Dental Terminology Ch. 6
1/164
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All about Emergency Care
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
165 Terms
Best treatment for emergencies
Prevent them from happening
Two of the fundamental methods employed in facility readiness
Patient health history and vital signs
Patient health history
Written and oral communication regarding the patient’s present and past health status, including medication, treatment, allergies, and health concerns
Vital signs
Body indications of the patient’s present health status, including blood pressure, pulse, respiration, temperature, and the patient’s concept of pain
Blood pressure (BP)
Indication of the pulsating force of blood circulating through the blood vessels at rest (diastolic) and while under the highest pressure of the circulating blood, the systolic pressure.
BP numbers are
Even
How are systolic and diastolic pressure numbers recorded
Systolic pressure placed before diastolic pressure numbers, Ex: 120/80 (systolic/diastolic)
Stethoscope
Device employed to intensify body sounds, it has a set of earpieces inserted into rubber tubing that combines the two ear tubes into one and extends to a metal bell-shaped or flat disc diaphragm, stethoscopes used in training may have two earpieces combined to one diaphragm for instructional purposes
Diaphragm
A thin layer over the disc end of the stethoscope that helps to enlarge or amplify pulse and body sounds
Sphygmomanometer
An instrument is available in portable, wall mounted, or mobile floor units and consists of a squeeze bulb on rubber tubing, an arm cuff, and a pressure or aneroid dial or a graduated marked mercury column, digital sphygmomanometers use only a wraparound cuff with machine read-out gauges; no stethoscope is required, the mercury column unit is considered the most reliable recorder and may be used to calibrate the aneroid system
Antecubital fossa
Interior depression or bend of the elbow’ the approximate area for the placement of the stethoscope diaphragm to determine blood-pressure sound. B
Brachial artery
Situated at the inside, upper arm area; selected site of blood-pressure cuff placement
Pulse
The beating force for blood circulating through arteries, which is classified according to rate, rhythm, and condition, pulse counts may be taken at various body areas
Accelerated
Faster pulse rate than normal or expected, aka “rapid”
Alternating
Changing back and forth of weak and strong pulsations
Arrhythmia
Irregular heartbeat or pulsations
Bradycardia
Pulse rate under 60 beats per minute (bpm)
Tachycardia
An abnormal condition of pulse rates over 100 bpd (except in children)
Deficit
Lower pulse rate at the wrist than at the heart site, “heart flutter”
Carotid pulse
Pulse at the neck
Cuff placement area
Around the bicep
Brachial pulse
Pulse at elbow
Radial pulse
Pulse at wrist
Febrile
Normal pulse rate becoming weak and feeble with prostration or illness
Frequency
Pulse count; number of pulsations, which differs with age, sex, body position, or health of patient
Types of pulse frequencies
Intermittent, irregular, regular, and thready
Intermittent frequencies
Occasional skipping of heartbeats
Irregular frequencies
Variation of force or frequency in pulse rate
Regular frequencies
Uniform pulse force, frequency, and duration
Thready frequencies
A fine, hard-to-locate, barely perceivable pulse
Respiration
The inhaling or breathing in of oxygen and the exhaling ort expelling of carbon dioxide
1 respiration count requires
An inspiration (breathing in) and expiration (breathing out)
Respirations are described according to
Rate, character and rhythemA
Absent
Suppresses respiratory sounds
Apnea
cessation of breathing, usually temporary
Cheyne-strokes
Respirations gradually increasing in volume until climax, and then subsiding and ceasing for a short period of time before starting again; may be noted in dying
Deep
Strong inhalation of air with exhalation
Dyspnea
Out of breath; difficult or labored breathing
Frequent
Rapid breathing that may be noted in children, those with disease, hysteria, or with a drug-induced condition
Rale
Noisy, bubbling sounds from lung mucous, heard on inhalation
Shallow
Short inhalation with small rise in chest
Slow
Fewer than 12 respirations per minute
Stertorous
Rattling, bubbling, or snoring sounds that obscure normal breaths
Temperature
The balance of heat loss and production in a body and may be taken at various sites, such as oral, rectal, axillary (armpit) and aural (ear)
Fever
Elevated body temperature, usually considered over 38.3 C (100-103 F)
Hyperthermia
Body temperature exceeding 40 C (104 F)
Hypothermia
Body temperature below 35 C (95 F)
Tympanic
(pertaining to eardrum) Measurement of body heat registered by an ear thermometer
Vital signs ranges
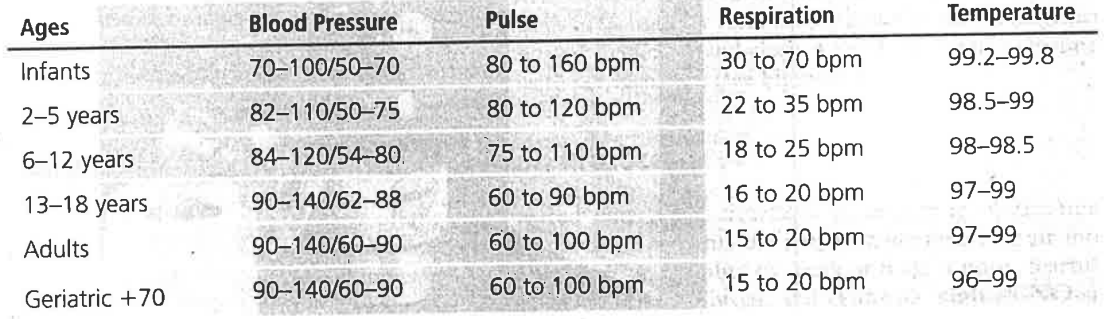
How is concept of pain measured
Patient rates the level of pain on a scale of 1-10 in intensity, any increase or decrease in pain may indicate the course of the disease, this vital sign is subjective compared to other vital signs
Emergency call list
Important phone numbers necessary in an emergency, which are located in a prominent position near every available phone
Oxygen source
Container with oxygen gas tank, colored green; obtained in various sizes and may be centrally supplied to each work station
Oxygen regulator
Device used to control the flow of oxygen
Oxygen flowmeter
Gauge used to adjust the flow amount of oxygen
Oxygen mask
Device placed over a patient’s nose and mouth to administer gas; may be clea or tinted plastic or rubber material
Demand-valve resuscitator
Device attached to an oxygen mask to apply pressure to the oxygen flow and thereby inflate the lungs
AMBU-bag
Handheld squeeze device with a mask that is placed over the patient’s nose and mouth and used to force atmospheric air into the patient’s lungs; may also be attached to the oxygen supply to force oxygen to lungsEmer
gnecy tray
A tray assembled with materials and items necessary for emergencies; often supplied in kit form with medicines, administration items, and chemicals to be used for various emergency events, must be updated frequently and close at hand, all dental personnel should know how to use each item
Airway obstruction
Occurs when a blockage prevents the patient from receiving air into the lungs
Symptoms of airway obstruction
Inability to speak or make a noise, fearfulness, opened eyes, clutching of throat, and cyanosis
Abdominal thrust
Quick, jabbing pressure and force at belt line to force air up the windpipe
Asphyxiation
Not breathing; a result of oxygen imbalance
Chest thrusts
Applying quick pressure on the chest to force air upward in the windpipe to dislodge the obstruction; may be used on pregnant women as a substitute for abdominal thrusts
Cricothyrotomy
(ring, shield, cut) An insert or cut into the thyroid and cricoid cartilage to introduce an emergency air supply
Gastric distension
A condition resulting from air having been forced into the abdomen instead of the lungs
Heimlich maneuver
Procedure in which abdominal thrusts are applied to a choking patient, which forces air from the diaphragm upward to expel a blockage in the airway
Hypoxia
A lack of inspired oxygen
Stoma
An artificial opening into the windpipe that is placed between the mouth and lung; the opening is at the frontal base of neck into the windpipe for air intake
Tracheotomy
A cut and an isertion of a tube into the trachea for an emergnecy air supply
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
CPR, combines artificial respiration with external cardiac massage CAB regimen is now what’s preffered
What is CAB
Compression, airway, breathing
CAB method
Perform immediate compression to distribute the oxygen already present in the lungs. The purpose of compressions is not to “restart the heart” but to circulate the victim’s blood supply
After 30 compressions, establish an open airway, and give two breaths
Maintain the breathing cycle with 2 breaths and 30 chest compressions at 100 compressions per minute rate
Compression should be 2 inches deep using 1 hand, unless for infants, then it’s 1.5 inches using two-fingers
Rescuers should avoid leaning on chest
If present at an emergency involving an unresponsive victim
It is wise to survey the immediate surroundings fort the presence of life-saving devices that could be used such as an AED
AED
Automated external defibrillator, a mechanical/electrical device used to revive and stimulate the heart of a patient in cardiac arrest, dated electrode pads are placed on the patient’s chest to determine if pulseless ventricular tachycardia or a ventricular fibrillation is occurring
Airway device
Tube inserted into the mouth and down the throat to provide air to the windpipe
Compression
Force applied to the chest, providing pressure on the heart to imitate a heartbeat or pulsation
Finger sweep
Using a finger on the mouth of an unconscious person to locate and wipe out any airway obstruction
Sternum
“breastbone” the flat bone between the ribs
Xiphoid process
Lowest portion of the sternum with no ribs attached
Most common symptom of shock
Syncope (fainting)
How many basic types of shock are there
9
Anaphylactic shock
Shock arising from a reaction to a body allergen
Cardiogenic shock
Shock arising from an improper heart action
Hemorrhage shock
Shock arising from excessive blood loss
Metabolic shock
Shock arising from endocrine diseases and disorders, such as diabetes
Neurogenic shock
Shock arising from nervous impulses
Postural shock
Shock arising from a sudden change in body positions
Psychogenic shock
Shock arising from mental origins
Respiratory shock
Shock arising from insufficient breathing
Septic shock
Shock arising from a microbial infection
Allergic reaction
Caused by a person’s sensitivity to a specific antigen that can result in a variety of symptoms
Anaphylaxis
An allergy reaction of the body resulting in lowered blood pressure, swelling of the throat, shock and even death
Itching
A condition of irritation to the skin, scalp, or mucous membranes
Erythema
(skin redness) a red rash or blotching of the skin
Edema
A tissue swelling, enlargement of a body area
Vesicle formation
(small blister) Small, water blisters
Urticaria
(vascular skin reaction) Commonly called hives or wheals
Asthma
(panting) A chronic disorder characterized by shortness of breath, wheezing, and coughing caused by spasms of the bronchial tubes or swollen mucous membranes
Extrinsic asthma
Resulting from allergens entering the body
Intrinsic asthma
Resulting from bronchial infection allergens