nucleophilic aromatic substitution
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
SN1 reactions for benzene
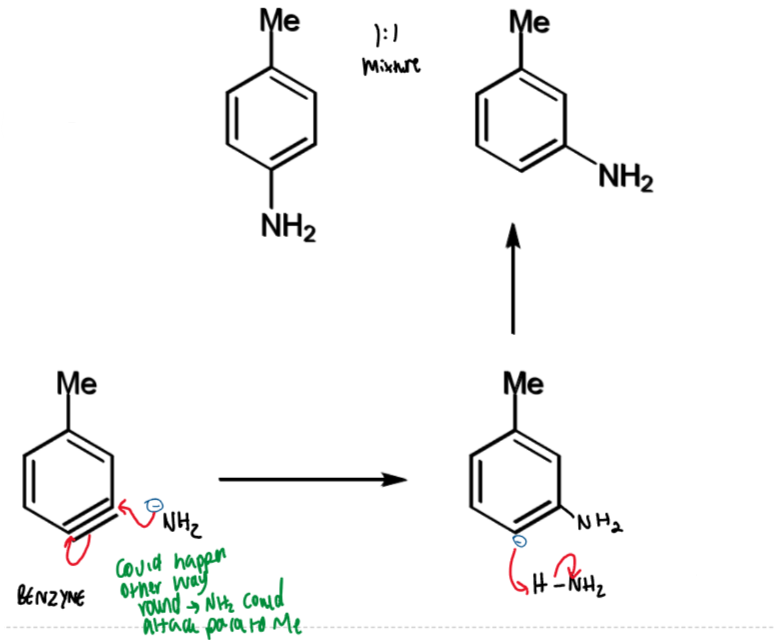
only happens for diazonium salts as this is the only compound with a good enough leaving group (N2)
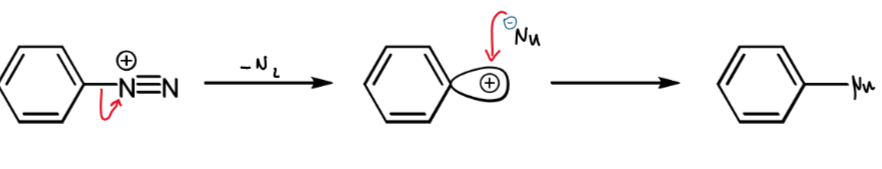
shortening of nucleophilic aromatic substitution
SNAr
when does SNAr happen
a good leaving group, eg F-, Cl-, Br- → NEVER H-
an ortho or para EWG eg -CF3, -F, -NO2
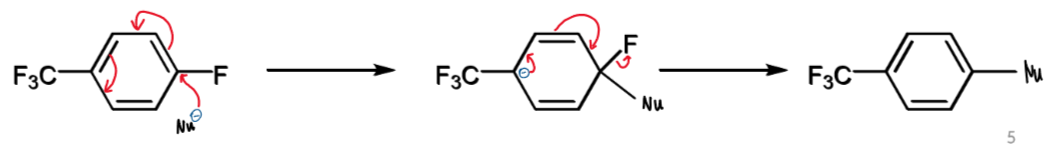
SN1 for this with nucleophile Nu
SN2 for benzene rings
NEVER happen
the σ* orbital is inaccessible inside the benzene ring
it is impossible to have inversion of the configuration
SN2 reactions don’t happen at sp2 hybridised carbons
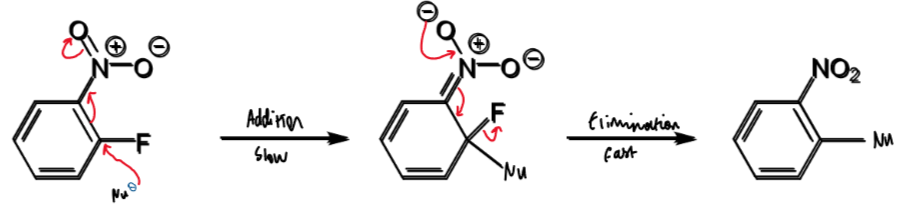
steps in SNAr
aromaticity broken first in addition (slow)
EWG required to stabilise the anionic intermediate
aromaticity restored in the second step, elimination (fast)
SNAr for this with nucleophile Nu
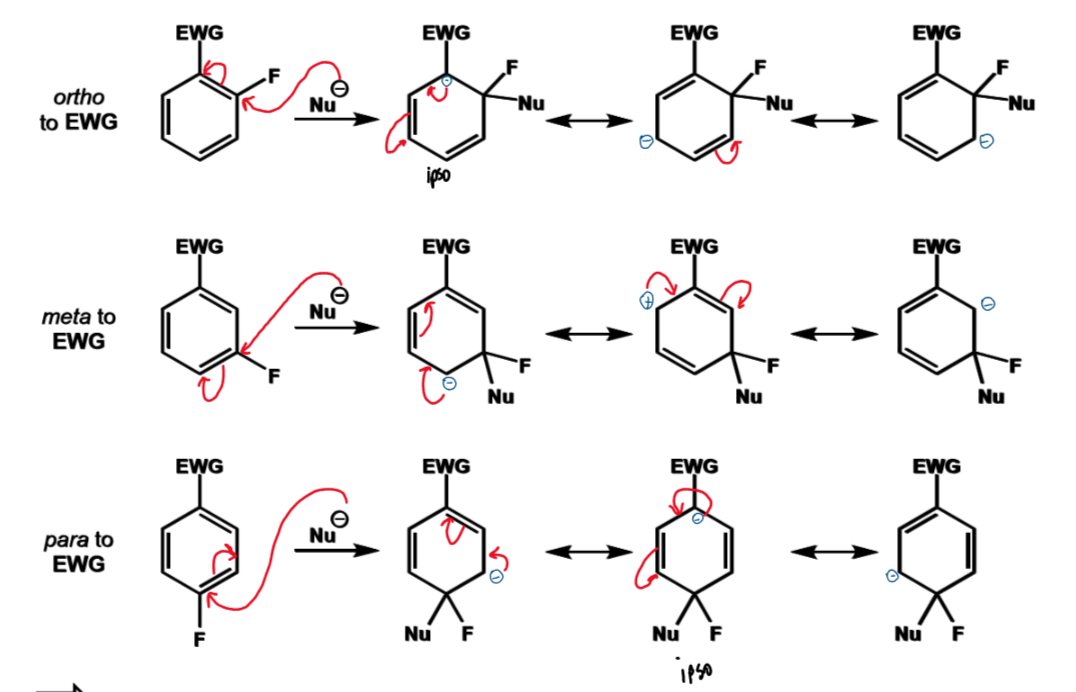
why is an o/p EWG needed
for o/p, anionic intermediate can be stabilised by putting the negative charge on the carbon with the EWG
this does not happen with meta
this means EWG activate the ring for SNAr, which is the opposite to SEAr in which they deactivate the ring, as in SNAr the ring need to be as electrophilic as possible
what is the best leaving group for SNAr
fluoride
why is fluoride the best leaving group
for SN2, the best LG is the most stable anion (I- > Br- > Cl- > >F-)
HX with lowest PKa is usually best
for SNAr this order is reversed:
best F- > > Cl- & Br- > I- worst
RDS is the addition step that breaks the aromaticity
the rate of bond cleavage is not important
fluoride has the best leaving group for SNAr because it is electronegative and speeds up the RDS
how is sodium amide (formula?) made and what are its properties
NaNH2
very strong base
made when sodium metal reacts with liquid ammonia
production of benzyne from p-chlorotoluene
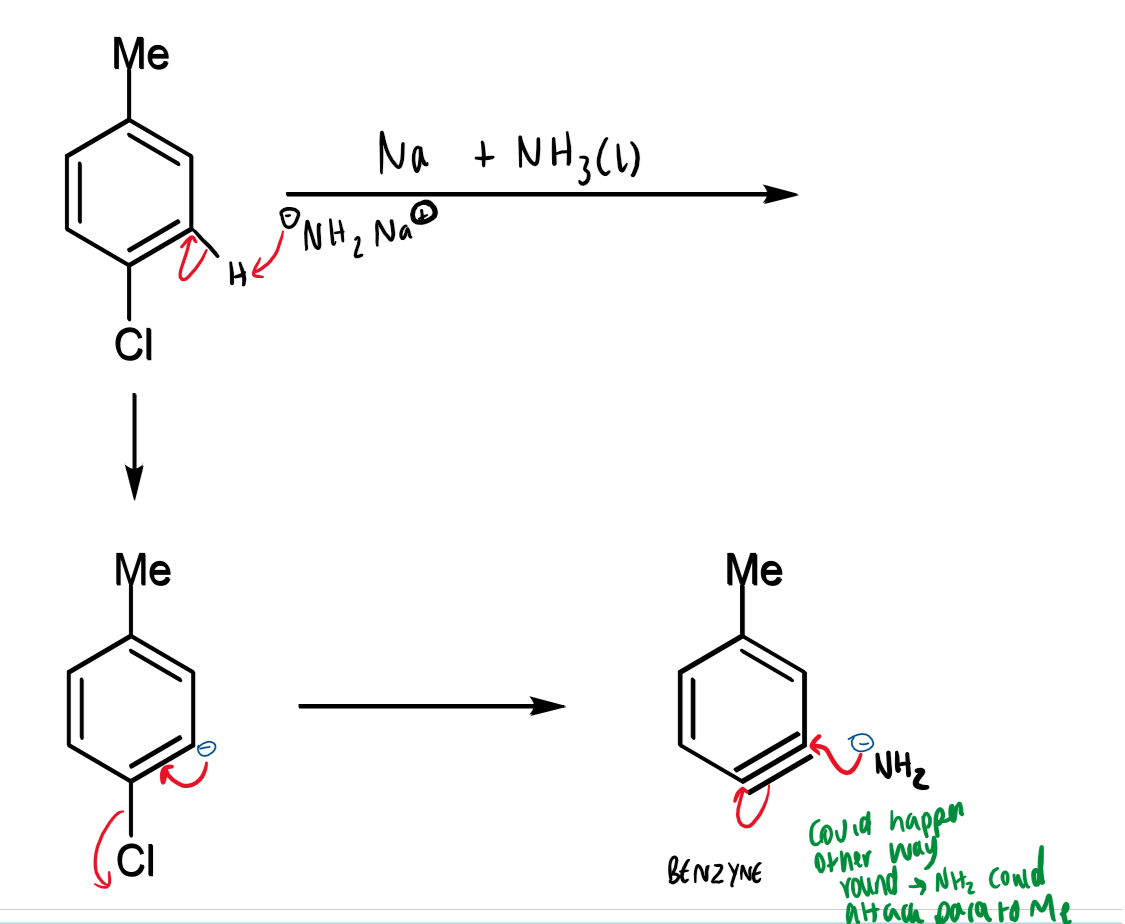
p-chlorotoluene and sodium amide
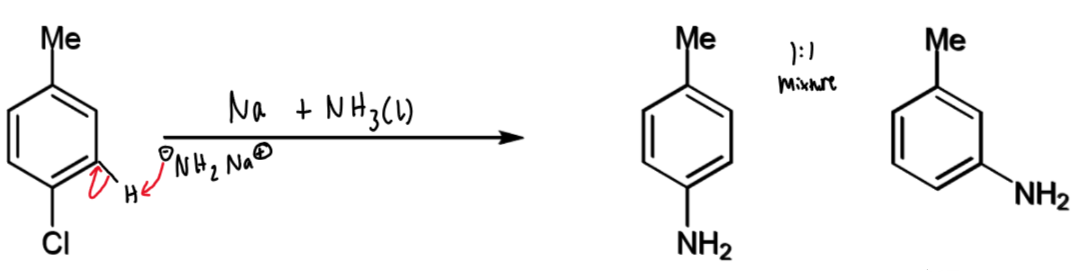
benzyne intermediate → aniline mixture
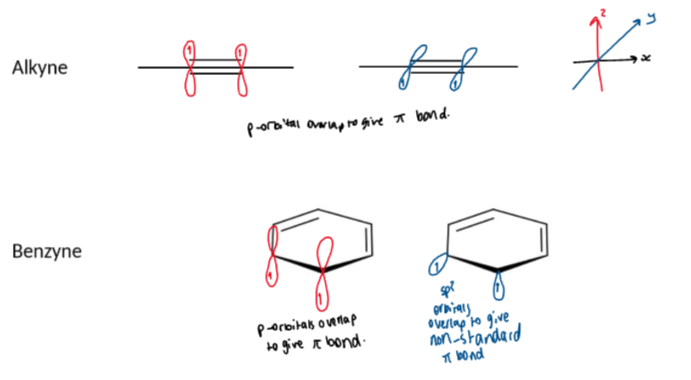
benzyne vs normal alkynes
alkynes require linear geometry for effective overlap of two orthogonal (perpendicular) pairs of p-orbital (along the y and z axes)
as benzyne is a six-membered ring the triple bond is not like normal linear alkynes - the extra pi bond comes from electrons in sp2 hybridised orbitals
benzyne has a low energy LUMO making it reactive to nucleophiles
other way to make benzyne
make via a diazonium salt
o-aminobenzoic acid can be converted into a diazonium salt that spontaneously loses carbon dioxide and nitrogen to make benzyne
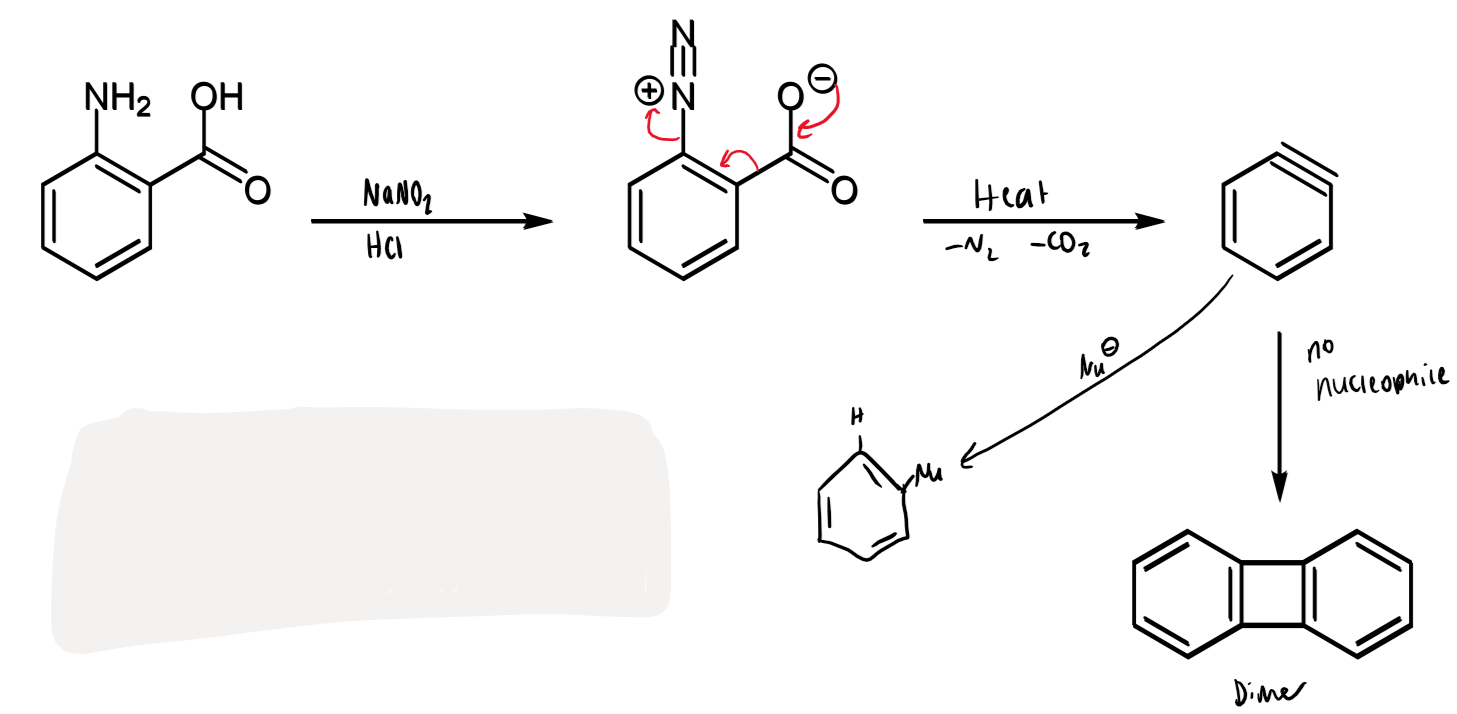
stability of benzyne
very reactive/unstable