HK 302 Exam 3 Pathology
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
majority of problems in the spine occur
where secondary curves meet the primary curves
lld - leg length discrepancy
one leg longer than the other causes never pelvis then corrected higher up at neck
scoliosis
lateral curvature of spine
kyphosis
excessive curvature of the spine, causing hunching of the back
- anterior concave
lordosis
excessive curvature of the lumbar spine
- posterior concave
intervertebral disc injury: micro tears in the annulus fibrosis
lead to changes in nucleus pulposus
micro tears in annulus fibrosis occur with
flexion and rotation with force
- commonly L4-L5 and L5-S1
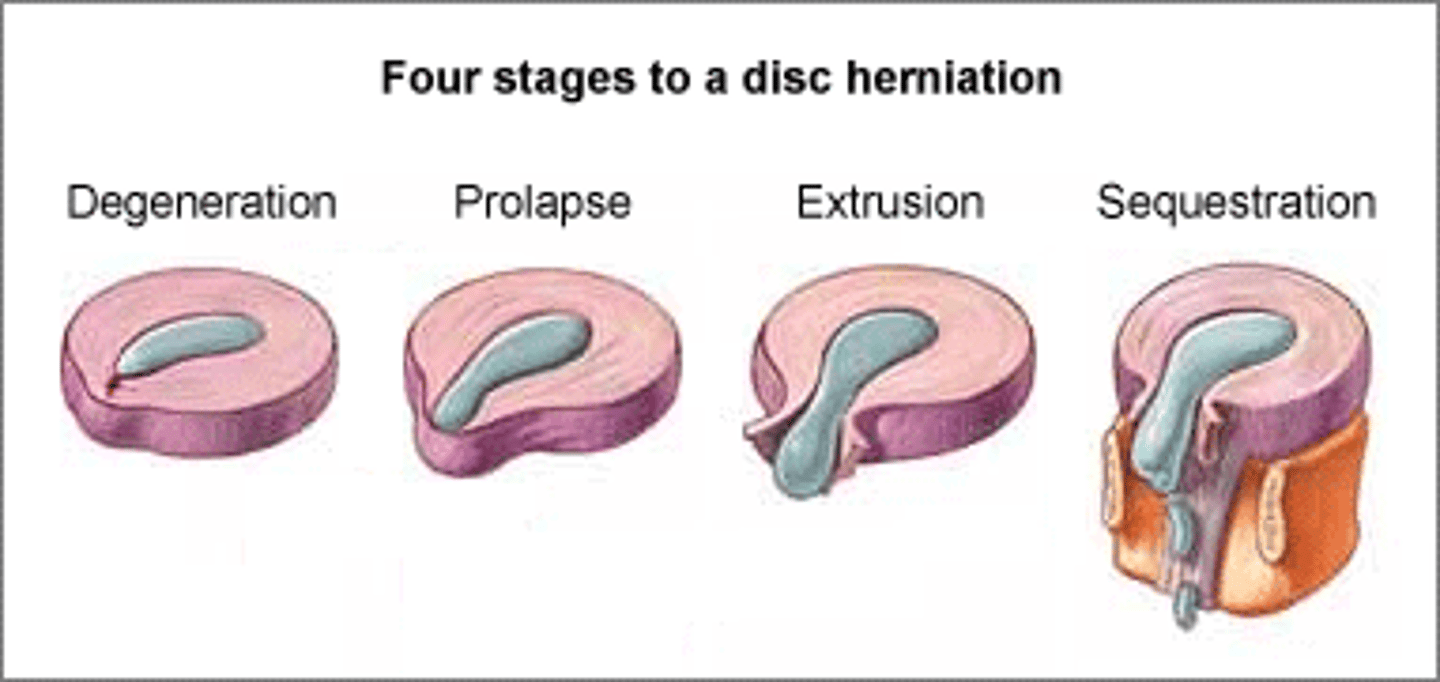
bulging disc
slight deformity in the nucleus
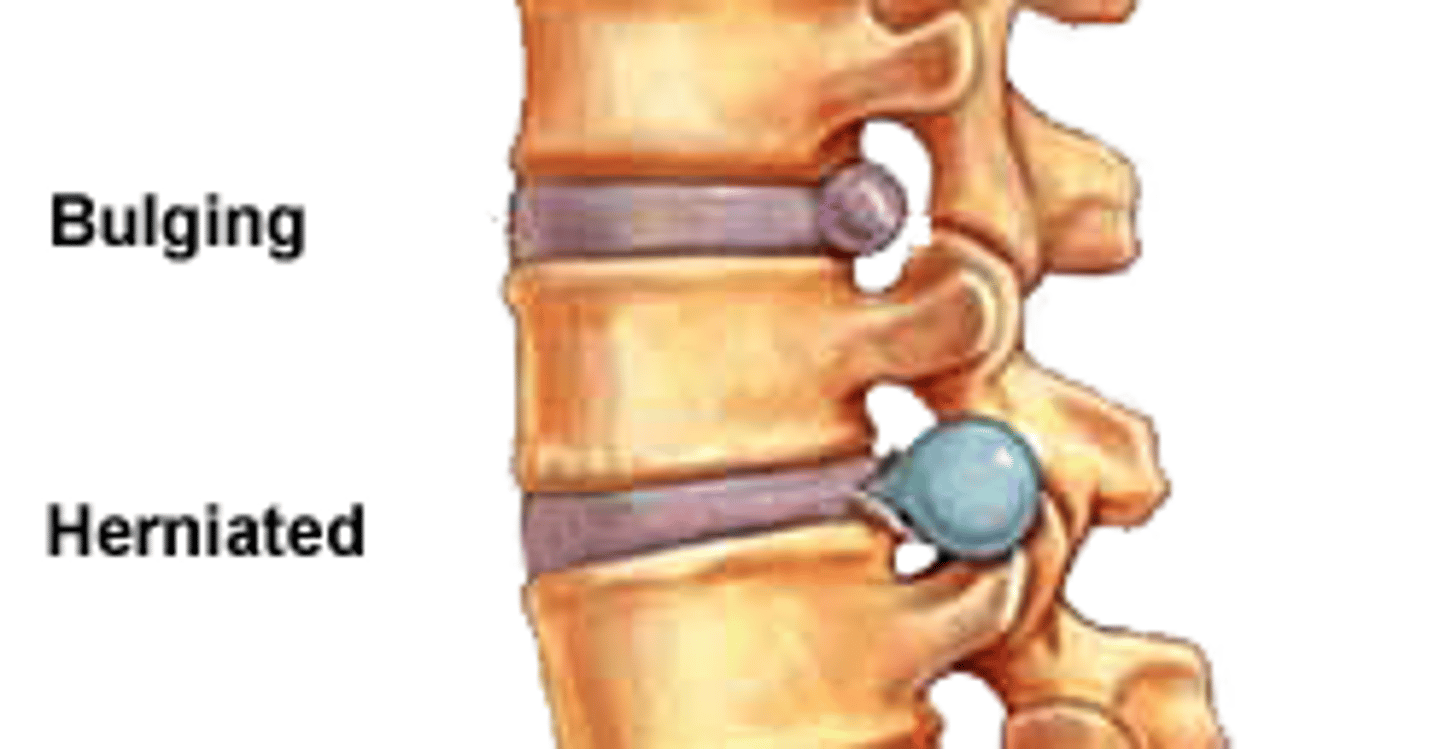
prolapsed disc
deformity extends through the annulus
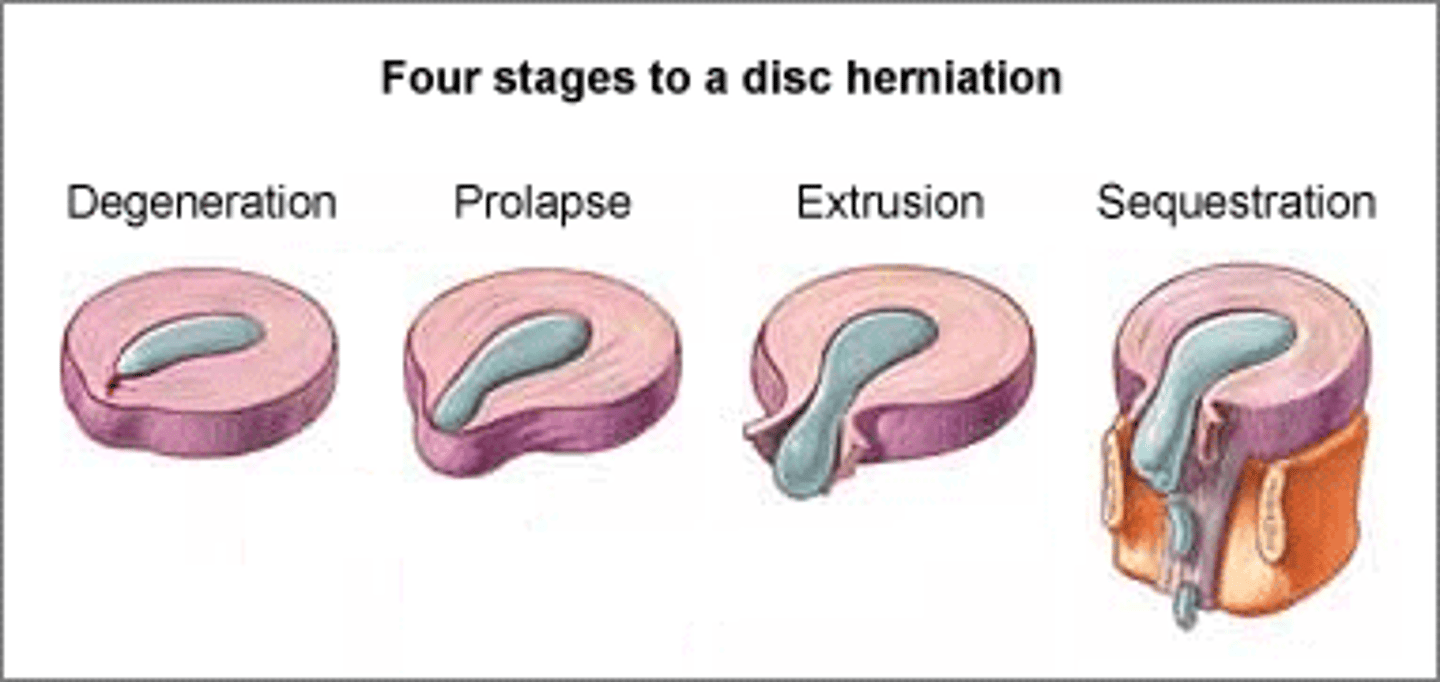
extruded disc
nuclear material moves into the spinal canal
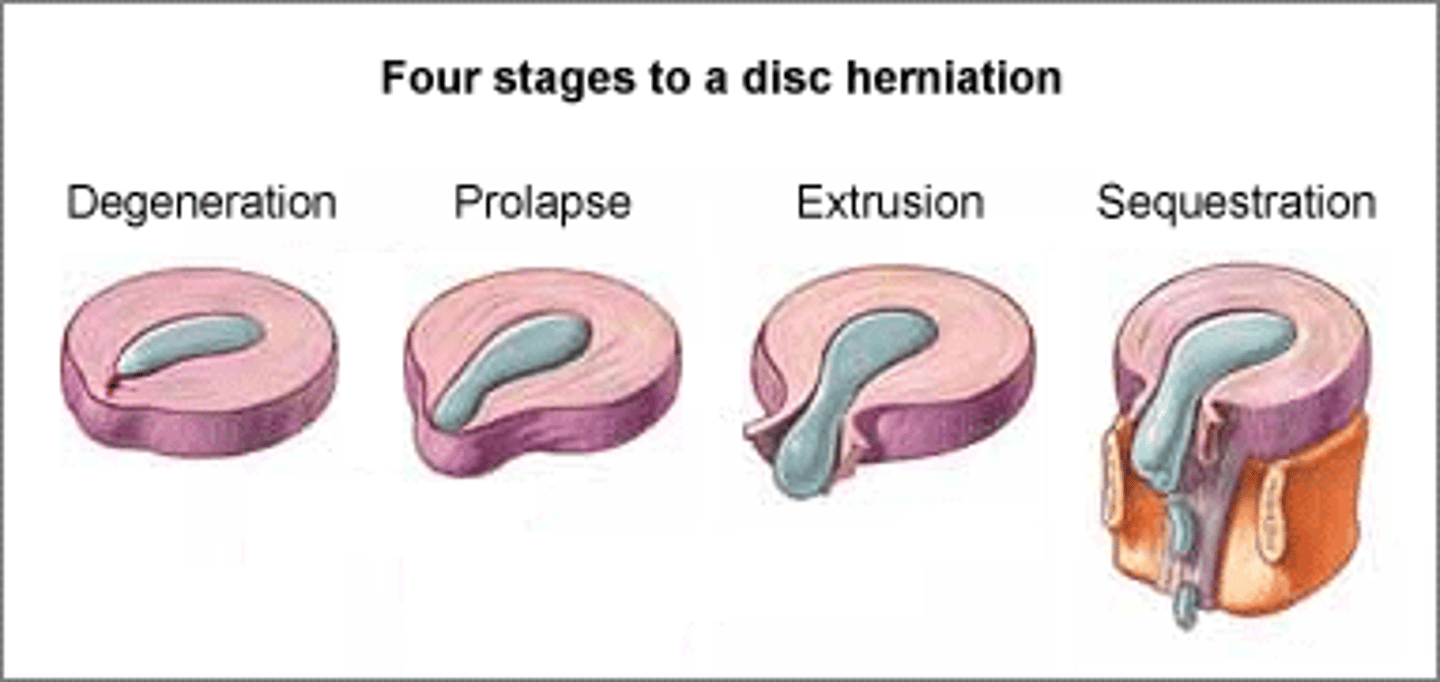
sequestrated disc
nuclear material separates from the disc
signs and symptoms of disc injuries
- pain does not occur until other structures are impinged upon (disc is aneural)
- suppressions of deep tendon reflex
- sharp shooting pain and muscle spasm
compression of the spinal nerve against the pedicle causes
sensory and motor deficits reflective of the associated dermatome and myotome
disc injuries can cause pain with
flexion and straight leg raise. more comfortable in extension or standing
management of intervertebral disc injuries
- ice/heat, muscle stim for spasms
- NSAIDs or muscle relaxant
- extension exercises (prone press-up cobra)
- spinal stabilization exercises
- mechanical traction
lateral stenosis
narrowing of the intervertebral foramen
- from bone spurs, dehydrated disc
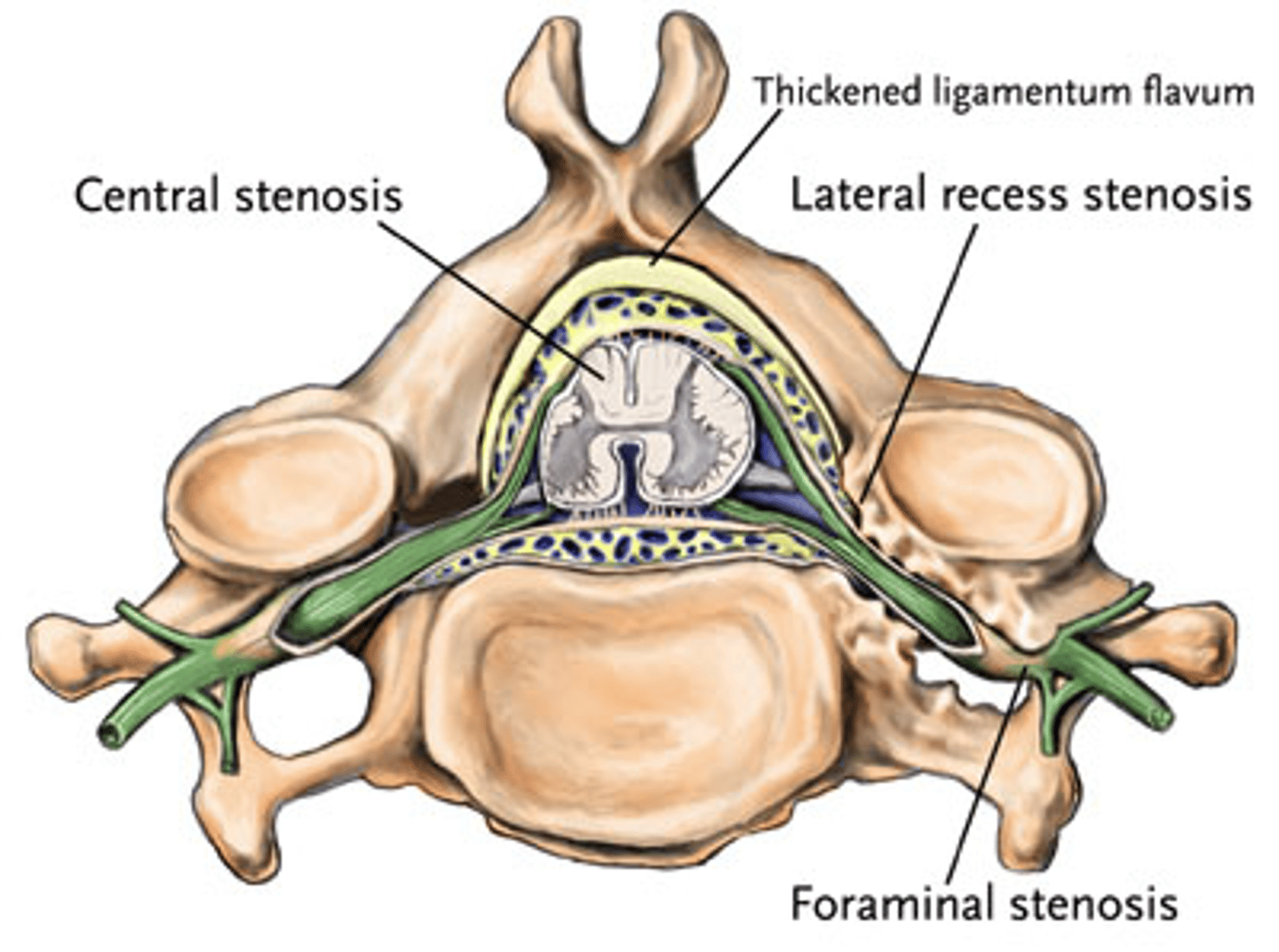
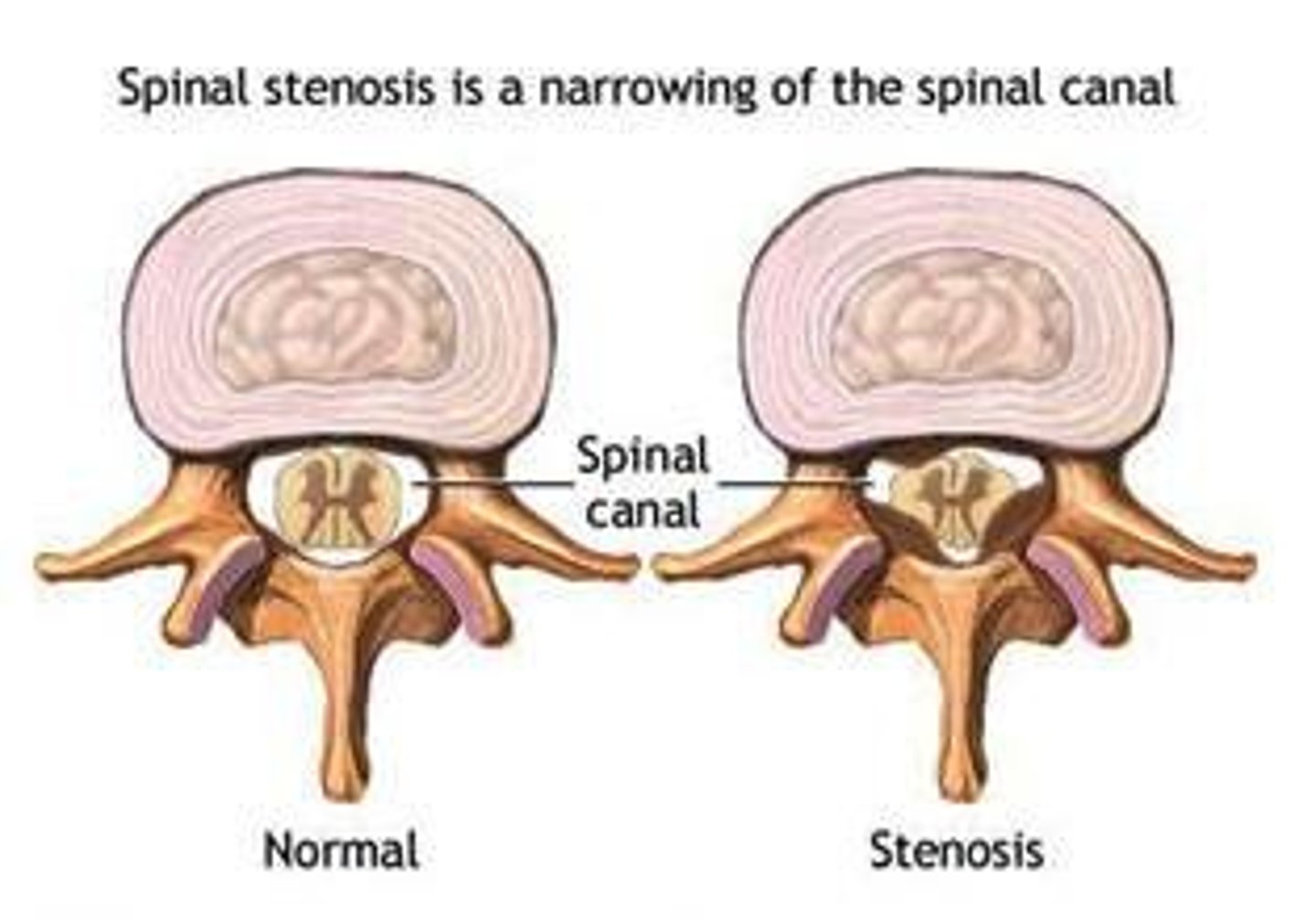
central stenosis
narrowing of the spinal cord (vertebral) canal/foramen
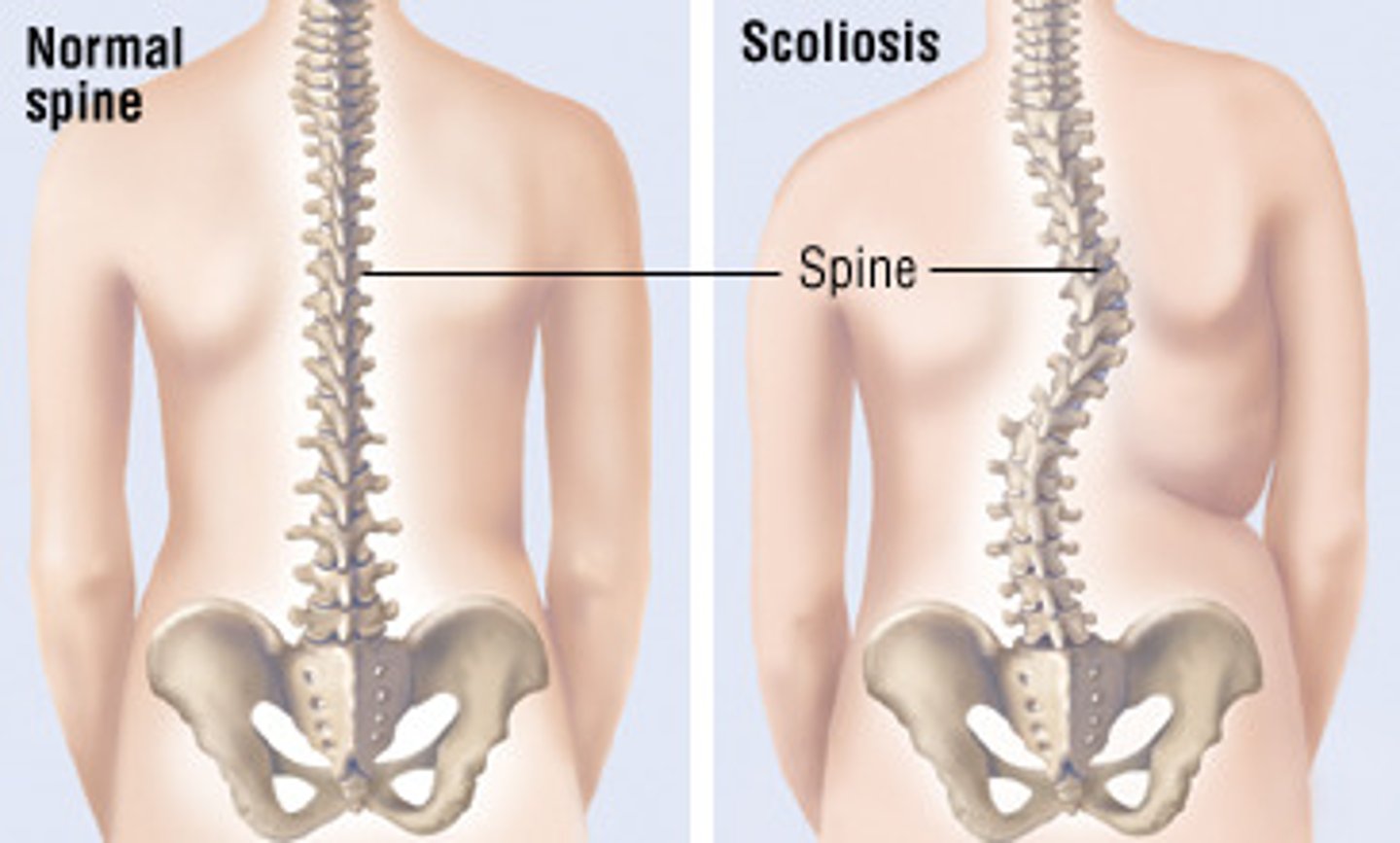
scoliosis full definition
abnormal curve in the frontal plane through the lumbar and thoracic spine
two types of scoliosis
- idiopathic adolescent scoliosis
- adult scoliosis
idiopathic adolescent scoliosis
typically found during onset of puberty
- can be treated if caught early
adult scoliosis
- can be from untreated adolescent scoliosis
- can be from aging and degeneration of the spine
+ golfing to the right every day
scoliosis treatment
- rehab only if curves measure less than 25 degrees
- bracing for curves of 25-40 degrees
- surgery recommended for curves greater than 60 degrees
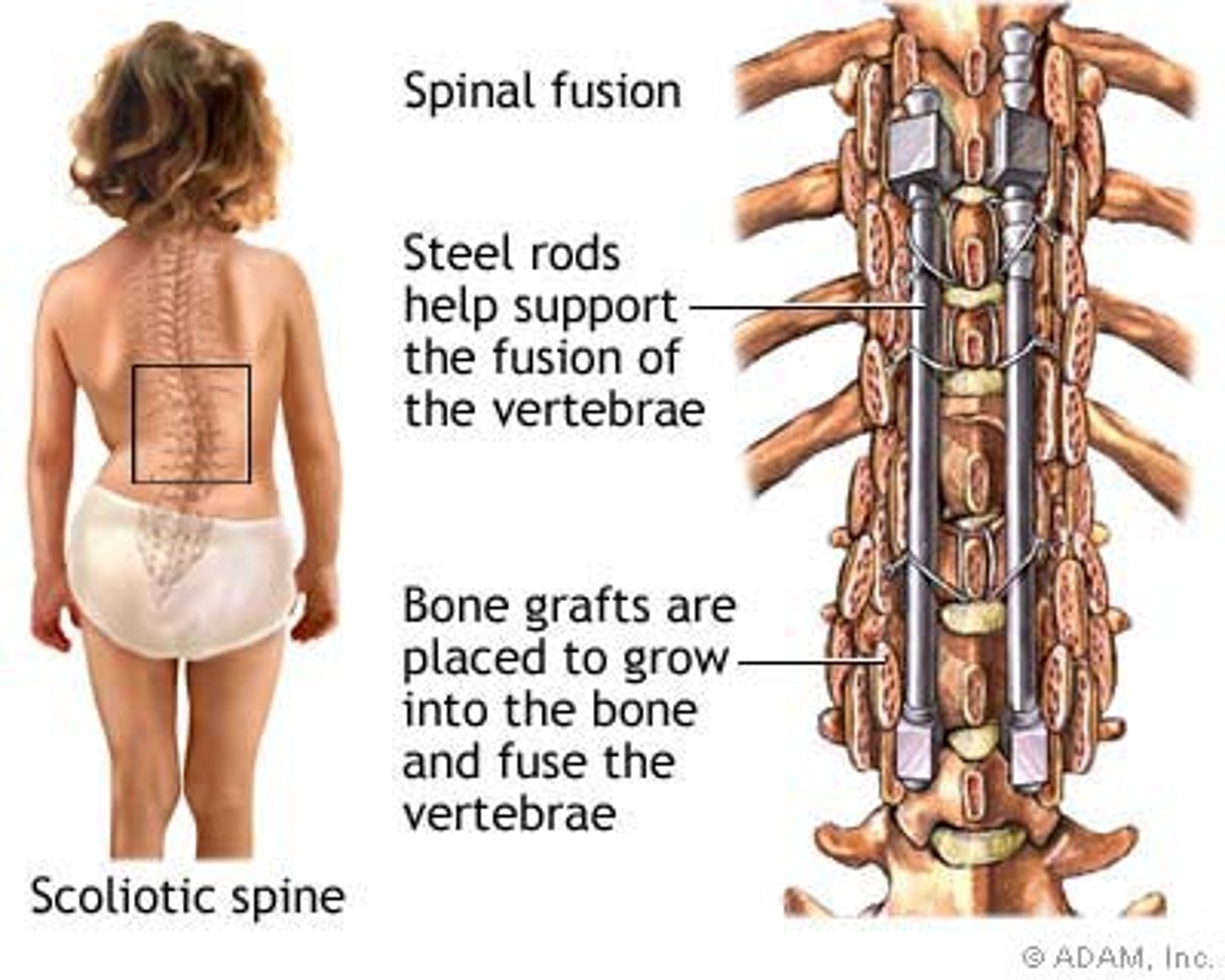
scoliosis surgery
for curve more than 60 degrees
- you lose mobility with a rod
spondylolysis
unilateral stress fracture of the pars interarticularis
- scottie-dog on x-ray fracture is collar
- hairline or complete
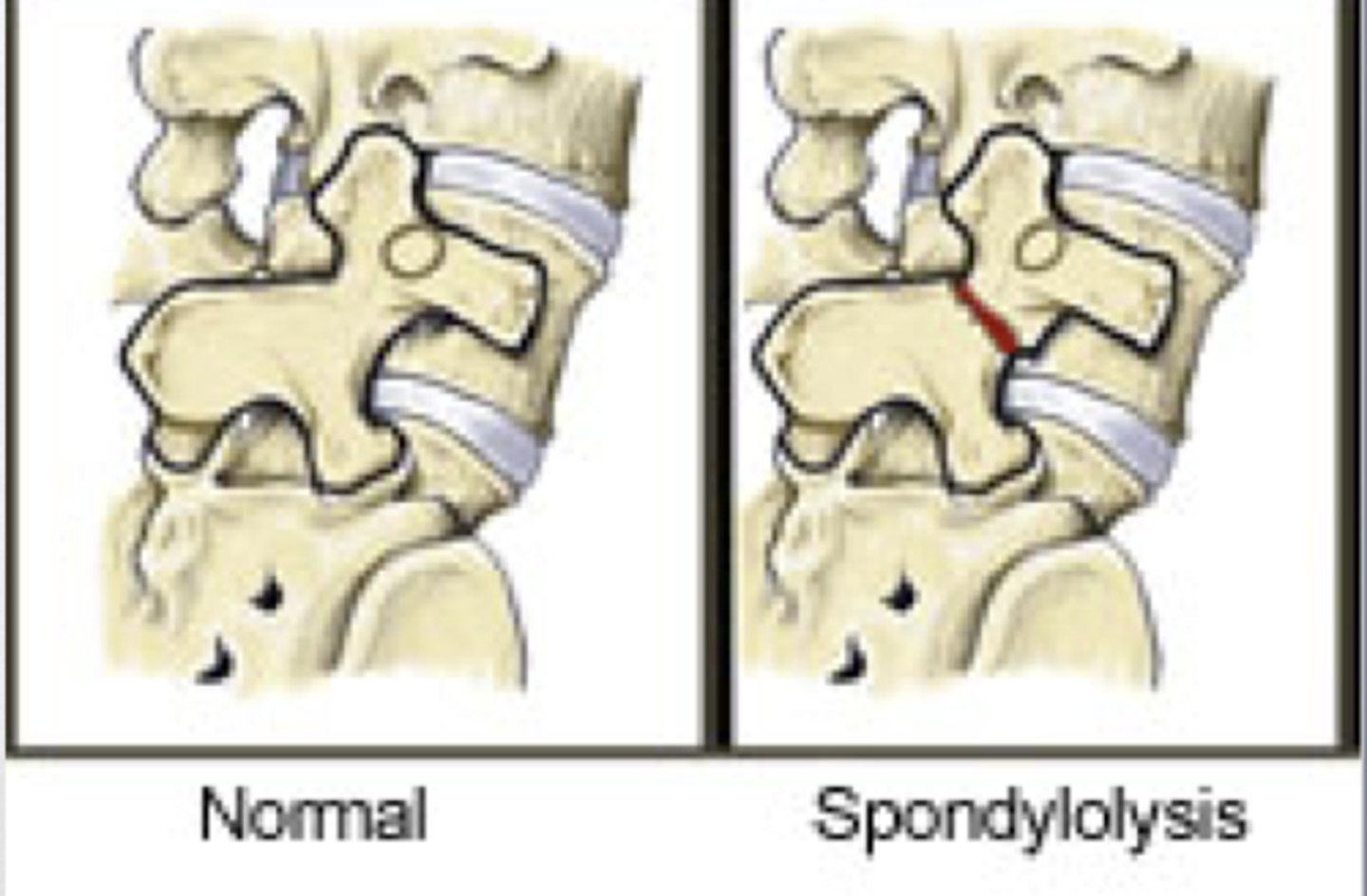
spondylolysis is
unilateral ONE SIDE
- still stable
spondylolysis mechanism
extension injury
- high jump - extend and rotate to one side over and over
spondylolisthesis
bilateral stress fracture of the pars interarticularis
- vertebral body instability and anterior translation
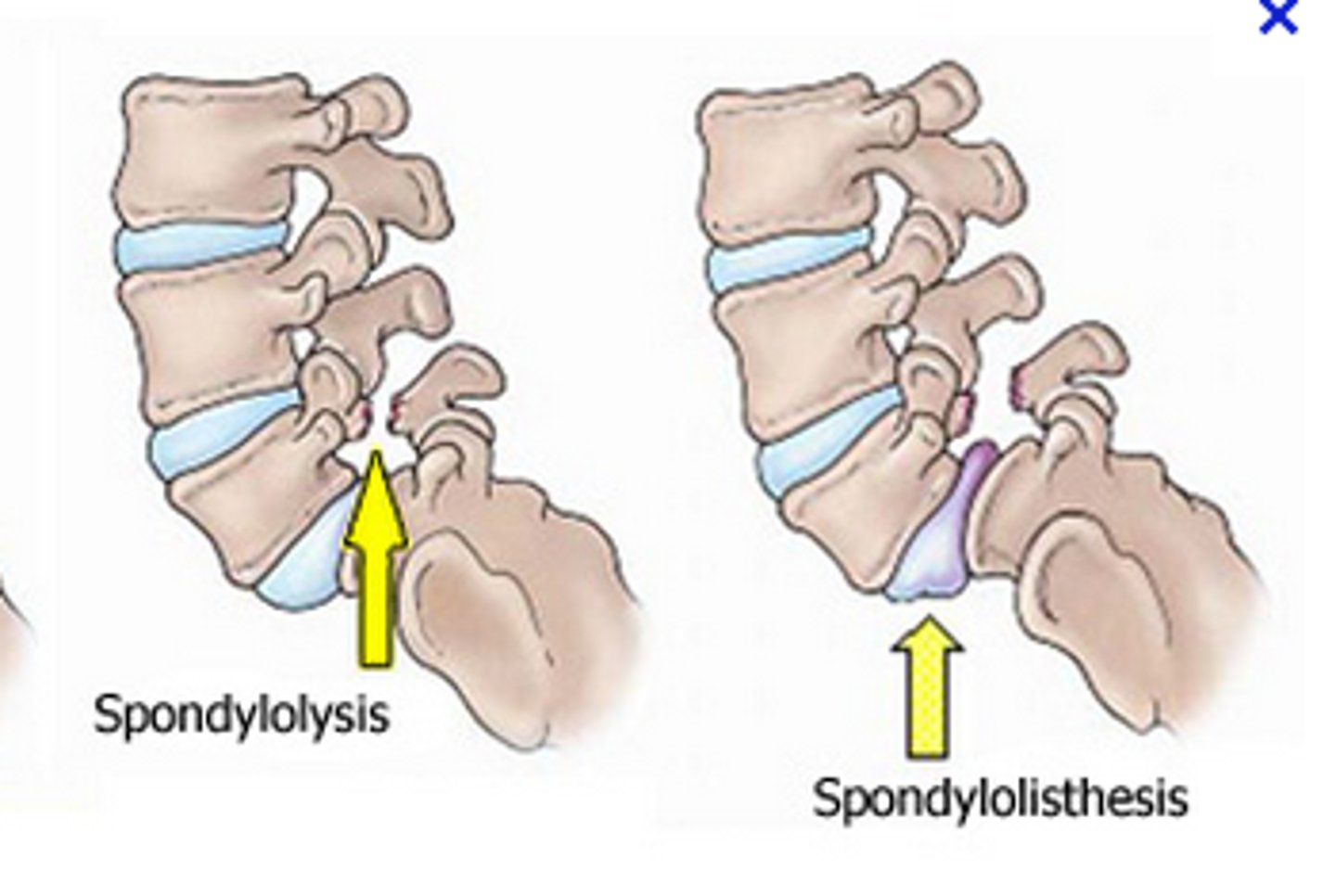
spondylolisthesis is
bilateral BOTH SIDES
- surgery
signs and symptoms of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis
- diffuse pain increased by activity and extension
- commonly L5-S1 or L4-L5
management of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis
- referred to doctor
- bone scan vs MRI for imaging
- bracing
- rest from activity
- therapeutic exercises for flexion and stabilization
transverse or spinous process fractures of lumbar spine
caused by a direct blow to the back or extreme forced motion
vertebral body compression fractures
- commonly seen at the thoracic lumbar junction
- dangerous due to the possibility of impingement on spinal canal
rule of thumb for spine compression fracture
stabilize until otherwise
- flexion could damage spinal cord and paralyze
costal chondritis
inflamed costal cartilage with chest pain
thoracic spine/rib fractures
- wedge fractures
- rib fractures
wedge fractures
occur with axial compression through the thoracic spine
- females with osteopenia are more likely to sustain fracture
rib fractures
occur either compression of the rib cage or from direct blow
- hurts to lay sown
- soft tissue injured when bone injured
Scheuermann's Disease - thoracic spine
- degeneration of the epiphyseal end plates of the vertebral bodies in adjacent segments
- creates thoracic kyphosis (flexion)
- 8-12 years old
scheuermann's disease is like
multiple wedge fractures in the thoracic spine
if under stress, accessory inhalation muscles assist diaphragm and external muscles
- stenoclidomastoid
- scalenes
- serratus anterior
- pec major
- serratus posterior superior
stabilize upper body allows accessory help (hands on knees)
if under stress accessory exhalation muscles will contract to force airflow
- internal intercostal muscle
- serratus posterior inferior
atlantoaxial ("no") instability occurs in
10 to 30% of children with Down syndrome
- x-ray may be needed to see if stable enough to play sports safely
cervical fractures
can range from minor to life-threatening based on type and location
- axial loading or extreme cervical flexion
hangman's fracture
bilateral pars interarticularis fracture of C2 - leaves dens unstable
- like a spondy in lumbar but in cervical
signs and symptoms of cervical fractures
- painful palpation over spinous processes
- radiation of pain, weakness, and numbness into dermatome/myotome
most common cervical fracture site is
C4, C5, and C6
signs of severe cervical fracture
paralysis and/or loss of bowel and bladder control
phrenic nerve significance (C3-C5)
innervation for diaphragm
- can't breath if damaged
- C 3 4 5 keep the diaphragm alive
it is crucial to practice
spine boarding
- communication w/ patient and each other
- tuck straps
skull fractures occur most often from
blunt trauma
- fall from elevation
- hit in head by object
- collisions with player/object
small objects at a high speed are worse than
large mass at slow speed
there is a high complication rate with
skull fractures
- brain injuries
- septic meningitis
septic meningitis
when skin and dura mater are both disrupted in fracture
- opening in head
signs and symptoms of skull fracture
- may not feel a defect with palpation
- CSF or blood coming from ears or nose
- ecchymosis around eyes or ears
- unequal pupil size
remember that signs
we can see as clinicians
remember that symptoms
we may not see and need to be told
how to tell if fluid is CSF
halo with napkin
ecchymosis around eyes or behind ear
raccoon eyes or battle's sign for ear
- bruising
unequal pupils are
fixed and not responsive to light
raccoon eyes are different than a black eye
bilateral from skull impact draining pressure
skull fracture short response
recognize, stabilize, refer
skull fracture management
- immediate EAP and hospital
- stabilize head and neck (issue possible neck injury!)
- treat for shock
- keep patient calm and communicate
concussion terminology does not reflect
- ding, bell rung, little concussed make it unserious
should be called mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI)
concussion can be a very serious injury
serious injury that causes lasting permanent neurological deficits
increased concussion research and more awareness in last 5-10 years
- treatment used to be sit in dark and do nothing
- now gradual progression back to activity and sport with what they can manage without exasperated symptoms
concussion =
widespread injury to brain rather than localized to one area
concussions can range from
mild to severe
- estimated that 1.6-3.8 million concussions occur in sports each year in US
signs of concussion (we can see)
- inappropriate emotions
- sadness
- sensitive to noise
- vacant stare
- glossy eyed
- vomiting
- nervousness
- drowsiness
- excess sleep
- fatigue
- poor balance and coordination
symptoms of concussion
- dizziness
- headache
- blurry vision
- in a fog"
- "slow"
- irritably
- loss of orientation
- nausea
- poor coordination
- ear ringing
- sadness
- seeing stars
- light sensitive
- noise sensitive
- sleep disturbance
- nervous
- memory problems
- personality chance
- distracted easily
different between signs and symptoms
- need athlete to tell us that they're nauseous or dizzy as a symptom
- its a sign when we can see them fall or throw up
post concussion syndrome
- mild to severe
- concussion symptoms last for days or months before resolving
do not allow athlete to return to play or progression of activity with post concussion syndrome until
all symptoms have resolved
second impact syndrome
occurs when a second concussion episode occurs before the first has resolved
- rapid swelling in brain increases intracranial pressure
- likely in teens
- life threatening
second impact syndrome - second hit
does not have to be a big hit for it to happen
focal cerebral injuries
localized
- epidural hematoma
- subdural hematoma
epidural hematoma
- aka extradural hematoma
- blow to the head or a skull fracture tears one of the meningeal arteries
- increased blood accumulation and creation of hematoma occurs quickly
why does epidural hematoma occur quickly
because the blood comes from a pumping artery
- within minutes to a few hours
subdural hematoma location
below dura
subdural hematoma is the most common
cause of death in athletes related to head trauma
subdural hematoma result from
tear in blood vessels that bridge the dura mater and the brain
- usually veinous - slower
- hours, days or weeks after trauma
signs and symptoms of hematoma
- briefly unconscious
- lucid period - still watch them and keep asking questions
as size of hematoma increases
- increasing headache
- drowsiness
- disoriented
- cognitively impaired
- decreased behavioral and motor ability
- cranial nerve dysfunction
- uneven pupil
unilateral dilated pupil
most common sign of epidural hematoma
muscle strains/joint sprains account for the bulk of all
low back injuries
acute back muscle strains or joint sprains
typically result from coupled motions involving rotation and either flexion or extension
chronic injuries of back
posture is the biggest contributing factor
- tightness in hamstrings/hip flexor is often biggest contributing factor
hamstring can effect back pain
tight hamstrings can flex hips too much and make erector spinae tight
treatment of muscle strains and joint sprains
- ice
- passive stretching for muscle spasm
- braces
- medications
- therapeutic exercise
bracing options for back injuries
corset or warm and for brace for posture
medications for back injury
muscle relaxant or NSAIDs
back injury impact on life
huge impact on daily living and function
to stretch out tight erector spinae muscles