Embedded Systems 1 - Flowcharts/Pseudocode & Numbers/Math
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What are the advantages of flowcharts & pseudocode?
- validating algorithm & steps
- determining key functions
- dividing up larger complex into smaller jobs
- segregate programs for design teams
- communication tool between stakeholders
What are flowcharts and pseudocode for?
methods to provide structure to a program
Flowchart/ Pseudocode Characteristics - Representation
Flowchart - symbolic, pseudocode - natural text
Flowchart/ Pseudocode Characteristics - Detail
Flowchart - too much detail = bad, Pseudocode - flexible
Flowchart/ Pseudocode Characteristics - Modification
Flowchart - hard to modify for large/complex implementations, Pseudocode - easy
Flowchart/ Pseudocode Characteristics - Structure
Flowchart - specific structure, symbols, Pseudocode is open-world
Flowchart/ Pseudocode Characteristics - Understanding
Flowchart --> easy to understand
Pseudocode --> more complex to understand
When is it better to use flowcharts instead of pseudocode?
smaller code jobs
When is it better to use pseudocode instead of flowcharts?
larger code jobs
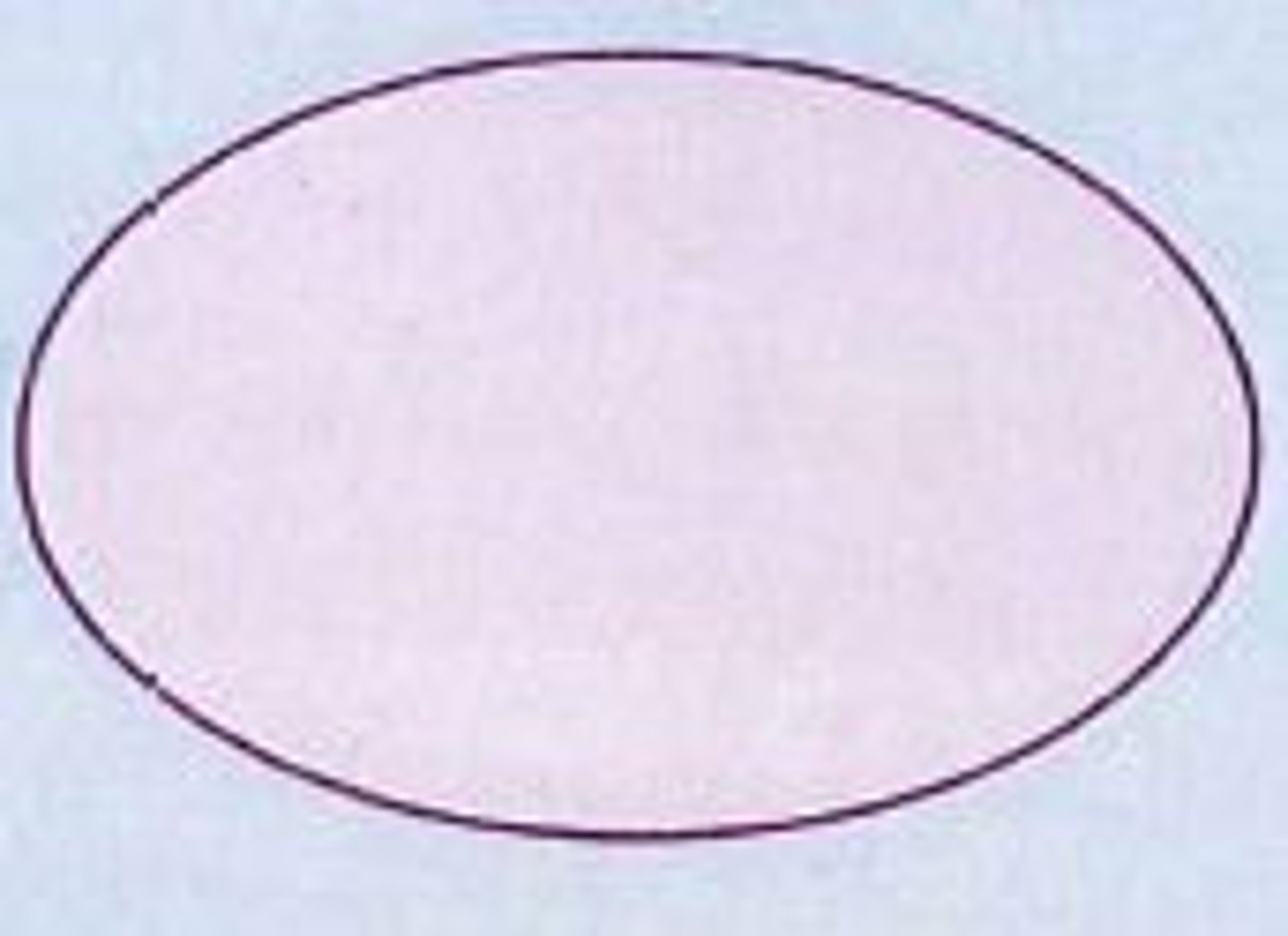
Flowchart symbol - Start/end
hotdog shape (long oval)
flowchart symbol - input/output
parallelogram
flowchart symbol - process
rectangle
flowchart symbol - decision/condition
diamond
flowchart symbol - delay
AND symbol [check slide 4]
In summary, flowcharts:
useful for planning stages or showing code graphically
In summary, pseudocode:
morphs along with code, mergeable to real code, but linear and does not give overall visual description
Convert #0b1011 to base 10
= 12^0 + 12^1 + 0 + 1*2^3 = 8 + 2 + 1 = 11
Base 16 (Hex) Digits
0-9, A= 10, B = 11, C=12, D=13, E=14, F=15
Convert 0xFE32 to decimal (base 10)
65044
Adding hex numbers: 0x0A + 0x08
0x12 = 18 (base 10)
Adding hex numbers
the same as decimal, except carry 16 instead of 10
Convert 0b110111 to decimal
55
Convert 170 to binary
0b10101010 (procedure: keep dividing by 2, first remainder is LSB, last remainder is MSB)
Convert 0b110101110010 to Hex and then to decimal
Hex = 0xD72
Decimal = 3442
Convert 65430 to Hex then to binary
Hex = 0xFF96 (keep dividing by 16 - procedure)
Binary = 0b1111 1111 1001 0110
Convert $ABCDEF to decimal
hex --> decimal
11,259,375
Convert %1010110 to decimal
86
Convert 120 decimal to binary
1111000
Convert %110101010010 to Hex then to decimal
Hex = 0xD52
Decimal = 3410
Convert 35210 to Hex then to binary
Hex = 0x898A
Binary = 0b00110101001000010000
Convert $AFCABE to decimal:
11,520,702
Convert $E4CFEA to binary:
9223372036854775807
Given n bits, how many values can you encode?
2^n -1
Byte
8 bits
Nibble
4 bits
kilobit (Kb)
2^10 bits = 1024 bits
kilobyte (KB)
2^10 bytes = 8192 bits
megabyte (MB)
2^20 bytes = 2^23 bits
Binary arithmetic - adding
Logically, adding is the XOR function per column, can also convert to decimal and add
0+0 = 0
1+0 = 1
0+ 1 = 1
1+1 = 10 (2)
Signed Numbers
- use MSB as the "sign" bit
0 = positive
1 = negative
- can think of subtractions as adds with a negative number
Signed Numbers 2's Complement (Represent a negative number as twos complement in binary)
Steps
1) Take the positive binary (MSB = 0)
2) Invert all bits
3) Add 1
Signed Numbers 2's Complement (twos complement --> negative number)
Steps
1) take twos complement number
2) subtract 1
3) invert all bits
ex) these steps give binary equal to 5, so you know the negative number is -5
2's complement range
8 bits: -128 to 127
general: (2^n-1)-1 positive numbers to 2^n-1 negative numbers, and the number 0
Twos complement: 8-3 = 8 + -3
0000 1000 (8)
1 1 1 1 1 101 (-3)
-----------------
0000 0101 (5)
Twos complement: 8-9 = 8+-9
0000 1000 (8)
1111 0111 (-9)
----------------
1111 1111 --> MSB is 1, so do reverse to find negative number (-1)
22+7 in binary, state if valid for signed and unsigned
00011101, valid for both
22-7 in binary, state if valid for signed and unsigned
00001111, valid for both
-22-7 in binary, state if valid for signed and unsigned
11100011, valid for signed only
-22+7 in binary, state if valid for signed and unsigned
11110001, valid for signed only
Before you start a math operation what two things must you know?
1) signed or unsigned
2) number of bits (8, 16, 32 etc)