9. Histology of the Oral Cavity and Salivary Glands
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
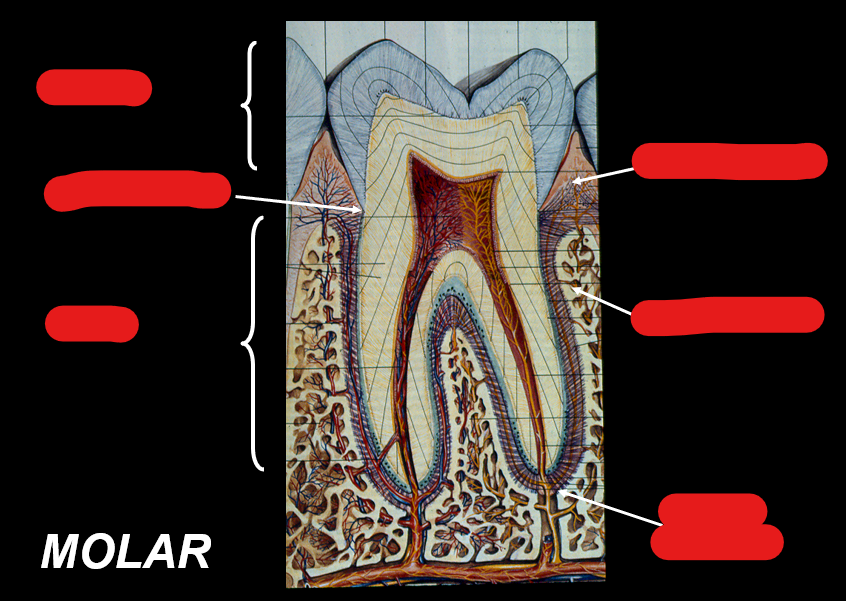
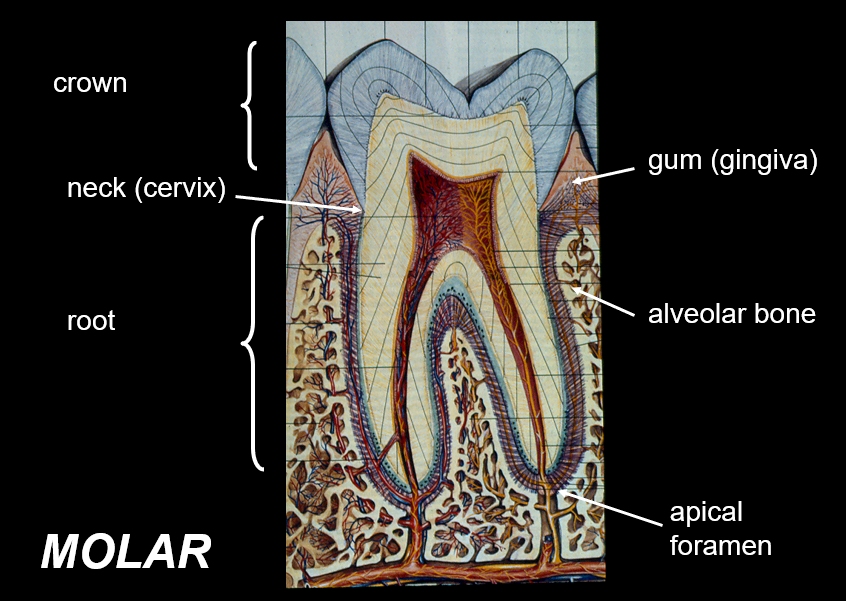
Identify the components in this figure
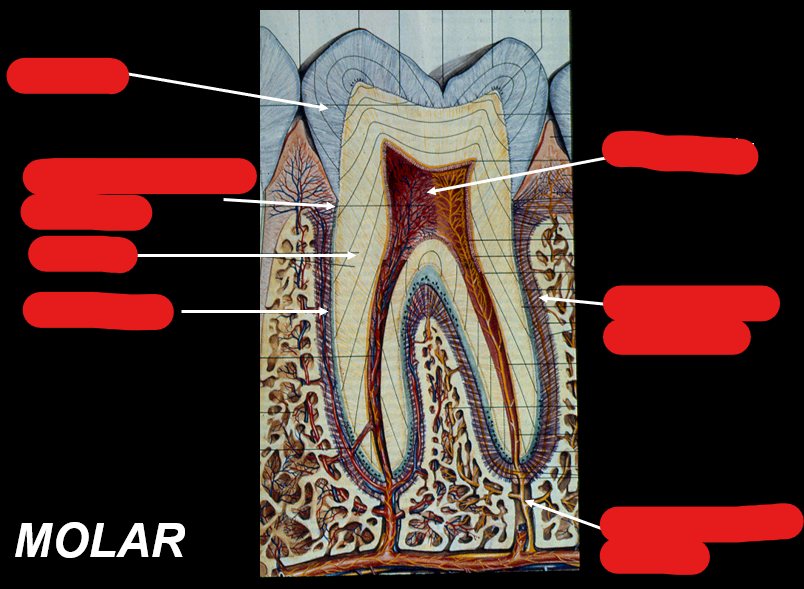
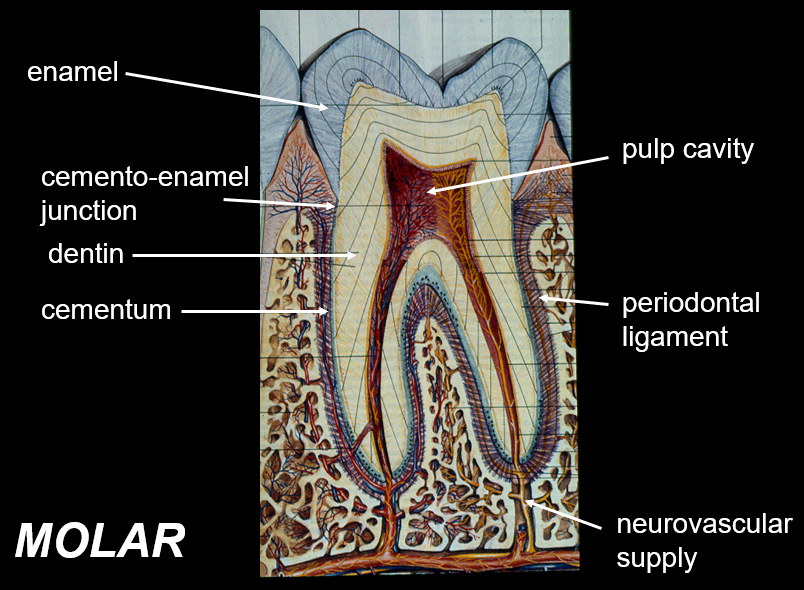
Identify the components in this figure
What is dentin?
Dentin is the predominant tissue of the tooth; is a hard tissue that makes up the majority of the tooth structure, surrounding the pulp chamber and extending throughout the tooth.
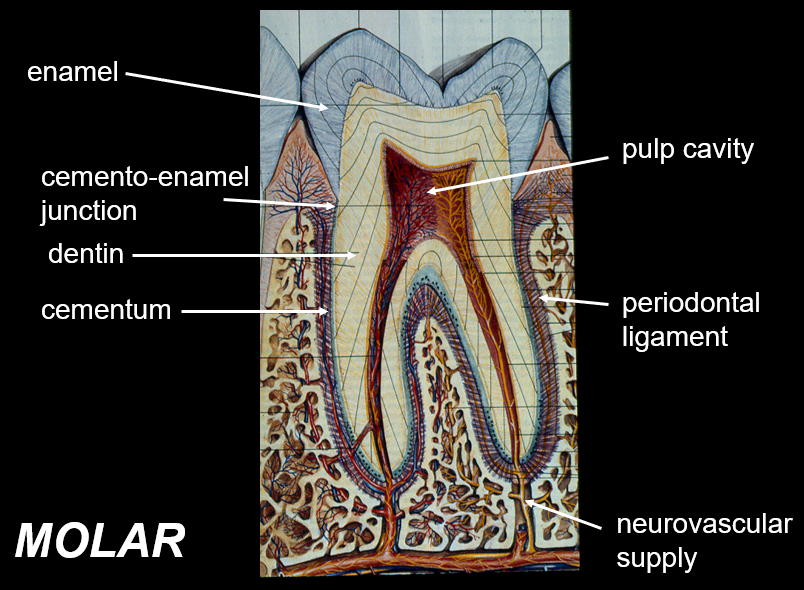
What is the function of the periodontal ligament?
prevents the root of the tooth from pushing on alveolar bone
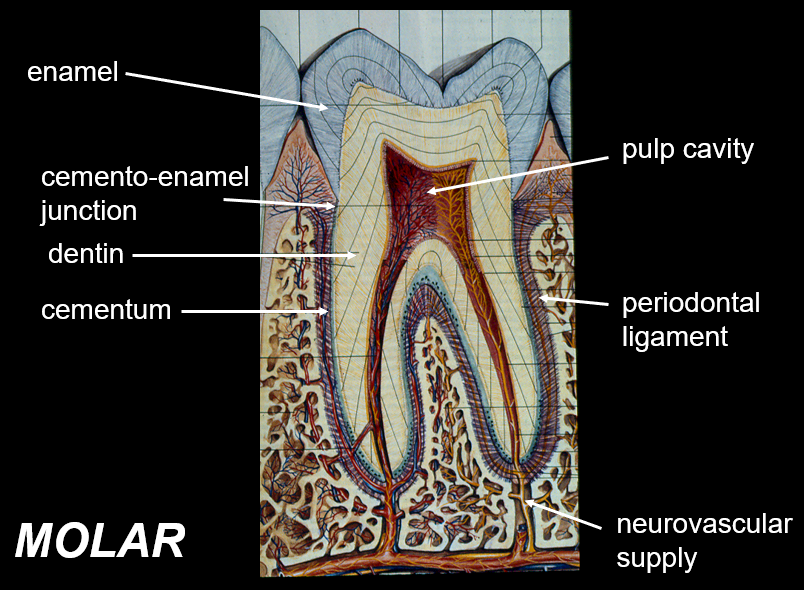
What is enamel?
covers the exterior of the crown of the tooth; hardest substance in the body; made of majority calcium salts
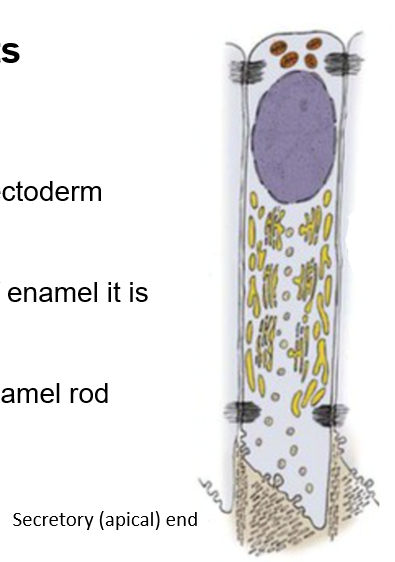
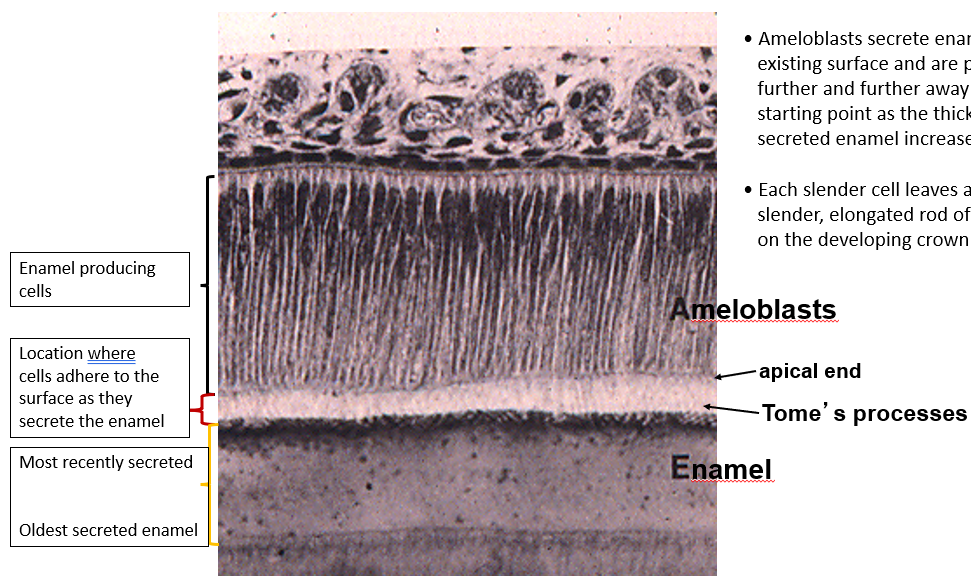
What is the function of ameloblasts?
produces enamel; it is derived from the ectoderm of the embryo
What is on the apical end of an ameloblast? What is its function?
Apical end has an extension (enamel rod) that the ameloblast uses to anchor to the surface of the enamel that it is producing and laying down
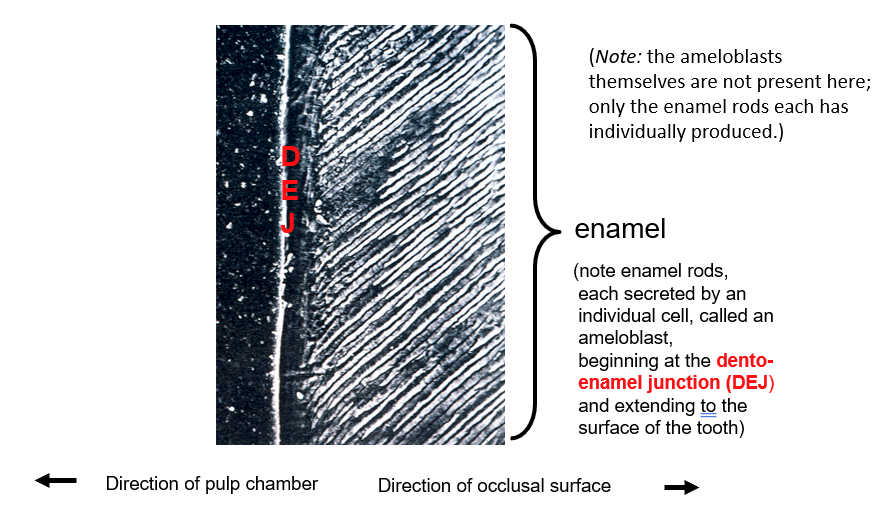
Enamel rods are secreted by __. They begin secreting enamel at the _ junction and extend to the surface of the tooth
ameloblast; dento-enamel junction
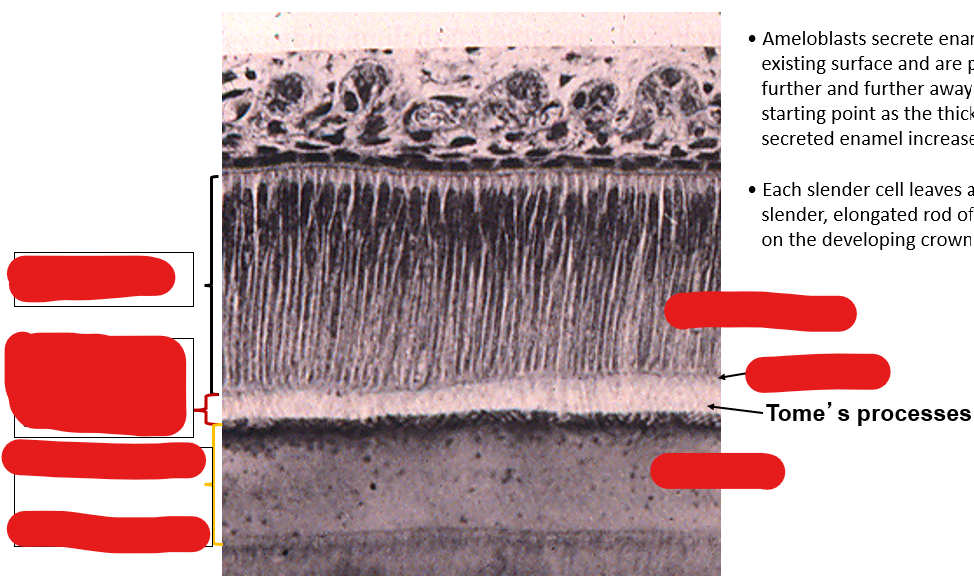
Identify the components in this image
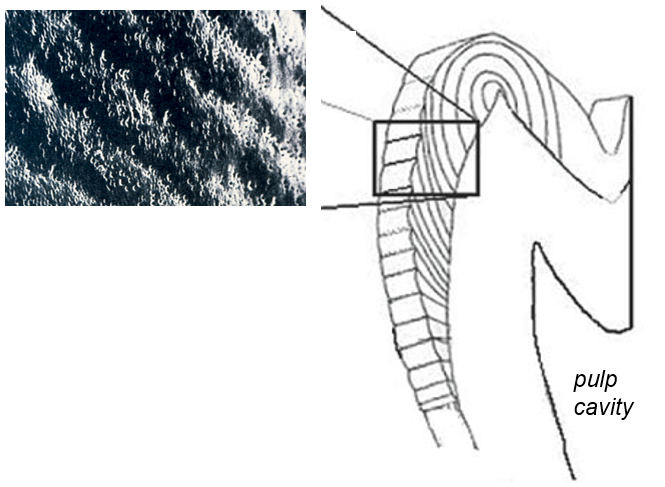
What is the pitting on the surface of enamel a remnant of?
ameloblasts anchoring to the enamel surface; enamel is never remodeled so features of enamel surface are permanent
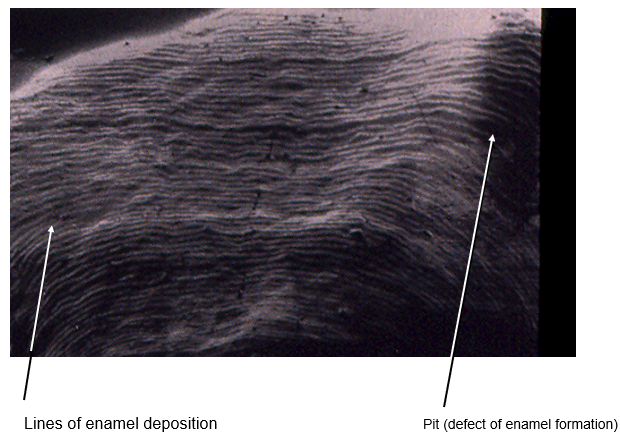
What is the cause of a defect in enamel formation?
can occur when ameloblast activity is disrupted due to local or systemic insult of the developing crown → stop or change enamel production
neonatal line forms in the baby during stressful event of childbirth
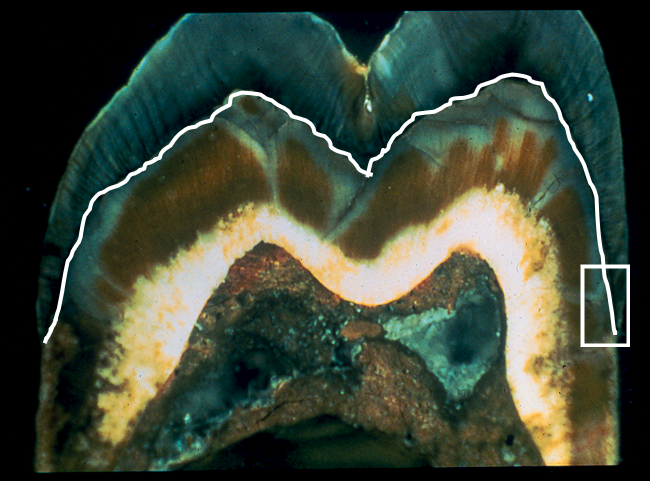
What is this?
dento-enamel junction
Dentin contain which type of collagen fibers?
collagen type I
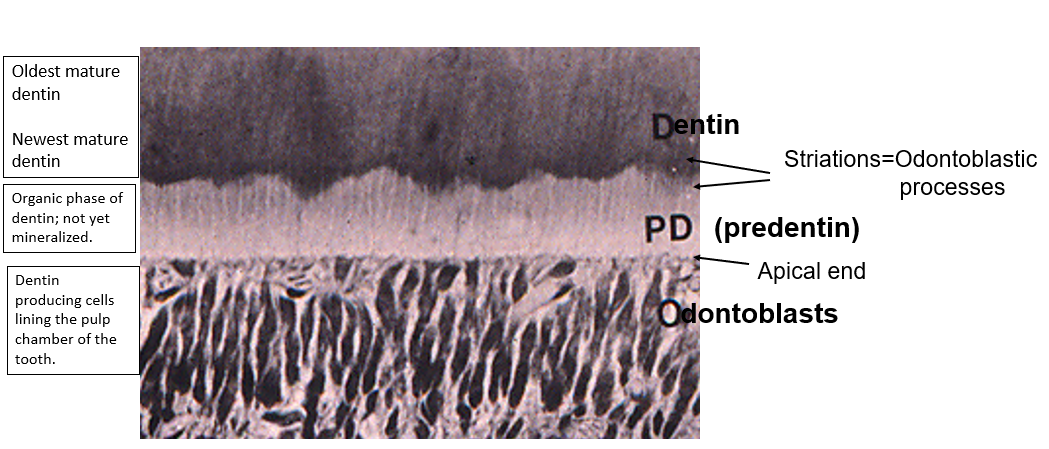
What is predentin?
organic phase of dentin prior to mineralization
What are odontoblasts?
cells that produce dentin; these cells line the pulp cavity of the tooth
What are odontoblastic processes?
branching process at the secretory end of odontoblasts; run entire thickness of dentin
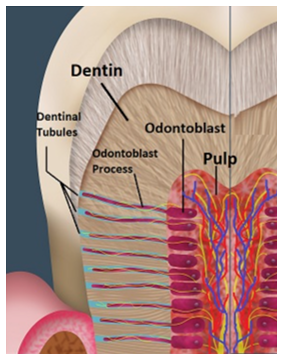
What are dentinal tubules?
tunnels from which odontoblastic processes run through
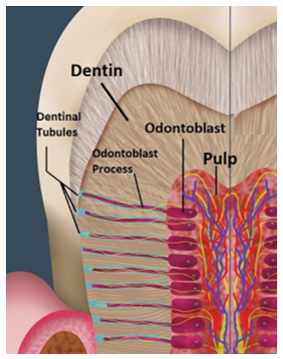
How are odontoblasts protected? What is the result of this?
Odontoblasts lie within the pulp cavity → they can continue to lay down dentin throughout life
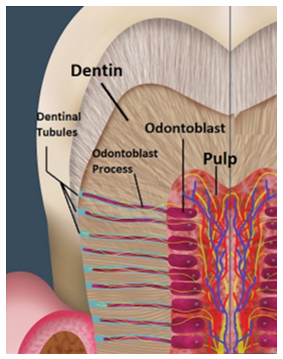
What type of stimulation allows for odontoblastic processes to lay down dentin when enamel is worn away in adults?
mechanical stimulation
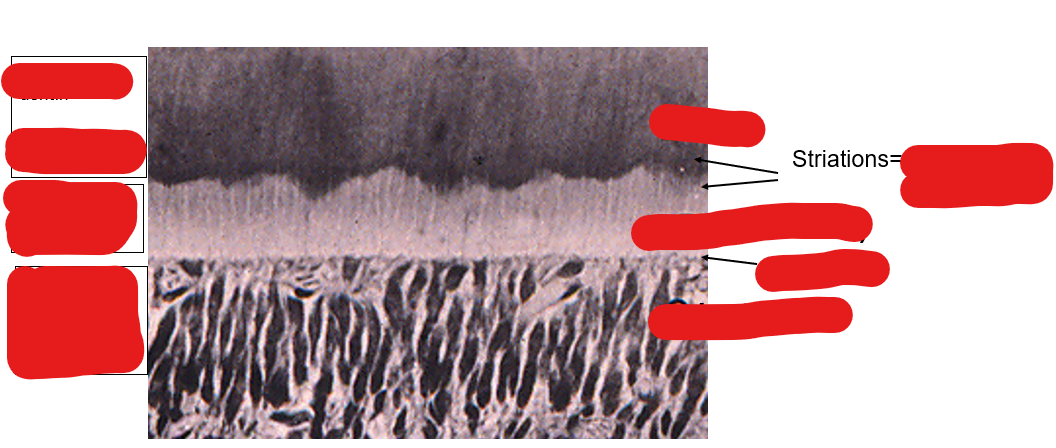
Identify these structures
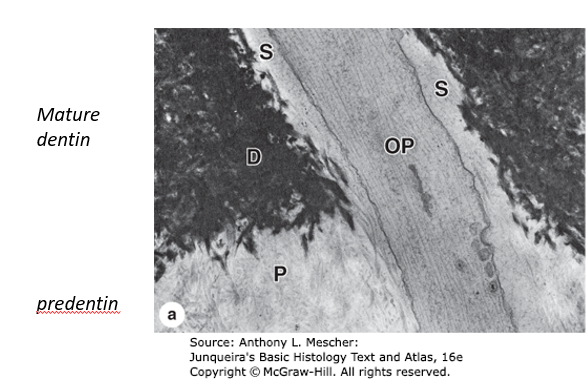
What is the structure labeled “S”? What is its function?
S = fluid filled space within dentinal tubules and surrounding odontoblastic processes; changes in fluid pressure detected by the process an stimulate the production of more dentin by the cell
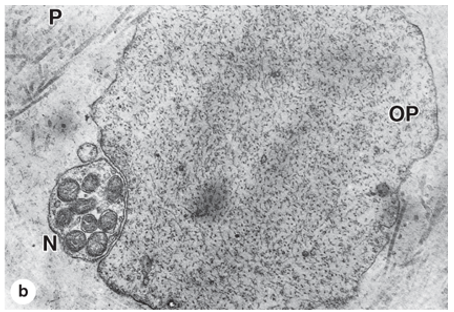
What is the structure labeled “N”? What is its function?
N = nerve next to odontoblast and predentin; transmits pain and temperature information from the dentin to the CNS where it’s perceived = mechanosensory
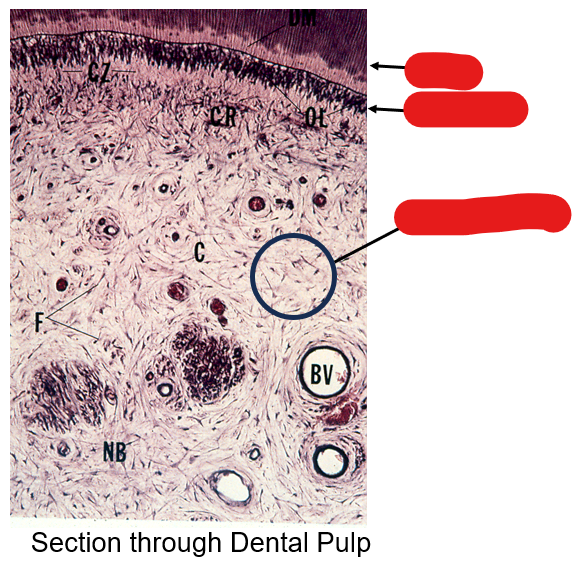
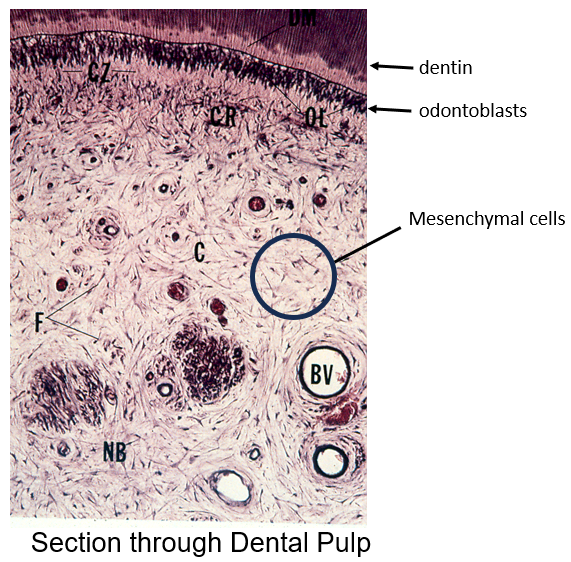
Identify these structures
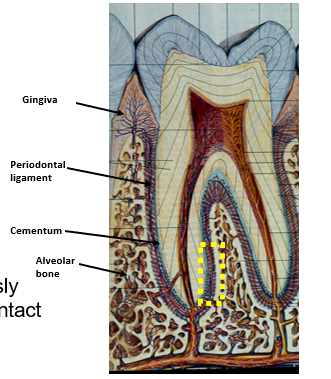
What are the coverings of the root of the tooth?
cementum - produced by cementocytes
periodontal ligament - collagen I fibers translate compression to tension and stimulate bone production
alveolar bone - insertion site of periodontal ligament
gingiva - mucous membrane
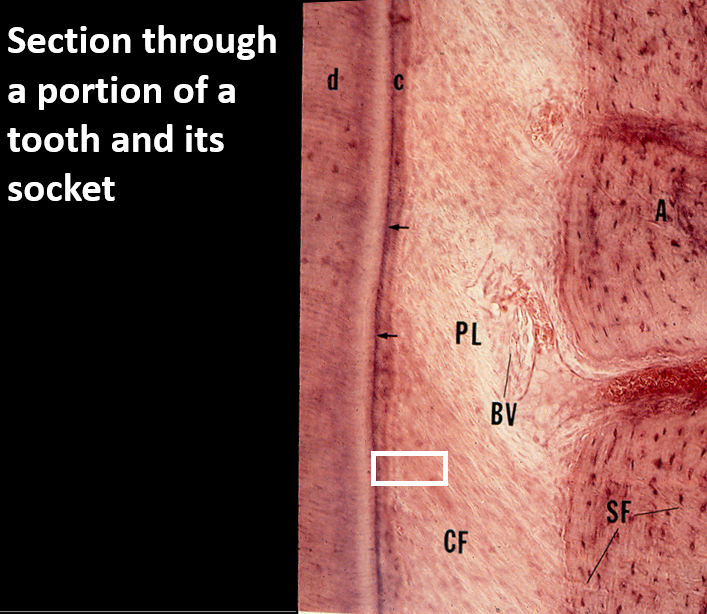
Identify these structures
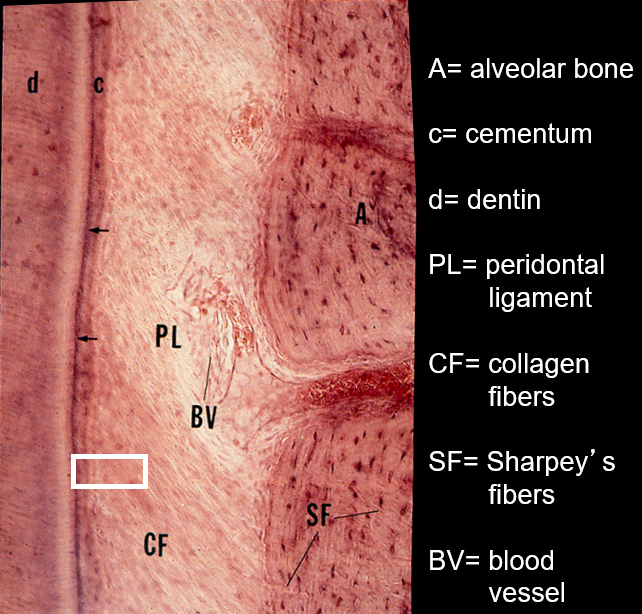
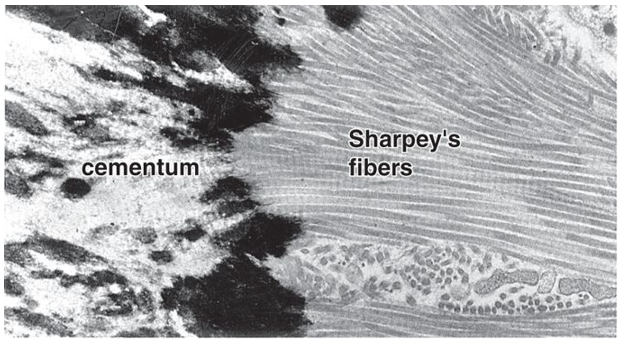
What are Sharpey’s fibers?
Sharpey's fibers are collagenous fibers that anchor the periodontal ligament (PDL) to the cementum of the tooth on one side and to the alveolar bone on the other side
What kind of force needs to be acted on the alveolar bone in order to maintain it? What provides this force?
tension; normal chewing
What is the dental lamina?
horseshow shaped ridge of embryonic tissue that forms during the early stages of tooth development and serves as the foundation for the initiation of tooth buds
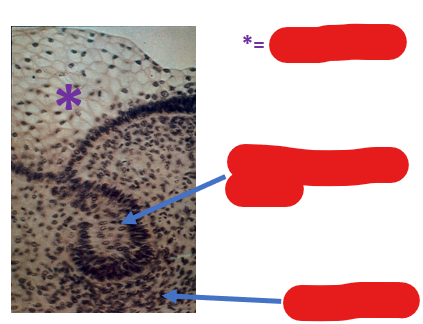
What are the components of a tooth bud? Identify them in this image
enamel organ of ectodermal origin
dental papilla of mesenchymal origin
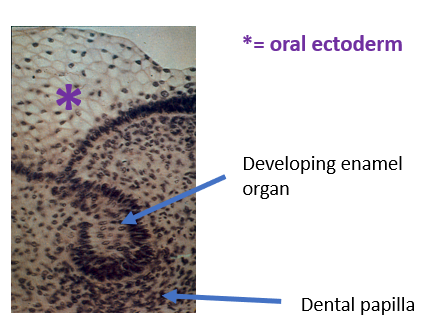
Describe the stages of crown formation
enamel organ form as cells in the center of bell-shaped cap breakdown
dental papilla forms from consolidating mesenchyme via signals from overlying enamel organ
cells of upper cap perforated by capillaries from surrounding tissues
cells of lower cap differentiate into ameloblasts
ameloblasts differentiate from inner enamel epithelium from stimulation by mesenchymal cells
ameloblasts induce superficial cells of dental papilla to differentiate into odontoblasts
odontoblasts secrete predentin
Predentin presence stimulates ameloblasts to begin secreting enamel
What are the stages of root formation?
cervical loop begins to curve under dental papilla
inner layer induces odontoblasts to lay down dentin of the root
dentin induces cementoblasts to differentiate from contiguous mesenchyme → secrete cementum
What happens if there is an interruption of the signaling cascade of tooth formation?
tooth formation will arrest at that juncture; fail to form or abnormal formation
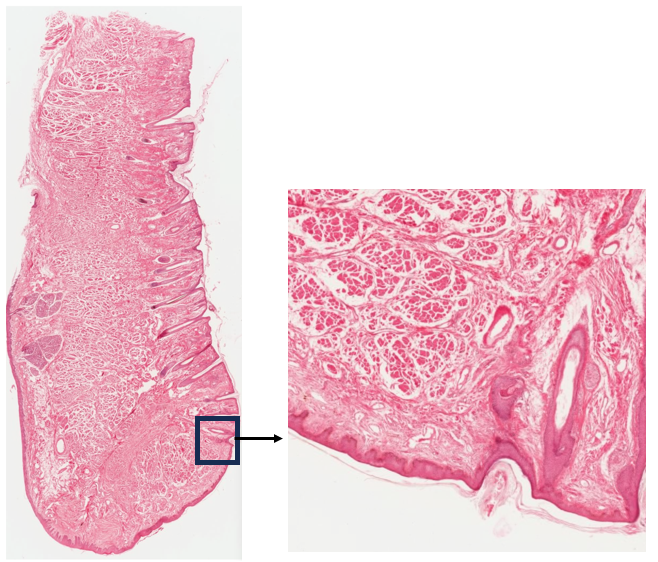
What is this structure? Identify the anterior, posterior, and vermillion border
Lip
anterior surface has hair follicles
no hair follicles on posterior side
red lip or vermillion border is indicated in the box; hair follicle present (transition)
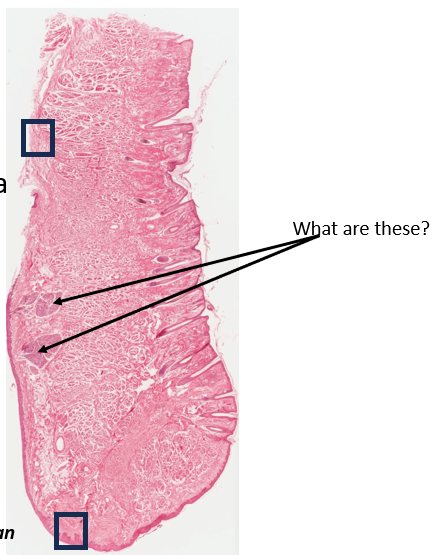
What are these?
labial salivary glands close to internal surface
What is gustatory mucosa?
located on the dorsal surface of the tongue and includes papillae and taste buds
What is masticatory mucosa?
covers the hard palate and includes gingiva; made of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
What is the lining/buccal mucosa?
makes up majority of oral mucosa; lines the cheeks and covers the soft palate; made of non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
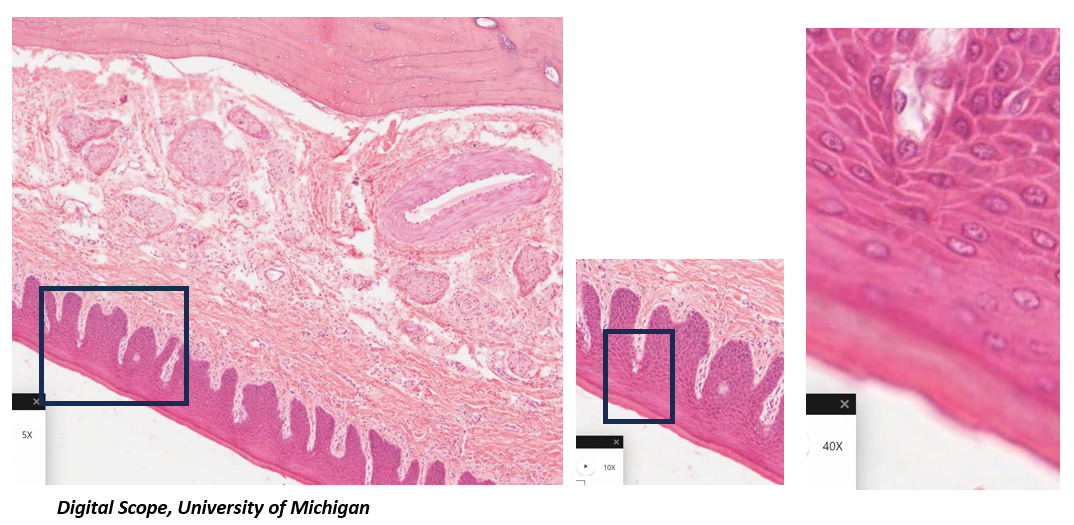
Which mucosa is present in this image? How do you know?
masticatory mucosa → presence of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
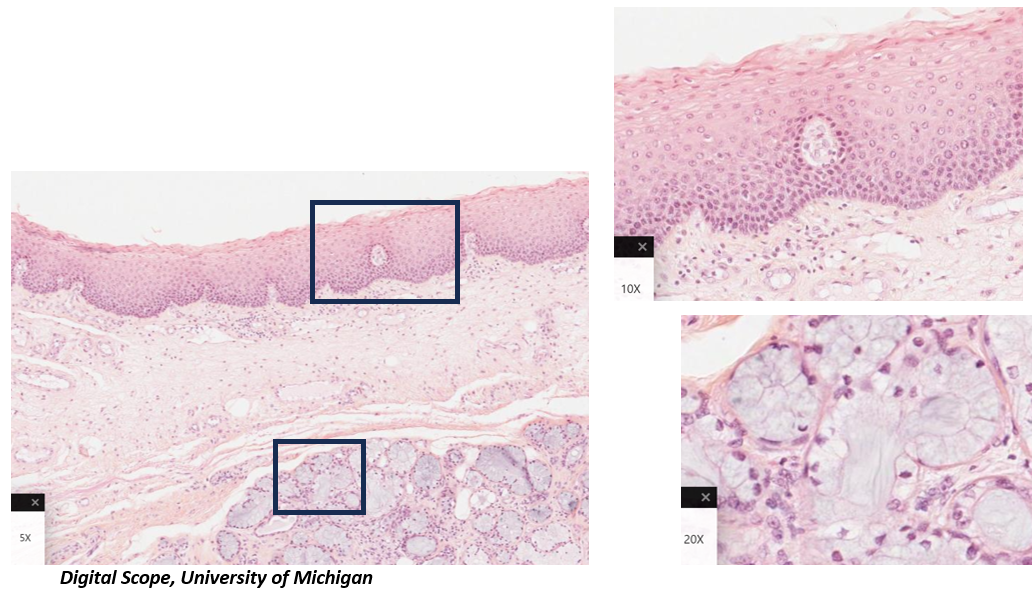
Which mucosa is present in this image? How do you know?
Lining mucosa of the soft palate → presence of non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
What are common features of salivary glands?
exocrine glands
empty into the oral cavity
What are the two main portions of exocrine glands?
secretory portion - contain cells that make and release product
excretory duct system - tubes for transport and delivery; membrane transport proteins can concentrate or modify secretory product
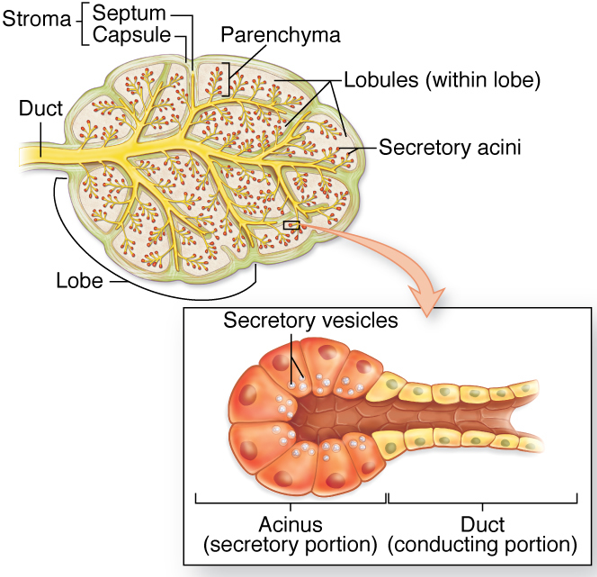
What are the stroma and parenchyma of exocrine glands?
stroma - supporting CT of gland
parenchyma - functional tissue
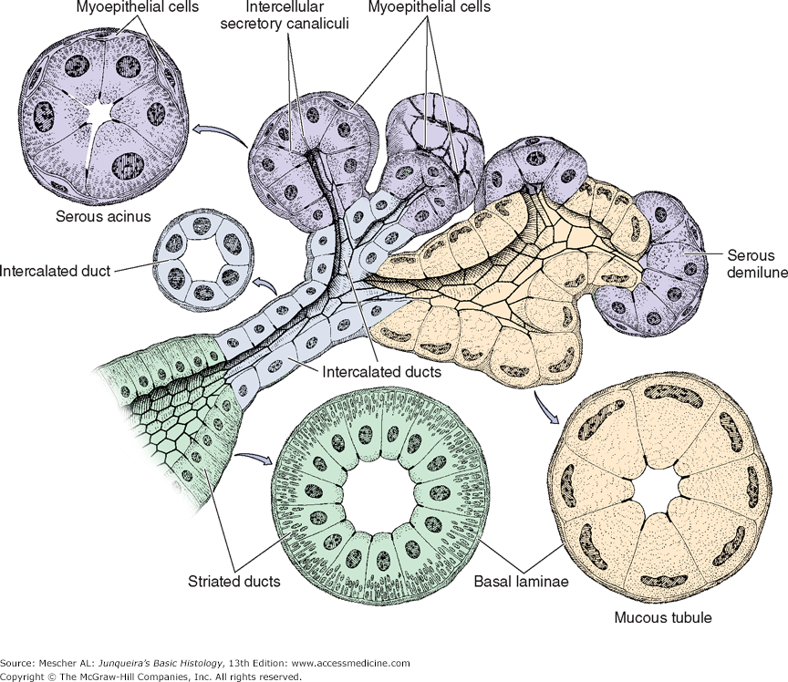
Serous producing cells of the secretory portion of salivary glands are organized into? Mucous producing cells are organized into?
Serous producing cells
serous acini
serous demilunes
Mucous producing cells
tubules
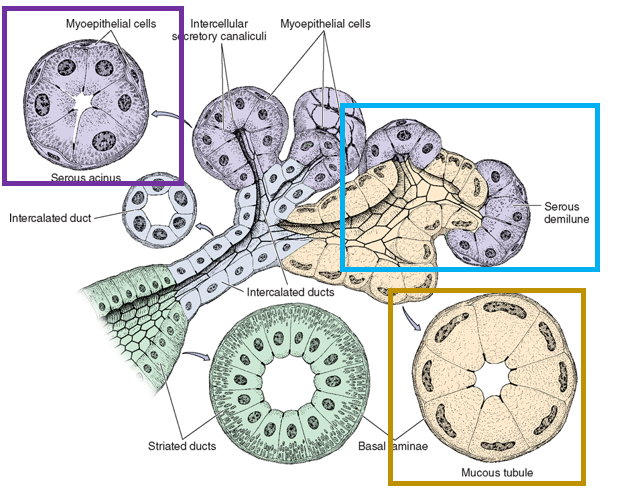
Serous glands stain (light/dark) and mucous glands stain (light/dark)
dark; light/pale
What is the function of myoepithelial cells in salivary glands?
contractile proteins that expel product into ducts
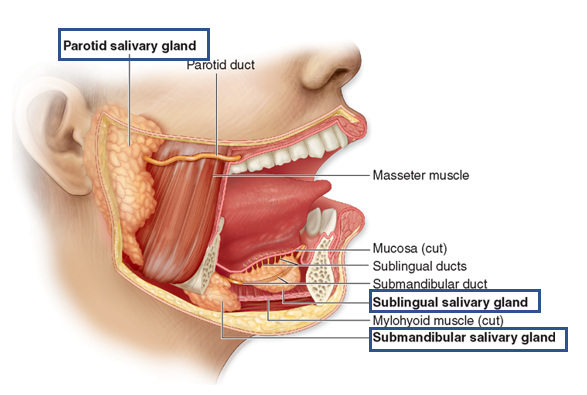
What are the major salivary glands? Where are they located?
parotid glands in cheeks
submandibular glands under tongue
sublingual under tongue
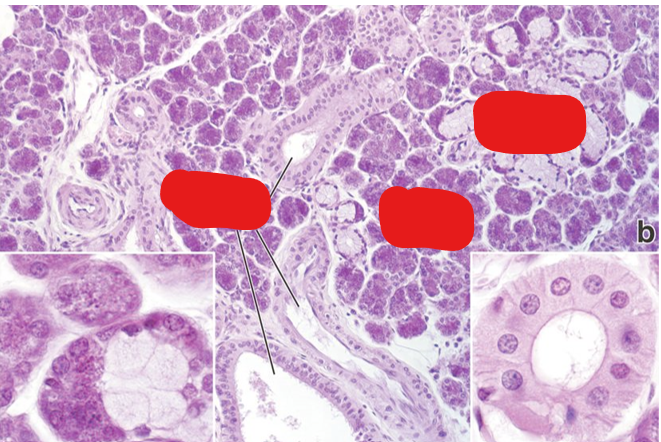
Identify the structures present in this H&E prep of a submandibular gland. Why are there so many mitochondria in these cells?
Many mitochondria to power active transport processes to modify salivary secretions
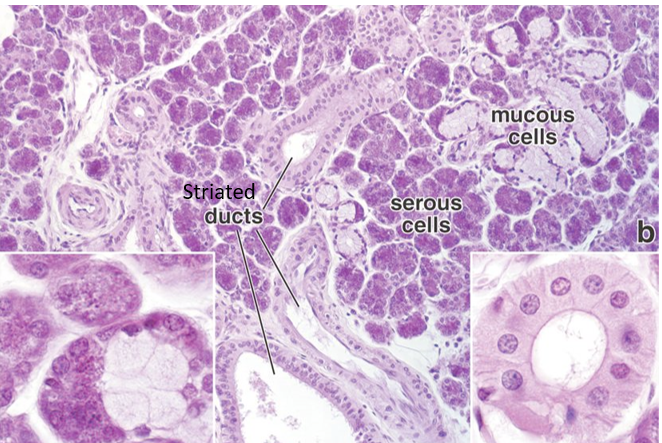
What are the types of ducts in salivary glands?
intercalated ducts - collect directly from acinus
striated ducts - collect from intercalated ducts
excretory - largest ducts that collect and deliver saliva
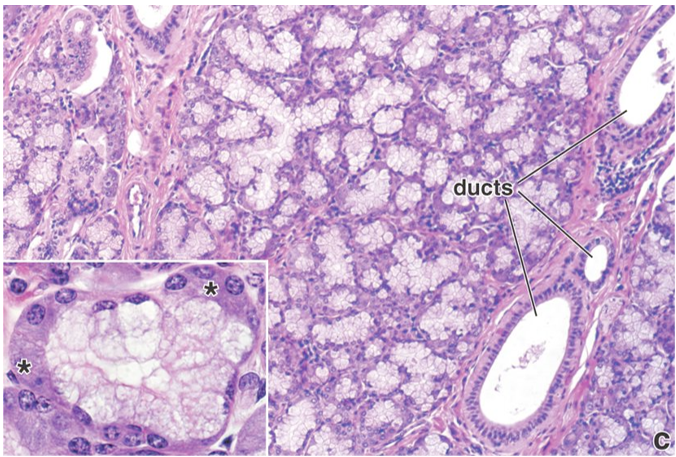
Which gland is this? Is it a serous, mucous, or mixed gland? What are some significant structures present?
Parotid gland → serous
cluster of adipocytes
dark stained granules
prominent nuclei
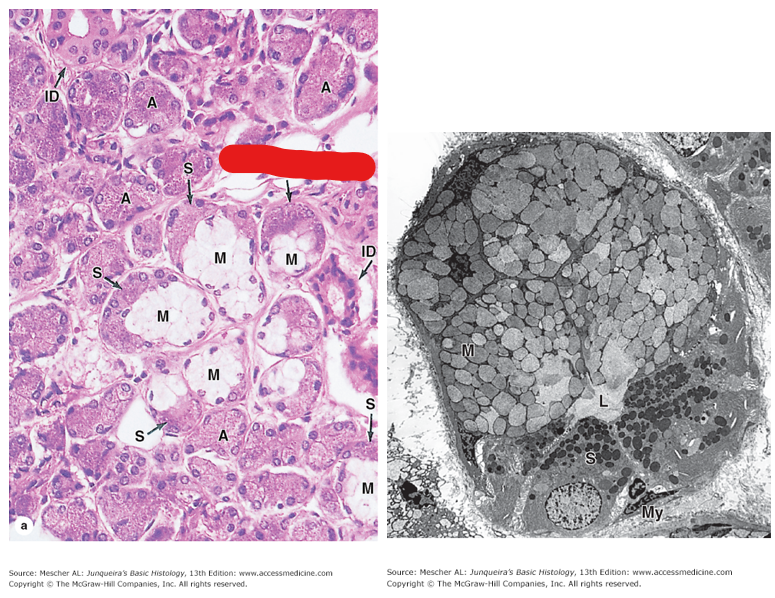
Which gland is this? Is it a serous, mucous, or mixed gland? What are some significant structures present?
Submandibular gland → mixed because both serous and mucous secretory cells are present
red line indicates a serous demilune
Which gland is this? Is it a serous, mucous, or mixed gland? What are some significant structures present?
Sublingual gland → mixed but predominantly mucous
flattened, basally located nuclei
serous demilune
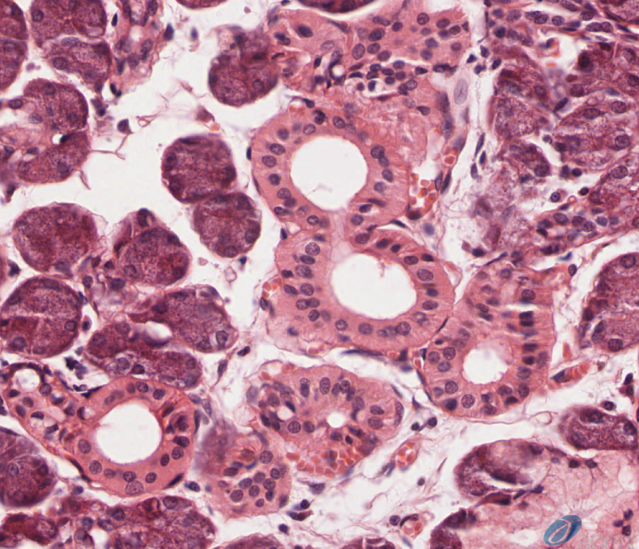
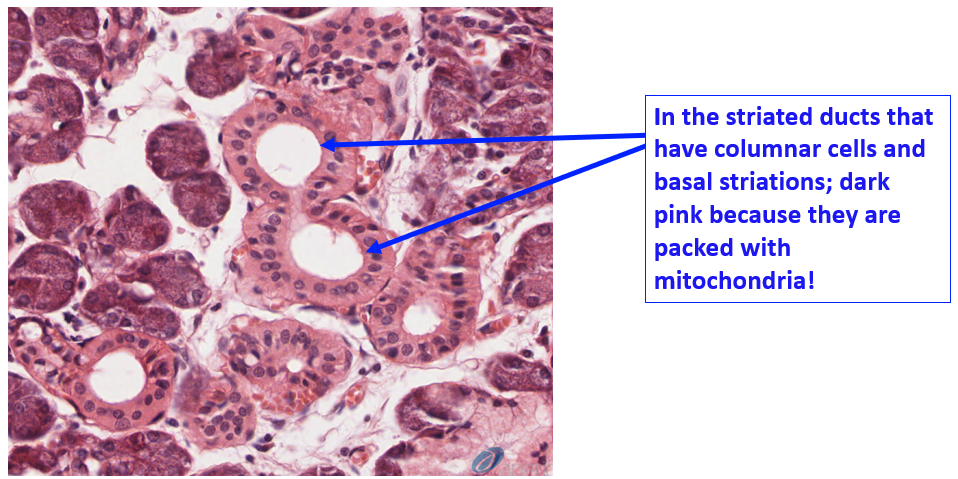
Identify the structures where modification of salivary secretions takes place
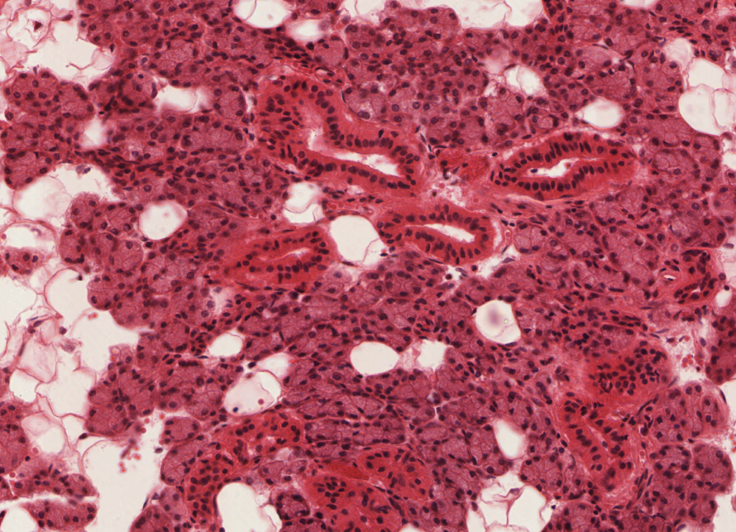
Identify the salivary gland that contains the highest proportion of serous acini
Parotid gland → plenty of adipocytes, but no mucous secretory units. There are some nice striated ducts shown in this section as well.
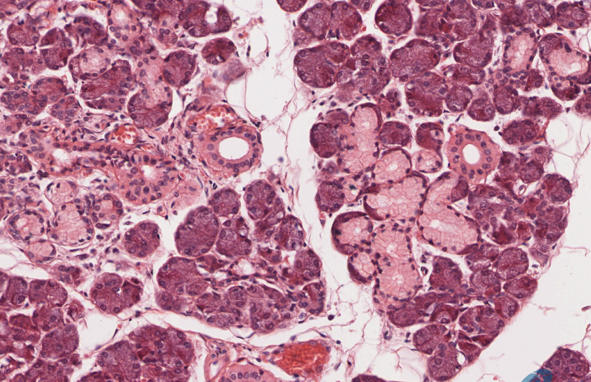
Identify this gland. Is it a serous, mucous, or mixed gland?
Submandibular gland → mixed because both serous and mucous secretory cells are present; serous predominates
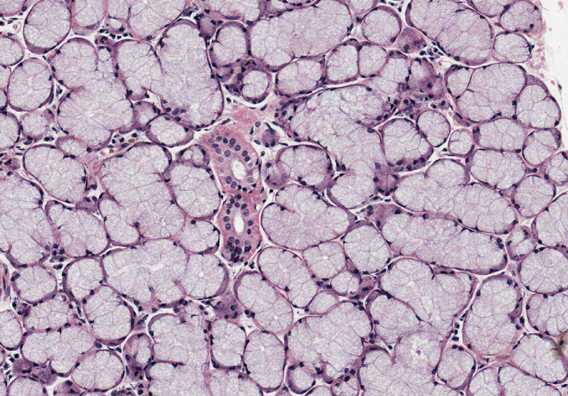
Identify this gland. Is it a serous, mucous, or mixed gland?
Sublingual gland → mixed but predominantly mucous; few serous acini and demilunes