ECSD Ch 14 - cleft lip & palate
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
unilateral incomplete cleft lip
A cleft on one side of the lip that does not extend into the nose
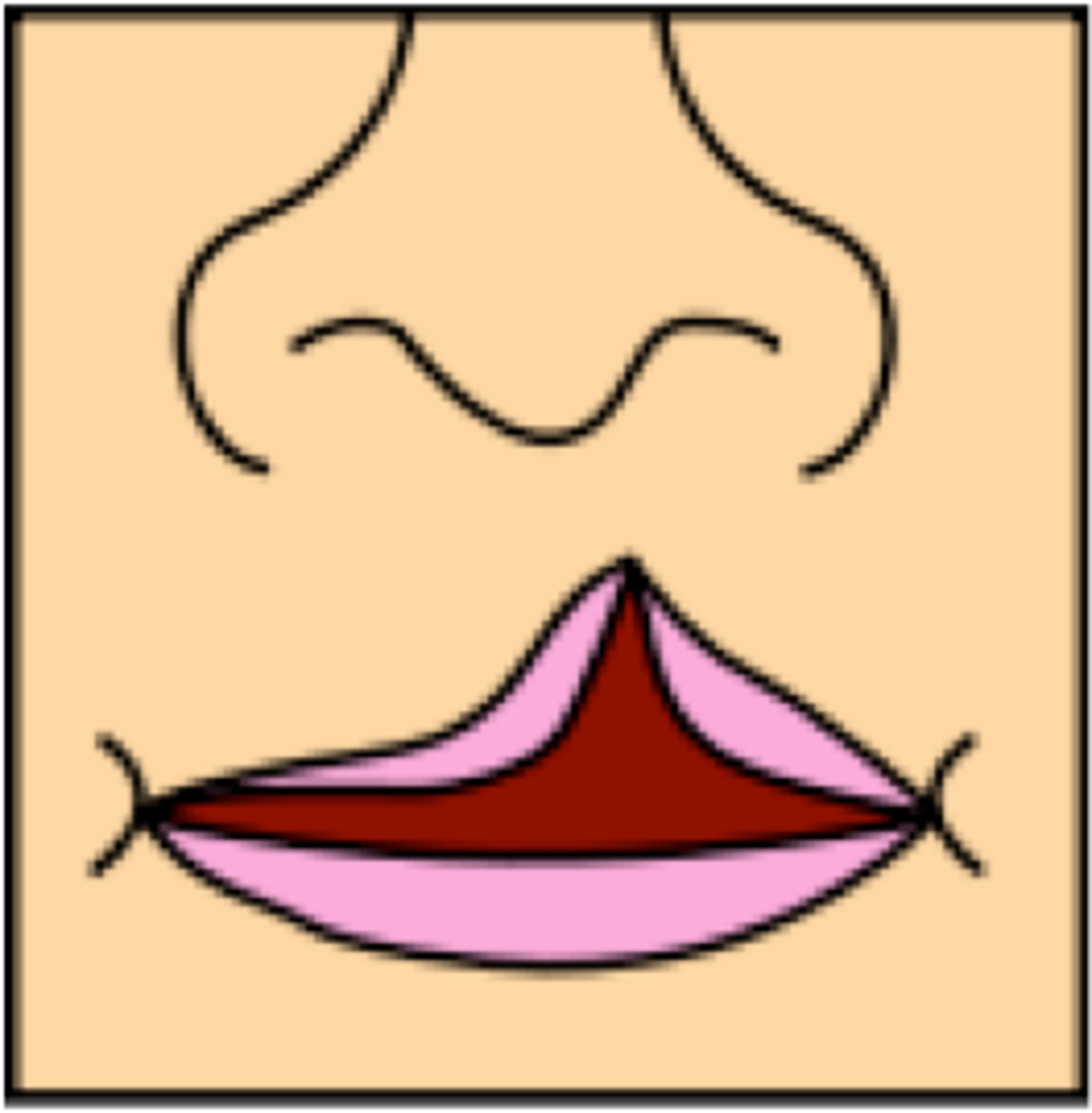

unilateral complete cleft lip
A cleft on one side of the lip that extends into the nose
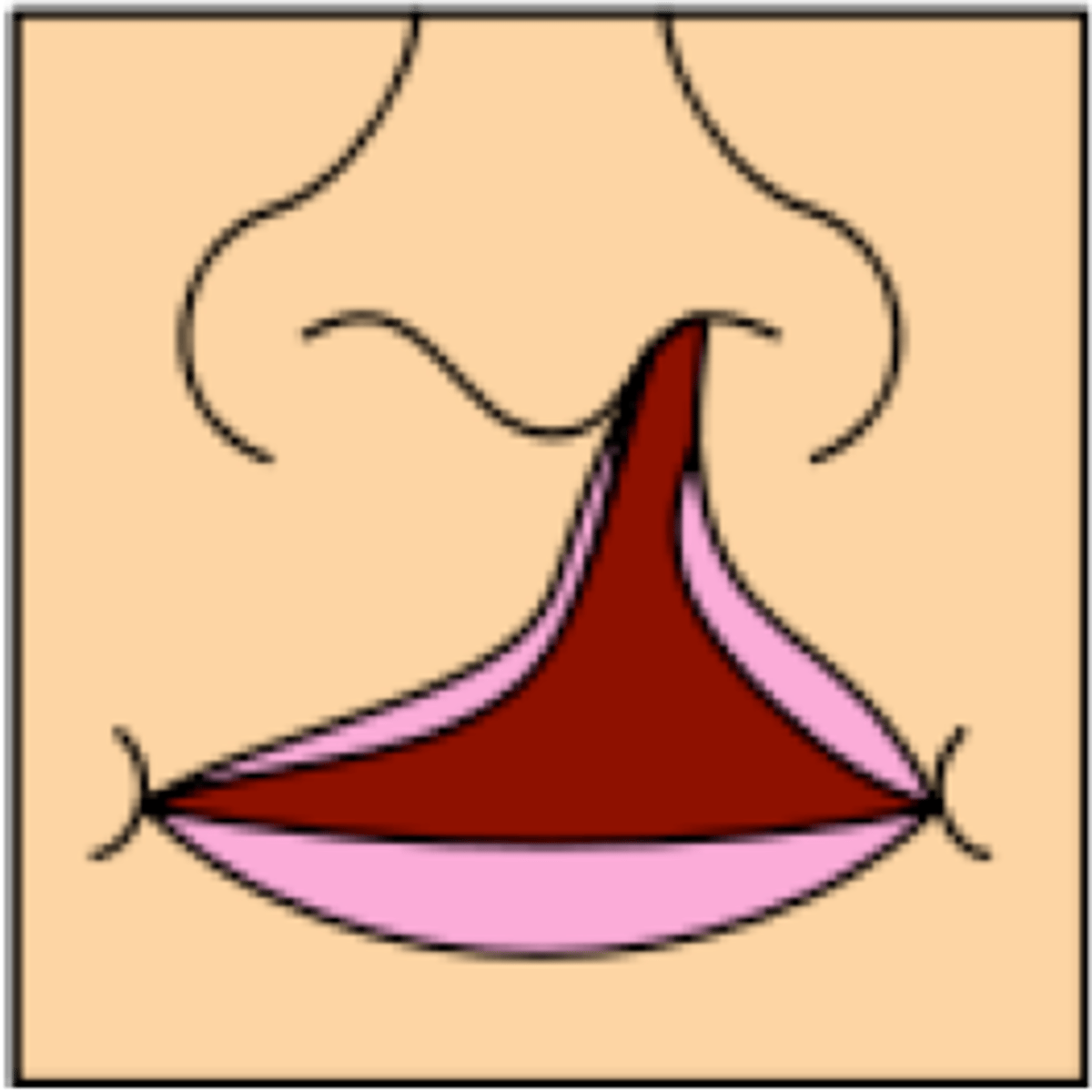
bilateral complete cleft lip
a cleft that involves both sides of the lip and extends into and involves the nose
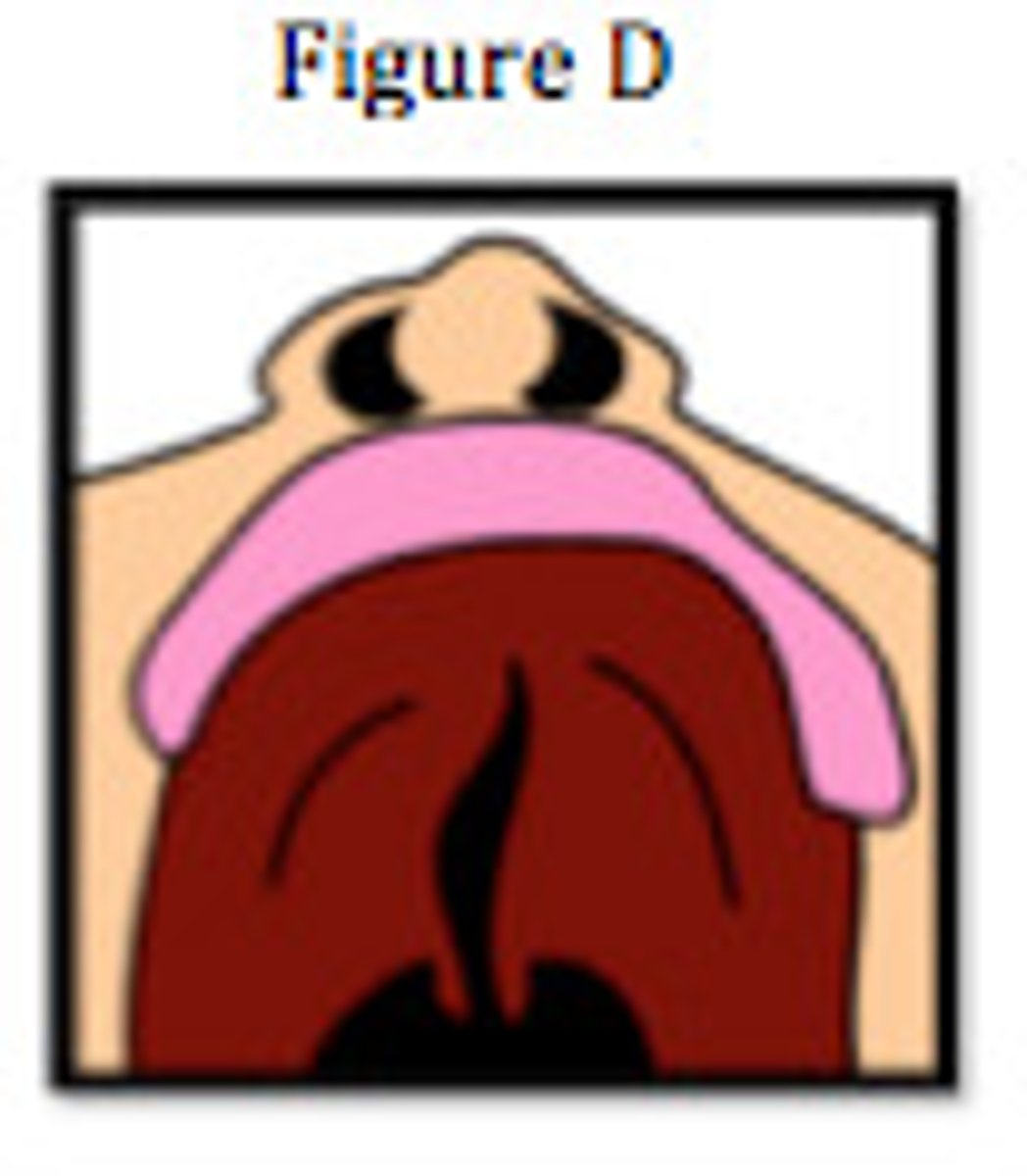
unilateral incomplete cleft palate
a partial cleft on one side of the palate
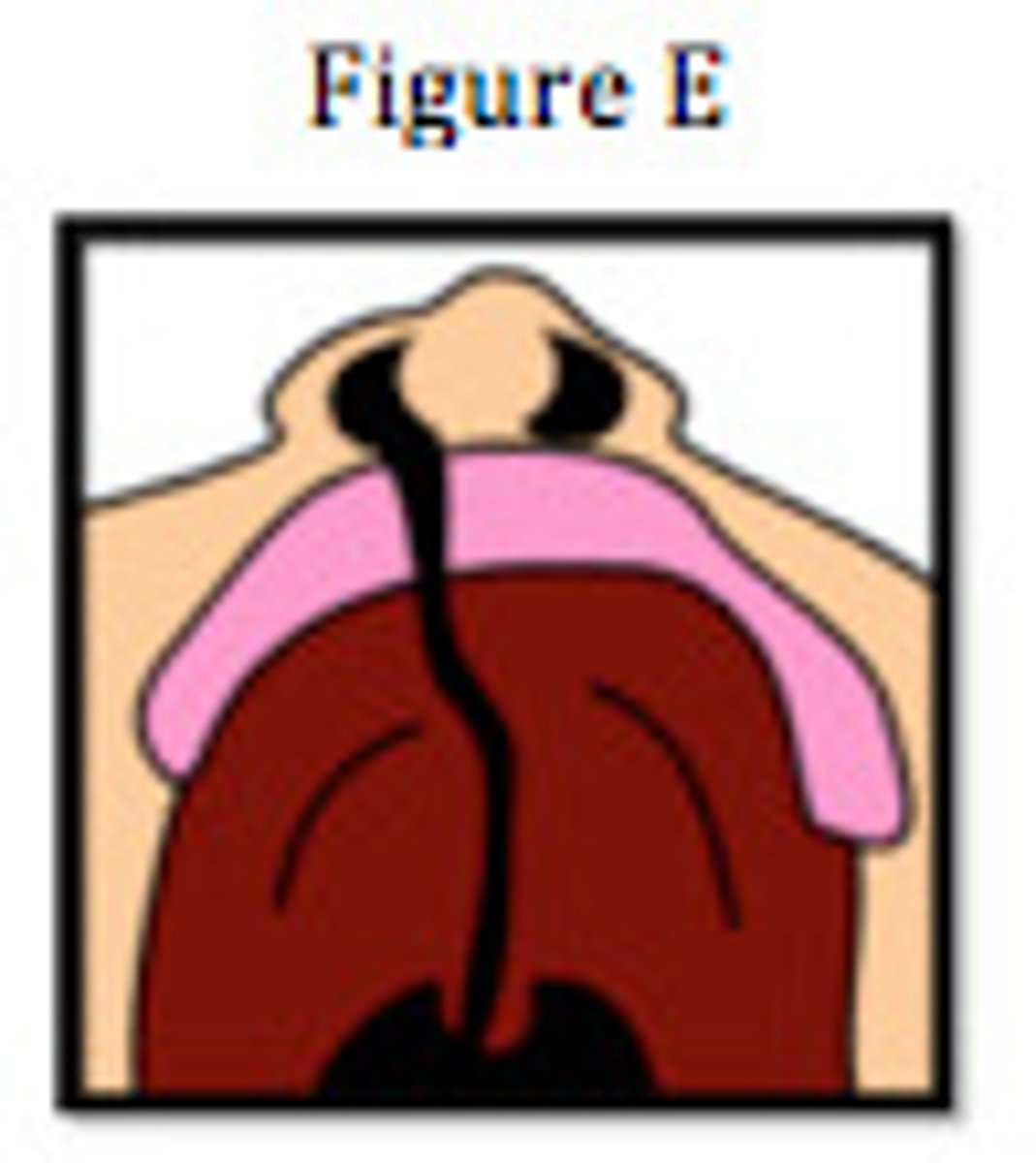
unilateral complete cleft lip and palate
a complete cleft of the palate and lip on one side
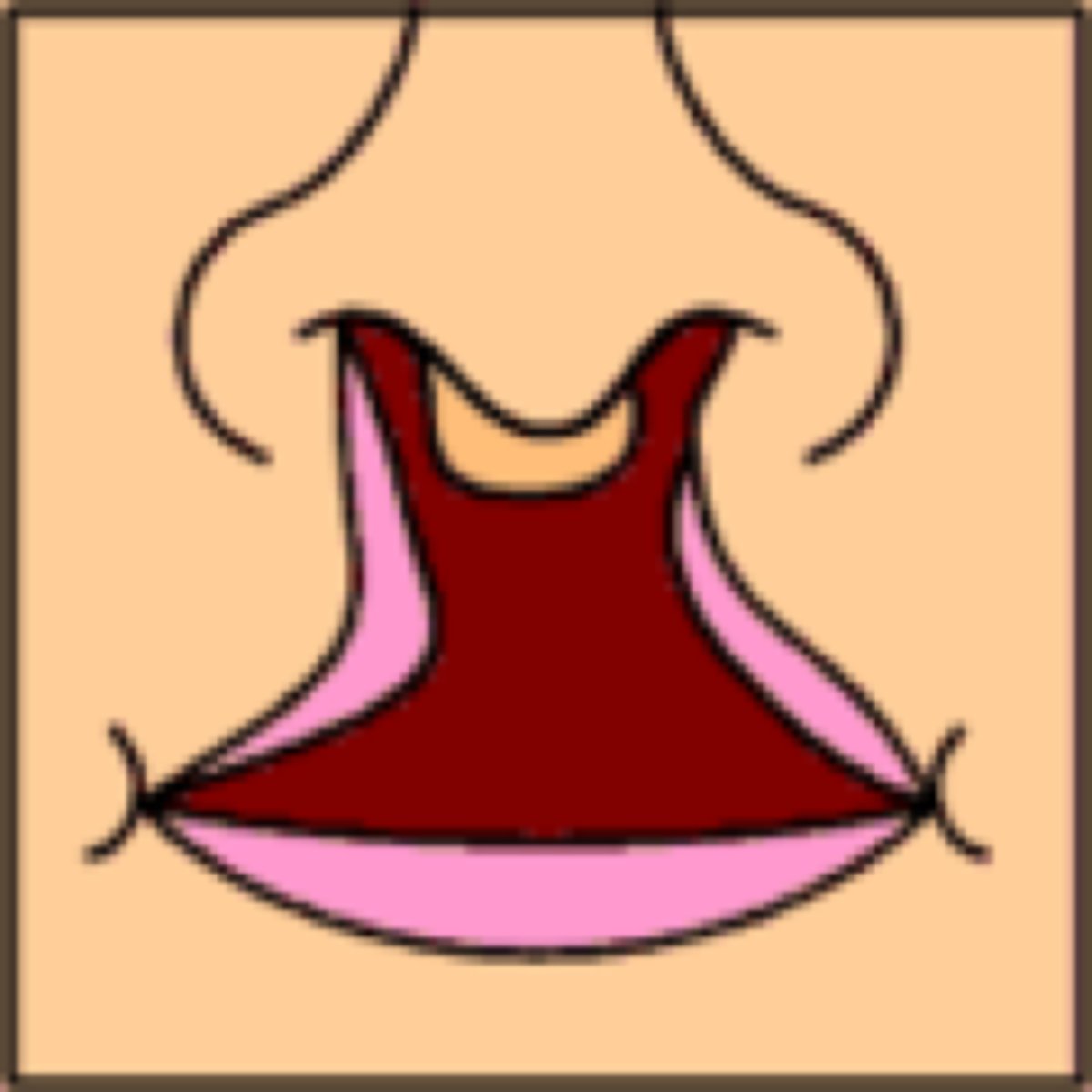
bilateral complete cleft lip and palate
a complete cleft of the palate and lip on both sides
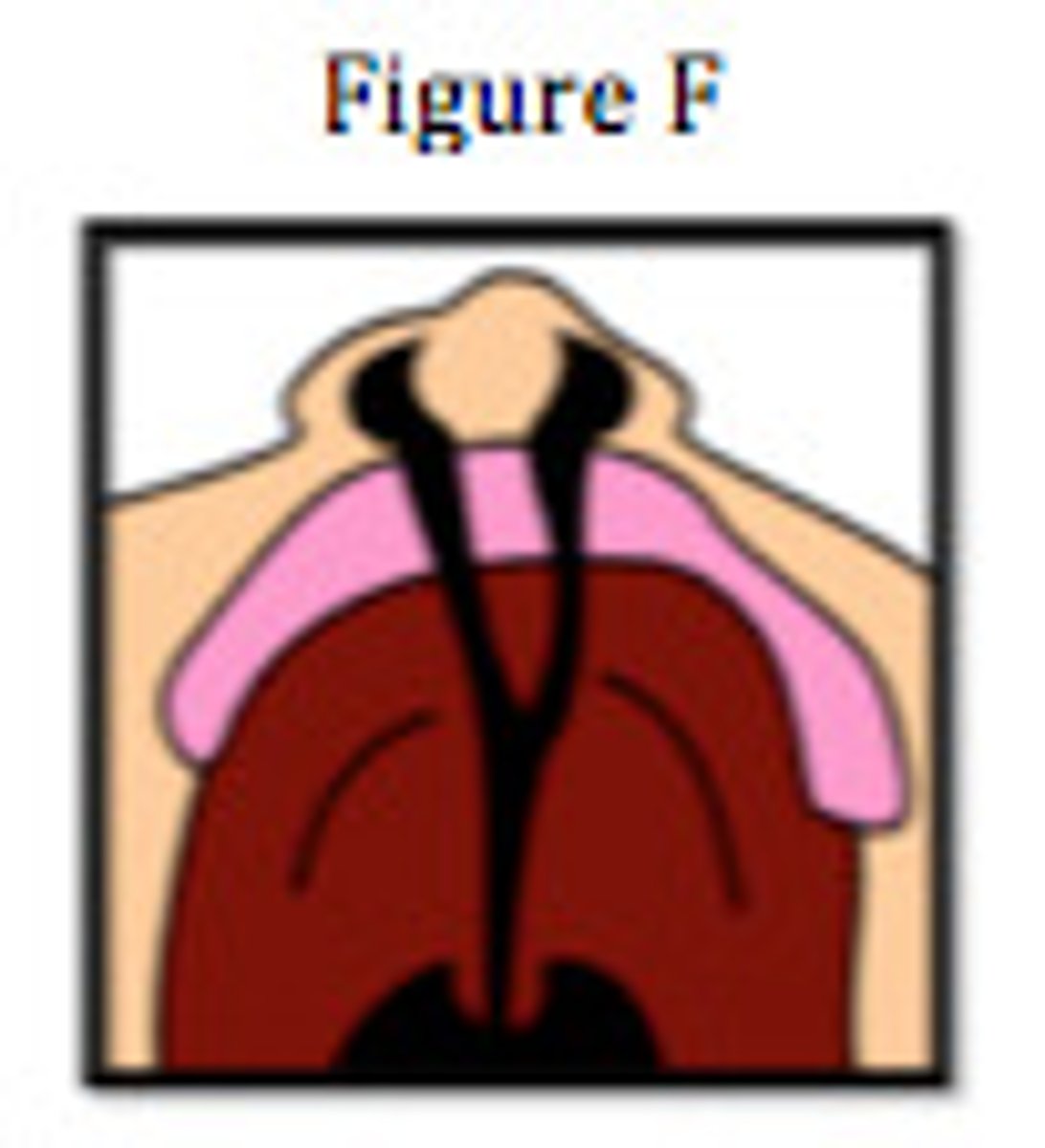
submucous cleft
A defect in the hard palate in the absence of an actual opening into the nasal cavity or a defect in the muscles of the soft palate that cannot be seen through the mucosal tissue but may cause disunity of the velar muscles, resulting in velopharyngeal incompetence and hypernasality
hypernasality
excessive nasal resonance
hyponasality
too little nasal resonance
velopharyngeal insuffiency
An anatomical defect of the velum that prevents adequate velopharyngeal closure
velopharyngeal incompetence
A dysfunction of an anatomically intact VP mechanism usually due to neuromuscular disorders.
velopharyngeal dysfunction
a condition where the velopharyngeal valve does not close consistently or completely during the production or oral sounds. May be due to either velopharyngeal insuffiency or imcompetenece
Rule of 10s
guideline for appropriate time for cleft lip repair — an infant must be at least 10 weeks of age, weigh 10 pounds, and have a hemoglobin count of 10 grams before lip repair
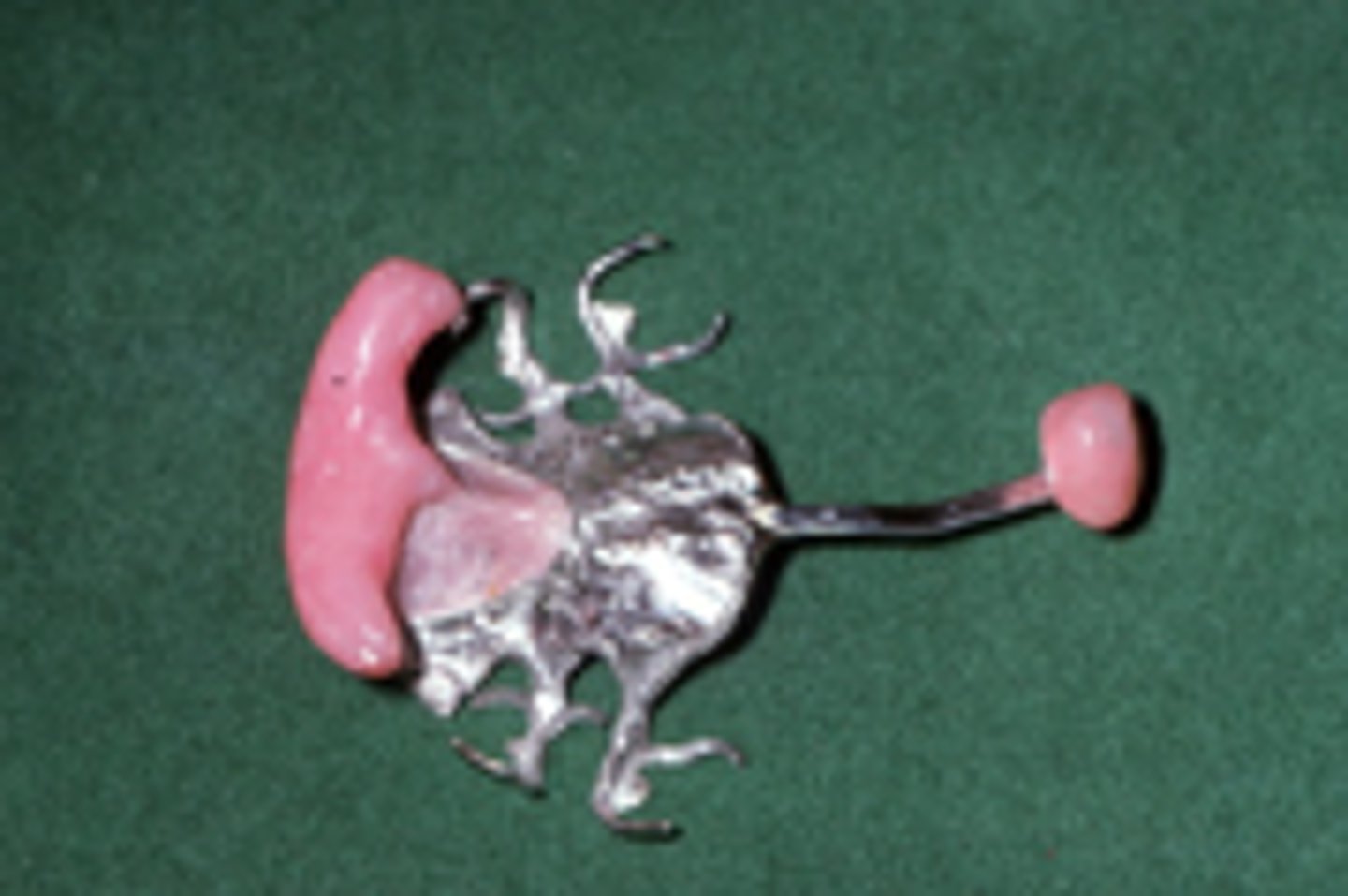
palatal obturator
An appliance used to fill the opening of a cleft palate until surgery can be performed.
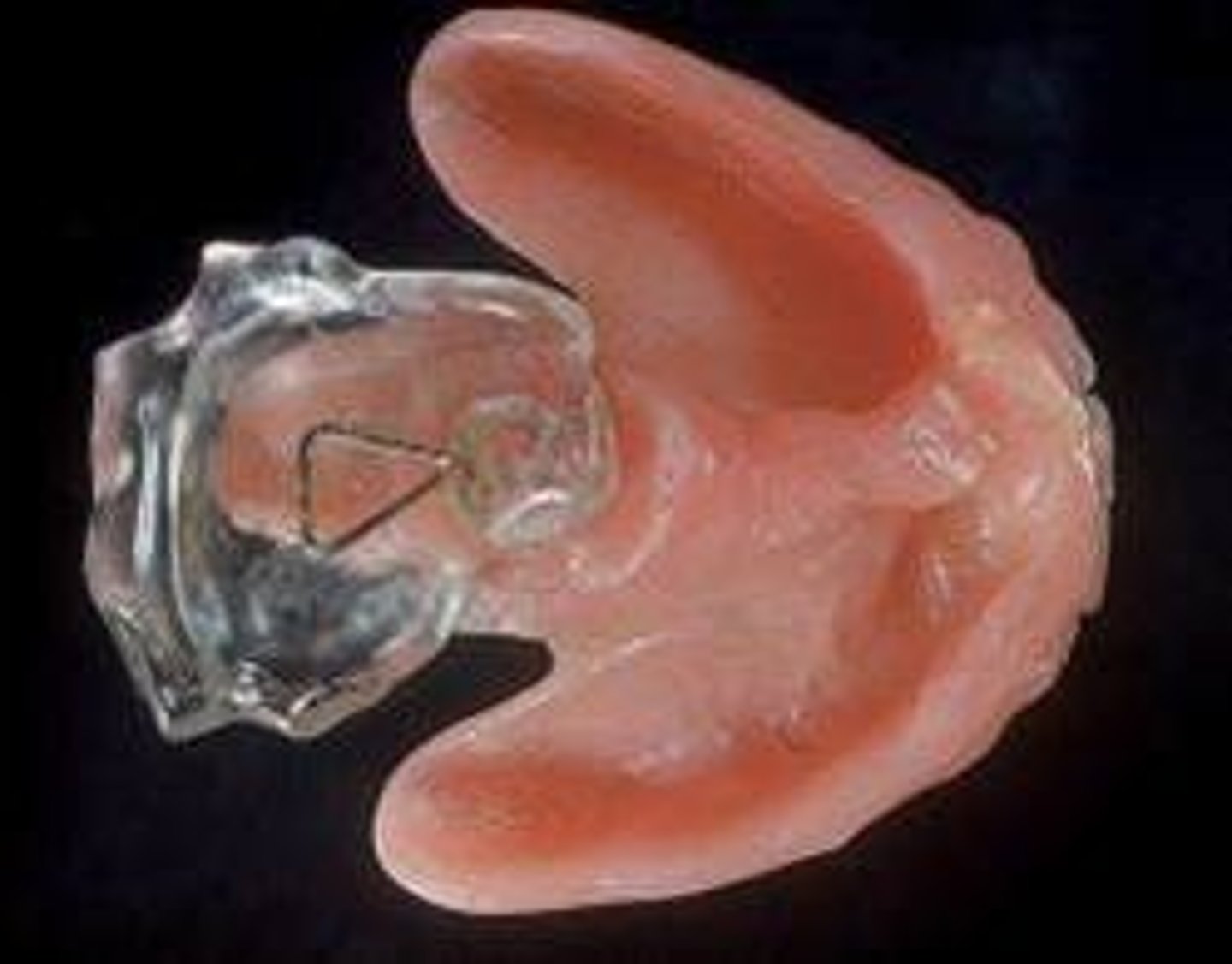
speech bulb obturator
A prosthetic device that may be considered when the velum is too short to close completely against the posterior pharyngeal wall; it consists of a retaining appliance and a bulb (usually made of acrylic) that fills in the pharyngeal space for speech.
problems w cleft lip and palate
difficulty/inability to feed, decreased nutrition, poor weight gain, poor hearing, hearing loss, middle ear infections, dental anomalies, resonance disorders, speech sound disorders