Chapter 4 - Genes and Cellular Function
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
how many rings are purines?
double ring
how many rings are pyrimidines?
single ring
what are the nitrogenous base(s) for purines?
Adenine (A)
Guanine (G)
what are the nitrogenous base(s) for pyrimidines?
Cytosine (C)
Thymine (T)
Uracil (U) - replaces T in RNA
three things that make up a nucleotide:
one sugar (deoxyribose)
one phosphate group
one nitrogenous base (purines / pyrimidines)
how is DNA paired
A purine on one strand bound to a pyrimidine on the other.
what does adenine (A) bind to?
**vice versa
thymine (T)
what does cytosine (C) bind to?
**vice versa
guanine (G)
how many hydrogen bonds in A-T?
two hydrogen bonds
how many hydrogen bonds in C-G?
three hydrogen bonds
gene
segment of DNA coding for the synthesis of a specific protein
genome
all the genes of one person
humans have about 20,000 genes
chromatin
one long DNA molecule and its associated proteins
nucleosome
strand of DNA coiled around the group of histone proteins
histone
proteins crucial for DNA packing
kinetochores
protein plaques on each side of centromere
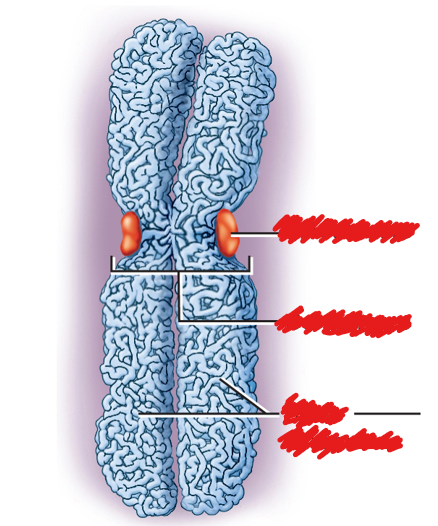
what is the orange thing in the middle?
kinetochore
transcription
copying genetic instructions from DNA to mRNAel
Messenger RNA
mRNA
carried code from nucleus to cytoplasm
protein cap that is recognition site for ribosome
Transfer RNA
tRNA
delivers a single amino acid to the ribosome
contains an anticodon
anticodon
series of 3 nucleotides that are complementary to the mRNA codon
translation
occurs at ribosome. sequence of mRNA is translated into amino acid sequence with help of tRNA
gene regulation
genes can be turned on and off
example of gene regulation?
mammary gland cells turn on gene for casein protein ONLY when breast milk is produced
stages of interphase
G1, S, G2
G1 - first gap phase
interval between cell birth and DNA replication
cell is normal and accumulates materials for next phase
S - synthesis phase
cell replicates all nuclear DNA and duplicates centrioles
G2 - second gap phase
interval between DNA replication and cell division
cell repairs DNA replication errors, grows and synthesizes enzymes for cell division
G Zero Phase
cells that have left the cycle and cease dividing for a long time (sometimes permanently)
heredity
transmission of genetic characteristics from parent to offspring
karyotype
chart of 46 chromosomes laid out in order by size
homologous chromosomes
1 chromosome from each pair is inherited from each parent
22 pairs autosomes
1 pair of sex chromosomes
female sex chromosomes
homologous pair of X chromosomes
XX
male sex chromosomes
one X and one much smaller Y
XY
tumor angiogenesis
growth of blood vessels due to energy hungry tumors
carcinoma
cancer in epithelial tissue
lymphoma
cancer in lymph nodes
melanomas
cancer in pigment cells of epidermis (melanocytes)
leukemia
cancer in blood forming tissues
sarcomas
cancer in bone, other connective tissue, or muscle
polygenic inheritance
genes at 2 or more loci contribute to ONE phenotype
pleiotropy
one gene produces multiple phenotypic effectse
epigenetic effects
mechanisms that alter the gene expression W/O changing the DNA base sequence
sugar in DNA/RNA
deoxyribose / ribose
site of action of DNA/RNA
nucleus / leaves nucleus → cytoplasm
function of DNA/RNA
synthesis of RNA and proteins / carries out instructions for DNA, assembles proteins
Transcription initiation
Protein transcription factor binds to promotor region near gene on template strand
Transcription elongation
RNA polymerase covalently bonds complementary RNA nucleotides to growing mRNA molecules
Transcription termination
Last triplet of gene is reached and the newly pre-mRNA molecule is ready for modification
Translation initiation
Initiator tRNA bind to mRNA start codon (Met) on the ribosome
Translation elongation
Next tRNA binds to open site allowing two amino acids to be covalently linked by a peptide
Translation termination
End of translation, occurs when ribosome reaches stop codon on mRNA (UAA, UGA, UAG)
Stop codons (3)
UAA (u are away)
UGA (u go away)
UAG (u are gone)