HLSC 128 Microbiology
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What are the two types of prokaryotes?
Eu-bacteria/”True bacteria”
Group that causes disease
Local environment
Archaebacteria/”Ancient bacteria”
Don’t cause disease
Isolated and extreme environment
What are the four types of eukaryotes?
Fungi
Protozoa
Multicellular animal parasites
Algae
Who made the quote: “Life only comes from life”?
Louie Pasteur
Describe the experiments Louie Pasteur had done to determine that life did not arise spontaneously from nonliving matter.
In his trials, he had heated flasks filled with broth with air and removed air (open and closed), and found that the broth was infested when the flask was open with air. He then heated the neck of the flask into an S-shape and left the flask open for air. Pasteur found that the broth was not present with microbes as they had gotten suck in the bends.
What is pasteurization?
It is a heating process to remove the bacteria from food and beverages. The purpose is to make them safe for consumption and extend shelf life.
What is fermentation?
It is the metabolic process of bacteria and yeast where they convert sugars into alcohol.
Who is the scientist that discovered the bacterium that causes anthrax?
Robert Koch
What are the Koch’s Postulates?
Experimental steps to prove that a specific microbe causes a specific disease.
What was Edward Jenner known for?
Edward Jenner was known for creating the first vaccine. In his time smallpox was a epidemic. He inoculated a subject with cowpox virus (fluid from a blister) and found that the subject had complete immunity from smallpox.
What are the building blocks of proteins called?
Amino acids
What are the four structures of a protein?
Primary structure
Polypeptide chain
Secondary structure
Helical shape made of a-helix sheets
Tertiary structure
Pleated structure made up of beta sheets
Quaternary structure
3D mix of a-helix and b-sheets
What prime carbon does ribose lose oxygen from?
2’
What are the five prokaryote shapes?
Spiral
Bacillus
Coccus
Coccobacillus
Pleomorphic

What shape is this? Describe it.
Spiral Vibrio, it is tender

What shape is this? Describe it.
Spiral Spirillum, it is rigid and moves by means of flagella

What shape is this? Describe it.
Spiral Spirochete, it flexible and moves by means of appendages called axial filaments which curve around its structure

What shape is this?
It is a single bacillus

What shape is this?
It is a diplobacilli
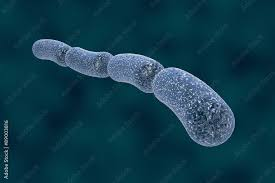
What shape is this?
It is a streptobacilli
What shape is this? Describe it.
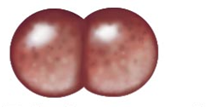
It is a diplococci. Produced when cocci divide and remain attached to eachother.
What shape is this? Describe it.
It is a streptococci. If cocci divides and forms a chain-like structure.
What shape is this? Describe it.
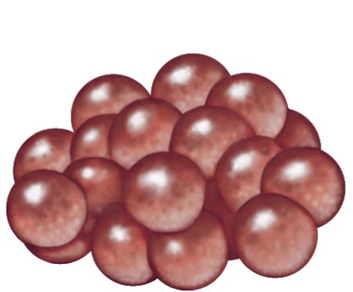
It is a staphylococci. Happens when cocci divide and bunch together into a grape-like structure
What does the glycocalyx do for a prokaryote?
Increases virulence
By its sugar sticky nature
Evades phagocytosis
Describe the structure of a flagella in a prokaryote.
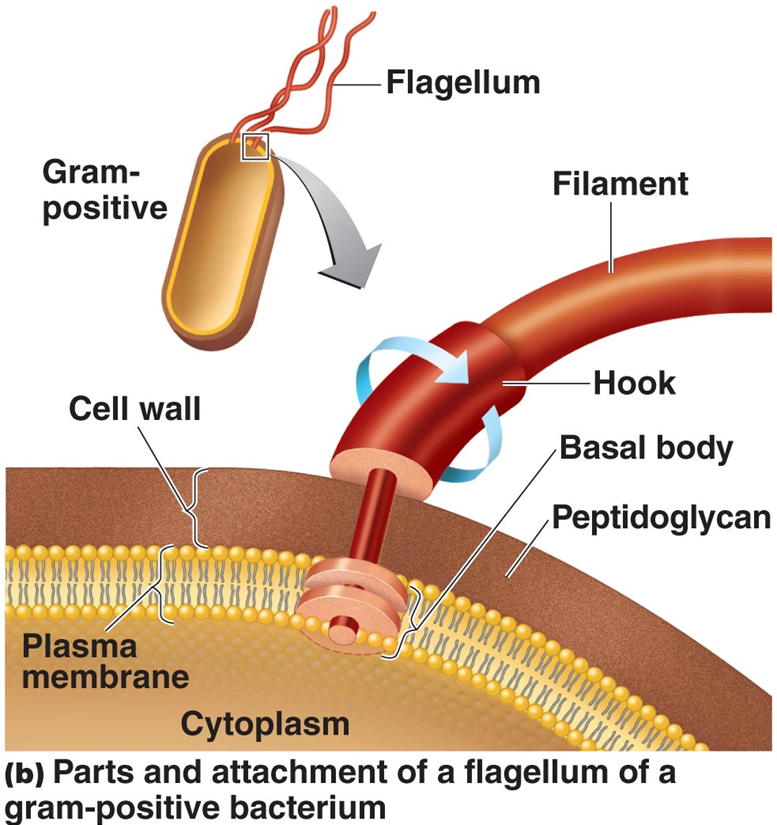
Made up of filaments which are made up of flagellin
Attached to a rotating protein hook
Anchored to the cell wall and plasma membrane by the basal body (two set of rings)
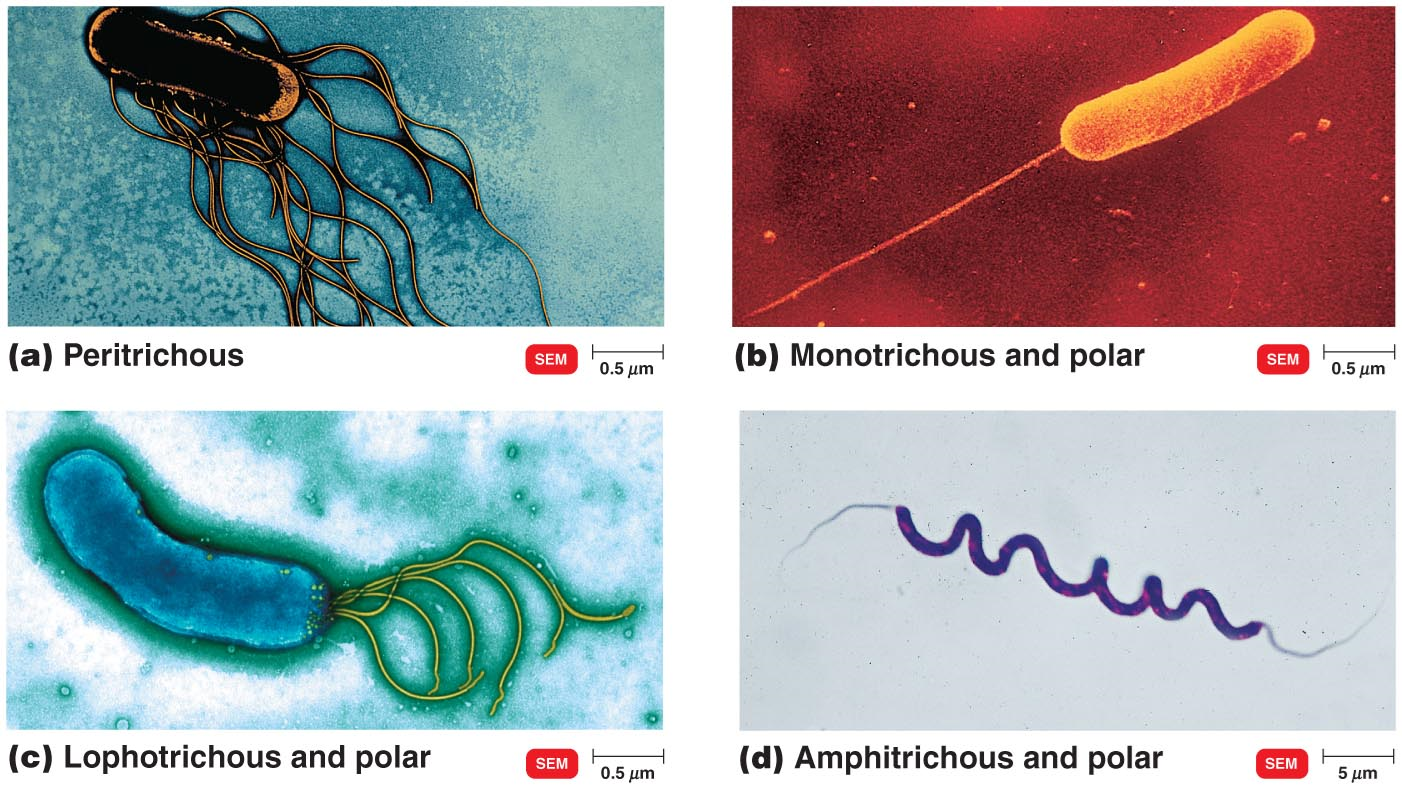
What are the four types of flagellum?
Monotrichous (singular/whip)
Amphitrichous (double sided whip)
Lophotrichous (bundle on one side)
Petrichous (arrangement is all around the cell)
What does it mean when flagella like to “run”?
This means that flagella keep moving and moving till they hit a barrier, where they tumble and change direction. They regain themselves from tumbling and start moving again to another direction repeating the tumbling motion against barriers.
Describe axial filaments/endoflagella.
Found in spirochetes
Anchored at one end of a cell
Rotate and wrap around cell with powerful spiral movements
What are pili?
Projections that connect from one cell to another to facilitate DNA transfer
What are fimbriae?
They are tiny projections from outside a cell’s surface, being shorter and thinner than flagella
Describe the “peptido” portion of Peptidoglycan.
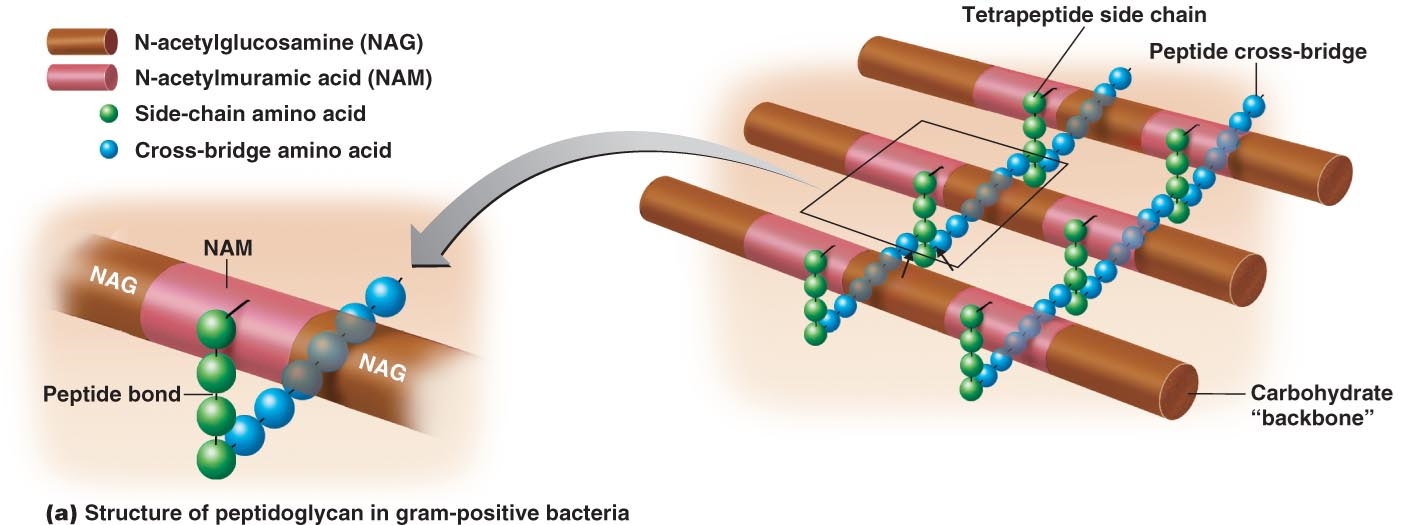
Polypeptide that connects the sugar backbone by peptide bonds with side-chains and cross-bridge amino acids
Describe the “glycan” portion of Peptidoglycan.
It is a polymer of glucose
Makes up sugar backbone that is NAM and NAG which form a wall
Describe a Gram-positive cell wall.
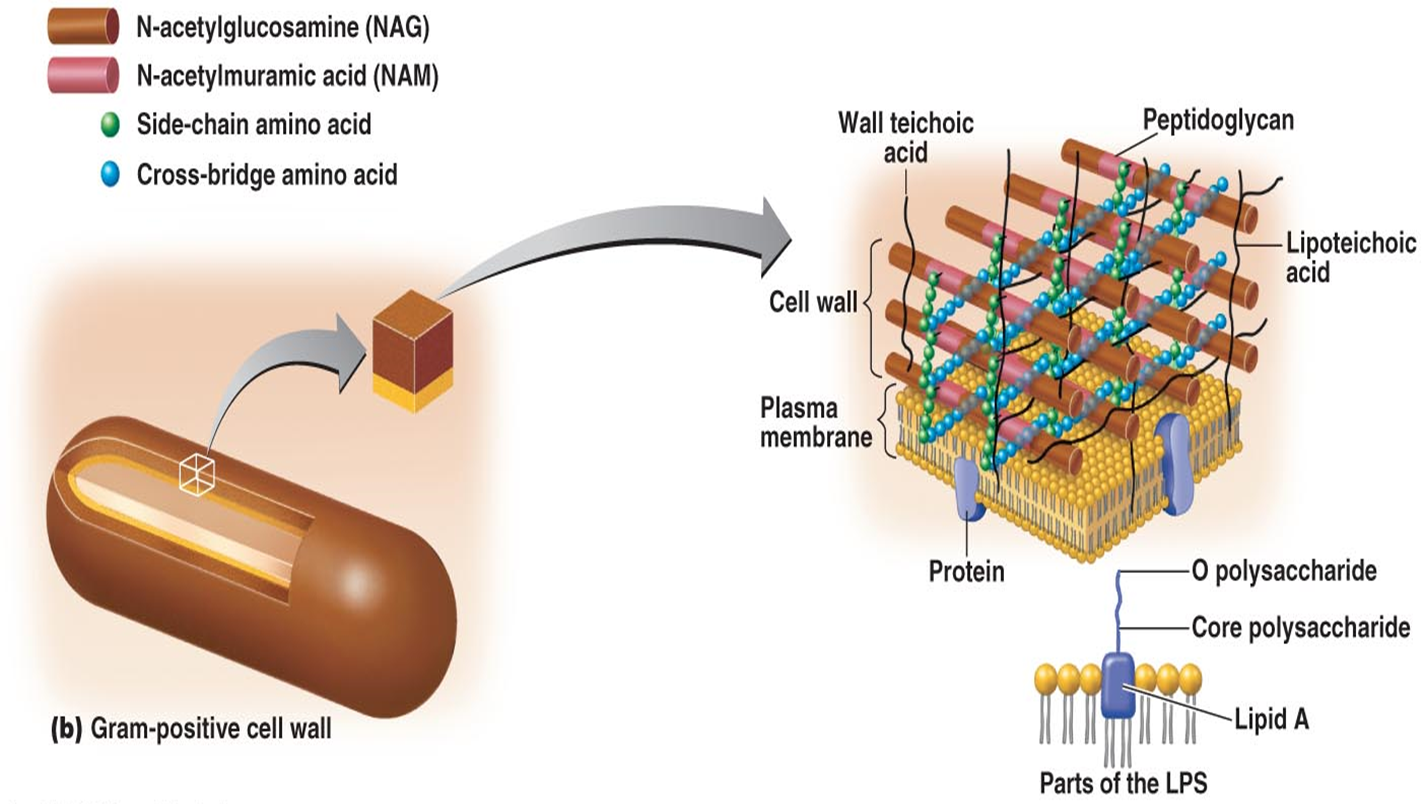
Contains several thick layers of peptidoglycan
Contain Teichoic acids
Describe Teichoic acids.
Mix of alcohol and phosphate
Two types
Ribityl (5 carbons)
Glycerol (3 carbons)
If remaining in wall they are called Lipoteichoic acids
Provide antigen specific nature and attract positive ions
Describe a Gram-negative cell wall.
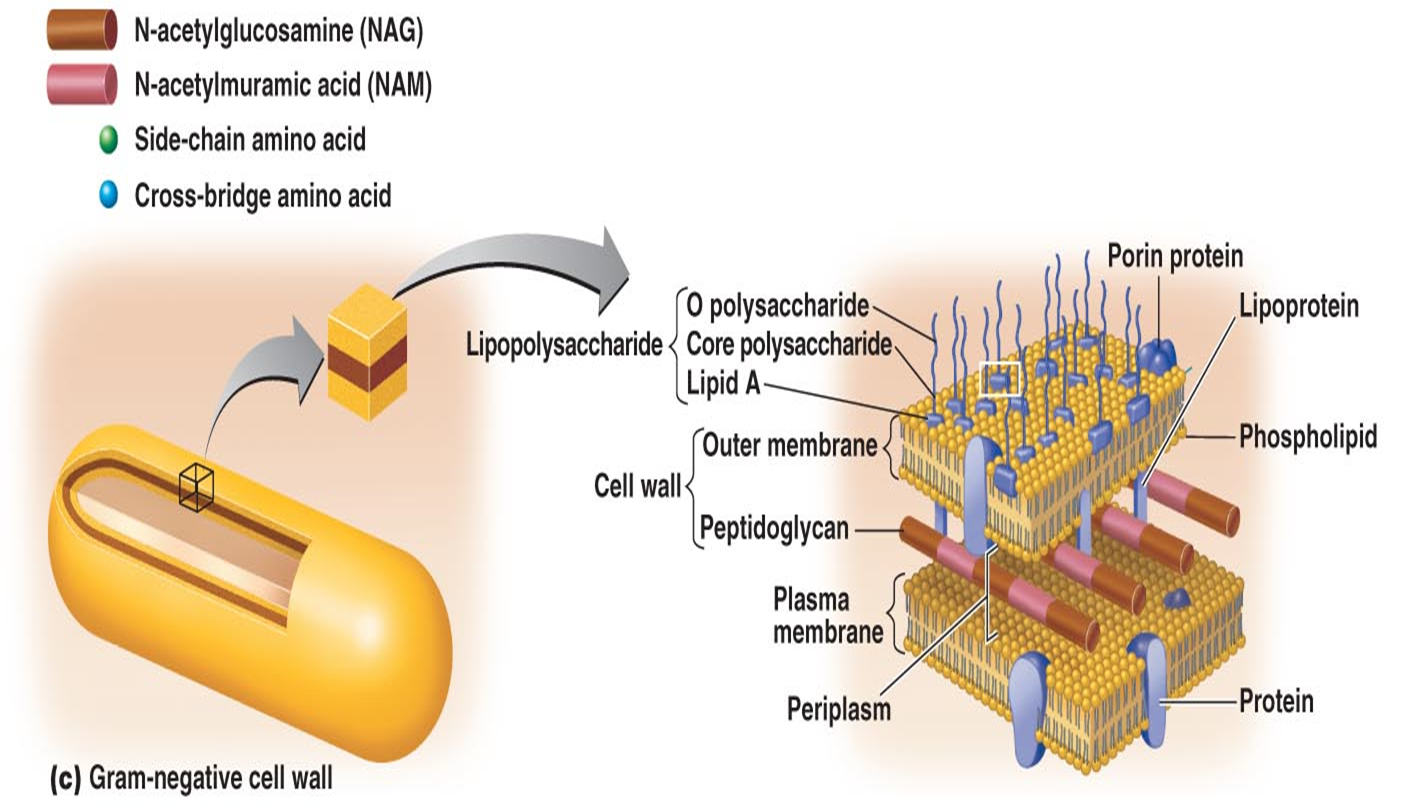
Outer membrane
Contains lipoproteins, porin protein channels, and lipopolysaccharides
Lipopolysaccharide is an endotoxin, which contains Lipid A that when released causes inflammatory response
Thin layer of peptidoglycan
Periplasmic space
What is an Acid-fast cell wall?
It is a waxy lipid later bound to PG that is made up of Mycolic acid
What is a mycoplasma’s cell wall?
No cell wall and only plasma membrane with sterols present
What is an archaea’s cell wall?
Archaea do not have cell walls, and the rare case they do is pseudo PG (false PG)
What does lysozyme digest when damaging peptidoglycan?
It digests the disaccharide, the backbone of glycan.
When a lyzosome digests the disaccharide in peptidoglycan, A Gram-positive devoid of cell wall is called a _______, while a gram-negative devoid of cell wall is called a _____
“protoplast”, “spheroplast”
Ribosome: ___S +__S = Complete 70S ribosome
30S + 50S
How is a holoenzyme (whole enzyme) made?
Inactive Apoenzyme (protein portion) + Cofactor activator (nonprotein portion)
Describe coenzymes. Give two examples.
A type of cofactor is a coenzyme
Accept/donate electrons from substrate
Act as electron carriers
e.g. NADP and FAD
What do enzymes do?
Act as biological catalysts
Lower activation energy
Active site is specific in nature
Unharmed in reaction—reused
What does penicillin do to peptidoglycan?
It inhibits the peptide brides that connect the backbone
Describe endospores.
Resting cells formed by Bacillus, Clostridium species (Gram+)
Resistant to desiccation, heat and chemicals
What does Clostridium Tetani cause?
Tetanus
What does Clostridium Botulinum cause?
Botulism
What does Clostridium Perfringens cause?
Gangrene
What does Clostridium Difficile cause?
Colitis
What is the exception to Gram negative species with endospore?
Coxiella Burneti which causes ammonia called Q-fever
How is endospore formed, and what returns to their vegetative state?
Sporulation, germination
How many membranes does an endospore have?
Two
Endospore contains DPA, what does it do?
Gives it resistance to endure time of rest and it is only found in endospores.
What is a basic dye?
A salt in which the color is in the positive ion
What is an acidic dye?
A salt in which the color is in the negative ion—used for negative staining
Describe capsule staining.
Mix bacteria in a solution containing India ink or nigrosin to provide a contrasting background and stain cells with simple stain
Shows up as light areas surrounding stained cells
Describe endospore staining
Malachite green dye cannot penetrate the endospore wall itself, so heat is applied to penetrate it.
It is washed with water to remove green dye from cell parts except endospores
Counterstain: Safranin is applied to stain portions of cell other than endospores
Endospores should appear green within a red/pink cell
Describe flagella staining
Carbol fuchsin to stain
Mordant: Potassium alum to enlarge and build up diamters of flagella
Flagella is a very tiny structure and is prone to breaking apart and floating away
What is negative staining?
A procedure that results in colorless bacteria against a stained background
What is a simple stain?
Staining microbes with a single basic dye, a mordant may be added to intensify stain
What are functions of a mordant?
Increase affinity of a stain
Coat structure to make it easier to see
Describe a Gram-stain procedure.
Staining a gram positive and a gram negative
Primary stain: Crystal violet basic dye that imparts a purple color to both cells
An iodine mordant is added, both cells appear dark violet
Decolorizing agent: Removes stain from some specie cells with an alcohol-acetone solution
Counterstain: Stained with safranin (basic red dye)
Gram+ retain original purple stain
Gram- lose purple stain and take on a pink color (counterstain)
Describe an Acid-fast stain procedure.
Only binds to bacteria with waxy material in their cell walls
e.g. Mycobacterium species: Detecting tuberculosis and leprosy
Primary stain: red dye Carbolfuchsin, and heated to enhance penetration and retention of dye
Decolourizing agent: Acid-alcohol, removes red stain from bacteria that are not acid-fast as they lack lipid components
Counterstain: Methylene blue
Red are tuberculosis acid-fast Gram+ cells
Blue are non-acid-fast cells