Physio Lect 7 - Electrocardiogram Normal Rhythm Part One
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
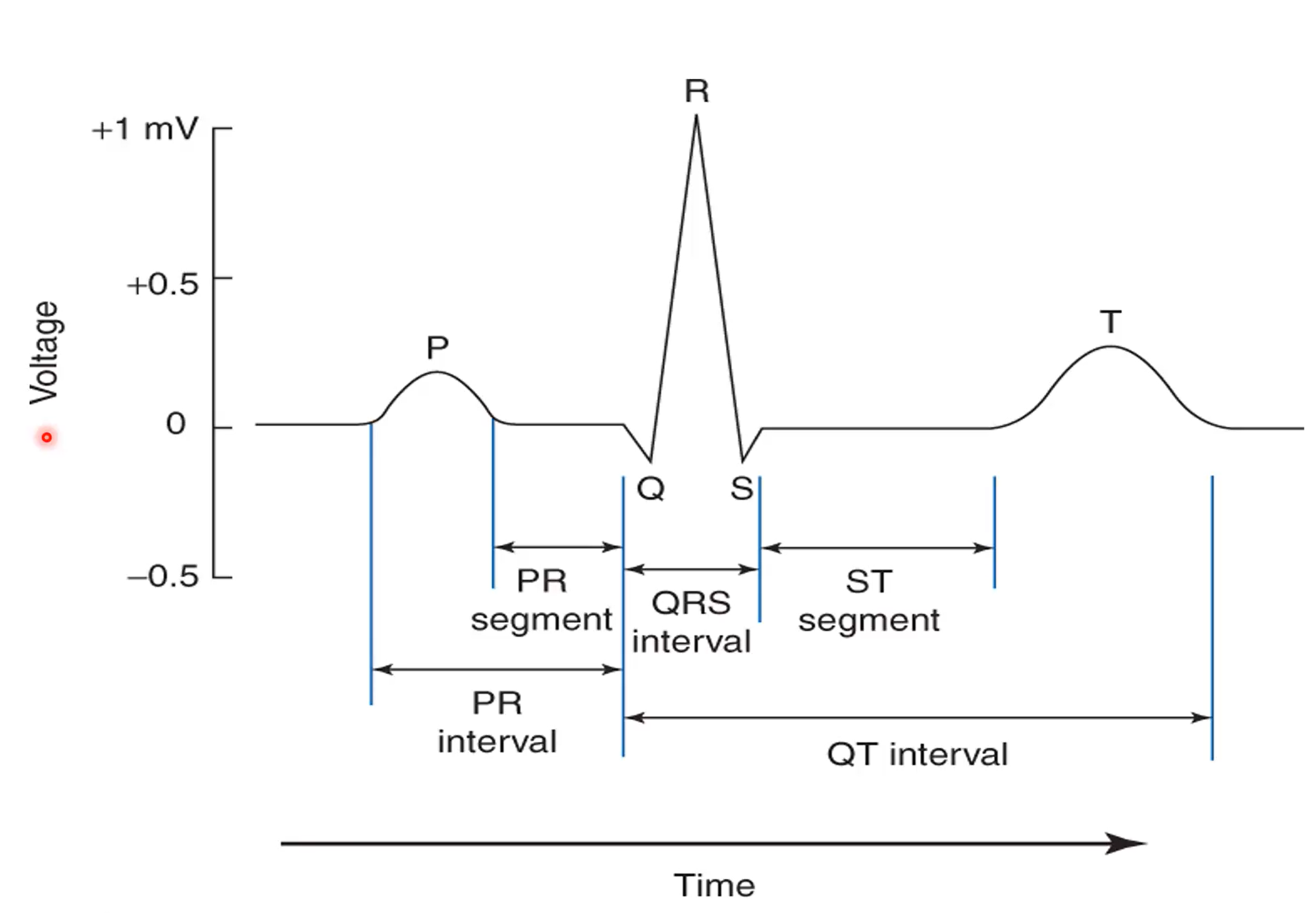
How many heartbeats does this represent?
one
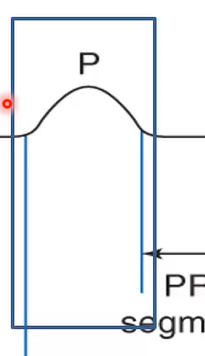
What does the P-wave coincide with?
Phase 0 of nodal action potential
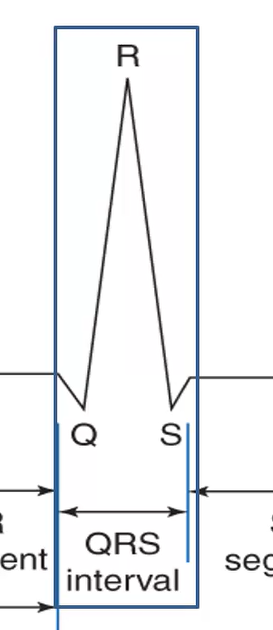
What does the QRS complex coincide with?
phase 0 of ventricular muscle cell action potential - ventricular depolarization
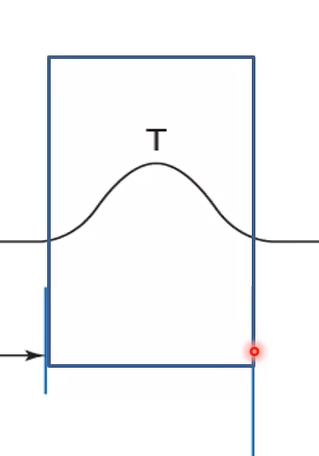
What does the T-wave coincide with?
Ventricular repolarization - phase 3 of muscle action potential
Why don’t we see atrial repolarization in an ECG?
falls under QRS complex - too small to see on the QRS voltage
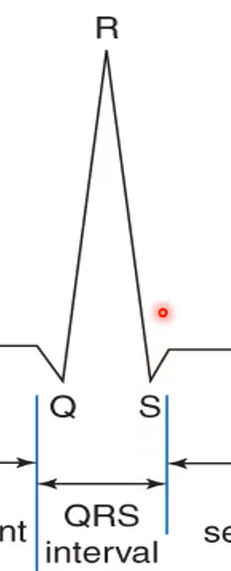
What does it mean if the QRS interval is longer?
There may be damage somewhere in the ventricle
What could it mean if the R-wave on an ECG is taller?
could mean there is more tissue - hypertrophy
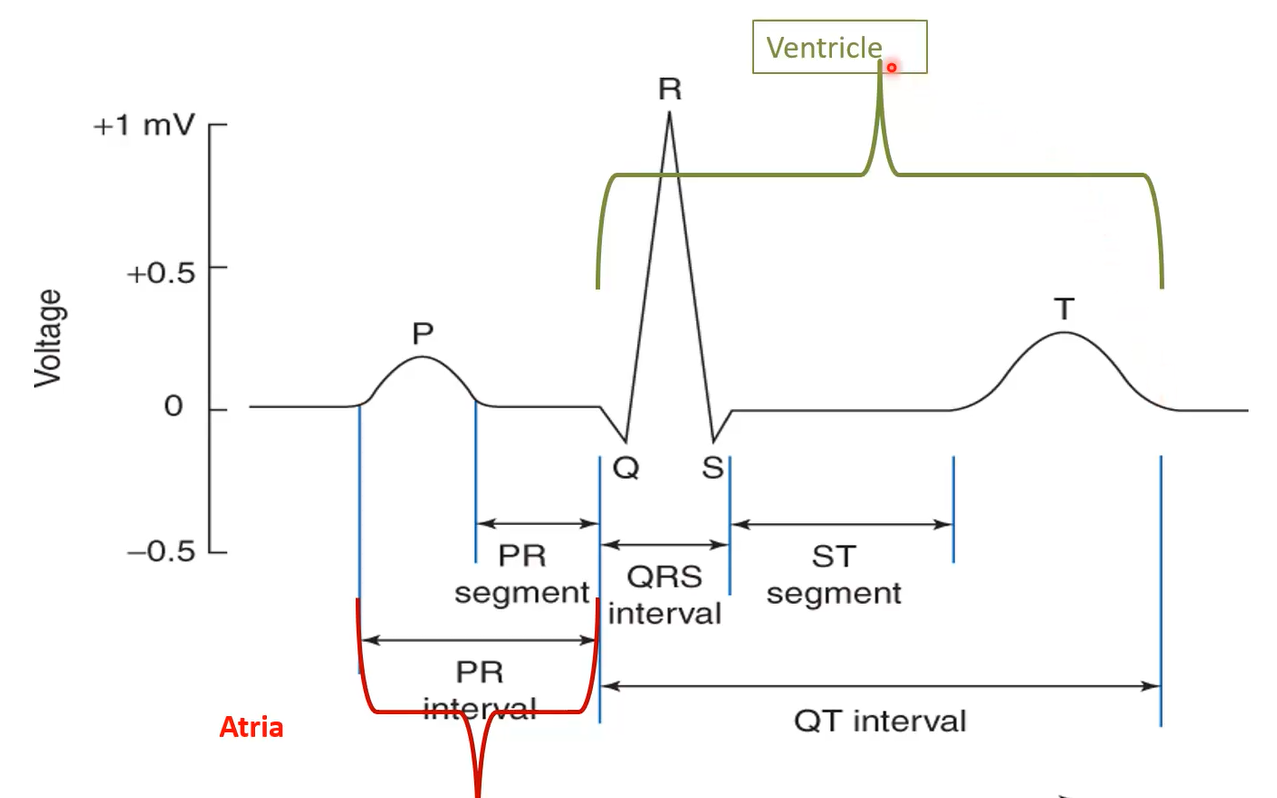
What interval is an indication of the Atria?
P-R
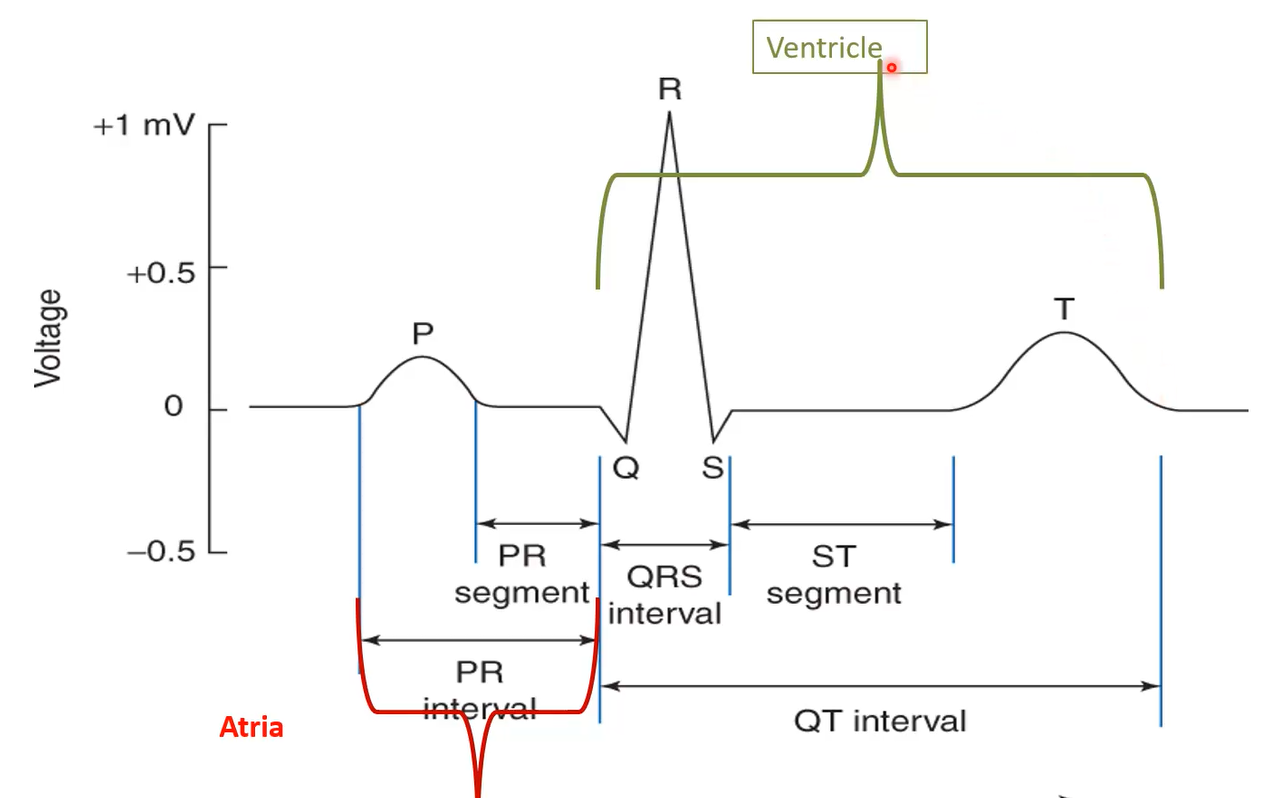
What interval is an indicator of the Ventricle?
Q-T
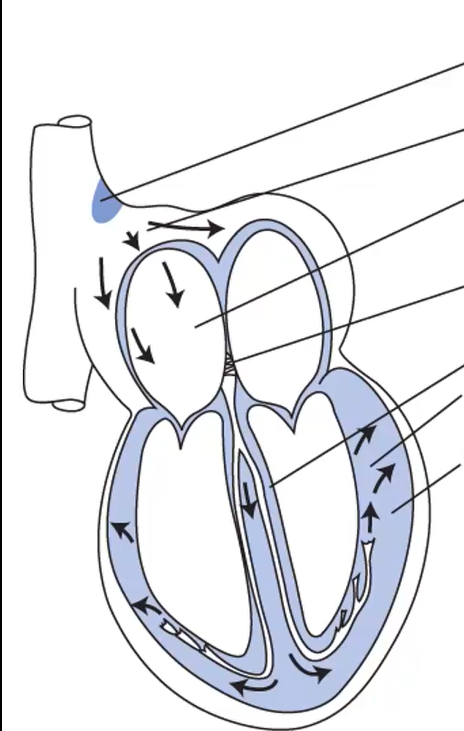
for each of these arrows identify what part of the heart is indicated
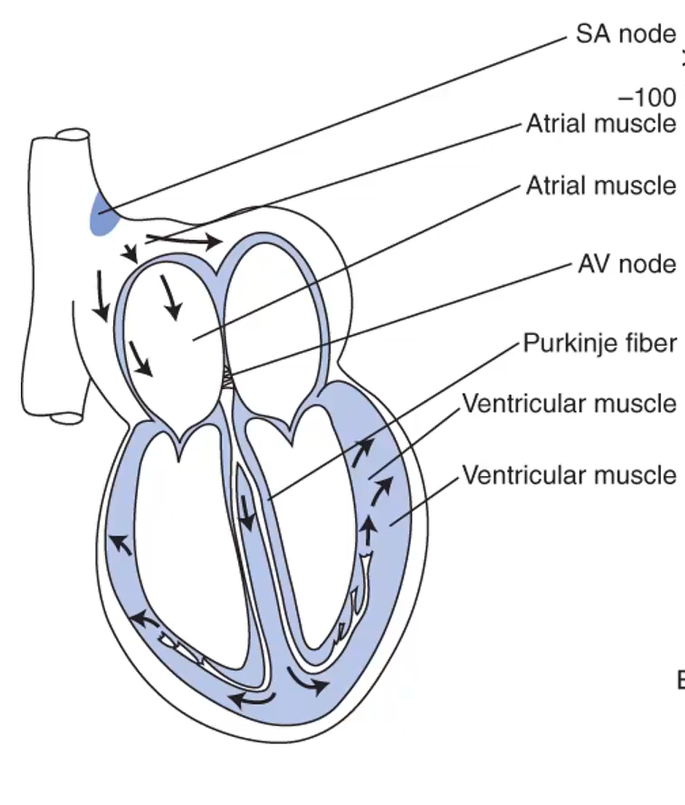
During the P-wave of the heartbeat, which of the following experience no action potential?
SA Node
Atrial Muscle
AV Node
Purkinje Fiber
Ventricular Muscle
Purkinje Fiber
Ventricular Muscle
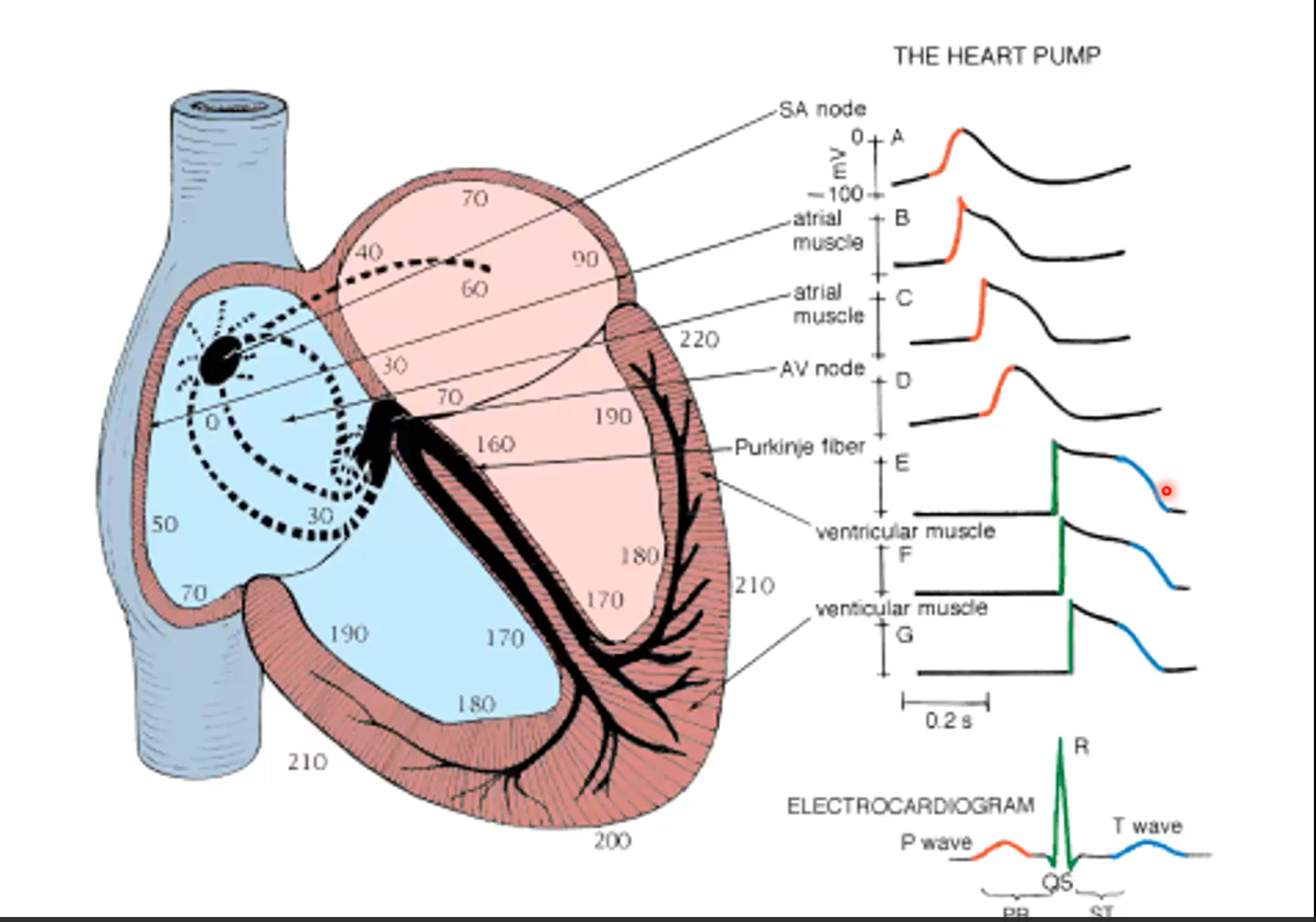
During the ST-Segment of the heartbeat, which of the following experience depolarization?
SA Node
Atrial Muscle
AV Node
Purkinje Fiber
Ventricular Muscle
Purkinje Fiber
Ventricular Muscle
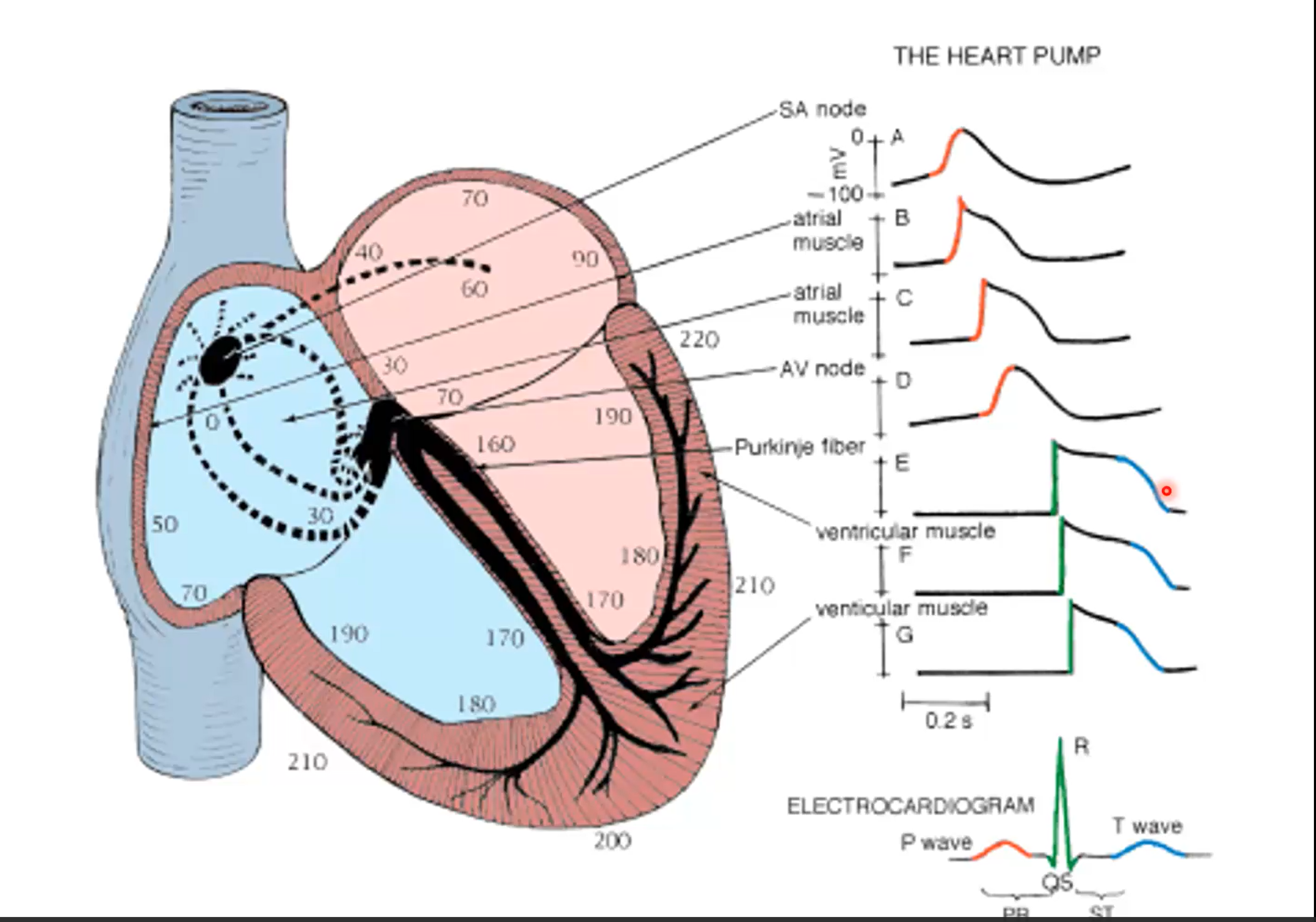
During the T-Wave of the heartbeat, which of the following experience repolarization?
SA Node
Atrial Muscle
AV Node
Purkinje Fiber
Ventricular Muscle
Purkinje Fiber
Ventricular Muscle
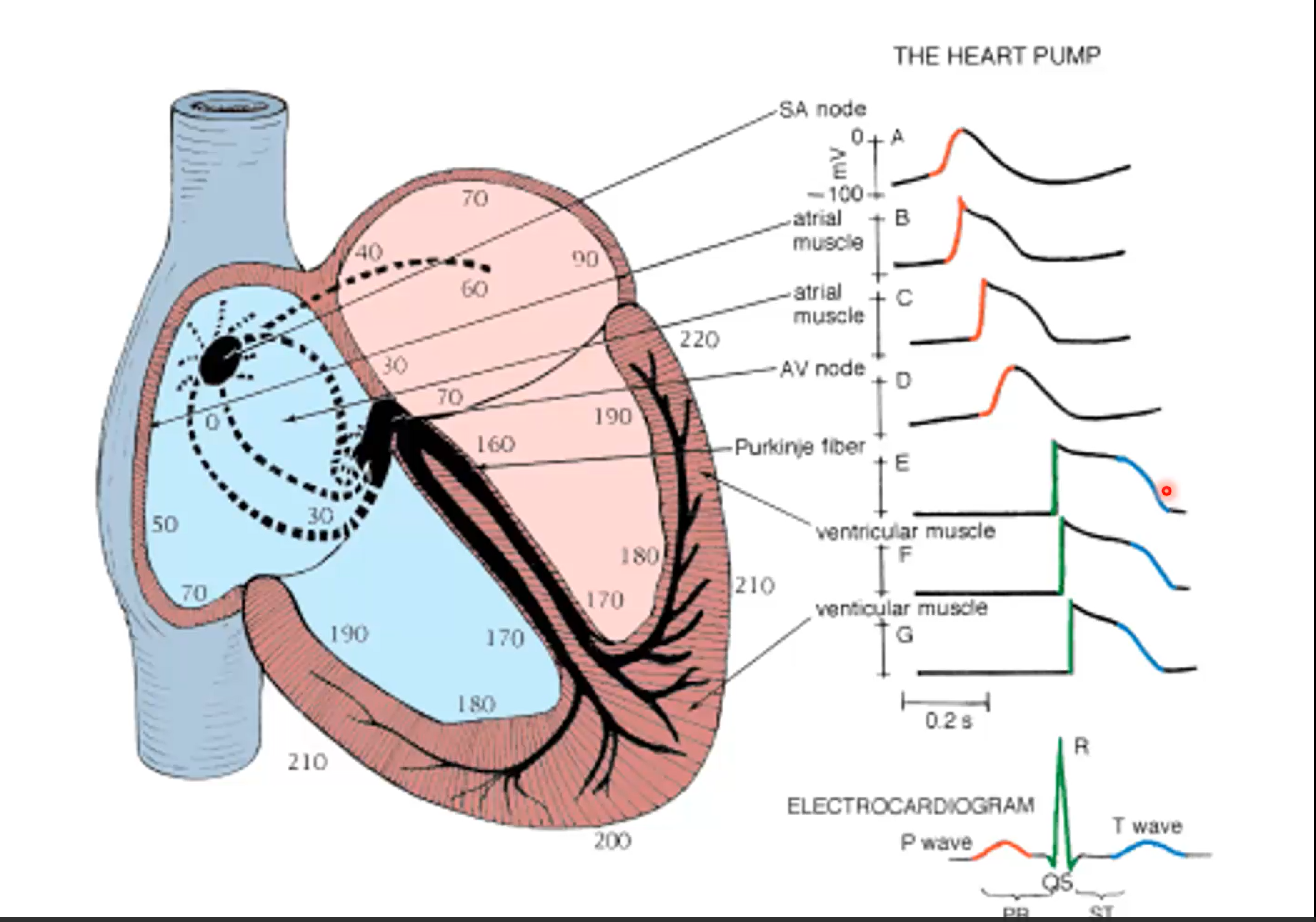
Inside of a cell is ___charge, outside of a cell is ___ charge.
negative
positive
What is depolarization?
when Na+ channels open and Na+ enters the muscle cell (phase 0 of muscle action potential) - cell becomes more positive
What is repolarization?
When the cell interior returns of a more negative state (phase 1-3 in a muscle cell)
What is a dipole?
two polse (one + one -) separated by a short distance
When can we find a dipole?
during depolarization and repolarization
When aren’t there dipoles?
during Muscle cell restin gmembrane potential or complete depolarization
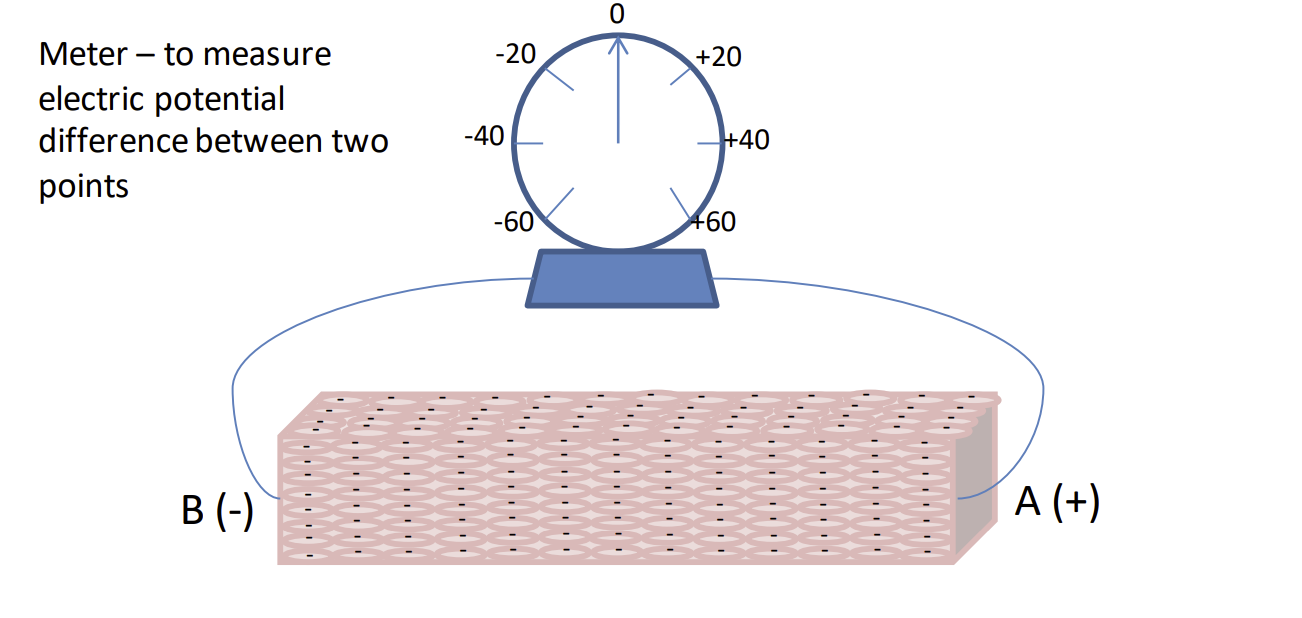
Resting Membrane Potential – all cells have a ______internal charge (______outside charge) so the electrical current is 0, no dipole exists
negative
positive
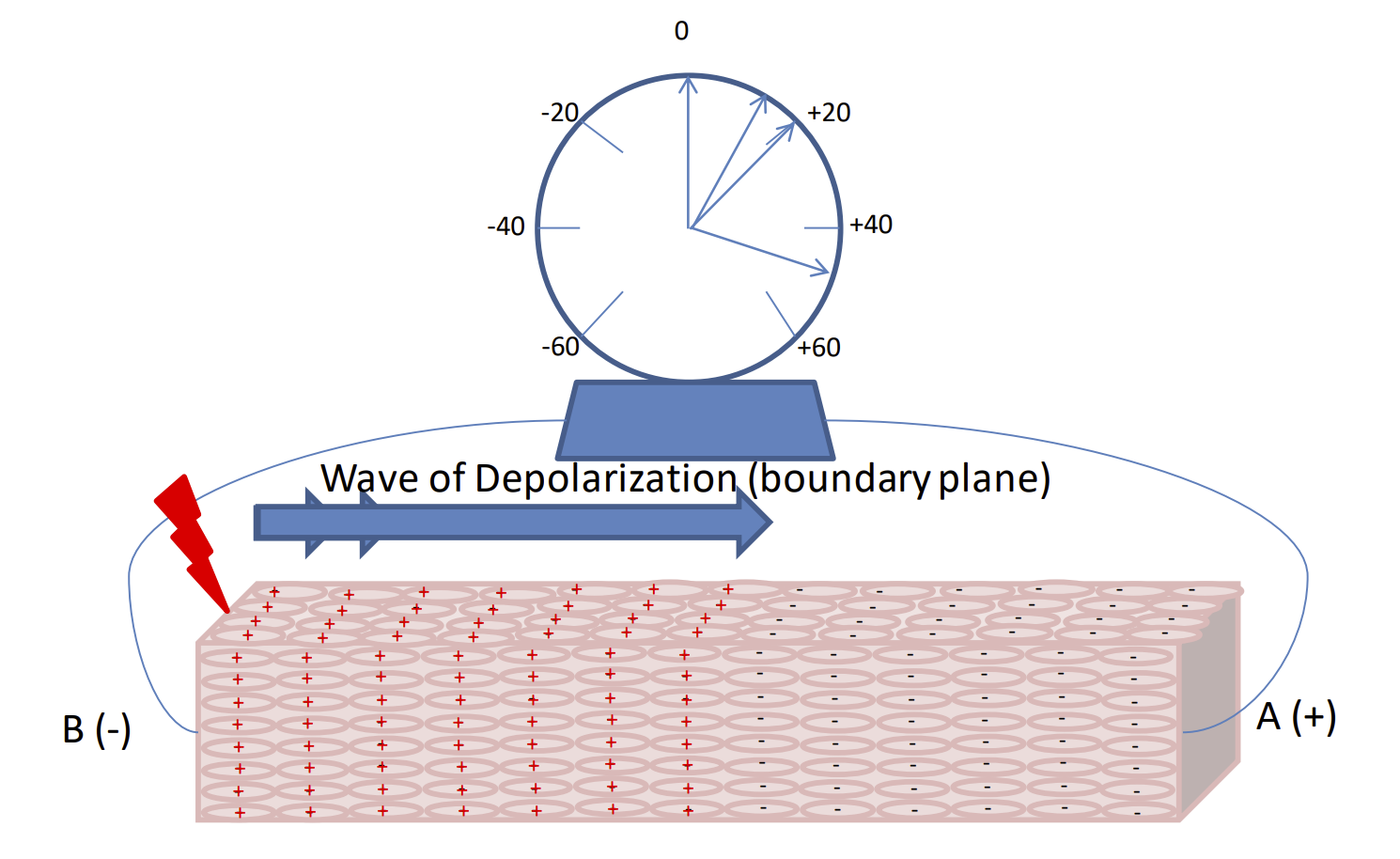
Stimulus creating an Action Potential – cells become _______internal (________outside the cell), vector is produced in the direction of depolarization (the vector always points towards resting cells) Maximum voltage is created when _____of the cells are depolarized and ____are repolarized (resting)
positive
negative
half
half
When attaching ECG, how many standard frontal leads are there? Where do they start and end?
3
Lead 1 - right arm to left arm
Lead 2 - right arm to left leg
Lead 3 - left arm to right leg
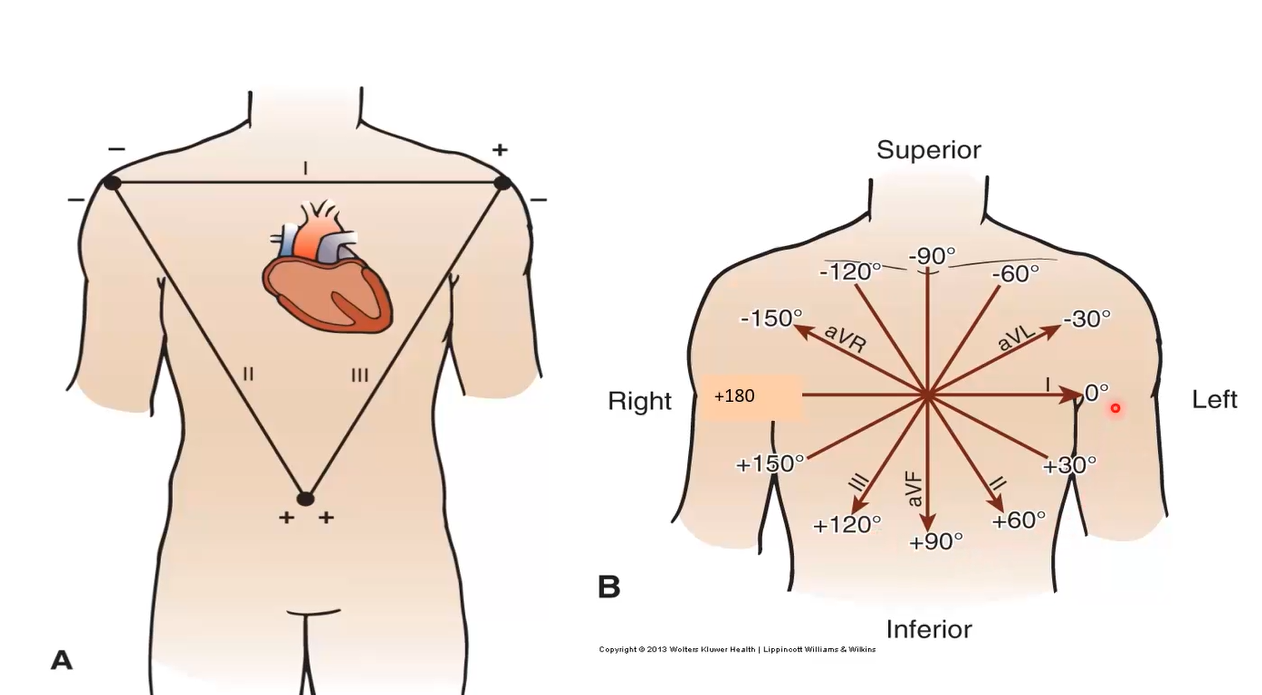
When attaching ECG, how many augmented leads are there(unipolar)? Where do they start?
3
aVR: augmented right, right shoulder
aVL: augmented left, left shoulder
aVF: augmented foot
When attaching ECG, how many precordial leads are there? Where do they start?
6
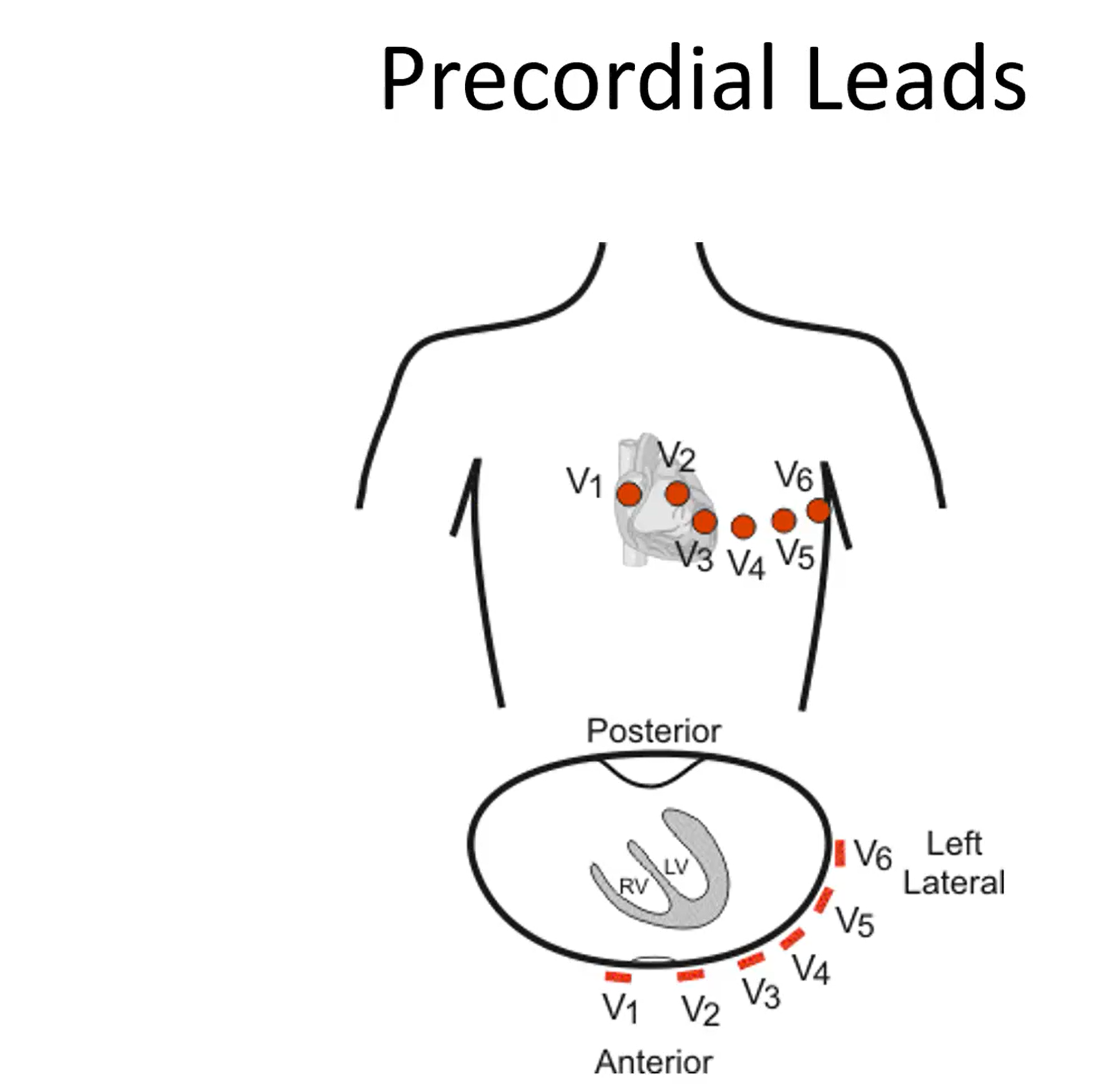
What does a 12 lead (6 precordial leads) provide?
A 3D indication of the heart
On every ECG activity given, what values should we assume for voltage scale and paper speed?
10 mm upward = +1 mV
25 mm = 1s