HGEO 100 Vocab
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
Concentration
The spread of geographic phenomena over a given area
density
A measure of the relationship between the number of geographic phenomena and a unit of area typically expressed as a ratio
Diffusion
The process of geographic phenomena spreading over space and through time
Distance Decay
The diminishing in importance and eventual disappearance of a phenomenon with increasing distance from its origin.
formal region
An area within which everyone shares in common one or more distinctive characteristics.
Functional Region
A region defined by the particular set of activities or interactions that occur within it
Spatial Perspective
observing variations in geographic phenomena across space
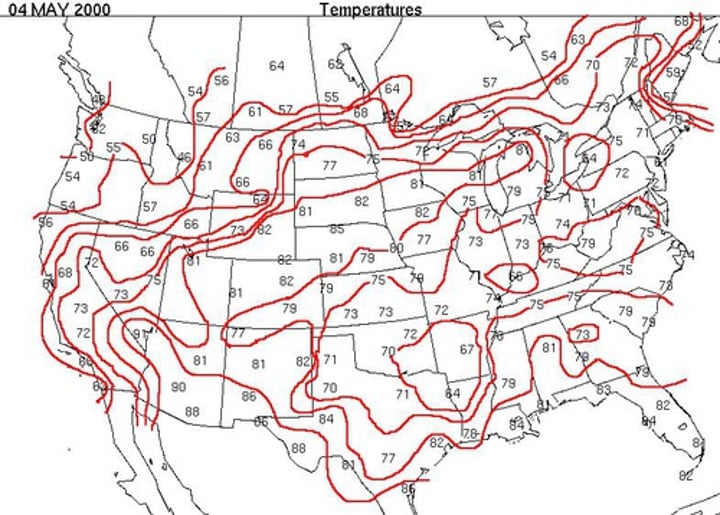
Isopleth Map
a map using lines to connect locations of equal data value
landscape
a large area with a particular kind of scenery, such as a desert landscape
Perception
The act of becoming aware through the senses
place
A location that has acquired particular meaning or significance.
Placelessness
The nature of locations that lack uniqueness or individual character; used for homogenous and standardized landscapes
remote sensing
The acquisition of data about Earth's surface from a satellite orbiting the planet or other long-distance methods.
scale
the relationship between the portion of Earth being studied and Earth as a whole
situation
the location of a place relative to other places
spatial interaction
The nature and extent of the relationship or linkages between locations; the extent of spatial interaction is related to the distances between locations and the physical and intangible connections between them.
vernacular region
An area identified on the basis of the perceptions held by people inside or outside the region, or both.
demographic transition
The historical shift of birth and death rates from high to low levels in a population
Dependency Theory
A theory that connects disparities in levels of development to the relationship between dependent and dominant states.
fecundity
A biological term for the potential capability of having children; refers to potential rather than actual number of live births.
Limits to Growth
A view that argues that both world population and the world economy will collapse because of insufficient available natural resources
Population pyramid
A graphic representation of the age and sec composition of a population
Possibilism
viewpoint that people, not environments, are the dynamic forces of cultural development
World Systems Theory
A set of ideas centered around the idea that the world is an interdependent system of countries linked together by an economic and political competition that shapes relations between core, semi-peripheral, and peripheral countries.h
Acculturation
The adoption of cultural traits, such as language, by one group under the influence of another.
centrifugal force
a force that divides people and countries
core-periphery
Core countries have high levels of development, a capacity at innovation and a convergence of trade flows. Periphery countries usually have less development and are poorer countries.
Cultural adaption
A complex of ideas, activities, and technologies that enables people to survive and even thrive in their environment
cultural region
an area in which a group of people share a similar culture and language
lingua franca
A language mutually understood and commonly used in trade by people who have different native languages
Malapportionment
Type of gerrymandering involving the creation of electoral distracts of differing population sizes to benefit a particular party
Rimland Theory
Nicholas Spykman's theory that the domination of the coastal fringes of Eurasia would provided the base for world conquest.
spectacle
places and events that are carefully constructed for the purpose of mass leisure and consumption
Central Business district CBD
The social, cultural, commercial, and political centre of the city; usually characterized by high rise office and residential towers, key municipal government buildings and civic amenities.
Central Place
An urban centre that provides goods and services for the surrounding population; may take the form of a hamlet, village, town, city, or megacity.
conurbation
an extended urban area, typically consisting of several towns merging with the suburbs of one or more cities.
donut effect
A term that refers to a pronounced difference in the growth rates between a core city
(slow growth or no growth) and its surrounding areas (faster growth).
Edge City
A large node of office and retail activities on the edge of an urban area.
Filtering
A process whereby housing units transition from being occupied by members of one income group to members of a different income group over time; downward filtering is more usual than upward filtering.
threshold
The minimum number of people needed to support the service
Urbanism
Way of life associated with a declining sense of community and increasingly complex social and economic organization as a result of increasing size, density, and heterogeneity.
Urbanization
An increase in the percentage and in the number of people living in urban settlements.
economic operator
A model of human behaviour in which each individual is assumed to be completely rational; economic operators maximize returns and minimize costs
economic rent
The surplus income that accrues to a unit of land above the minimum income needed to bring a unit of new land into production at the margins of production
location theory
A body of theories explaining that spatial distribution of economic activities.
primary activities
Economic activities in which natural resources are made available for use or further processing, including mining, agriculture, forestry, and fishing.
principle of least effort
Considering a guiding principle in human activities, refers to minimizing distances and related movements.
Rational Choice Theory
The theory of social life can be explained by models of rational individual action, an extension of the economic operator concept to other areas of human life
Satisficing behaviour
A model of human behaviour that rejects the rationality assumptions of the economic operator model, assuming instead that the objective is to reach a level of acceptable satisfaction
Secondary products
Products made from raw materials and used in the manufacture of finished products.
Tariff
A tax or customs duty imposed on imports from other countries.
Tertiary activities
those parts of the economy that fulfill the exchange function, that provide market availability of commodities, and the bring together consumers and providers of services
Time-space convergence
A decrease in the friction of distance between locations as a result of improvements in transportation and communication technologies
anthropocentric
A worldview which regards humans as the most important part of any ecosystem, the opposing view to the ecocentric perspective.
Cornucopians
Those who argue that advances in science and technology, along with cultural adaption, will continue to create resources sufficient to support the growing world population and mitigate environmental change.
Ecocentric
a worldview that places equal value on all living organisms and the ecosystems in which they live
Stock resources
Minerals and land that take a long time to form and hence, from a human perspective, are fixed in supply
Cartography
science or art of making maps
Chloropleth Map
A thematic map that uses tones or colors to represent spatial data as average values per unit area.
Distance
A measure of the amount of space between two or more locations; can be measured in both absolute terms (physical distance) and relative terms (time,distance,economic distance, or psychological distance)
friction of distance
the increase in time and cost that usually comes with increasing distance
Geography
the study of the earth's physical and cultural features
GIS
Geographic Information system: A computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data.
GPS
Global Positioning System:A system that determines the precise position of something on Earth through a series of satellites, tracking stations, and receivers.
Human Geography
the spatial analysis of human population, its cultures, activities, and landscapes.
Latitude
Distance north or south of the equator
location
A particular position in space; a specific part of the earths surface; used in absolute relative and nominal forms.
pattern
the geometric arrangement of objects in space
region
A part of the earths surface that displays internal homogeneity and is relatively distinct from surrounding areas according to certain criteria
site
The physical character of a place
space
the areal extent of something
toponym
the common name given to a location (a place name)
carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support
Census
the official count of a population
Demography
Scientific study of human populations.
development
the process of change that occurs during an organism's life to produce a more complex organism
developmentalism
An analysis of cultural and economic change that treats each country or region of the world independently in an evolutionary manner; an approach that assumes that all areas are autonomous and will proceed through the same series of stages of development.
doubling time
The number of years needed to double a population, assuming a constant rate of natural increase.
Ethnocentric
believing in the superiority of one's own ethnic and cultural group, and having a corresponding disdain for all other groups
life cycle
The generation-to-generation sequence of stages in the reproductive history of an organism.
population momentum
The tendency for pop
Replacement level fertility
the total fertility rate required to offset the average number of deaths in a population in order to maintain the current population size
centripetal force
An attitude that tends to unify people and enhance support for a state
Chain Migration
pattern of migration that develops when migrants move along and through kinship links
Critical Geography
Geographic scholarship that focuses on social justice and helping people through scholarly research
ecotourism
A form of tourism that supports the conservation and sustainable development of ecologically unique areas
hegemony
leadership or dominance, especially by one country or social group over others.
Iconography
the study of a group of representative pictures or symbols
nation-state
A political unit that contains one principal cultural group that gives it its identity
Topophilia
The affective ties that people have with particular places and landscapes; love of place.
Topophobia
hate/fear of a place
primate city
The largest settlement in a country, if it has more than twice as many people as the second-ranking settlement.
slum
poor, crowded, and run-down urban neighborhoods
suburb
a residential district located on the outskirts of a city
Urban sprawl
the uncontrolled expansion of urban areas.
urban structure
the arrangement of land use in urban areas
Zoning
Legal restrictions on land use that determine what type of urban activity and building form are allowed to take place on particular parcels of land.
Globalization
Actions or processes that involve the entire world and result in making something worldwide in scope.
Normative Theory
A theory on what might happen rather than what actually does happen. The aim is to seek what is rational, or optimal.
Offshoring
The outsourcing of work to another country; usually involves companies in more developed economies shifting work to less developed economies.