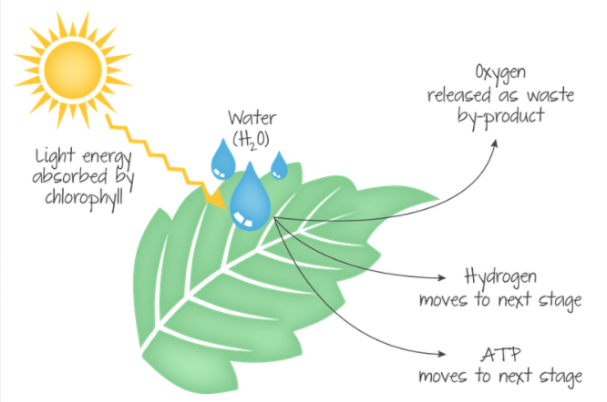
Light Reaction
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
IB Bio Unit 5 SL year 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
2 halves of photosynthesis
light reaction, and calvin cycle

where light reactions occur in photosynthesis
in the thylakoids
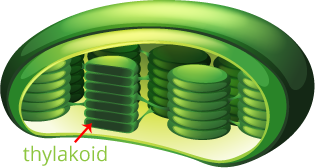
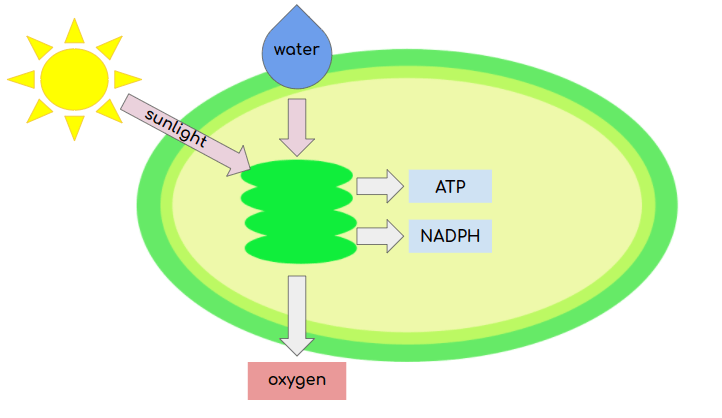
Light Reaction description (Photosynthesis)
Uses photosynthetic pigments (ex chlorophyll) to absorb light, Splits H2O, releasing O2 as a byproduct, Produces ATP and NADPH for the Calvin Cycle
where the calvin cycle occurs
in the stroma
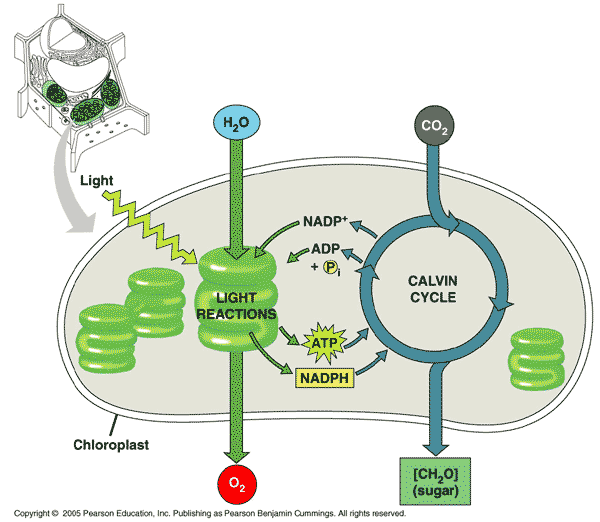
Calvin cycle description
Uses ATP and NADPH from the light reaction, Carbon fixation of CO2 from the atmosphere, Produces Sugars (glucose)
light reaction inputs
sunlight, water, ADP, NADP+
light reaction outputs
O2, ATP, NADPH
calvin cycle inputs
CO2, ATP, NADPH
calvin cycle outputs
sugars, ADP, NADP+
why plants do not convert CO2 into O2
plants dont absorb CO2 and produce O2, they are 2 separate processes. the oxygen produced was not the oxygen that was in the carbon dioxide
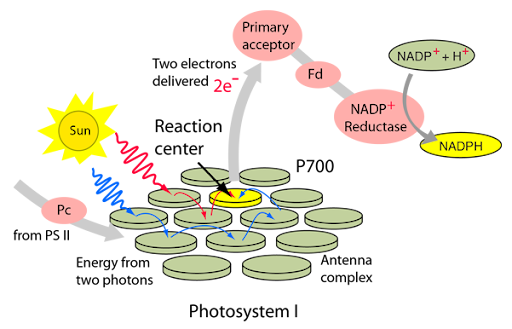
photosystems location
Integral protein complexes located within the phospholipid bilayer of the thylakoid membrane
type of molecules in photosystems
chlorophylls and other accessory pigments that will absorb light energy
how photosystems absorb light
Photons of light strike the pigment molecules within the photosystem, which creates excited electrons
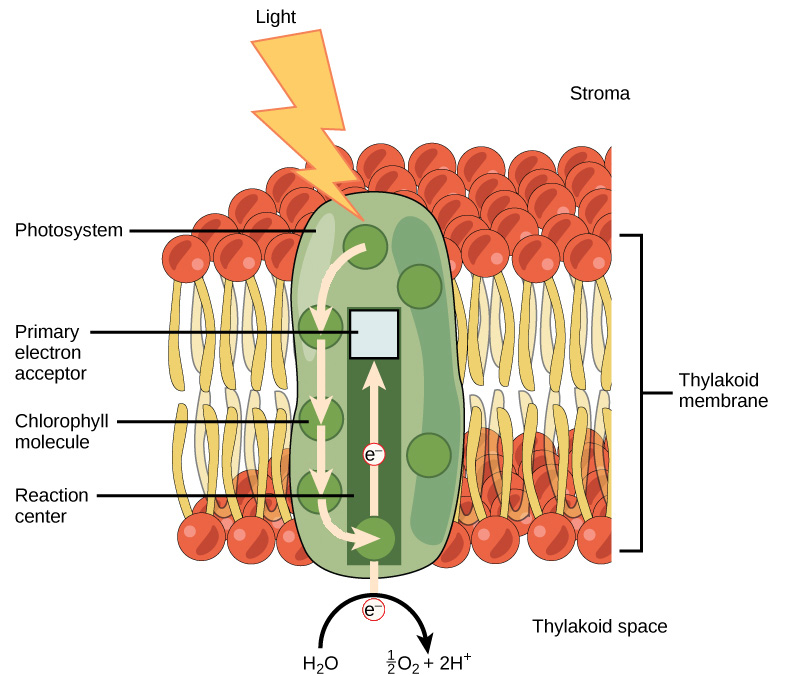
electrons in pigment molecules that contain extra energy that is used to create ATP
excited electrons
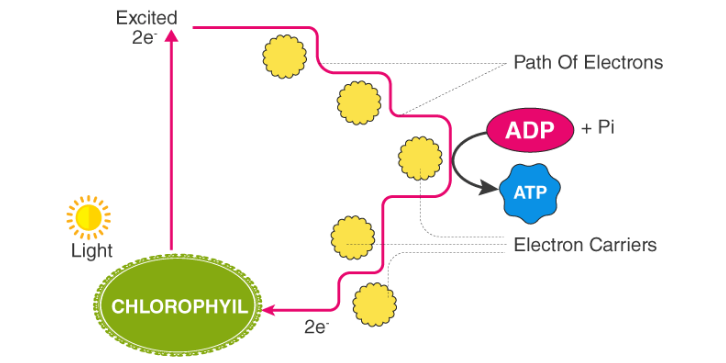
photophosphorylation
the process of utilizing light energy from photosynthesis to convert ADP to ATP, which will go to power the calvin cycle. electrons are ultimately transferred to electron carriers.
electron carrier that becomes NADPH when it picks up 2 electrons
NADP+
photolysis
the process of using light energy to break water molecules in order to replace missing electrons in the photosystem, occurs in thylakoid space, O2 is created as a by product, electrons from H2O are transferred to the photosystem.