calcium channel blockers, digoxin, beta blockers
may need ablation or cardioversion
Interventions for A-Fib and Atrial flutter
Supplemental O2, fall precautions
medications to decrease HR (calcium channel blockers, beta blockers, digoxin) Adenosine for HR >150 bpm
Anticoagulants, client teaching about safety, monitor INR, PT, PTT, diet
prepare client for cardioversion or ablation
A-Fib does not convert to normal sinus, keeps HR below 100 bpm with medication
Interventions for Ventricular tachycardia (w/ & w/o pulse)
CALL RAPID
W/ Pulse:
give Amiodarone (1st), lidocaine, or procainamide
prepare for cardiac ablation
W/o Pulse:
begin CPR until defibrillator is connected
defibrillate starting at 120 then increasing until reaching 200 joules
Follow ACLS protcols for med admin
prevention: client may need ACID device implanted for future episodes
Interventions for Ventricular fibrillation
CALL CODE
Begin CPR
Give O2 (May need intubation)
Follow ACLS protocol for meds. (Amiodarone, Lidocaine, vasopressin)
Defibrillate
PT may need AICD
Supraventricular tachycardia interventions
Give adenosine (stops HR then restarts)
vagal manuver
Asystole Interventions
Begin CPR
Give O2/ABG results/O2 sat
Follow ACLS protocols for med admin. (Epinephreine)
Prepare to defibrillate if rhythm returns. DO NOT DEFIBRILLATE IF NO RHYTHM