biochem + evolution
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
________ are molecules that are made up of simple units called nucleotides.
Nucleic acids
________ are organic compounds of mono/poly/di-saccharides that contain Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen.
Carbohydrates
________ are organic compounds (no monomer) that contain Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen.
Lipids
________ are organic compounds made of amino acids that contain Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, and Sulfur.
Proteins
________ are organic compounds of nucleotides that contain Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, and Phosphorus.
Nucleic Acids
________ is when polymers can also be broken down into monomers.
Hydrolysis
Most carbohydrates are categorised as either ________, disaccharides, or polysaccharides.
monosaccharides
________ contains the hereditary "blueprints "of all life.
DNA
________ are the individual building blocks of a polymer.
Monomers
The ________ ions in a solution will indicate whether it is acidic, basic, or neutral.
concentration of hydrogen
________ are negatively charged-) (particles.
Electrons
________ are also influenced by whether the solution in which they occur is acidic, basic, or neutral.
Reactions
________ is essential for protein synthesis.
RNA
________ are positively charged (+) particles.
Protons
It is a(n) ________ for cells.
energy source
________ contain two fatty acid "tails "and one negatively charged phosphate "head.
Phospholipids
Dehydration
A(n) ________ is lost in the reaction, and a larger compound is formed.
water molecule
Carbs and Lipids contain ________, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms.
carbon
________ are chains of building blocks in macromolecules.
Polymers
________ is an important part of the food we eat, and it is the product made by plants during photosynthesis.
Glucose
________ are building blocks of proteins.
Amino acids
________ affects whether an amino acid is more hydrophobic or more hydrophilic.
Side chain polarity
________ are made up of many repeated units of monosaccharides.
Polysaccharides
It is formed when four ________ interact with each other and is a quaternary structure.
separate polypeptide chains
A solution is acidic if it contains a(n) ________ ions (H+)
lot of hydrogen
They contain carbon, hydrogen, ________, and nitrogen and phosphorus.
oxygen
________ are uncharged particles.
Neutrons
________ are the unit of life and are the building blocks of the physical world.
Atoms
________ and starch are sugar storage molecules.
Glycogen
The ________ is logarithmic and represents a tenfold change in hydrogen ion concentration.
pH scale
When the polypeptide begins to twist it begins forming either a coil (known as a(n) ________) or zigzagging pattern (known as beta- pleated sheets)
alpha helix
When ________ sometimes interact with each other, they form a quaternary structure.
different polypeptide chains
Once a(n) ________ and folds on itself, it forms a 3D structure called a protein.
polypeptide chain twists
The ________ formed from two glucose molecules is maltose.
disaccharide
If a(n) ________ is joined together in a "string, "the resulting organic compound is called a polypeptide.
group of amino acids
Each triglyceride is made of a glycerol molecule (also called the glycerol backbone) with three ________ attached to it.
fatty acid chains
Some atoms have the ________ but differ in the number of neutrons in the nucleus.
same number of protons
________ are important for structure, function, and regulation of your tissues and organs.
Proteins
________ are important due to their non- polar structures, they function as structural components of cell membranes, sources of insulation, signalling molecules, and a means of energy storage.
Lipids
It generally increases ________, except at very high temperatures.
membrane fluidity
A(n) ________ is covered in hydrogen.
fatty acid chain
A(n) ________ is formed when electrons are shared between atoms.
covalent bond
________ with carbon are organic molecules and ________ that do not contain carbon atoms are called inorganic compounds.
Molecules
The ________ contributes to another property of water known as surface tension.
cohesion of water molecules
When two ________ are joined, the bond is called a glycosidic linkage, and the resulting sugar is called a disaccharide.
monosaccharides
________ are important because of some unique properties they possess, regards to water.
Phospholipids
________ have a strong tendency to stick together.
Water molecules
________ and fructose can be depicted as either "straight "or "rings ..
Glucose
are substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means
Elements
Just add water
To break up the disaccharide and form two monosaccharides
hydrophobic and uncharged
non-polar
hydrophilic and charged
polar
polar (hydrophilic) and charged
ionic
Electronegativity
describes how much an atom wants an electron (how likely it is to attract)
how electrons are shared
Atoms can share an electron if their electronegativity is similar. If they have a more prominent difference an electron can be transferred.
non-polar
a covalent bond that shares electrons evenly
polar
a covalent bond that shares electrons unevenly, uneven charge
ionic
a bond where an electron is stolen, resulting in negatively and positively charged ions
ion
an atom that has lost or gained an electron and is charged
hydrophobic
lipids (C-H bonds r non polar)
non-polar and fat soluable. They repell water or move away from water.
hydrophilic
glucose + other sugars
salt
polar and water-soluable. They move toward water.
hydrogen bond
A fairly weak bond between two polar molecules or polar portions of larger molecules. The molecules involved always have a hydrogen covalently bound to a more electronegative element like O or N
phosphate
A high energy functional group. Negative charge. Makes larger molecules (like proteins) unstable when added.
Protein structure
There four levels of protein structure. Primary is amino acid sequence. Secondary is hydrogen bonds form beta sheets or alpha helices, third level is those secondary structures folding in different ways due to hydrophilic interactions, hydrophobic interactions (Van der Waals forces), charged attractions, or disulfide bridges. Note that structural levels 1-3 all relate to one single polypeptide chain. Fourth level is multiple polypeptides coming together to form the final protein.
polypeptide
a linear organic polymer consisting of a large number of amino-acid residues bonded together in a chain, forming part of (or the whole of) a protein molecule.
dehydration synthesis
Forming a polymer by removing an H and OH from two monomers (a H20 molecule)
saturated
containing the greatest possible number of hydrogen atoms, and so having no carbon–carbon double or triple bonds.
unsaturated
having carbon–carbon double or triple bonds and therefore not containing the greatest possible number of hydrogen atoms for the number of carbons.
carb structure

lipid structure

protein structure
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/protein-structure-373563_final11-5c81967f46e0fb00012c667d.png)
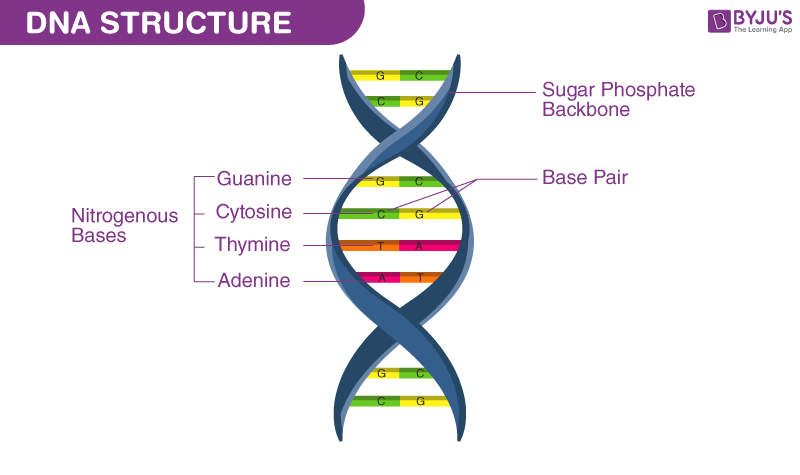
DNA structure
covalent bonds (in organic molecules)
glycosidic for carbs
peptide for proteins
phosphodiester for DNA
ester for lipids
protein synthesis
You will need to be able to transcribe and translate a gene. Remember, transcribe means copy DNA to mRNA and translate means use an amino acid decoder to change the mRNA code into an amino acid sequence.
bacteria
|
archea
Unicellular
No nucleus
Cell Wall with peptidoglycan
Prokaryotic
evolution
the change in a population overtime
eukaryotes
Have membrane bound organelles.
Can be unicellular or multicellular
Plants, Animals, Fungi, Protist
Have a nucleus
Many have cell wall
Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have…
cell membranes, ribosomes, common sets of metabolic pathways, replicate DNA semiconservatively, and use their DNA has genetic material that codes for proteins
evidence for endosymbiosis
mitochondria and chloroplasts have circular, single stranded DNA. Single stranded, circular DNA is found exclusively in prokaryotes. This supports the theory because these characteristics would allow the mitochondria and chloroplasts to survive on their own.
Mitochondria
eukaryotic cells
chloroplast
plants and algae
Be able to apply the theory of natural selection to the appearance of antibiotic resistance in bacteria
when germs like bacteria and fungi develop the ability to defeat the drugs designed to kill them. That means the germs are not killed and continue to grow. Resistant infections can be difficult, and sometimes impossible, to treat.
Bacterial Resistance
resistant
bacteria dont die
Bacterial Resistance
susceptible
bacteria die
Bacterial Resistance
antibiotic
medicine that kills bacteria
how new traits can arise in bacteria
mutations