Errors in Memory Construction and Eyewitness Testimony
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Source Monitoring
Source memory is the process of determining the origins of our memories.
Source Monitoring Error
Misidentifying source of memory.
Cryptoamnesia
Unconscious plagiarism of another's work due to a lack of recognition of its original source.
Jacoby et al. (1989) Experiment
Participants read a list of non-famous names; some misidentified non-famous names as famous after 24 hours.
Misinformation Effect
Misleading information presented after a person witnesses an event can change how that person describes the event later.
Misleading Postevent Information (MPI)
This kind of information is what misleads a person's recollection of an event.
Loftus and colleagues (1975) Experiment
Participants saw slides of a traffic accident and were misled about the presence of a yield sign.
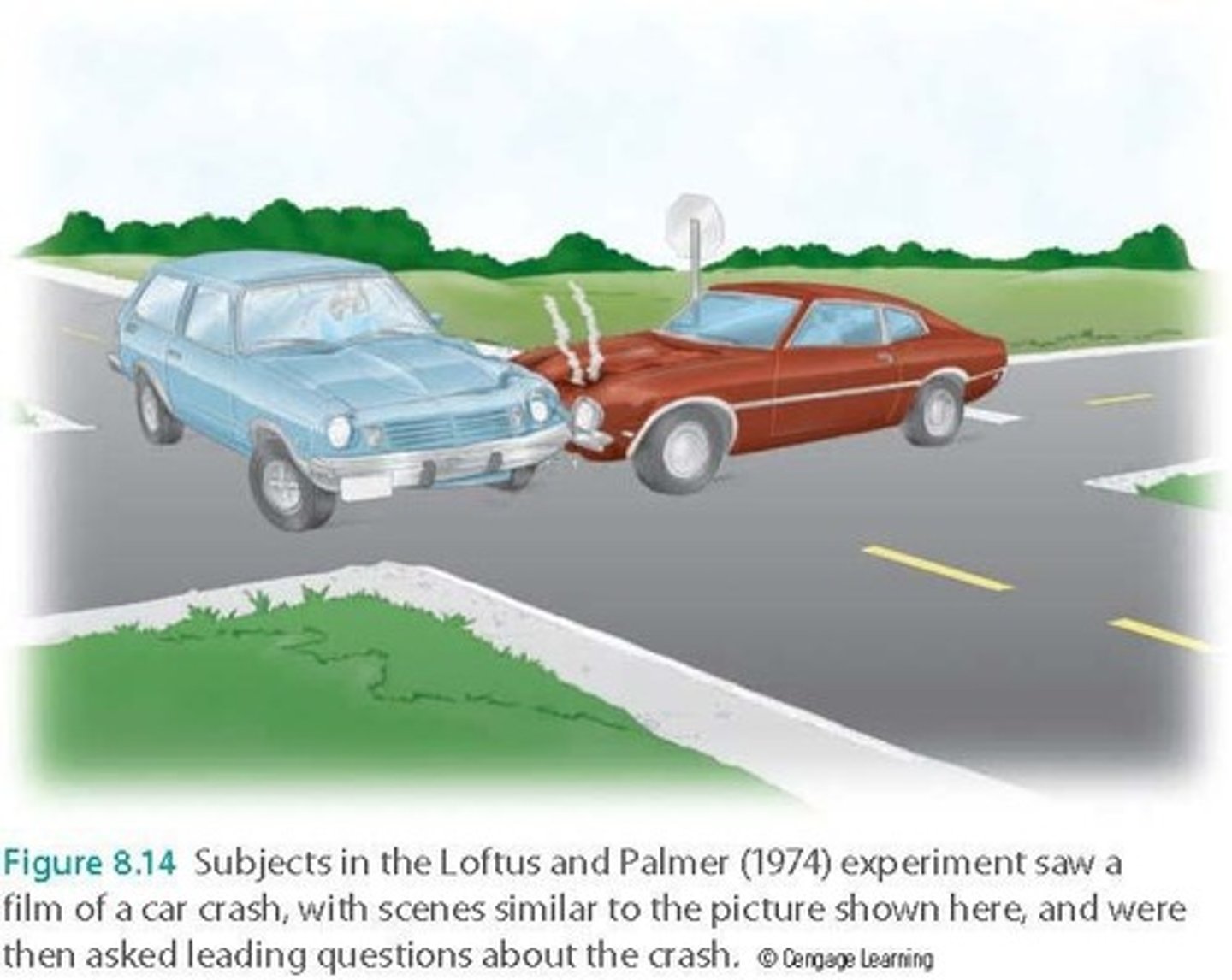
Loftus and Palmer (1974) Experiment
Participants who heard the word 'smashed' reported higher speeds of cars than those who heard 'hit'.

Pragmatic Inferences
Inferences based on knowledge gained through experience.
Schema
Knowledge base about some aspect of the environment.
Script
Conception of sequence of actions that usually occurs during a particular experience.
False Memories
Memories that participants believe to be true but are actually distorted or fabricated.
Errors in Eyewitness Testimony
Eyewitness testimony can be inaccurate, leading to mistaken identity and wrongful convictions.
Power of Suggestion
The influence that misleading information can have on memory recall.
Construction of Memories
The process that allows us to fill in the blanks but can also lead to errors.
Making Inferences
Memory can be influenced by inferences that people make based on their experiences and knowledge.
Example of Schema Activation
Reporting 'facts' about magazines in a doctor's office waiting room that were not present.
Jacoby et al. (1989) Results
After 24 hours, some non-famous names were misidentified as famous due to familiarity.
Errors in Eyewitness Testimony—other examples
Mistakes about the sequence or details of events can occur due to memory construction.
Eyewitness Testimony Improvements
Informing witnesses that the perpetrator might not be in the lineup and using fillers similar to the suspect.
Sequential Presentation
A technique used in lineups to improve identification accuracy by presenting suspects one at a time.
Memory Test Method
Participants listen to a list of words and then recall as many as they can.
Hyman et al. (1995) Methods
Participants discussed childhood experiences, and new details were added by the experimenter.
Hyman et al. (1995) Results
Participants 'remembered' new events as actually happening after discussion.