L12 - Legislation and Welfare Kennels and Catteries
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Animal Boarding Establishment Regulations 1974
Regulations for Northern Ireland's boarding establishments.
Animal Boarding Establishments Act 1963
Applies to licensed establishments in Scotland and Wales.
Animal Welfare (Licensing of Activities) 2018
Regulations for animal welfare licensing in England.
Animal Welfare (Licensing of Activities) 2021
Regulations for animal welfare licensing in Scotland.
Animal Welfare (Licensing of Activities) 2021
Regulations for animal welfare licensing in Wales.
Animal Welfare Act 2006
Legal framework for animal welfare in boarding establishments.
Licence Requirement
Mandatory for businesses boarding dogs and cats.
Local Authority Application
Licences must be applied for through local authorities.
Display of Licence
Licences must be visibly displayed at the establishment.
Schedule 4: Part 1-4
Specific provisions for dog and cat boarding.
Home Boarding
Legally recognized for the first time in 2018 regulations.
Day Care
Legally recognized for the first time in 2018 regulations.
Puppy Farming
Illegal breeding practices targeted by updated regulations.
Illegal Puppy Trade
Prohibited practice addressed by recent legislation.
Suitable Environment Provision
Requirement for adequate living conditions for boarded animals.
Monitoring of Behaviour
Regular assessment of animal behavior and training.
Record Keeping
Mandatory documentation of animal care and welfare.
Protection from Pain
Ensuring animals are safeguarded against suffering and injury.
Application Form Sections 1-6
Basic information required for licence application.
Section 5 Requirement
Maximum number of animals must be specified.
Section 7 Documentation
Requires extensive supporting documents, including floor plans.
HMRC Registration
Business must be registered with HMRC for licence.
Minor Differences
Legislation varies slightly by country within the UK.
Lighting Review
Assessment of lighting conditions for animal welfare.
Heating Review
Evaluation of heating systems for animal comfort.
Ventilation Review
Analysis of air circulation in animal facilities.
Water Supply Review
Inspection of accessible and clean water sources.
Risk Assessment
Evaluation of potential hazards in animal care.
Evacuation Plan
Strategy for safely removing animals in emergencies.
Health Plan
Document outlining animal health management strategies.
Disposal of Excreta
Methods for safe waste management in facilities.
Noise Minimization Proposal
Strategies to reduce noise affecting animal welfare.
Public Liability Insurance
Insurance protecting against claims of negligence.
Disqualifications Declaration
Disclosure of any legal disqualifications or convictions.
Supporting Documentation
Additional materials required for licensing applications.
Animal Activity Star Rating System
Rating system for animal care facilities' standards.
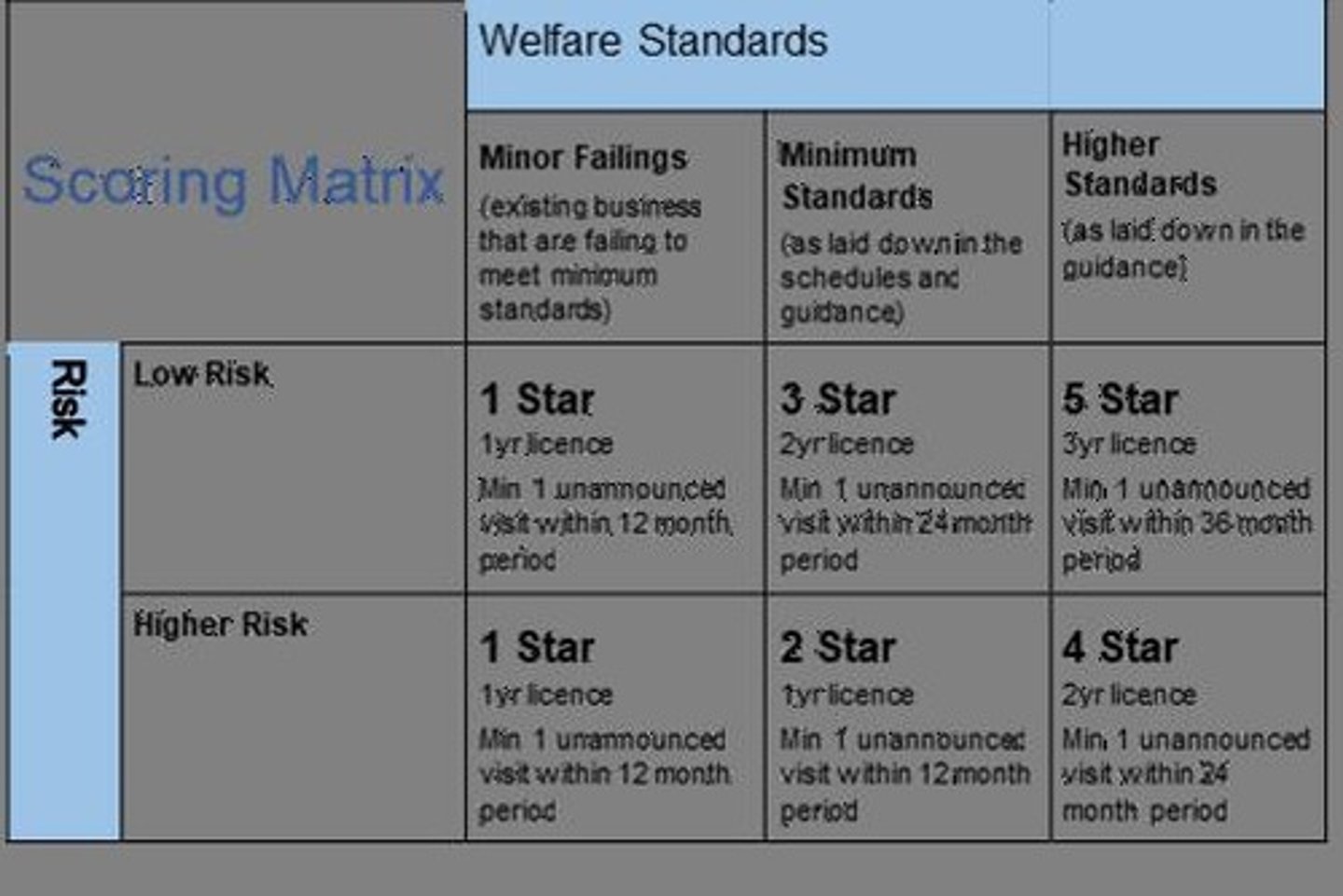
Higher Standards
Optional criteria for achieving better licensing ratings.
Minimum Standards
Essential requirements all businesses must meet.
Longer Licence Duration
Extended licensing period for higher-rated facilities.
Inspection Frequency
Regular checks by authorities post-licensing.
Veterinary Role
Responsibilities of vets during inspections and applications.
Sample Processing
Taking samples for testing upon authority request.
Licence Fees for Dogs
Costs associated with dog-related licensing applications.
Licence Fees for Cats
Costs associated with cat-related licensing applications.
Statutory Guidance
Official instructions for local authorities on licensing.
Local Authority Inspections
Evaluations conducted by local authorities for compliance.
Local Authority (LA)
Government body overseeing animal welfare inspections.
Veterinary Surgeon
Professional providing health guidance and assessments.
Welfare Considerations
Factors affecting animal well-being in care facilities.
Kennel Syndrome
Condition caused by stress in confined dogs.
Five Freedoms
Framework for assessing animal welfare needs.
Freedom from Hunger
Access to adequate food and water.
Freedom from Discomfort
Provision of a suitable living environment.
Freedom from Pain
Absence of injury and disease.
Freedom to Express Normal Behaviour
Ability to engage in natural activities.
Freedom from Fear
Protection from distress and anxiety.
Physiological Indicators
Biological measures reflecting animal health status.
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
Regulates involuntary physiological responses.
Direct Measures
Immediate physiological responses like heart rate.
Indirect Measures
Long-term physiological changes like adrenal enzyme levels.
Measurement Error
Inaccuracies in data collection during assessments.
Behavioural Observation
Monitoring actions to assess animal welfare.
Fearful Behaviour
Responses indicating stress and anxiety in animals.
Self-Mutilation
Injurious behaviour stemming from anxiety or stress.
Weight Loss
Physiological response to prolonged stress exposure.
Loose Faeces
Sign of stress affecting digestive health.
Paw-Lifting
Appeasement gesture indicating anxiety or fear.
Shivering and Trembling
Physical signs of high psychological stress.
Environmental Impact on Welfare
Influence of surroundings on animal health.
Coprophagy
Consumption of feces indicating nutritional imbalance or boredom.
Sore Feet
Pain from wet floors or intense activity.
High Vocalisation
Barking or whining indicating frustration or distress.
Kennel Chewing
Coping mechanism for confinement or distress.
Repetitive Behaviour
Actions like pacing or spinning due to stress.
Increased Activity
Heightened movement possibly indicating anxiety.
Decreased Activity
Lack of movement leading to learned helplessness.
Fear Aggression
Aggressive behavior stemming from fear.
Self-Mutilation
Over-grooming due to stress or anxiety.
Body Language
Eyes and ears indicators of cat emotions.
Habituation
Adjustment to stimuli, reducing effectiveness over time.
Exercise Benefits
Reduces stereotypical behaviors and promotes welfare.
Human Interaction
Regular engagement improves animal welfare significantly.
Classical Music
Shown to reduce stress in dogs and cats.
Audiobooks
Can reduce stress when combined with music.
Olfactory Stimulation
Use of scents like lavender for relaxation.
Social Contact
Off-lead play enhances dog welfare and social skills.
Toys and Food Enrichment
Safe, engaging items to maintain animal interest.
Hiding Places
Essential for cats to feel secure and safe.
High Areas
Elevated spaces provide comfort for fearful cats.
Welfare Constraints
Time, money, and facility type affect animal care.
Legislative Considerations
Regulations governing kennels and catteries must be understood.