58. Breast carcinoma. Pathogenesis, types, prognosis
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Breast cancer - epidemiology?
Most common cancer in women
- Second most common cause for cancer mortality
- Is related to increased estrogen
- Non-invasive and invasive types
- The tumors develop from different parts of the TDLU
Where does breast cancer most frequently occur?
Upper outer quadrant of the breast
Who is breast cancer most commonly seen in?
Older, post-menopausal women
- If it occurs in younger women, it is rather hereditary than sporadic
• 90% of cases are sporadic
• 10% of cases are familial
It is rare in men
Lifetime risk of developing breast cancer?
1 in 8 women (12,5%)
- It is very high
(Data taken from American women)
Etiology - breast cancer?
- Female gender
- Risk increases after age 30
- Western countries
- Positive family history
Increased estrogen exposure:
- Nulliparity
- Early menarche
- Estrogen-containing contraceptives
- Obesity
- BRCA1 and BRCA2 (germ-line mutations)
- Atypical hyperplasia in benign breast disease
Pathology of breast cancer?
- Overexpression of HER2/NEU proto oncogene -> in 30% of invasive breast cancer
- Expression of estrogen receptors (ER) and/or progesterone receptors (PR) in the cancer
How should breast cancers be examined?
Immunopathologically
- To see which of the three proteins that are expressed (HER2/NEU, ER or PR) in the cancer
There exists treatment specifically for each of them -> improving the prognosis
Triple negative cancers?
- No HER2/NEU proto oncogen overexpression
- No estrogen receptors (ER)
- No progesterone receptors (PR)
on the tumor cells
They have poor prognosis, as the specific treatment is useless in these cancers
Pathology behind familial cases of breast cancer?
Mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 are most common
- These germ-line mutations are found in 1/3 of cases with hereditary breast cancer
BRCA-genes are rarely mutated in sporadic cases of cancer
BRCA function?
Is normally a tumor suppressor - involved in DNA repair
When mutated, it is silenced (there is already a germ-line mutation, so only one hit is needed)
Increased estrogen exposure and breast cancer?
Increased estrogen -> highly associated with breast cancer
- Obesity
- Early menarche
- Nulliparity
= will all cause increased estrogen/progesterone ratio
Estrogen -> stimulates production of Growth factors -> promote tumor development
What can be protective measures against breast cancer?
Factors which reduce unopposed estrogen exposure, like:
- Late menarche
- Breast feeding
Types of breast cancers?
Non-invasive carcinoma:
- Ductal carcinoma in situ
- Lobular carcinoma in situ
Invasive carcinoma:
- Invasive ductal carcinoma
- Invasive lobular carcinoma
- Tubular carcinoma
- Mucinous carcinoma
- Medullary carcinoma
- Mastitis carcinomatosa
- Other types
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)?
Most common non-invasive carcinoma
Tumor cells:
- Originate from the duct of TDLU -> fills the duct of the breast
- Does not invade the past the basement membrane of the ducts (if it does, it becomes invasive carcinoma)
Calcification of DCIS?
Tumor cells in the centre of the ducts will die by necrosis -> as they do not receive enough oxygen
- Forms calcification -> visible on mammography
Comedo type?
Is high-grade DCIS
- Severe atypia
- Extensive central necrosis and calcification
Treatment DCIS?
Surgery and irradiation -> curative in almost 100% of cases
(Is rarely a palpable mass, and is often discovered during routine mammography)
Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS)?
Originates from the lobules in TDLU
- Tumor cells does not invade past the basement membrane of the lobules
- Does not produce calcifications or masses -> therefore often incidentally discovered
Treatment LCIS?
Are often multifocal and occurs in both breasts simultaneously (compared to DCIS)
- Not removed surgically, but rather treated with chemotherapy
Why are the LCIS tumor cells disconnected from each other?
They have lost an intracellular adhesion molecule "E-cadherin"
- Causes them to be disconnected from each other
What are common clinical findings of the subtypes of invasive breast carcinoma?
- Firm, palpable mass
- Skin retraction
- Nipple retraction
- Orange peel-like skin
- Nipple discharge
Invasive ductal carcinoma?
Accounts for 80% of invasive carcinomas
- Occurs when DCIS invades past basement membrane
• 2/3 express estrogen/progesterone receptors
• 1/3 express HER2/NEU
Histology of Invasive ductal carcinoma?
Tumor consists of duct-like structures embedded in a desmoplastic (fibrous) stroma
The desmoplastic stroma causes the tumor to be hard and firm and visible on mammography
Invasive lobular carcinoma?
Accounts for 5-10% of invasive carcinoma
- Occurs when LCIS invades past the basement membrane of the lobules
- Tumor cells lack E-cadherin -> they wont form structures
- May form single rows of cells
- Almost all express ER/PR, very few express HER2/NEU
What type of cells may be present in invasive lobular carcinoma?
Signet ring cells
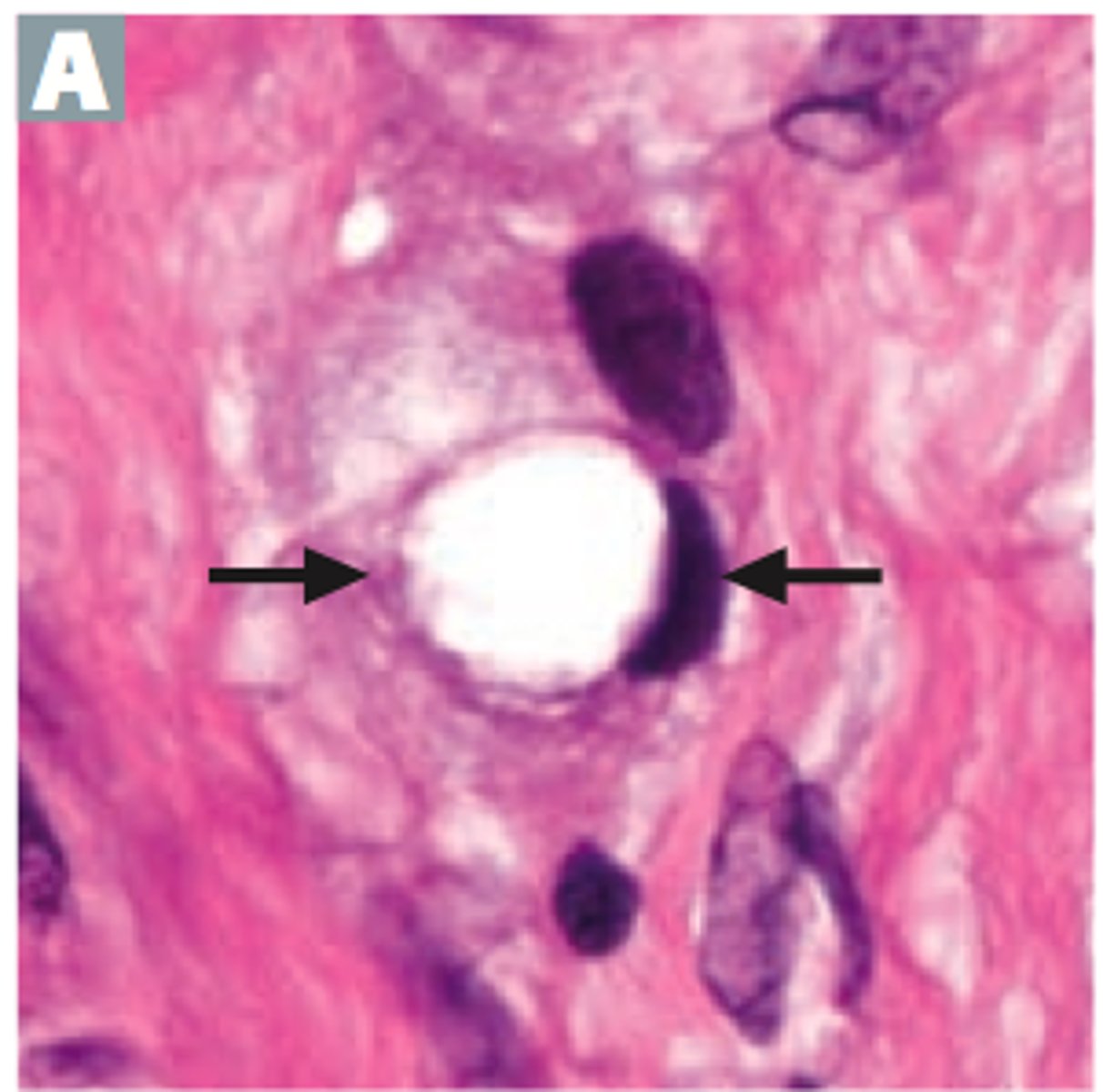
Tubular carcinoma?
Characterized by the presence of well-formed tubular or glandular structures infiltrating the stroma
- This type has a favourable prognosis
Mucinous carcinoma?
Accounts for 1-2% of invasive carcinoma
- Tumor cells have lost their orientation
- Instead of secreting mucus into a lumen, they secrete mucus outwards
= Tumor cells are surrounded by "pools of mucus"
This type has a favourable prognosis
Medullary carcinoma?
High-grade tumor cells with inflammatory infiltrate
- More frequent in women with BRCA1 mutations
- Consists of sheets of large anaplastic cells with well-circumscribed pushing borders
- Clinically: can be mistaken for fibroadenomas
Are triple-negative cancers
Mastitis carcinomatosa (inflammatory breast carcinoma)?
Rare and aggressive form of breast cancer
Breast is inflamed -> w/ erythema and edema
- Sterile inflammation => occurs because tumor cells have filled the lymphatic vessels of the breasts
= Similar to lymphangitis carcinomatosa
When should mastitis carcinomatosa be suspected?
In women with mastitis that does not resolve with antibiotics
What is an important feature with mastitis carcinomatosa?
Mastectomy is not performed
Instead: chemotherapy and irradiation
Diagnosis of breast cancer?
- Routine mammography in post-menopausal women
- Women with self-palpated breast lump (is more and more rare, due to mammography)
What can mammography detect?
Calcifications
- Which occurs in most breast cancers
- Can also be present in benign conditions like fat necrosis/sclerosing adenosis
How to distinguish benign breast lesions from cancer histologically?
Myoepithelial cells
- These are absent in cancers
Prognosis of breast cancer?
Based on TNM staging
- Distant metastasis (M1) is very poor prognosis -> but rare
Many cases present with spread to the axillary lymph nodes -> biopsy can determine stage and prognosis
Sentinel lymph node biopsy?
Procedure where the axillary lymph nodes are biopsied
- During this procedure: breast is injected with radioactive material -> the material will drain to the sentinel lymph node -> is the one node that is removed and examined
Due to this method, we only have to remove one node and not all of them.
- This would cause lymphedema of the patient's arm -> should be avoided
Worst prognosis to best - breast carcinoma?
Inflammatory carcinoma > invasive ductal carcinoma > the rest
Which invasive breast carcinoma is always triple negative?
Medullary carcinoma
Complications of breast cancer?
Paget disease:
- Condition where tumor cells originating from DCIS or invasive carcinoma replace the epithelial cells of the epidermis of the nipple
Metastasis:
- Can do it anywhere -> most commonly to lungs, skeleton and liver
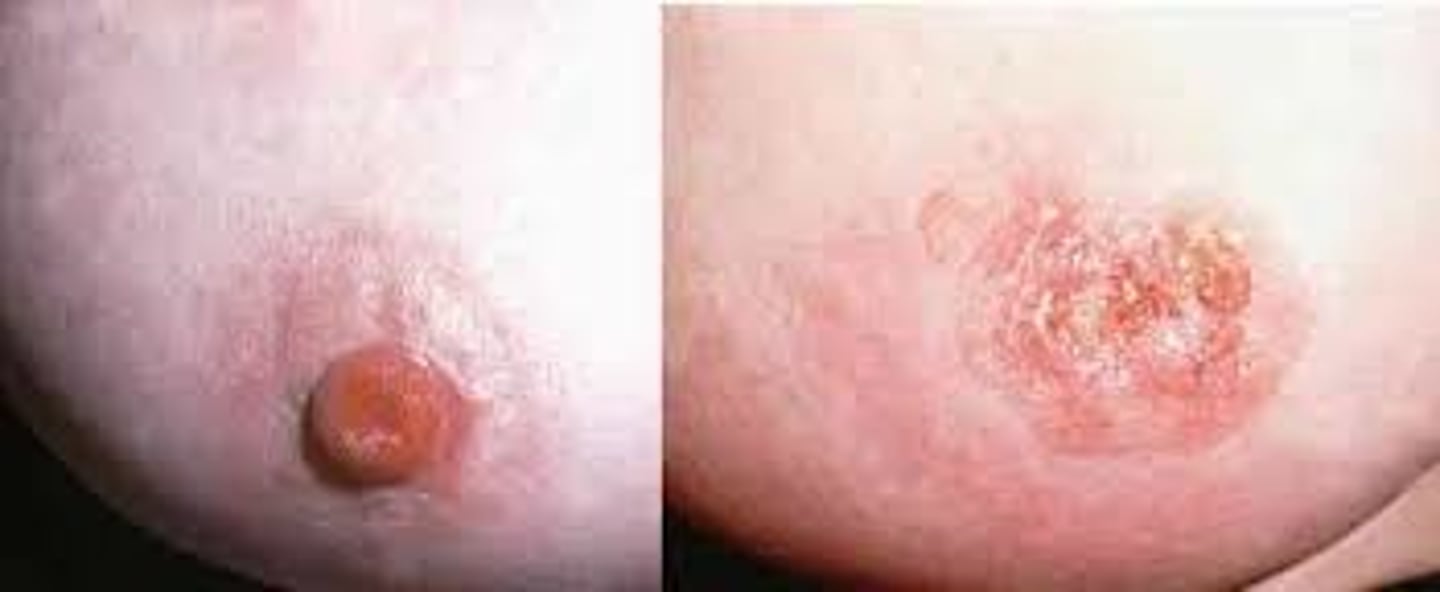
How is the nipple in paget disease?
Firm
Ulcerated
Hyperkeratotic
Inflamed
Treatment - breast cancer?
• Mastectomy -> removal of breast
• Chemotherapy
Women with high risk for developing breast cancers -> like positive BRCA mutation
= offered prophylactic double mastectomy
How to treat patients with tumor expressing both ER and PR?
Can often be treated with anti-estrogenic drugs like Tamoxifen
(Treatment is less likely to succeed if only one of the receptors are expressed)
Tumors expressing HER2/NEU?
Codes for a membrane-bound protein -> is related to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)
Can be treated with Herceptin -> a monoclonal antibody that binds to and inhibits its function