Chapter 5 - Xray Tube
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
actual focal spot:
area of x-ray tube actually bombarded with filament electrons
anode:
the positive end of the x-ray tube that provides the target for electron interactions to produce x-rays
also an electrical and thermal conductor
anode heel affect:
phenomenon resulting from the angling of the target face that causes the intensity of the x-ray beam to be less on the anode side because the “heel” of the target is in the path of the beam
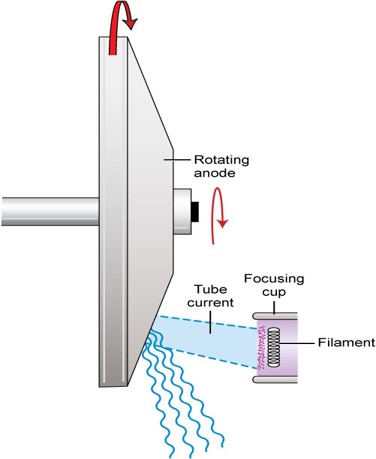
cathode:
the negative end of the x-ray tube and source of electrons
effective focal spot:
the x-ray beam area as seen from the perspective of the patient
filament:
a coil of wire, usually 7-15 mm long
1-2 mm wide
usually made of tungsten with 1-2% thorium added
focusing cup:
a metal shroud that is made up of nickel and surrounds the x-ray tube filaments on their back and sides, leaving the front open and facing the anode target
heat units (HU)
a measure of the amount of heat stored in a particular device
induction motor:
an electric motor in which the shaft is rotated through mutual induction
leakage radiation:
photons produced in the x-ray tube that are traveling in directions other than toward the patient
line-focus principle:
a principle that states: by angling the face of the anode target a large actual focal spot size can be maintained and a small effective focal spot size can be created
protective housing:
a lead-lined metal structure that provides solid, stable mechanical support and serves as an electrical insulator and thermal cushion for the x-ray tube
rotor:
a part of an induction motor made of an iron core (iron bars embedded in the copper shaft) surrounded by coils and located in the center of the stators
space charge:
a cloud of electrons formed by the focusing cup as electrons are boiled off of the filament
space-charge effect:
the self-limiting factor caused by the space charge reaching a size commensurate with the current used and making it difficult for additional electrons to be emitted
stator:
a part of an induction motor made up of electromagnets arranged in pairs around the rotor
target window:
a thinned section of the x-ray tube enclosure that is the desired exit point for the x-rays produced
thermionic emission:
the literal boiling off of electrons from a filament by a flow of electrical current
Which of the following reduces leakage radiation to required standards?
the protective housing
Which component of the x-ray tube is responsible for concentrating the electron cloud?
the focusing cup
The x-ray tube is part of the:
x-ray circuit secondary
A technique of 80 kV, 400 mA, 0.8 seconds is to be used on a 3-phase, 12 pulse machine. How many heat units are produced with a single exposure?
36,096 (HU)
The intensity of the x-ray beam is less:
on the anode side
Causes of tube failure are most often related to which of the following characteristics?
thermal
What metal is added to the filament to increase thermionic emission and extend tube life?
thorium
A small anode target angle:
results in an increase in anode heel effect
A dual focus tube refers to a tube with:
two filaments
The purpose of the line focus principle is to create which of the following?
large actual and small effective focal spot size
A technique of 50 kV, 100 mA, 0.1 seconds is to be used on a 3-phase, 6 pulse machine. How many heat units are produced with a single exposure?
675 (HU)
A protective housing provides solid mechanical support. Examples:
lead-lined structure
oil bath
cooling fans
electrical insulation
large cables
absorbs stray photons
The general-purpose x-ray tube is an electronic vacuum tube that consists of the following:
an anode
a cathode
an induction motor
encased in a glass or metal enclosure
The main purpose of the enclosure is to maintain a vacuum within the tube to prevent:
electrical arcing - when an electrical current jumps across a gap between conductors, creating a visible and often audible discharge of electricity
There are two varieties of x-ray tubes:
glass and metal
The glass envelope variety is generally made of borosilicate glass because:
it is heat resistant
Why is the metal-envelope type of X-ray tube preferred in certain applications over the glass-envelope type?
provides a constant electric potential between the electron stream from the cathode and the enclosure, thereby avoiding the arcing problem and extending tube life
The anode is the positive end of the tube.
It provides the target for:
electron interaction to produce x-rays
it serves as an electrical and thermal conductor
Some of the electrons interact with the target to produce x-rays, and the rest:
continue on as current flows through the x-ray circuit
There are two types of anodes:
stationary and rotating
What are the materials for an anode?
copper
molybdenum
tungsten
rhenium
The anode is rotated using an induction motor. The two major parts of this motor are:
the stator: made up of electromagnets
the rotor: made of an iron core surrounded by coils
When the angle of the target face is less than 45 degrees, the effective focal spot will be:
smaller than the actual; it gets absorbed in the anode
The target angles for a general-purpose tube are:
7 to 18 degrees
(12 degrees is the most common)
The smaller the anode angle, the smaller the:
effective focal spot will be while maintaining a large actual focal spot area
A smaller effective focal spot produces:
a sharper image
The angle of the anode causes the intensity of the x-ray beam to be:
less on the anode side because some of the x-rays are absorbed in the target heel
The cathode is the negative end of the tube that provides:
the source of electrons needed for x-ray production
made up of the filaments and the focusing cup
The three things needed to produce x-rays are now present:
a large potential difference to give kinetic energy to the filament electrons (provided by kVp)
a vehicle on which kinetic energy can ride (a quantity of electrons provided by mAs)
a place for interaction (the target of the anode)
As the filament electrons penetrate the target surface, they interact with:
the atoms of tungsten, generating heat and x-rays
Most of the factors that can shorten x-ray tube life are within the radiographer’s control:
frequent use of very high or maximum exposure factors
use of lower but very long exposure factors
overloading the filament
Three processes of heat transfer are at play:
conduction of heat by heat-tolerant materials
radiation of heat energy from anode to oil bath
convection of heat into the room by cooling fans
Heat units are calculated by:
multiplying kVp x mA x S x C
C = correction factor depends on generator
High frequency = 1.45