2. Geosphere Part 1
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
primary wave (P-wave)
seismic wave that squeezes and pulls rocks in the same direction that the wave travels, causing rock particles to to move back and forth
secondary wave (S-wave)
seismic wave that causes rock particles to move at right angles to the direction of the wave
surface wave
seismic wave that moves in two directions as ti passes through rocks, causing he ground to move both up and down and from side to side
focus
point of the initial fault rupture where an earthquake originates that usually lies at least several kilometers beneath the Earth's surface
epicenter
point on Earth's surface directly above the focus of an earthquake
magnitude
measure of the energy released during an earthquake, which can be described using the Richter scale
tsunami
large, powerful ocean wave generated by the vertical motions of the seafloor during an earthquake; in shallow water, can form huge, fast-moving breakers exceeding 30 m in height that can damage coastal areas
strike slip fault
a type of fault where rocks on either side move past each other sideways with little up or down motion
normal fault
a type of fault where the hanging wall slides downward; caused by tension in the crust
reverse fault
a type of fault where the hanging wall slides upward; caused by compression in the crust
viscosity
a substance's internal resistance to flow
hot spot
unusually hot area in Earth's mantle that is stationary for long periods of time, where high-temperature plumes of mantle material rise toward the surface
theory of plate tectonics
states that the Earth's crust and upper mantle are broken into plates, which are huge rock slabs that move in different directions and at different rates over Earth's surface
divergent boundary
place where two of Earth's tectonic plates are moving apart; is associated with volcanism, earthquakes, and high heat flow, and is found primarily on the sea floor
rift valley
long, narrow depression that forms when continental crust begins to separate at a divergent boundary
convergent boundary
place where two of Earth's tectonic plates are moving toward each other; is associated trenches, island arcs, and folded mountains
subduction
process by which one tectonic plate slips beneath another tectonic plate
transform boundary
place where two tectonic plates slide horizontally past each other that is characterized by long faults and shallow earthquakes
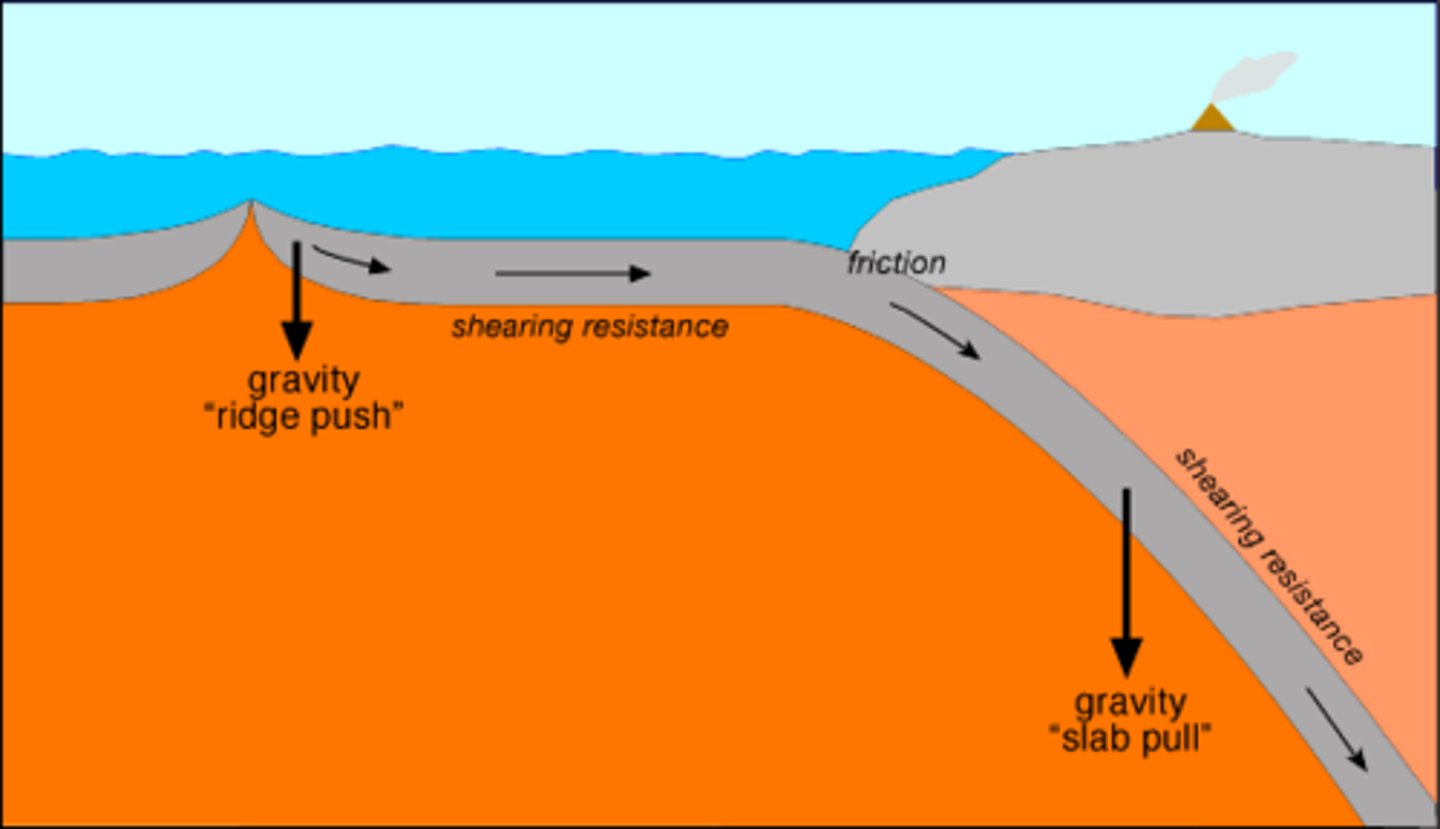
ridge push
tectonic process associated with convection currents in Earth's mantle that occurs when the weight of an elevated ridge pushes an oceanic plate toward a subduction zone
gravity pull
tectonic process associated with convection currents in Earth's mantle that occurs as the weight of the subducting plate pulls the trailing lithosphere into a subduction zone
mantle convection
a recurring current in the mantle that occurs when hotter, less dense material rises, cools, and then sinks again. This current is believed to be one of the driving forces behind tectonic plate movement.
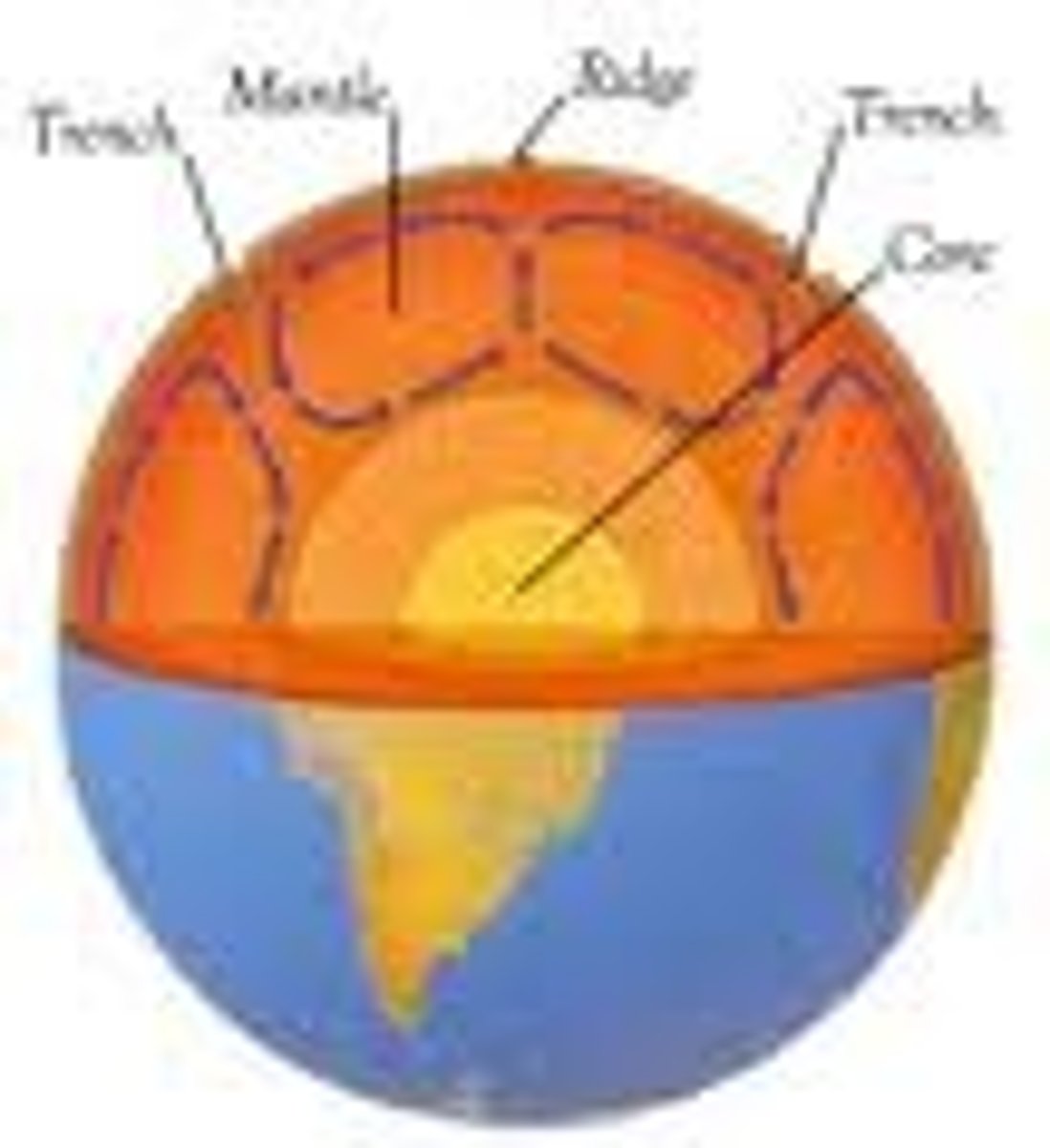
midocean ridge
a long line of sea-floor mountains where new ocean crust is formed by volcanic activity along a divergent boundary
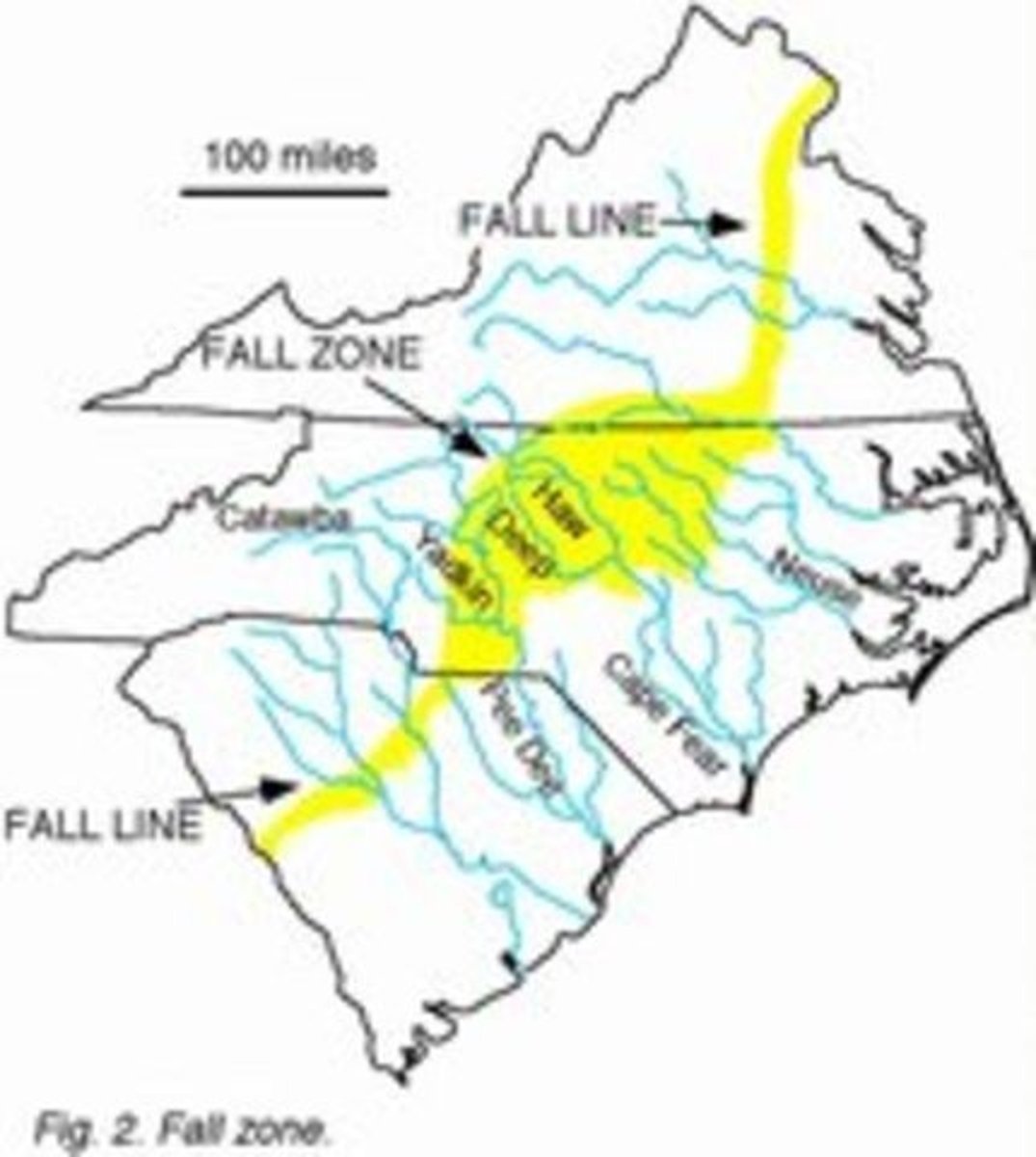
fall line
a boundary in the eastern United States where rivers cross the higher, harder, crystalline rock of the Piedmont and drop to the lower, softer, sedimentary rock of the Atlantic Coastal Plain due to increased weathering and erosion.