Bio 181 exam 3
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
The main characteristic all fungi have
double cell wall with chiten
Fungi’s sources of energy
Dead plants and animals ( Decomposers)
Alive plants, animals, and bacteria
Materials
Haploid-Dominant lifestyle
Fungi spend most of their life in the haploid stage of the lifecycle
The only unicellular fungi that reproduces asexually
Microsporoida
Polar Tubes
Used by microsporida to inject themselfs into living cells and reproduce by fission
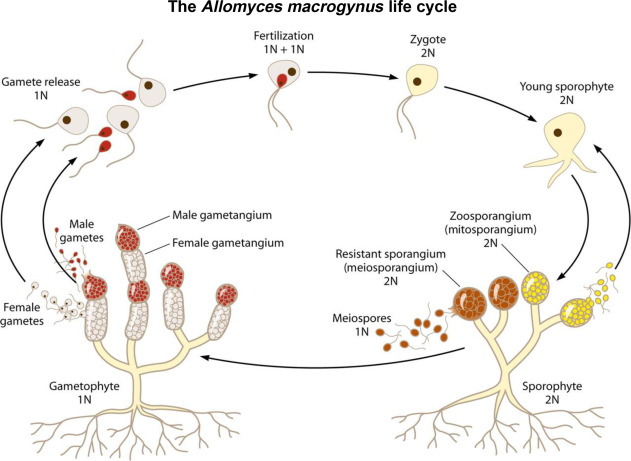
The fungi with motile cells live in freshwater habitats
Chytridiomycete
Motile cells
Spore cells that have flagella that can swim
chytridomycetes life cycle
zygomycetes
Has zygospores, are coenocytes, and only sexually reproduce in stressful situations
Zygomycetes life cycle
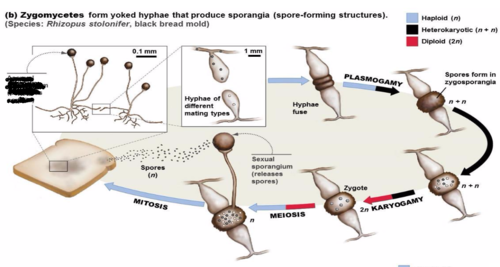
Plasmogamy
Union of cytoplasm without the fusion of nuclei
Kayrogammy
the union of nuclei to create a zygote
What zygospores are not
zygospores are not alteration of generations
Glomeromycota
Are coenocytic and have arbuscules
Arbuscules
Structures that live inside plant cell walls, provides essential nutrients to plants and gains carbon from the plants.
Basidiomycota
Fungi that form Basidium and are ectomycorrhizal
Ectomycorrhizal
Penetrate plant wall cells but foes not live in plant cells
Basidium
The reproductive structure of a basidiomycota
Basidiomycota life cycle
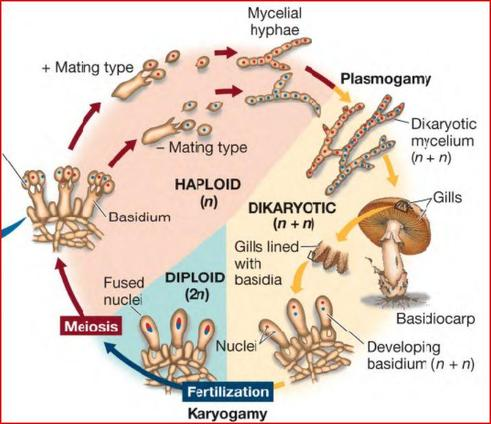
Dikaryotic
contains two genetically distinct haploid nuclei
Heterokaryotic
contains two or more genetically different nuclei within a single cytoplasm
Ascomycetes
Make an Ascus, a spore producing body
Mesoproterozoic
boring billion, no environmental events, resulted in little species richness
Neoproterzoic
Period of massive change, warming, and cooling events, with the gradual beginnings of freshwater lakes and pools
What the Neoproterozoic period resulted in
High species diversity, selective pressures, and some organisms transitioning to land.
Bio and chemical weathering and their importance
Withering by either acid rain or bacteria and fungi that process rock
Helped create soil and allowed plants to transition to land
Neo protozoic period, allopatric or sympatric speciation?
Allopatric, separated species are either divided by layers of ice and rock or through the creation of freshwater revisors
Hyphae
each of the branching filaments that make up the mycelium of a fungus
Fungi’s transition to land
Some fungi used rocks from land as a source of carbon and nutrients, and formed a symbiotic relationship with early plants (they create soil and trade nutrients)
Non-Vascular Plants
Plants that lack vascular tissues, such as lignin, which acts as a reinforcement to keep water inside. But do have water-conducting cells, such as xylem.
What are the four characteristics that all land plants have
waxy cuticle
UV radiation protection
Vascular Tissue and Structural Support
Reproduction in dry conditions - Haploid-diplontic
What plants use for gas exchange because of the waxy cuticle
Stomate
Haplotic Lifestyle
When the multicellular phase is haploid, originally in green algae
Why does a haplotic lifestyle not work on land?
In a haplontic life cycle, haploid gametes are released and must swim in water to find and fuse with other gametes to form a diploid zygote. On land, this is an inefficient and unreliable method of reproduction. The evolution of a protective, drought-resistant diploid sporophyte allows for the airborne dispersal of spores, freeing reproduction from the constant need for a moist environment.
Haplo-diplontic lifestyle
Both haploid and diploid stages can be multicellular, allowing spores to disperse through air instead of water
Basic Plant life style
Sporophytes do meiosis to make spores
spores do mitosis to make gametes
gametophytes do mitosis to make gametes
gametes do fertilization to make sporophytes

Antheridia
The part of the gametophyte that makes spores
Archegonium
Part of the gametophyte that makes the egg, and where the egg is fertilized
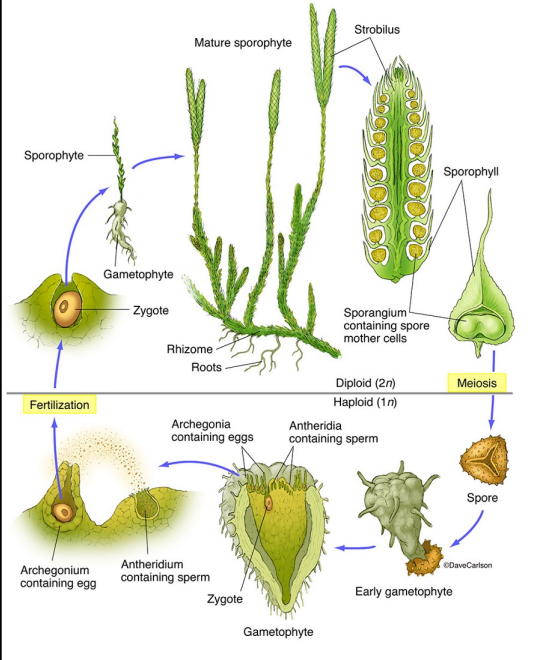
Bryophyte lifecycle
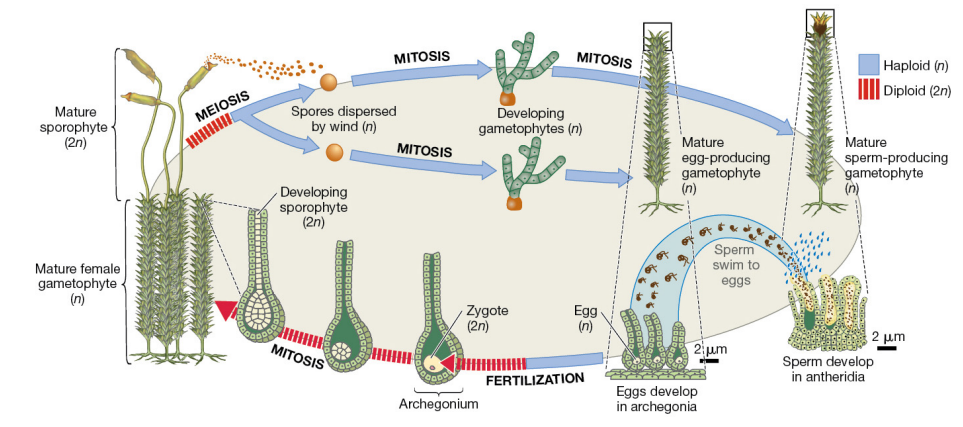
Sporangium
The diploid phase and the sporophyte part of the bryophyte
What do zygospores (in zygnematophyceae and zygomycota) have in common with plants?
They have similar chemical and structural components found in spores of bryophytes and lycophytes, possible consequence of Snowball Earth as it allows them to survive extreme temperatures
Sister taxa to plants
zygnematophyce - have a very diffrent life cycle to land plants
The differences of lycophytes than bryophytes
Sporophyte-dominant lifestyle
Lignified vascular tissue with xylem and phloem (vascular tissue in plants that conducts sugars and other metabolic products)
can be both exosporic and endosporic
Can be homosporous or heterospores
Sporophyte dominate lifestyle
A plant that spends most its life in its diploid form
lignified vascular tissue allows for
Allows plants to grow bigger, water can conduct through the veins more easily
Exosporic
Archegonia and archegonia develops outside the spore
exospores
archegonia and archegonium develops inside the spore
Sporangium
where sporangium’s are held for lycophytes and ferns
homosporous
a plant that produces only one type of spore, which then develops into a gametophyte capable of producing both male and female gametes
Heterosporous
plants that produce two different types of spores: smaller, male microspores and larger, female megaspores
heterosporous life cycle
Sporophytes have megasporophylls that produce megasporangia that contain megaspore mother cells (all 2N) that undergo meiosis to produce megaspores (1N) Sporophytes have microsporophylls that produce microsporangia that contain microspore mother cells (all 2N) that undergo meiosis to produce microspores (1N) Megaspores grow via mitosis into megagametophytes that contain archegonia that produce eggs (all 1N) Microspores grow via mitosis into microgametophytes that contain antheridia that produce sperm (all 1N) Sperm are released from antheridia and swim down the neck of an archegonium to fertilize the egg (all 1N) to produce a zygote (2N)
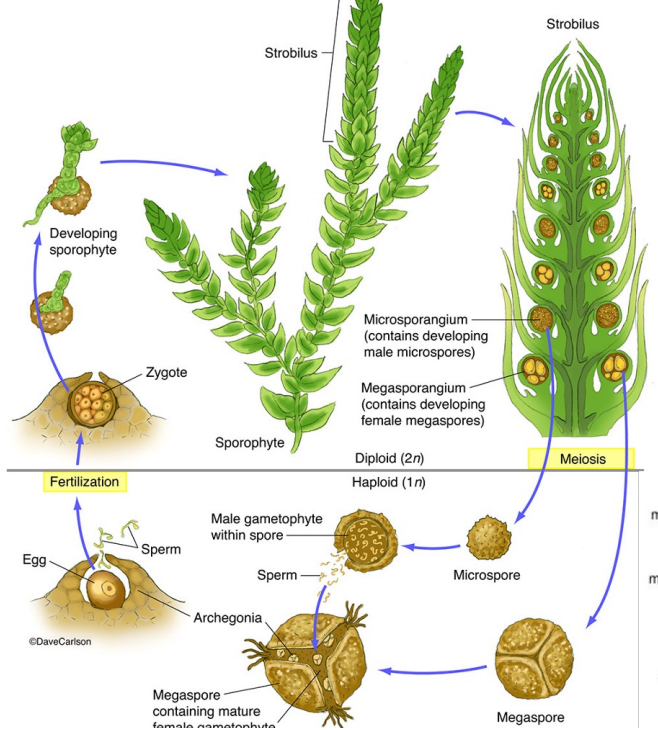
Homosporous lycophyte life cycle
What does branched veins allow for?
it allows for bigger leaves and plants as the veins can reach further
What are key synapomorphies shared by all green plants?
Double-membraned chloroplasts, chlorophyll a & b, carotenoid pigments, sugar stored as starch, and cell walls with cellulose and pectin.
Why are green plants considered monophyletic while green algae are paraphyletic?
Because green plants include all descendants of a common ancestor, whereas “green algae” excludes land plants even though they share that ancestor.
What is the evolutionary significance of Streptophyta?
Streptophyta share specialized metabolic pathways (like photorespiration) and gave rise to land plants, unlike Chlorophyta which remained primarily aquatic.
What evolutionary pattern links fungi and plants over time?
Origin of terrestrial fungi → origin of terrestrial green algae
Origin of AMF (arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi) → origin of land plants
Origin of EMF (ecto-mycorrhizal fungi) → diversification of land plants
Diversification of EMF → diversification of flowering plants
What were the six major challenges early plants faced on land?
Acquiring water for photosynthesis and reproduction
Drought stress
High irradiance and oxidative stress
Freezing temperatures
Anchoring to substrates
Building self-supporting structures in air
Why is Zygnematophyceae considered the closest living relative to land plants?
they share stress-response and hormone-signaling genes found in all land plants. Genes for multicellularity and terrestrial pre-adaptation.
What structural and chemical features make zygospores key to land adaptation?
Zygospore walls contain sporopollenin and lipid droplets, similar to land plant spores and pollen, providing UV and desiccation protection.
How did fungi contribute to the success of land plants?
Early terrestrial fungi broke down rocks, decomposed bacteria, and created primitive soils—preparing land for plant colonization.
What does Prototaxites tell us about early terrestrial ecosystems?
It was a giant (over 20 ft tall) ascomycete-like organism dominant 500 MYBP, showing fungi’s major role before vascular plants diversified.
Adaptations for plants to live on land
Adaptations:
Development of protective spores (zygospores) with thick, sporopollenin-rich walls for UV and desiccation resistance
Formation of mutualistic relationships with fungi (e.g., mycorrhizae) for nutrient uptake and soil stabilization
Acquisition of genes for stress tolerance and hormone signaling from soil bacteria
Evolution of stronger cell walls and structural support mechanisms
Enhanced water regulation and stress response pathways for life outside aquatic environments