Chapter 15 - Transcription & Translation
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Used the ch. 15 wrap-up and slides
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Order of events for the central dogma
DNA → RNA → Protein
Replication on DNA inside the nucleus
DNA is transcribed into RNA inside the nucleus
RNA is translated into proteins in the cytoplasm
Protein synthesis occurs in ribosomes in the cytoplasm
Beadle and Tatum’s experiment
One enzyme, one gene hypothesis - surmised that each gene would influence a specific step in a metabolic pathway
Knowledge formed based on their findings:
Genes encode for proteins other than enzymes
Genes may encode a subunit
Some genes encode for non-coding RNA’s
Many genes have more than one exon & can be processed differently to develop different proteins
Define the term gene
specific sequence of nucleotides on a strand of DNA
aid i the development of specific traits
usually result in a protein product
before protein synthesis… an RNA copy called “transcript,” of the gene must be made (mRNA)
Reading Genetic Code
A gene is interpreted by reading the codons but… these codons must be read in the correct reading frame
Which nucleotide starts the first codon of the coding region of the gene
Always starts with the “start codon” AUG which encodes the amino acid Methionine
Prokaryotic gene expression
Happens solely in the cytoplasm
Do not require RNA transcript modification- their RNA transcripts can be translated immediately after being transcribed
RNA transcript can be transcribed and translated at the same time
multiple polymerases can transcribe a single gene
numerous ribosomes can concurrently translate the mRNA transcripts into polypeptides (polyribosomes)
This can allow a specific transcript and/or specific protein to rapidly reach high concentration in a cell
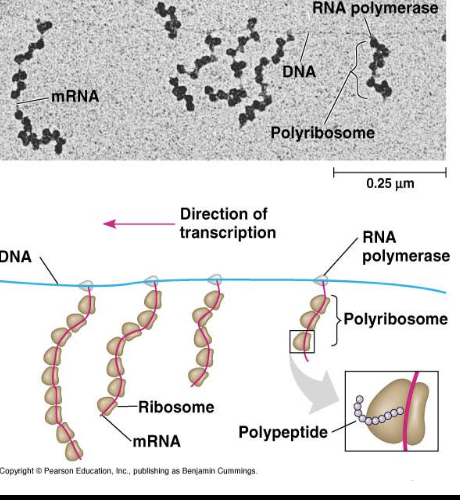
Eukaryotic gene expression
transcription and mRNA modification occur in the nucleus
translation occurs in the cytoplasm
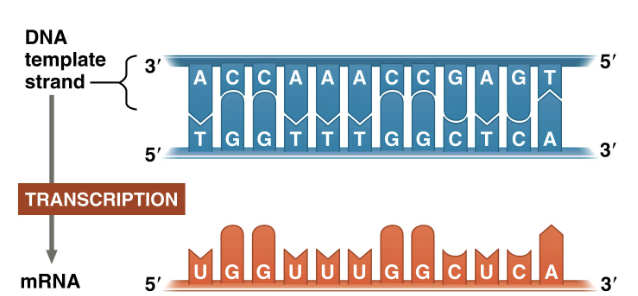
Overall process of transcription
The gene sequence determines the sequence of bases along the length of a mRNA molecule. RNA is compromised of A, U, C, G
Occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells
RNA polymerase is THE enzyme (she is THAT girl)
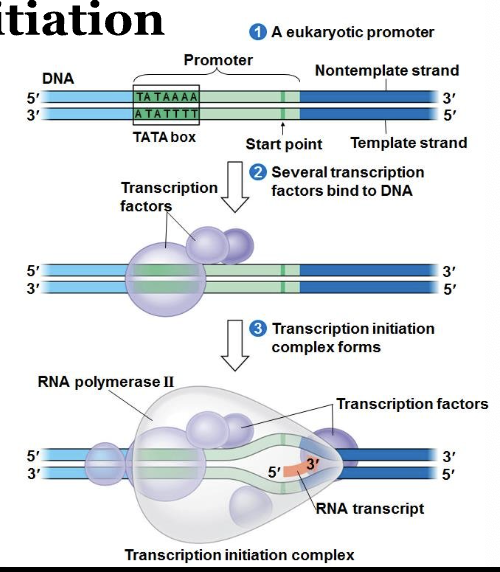
What do promoter sequences do in the initiation phase of transcription?
A sequence of DNA that serves as recognition and recruitment site for transcription factors and RNA polymerase
What do transcription factors do in the initiation phase of transcription?
Proteins that aid in the initiation and regulation of transcription
What do RNA Polymerases do in the initiation phase of transcription?
Synthesize the RNA transcript
Breaks hydrogen bonds between DNA strands and links together RNA nucleotides (same base pairing rules except RNA uses uracil instead of thymine)
RNA polymerase can only add nucleotides onto the 3’ end of the growing RNA transcript
Several types (I, II, III)
What are the steps for initiation in transcription
Transcription factors bind to promoter region of the gene needing transcription
T-factors recruit RNA polymerase to bind and form an initiation complex
RNAP will then recognize this start sequence and begin to synthesize the RNA transcript in a 5’ to 3’ direction
Reads 3’ to 5’
Writes 5’ to 3’
What is the importance of the elongation phase in transcription
It is where the production of the RNA transcript occurs
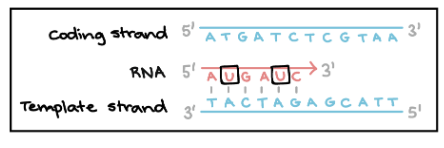
What is the role of RNAP in the elongation phase in transcription
Unwinds DNA to access the template strand (only exposes around 10-20 nucleotides at a time)
Connects the RNA nucleotides using DNA as a template
produces RNA transcript in a 5’ to 3’ direction
Temporary attachment
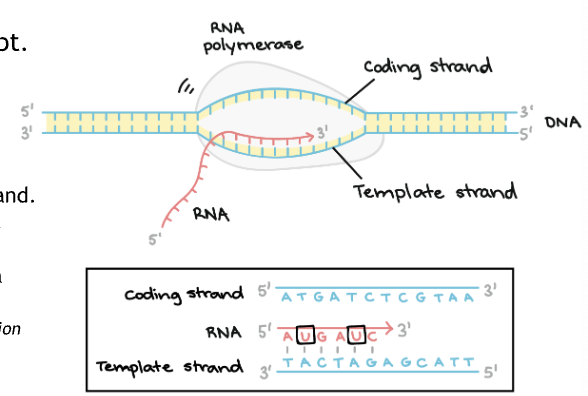
What are the steps for the elongation phase of transcription
RNAP unwinds DNA
RNAP reads 3’ to 5’ direction the the DNA nucleotides from the template strand and attaches RNA nucleotides
RNA nucleotides are joined to the previous one on the 3’ end by a phosphodiester bond along its backbone
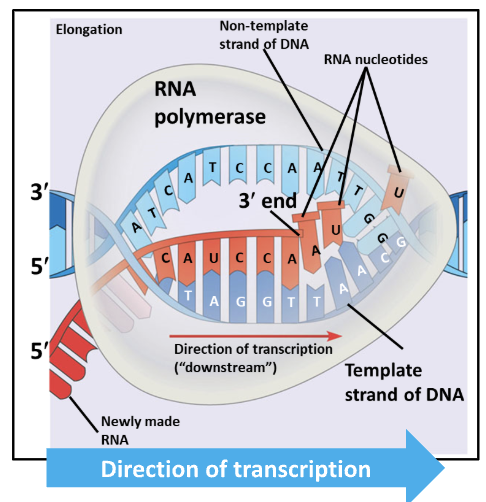
What is the role of terminator sequences in the termination phase of transcription
sequences of DNA at the end of a gene that is transcribed and signals the RNA transcript is complete
What are the steps for termination in transcription
RNAP reaches and transcribes the termination sequence
RNA transcript is released by RNAP
RNAP detaches from the DNA, ending transcription
GOAL of termination phase is to completely disassociate RNAP from DNA by stopping transcription and releasing the new RNA strand
How does the termination phase of transcription vary for prokaryotes versus eukaryotes
Pro- RNAP reads through a termination sequence and causes it to dissociate from the DNA, RNA is immediately ready for translation
Euk- RNAP reads through Polyadenylation sequence, the end of RNA transcript is then bound by proteins causing the RNAP to disassociate from DNA, RNA will need additional processing
What are the two mechanisms put on the ends of mRNA transcript
5’ cap and the Poly-A-tail
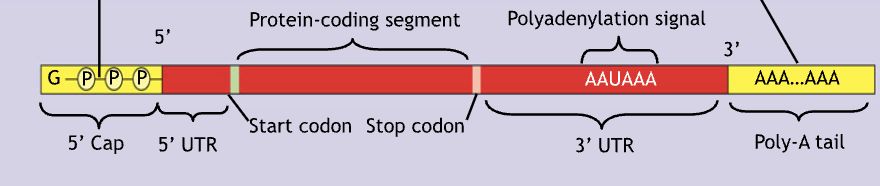
What is the function of the 5’ cap
modified guanine nucleotide placed on the 5’ end of the mRNA transcript
Necessary to maintain mRNA stability and recognition
What is the function of the poly-A-tail
placed on the 3’ end of mRNA transcript, string of 50-250 Adenine nucleotides that can vary in number depending on the transcript, cell type, and organism
Tail acts as a timer for how long you stay in the cytoplasm as a functioning mRNA
How does RNA splicing work and why is it important
Process of removing introns and joining together exon sequences to form a mature mRNA transcript
Ensures that only coding sequences are translated; exons
Removes introns (noncoding sequences) and joins exons
spliceosomes - complexes made of protein and catalytic RNA (riboenzymes)
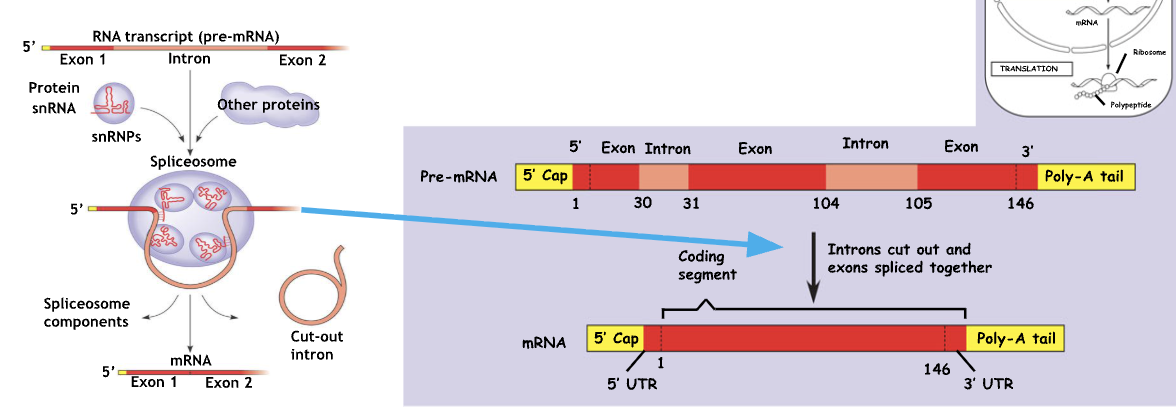
Why do we care about introns
They allow for alternative splicing - the inclusion of differing sets of exons or differing mature mRNA produced from the same gene
Polypeptides within proteins often have discrete structural and functional regions called domains, each exon can encode for a different domain
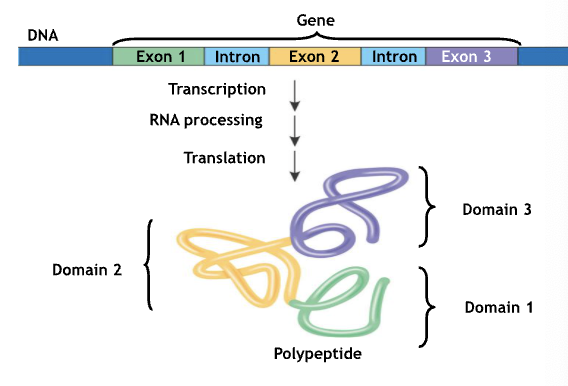
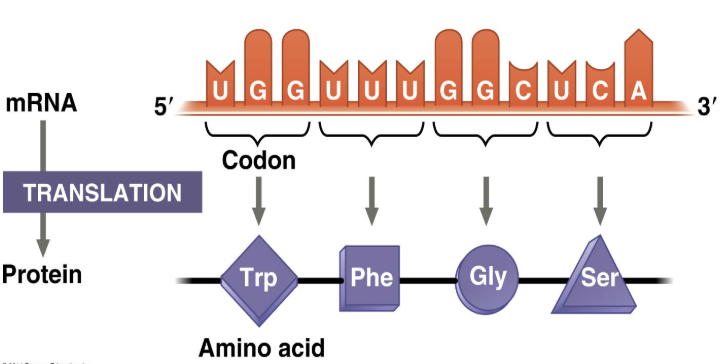
Generally speaking, what happens during translation
The mRNA sequence determines the sequence of amino acids in the primary structure of the polypeptide; RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide
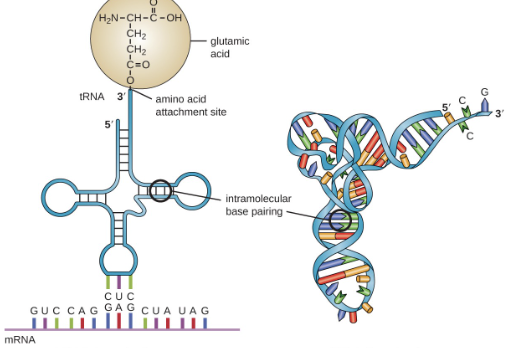
What is tRNAs role in translation
carry a specific amino acid on 1 end
have an anticodon on 1 end
single RNA strand that is about 80 nucleotides long
utilize a specific Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase to attach its amino acid
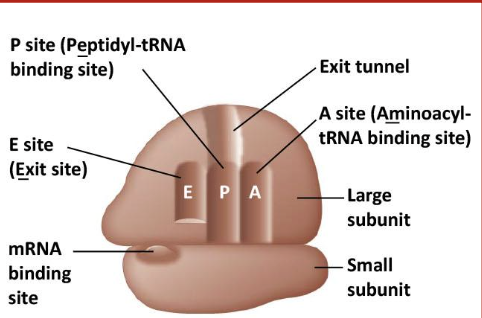
What is the ribosomes role in translation
Protein and rRNA complex that facilitates the reading of mRNA and production of the corresponding polypeptide
achieved through the pairing of mRNA codons with tRNA anticodons
Consists of 2 ribosomal subunits: large which brings in tRNA, and small that binds mRNA
Has 3 binding sites: E, P, and A
What is the role of mRNA in translation
Molecule that directs the recruitment of tRNA molecules and production of the polypeptide
Very specific sequence of RNA, unique to the polypeptide it will be used to create
mRNA is bonded to the small ribosomal subunit
read every 3 base codons in a 5’ to 3’ fashion
AUG = start codon
Each codon is bonded to a tRNA anticodon
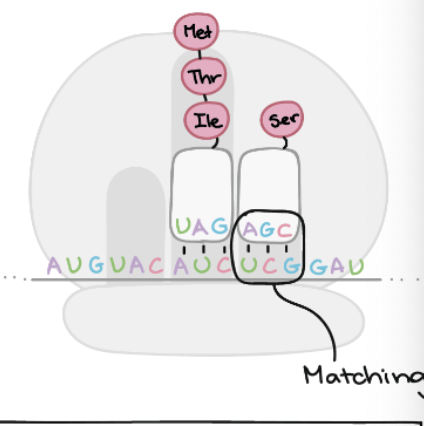
What is the role of the polypeptide in translation
End product of translation by the assembly of amino acids bonded together in a specific sequence
interaction of one tRNA in the P site with another tRNA in the A site
Directed by the bonding of mRNA codon to the anticodon of a tRNA
Occurs in the ribosomes found in the cytoplasm of the cell
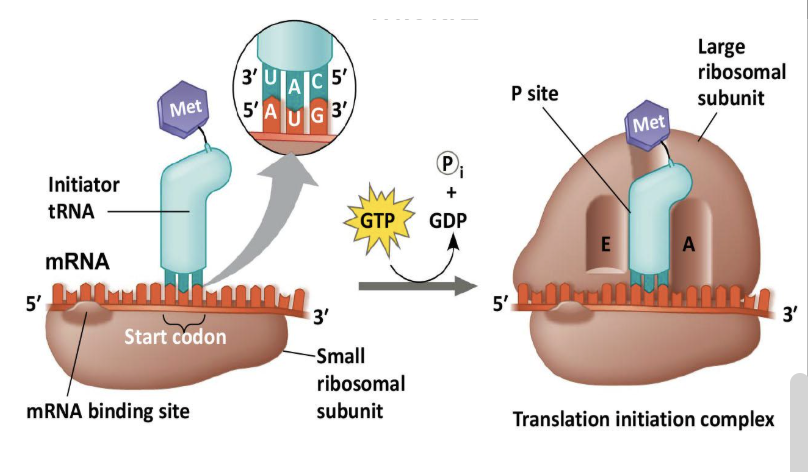
What are the steps of the initiation phase in translation
Assembly step that brings mRNA, initiator tRNA, and 2 subunits of the ribosome together
mRNA binds the small ribosomal subunit
Start codon is located
Initiator tRNA binds to start codon
Energy is used to recruit and bind large ribosomal subunit
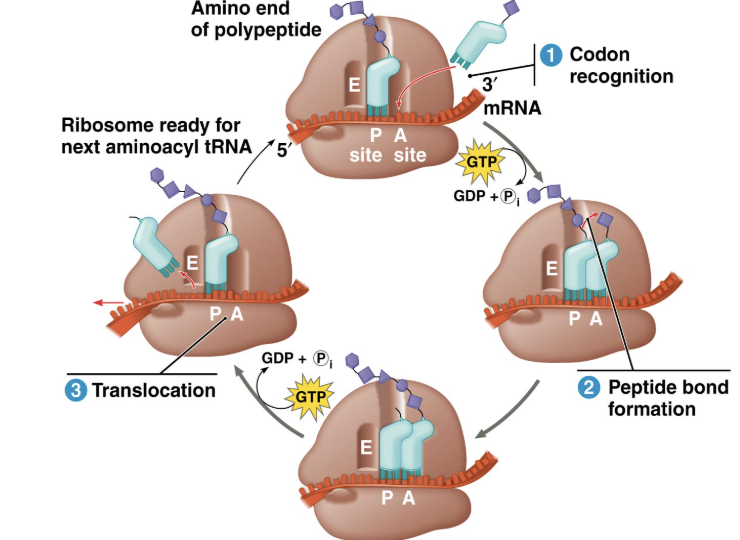
What are the steps of the elongation phase in translation
Reading stage where amino acids are bonded to each other; building a polypeptide chain out of the P site
tRNA enters the A site and bonds its anticodon with the corresponding codon of mRNA
The growing polypeptide chain is attached to tRNA in P site, forms a peptide bond with amino acid attached to the tRNA in the A site
mRNA is shifted further along, causing bonded tRNAs to shift sites. tRNA in the P site breaks its bond with mRNA and enters E site. The tRNA in the A site is shifted to the P site as it now has the growing polypeptide chain attached
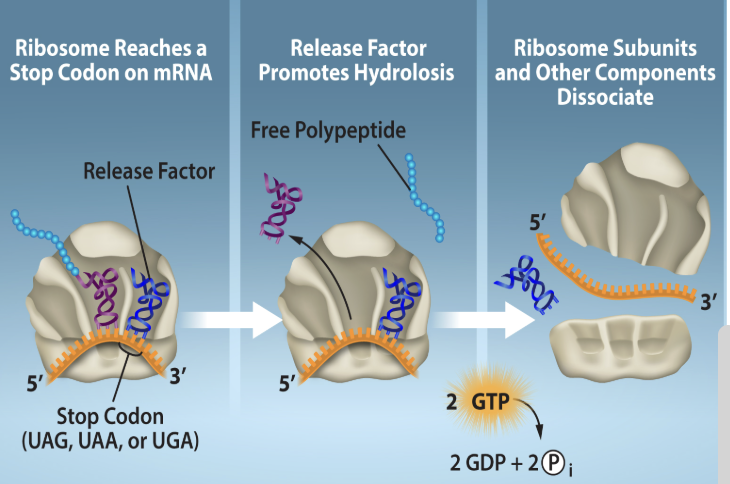
What are the steps of the termination phase in translation
Stage is reached when the stop codon is recognized in the mRNA
Stop codon in the mRNA is reached and recognized
Release factor is recruited and binds to the stop codon causing the hydrolysis of the polypeptide from the tRNA
Bonding + energy is utilized to cause the disassociation of the translation components
Point mutations
changes in a single base pair within the genome, when occuring in a gene these mutations can affect the structure and function of the overall gene product
Substitution point mutation
Silent (synonymous) - the single base pair change does not cause an amino acid change in the polypeptide
Missense (non-synonymous) - the single base pair change causes an amino acid change in the polypeptide; can be detrimental or not noticed at all
Nonsense - the single base pair change causes a change from an amino acid to a stop codon; very detrimental
Insertion point mutation
the addition of one base pair within the genome
Deletion point mutation
the removal of one base pair within the genome
Frameshift mutations
changes in nucleotide base pairs within the genome that causes a reading frame shift
Can occur as insertion or deletion
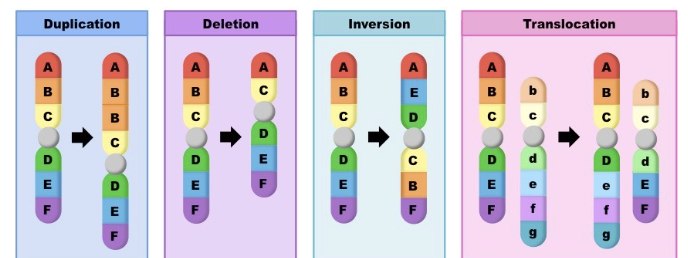
Chromosomal mutations
Very large scale nucleotide changes within a chromosome’s DNA
Insertions - addition of many nucleotides into the chromosome
Deletions - removal of a section of the chromosome
Translocations - part of one chromosome is removed and inserted to somewhere in another chromosome
Inversions - reversal of a segment of the chromosome
Fusions - when two genes come together to form one new hybrid gene
Duplications - copy of a region of the chromosome
Mutagens
physical or chemical agents that can cause mutations
radiation, x-rays, UV
Carcinogens
Spontaneous mutations
can occur during DNA replication, recombination, or repair