Biological molecules: Water and carbohydrates
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
How do hydrogen bonds form between water molecules?
Water is polar; slightly -ve oxygen atom and slightly +ve hydrogen atoms are attracted
Are hydrogen bonds weak or strong
Weak individually, strong in large numbers
Why are hydrogen bonds constantly breaking and reforming
Hydrogen bonds are weak when only few of them
Properties of water
Excellent solvent; transport medium; high SHC; high LHE; less dense as solid; high surface tension
Describe water’s high SHC
Hydrogen bonds can absorb lots of e; takes lots of e to heat up water; so suitable habitat; maintain optimum temp within cells
Describe water’s high LHE
Takes lots of e to overcome hydrogen bonds; lots of heat lost when little water evaporates; so good for thermoregulation, transpiration
Describe water’s cohesion
Polar molecules; large number of H bonds collectively strong; highly cohesive; chain of water molecules pulled up; allows for transpiration stream; transport medium e.g. blood
Describe water’s solubility
Polar; -ve O end attracted to +ve ions; +ve H end attracted to -ve ions; so good solvent
Name 4 roles of water which relate to its properties
Solvent; transport medium; coolant; habitat
Name physical properties of water which support life
Ice is less dense; cohesion and adhesion; surface tension; solvent; transparent
How does ice being less dense support life
Floats so habitat e.g. polar bears; freezes bottom up so water below is insulated
Describe how surface tension of water supports life
Allows for movement on water surface e.g. pond skaters
How does water’s role as a solvent support life
Medium for chemical reaction; transport of dissolved substances e.g. glucose in blood, ions in transpiration stream
What is a macromolecule
Very large molecule
What is a monomer
A single unit e.g. monosaccharide, amino acid
What is a polymer
Chains of monomers connected to one another
Polymer vs macromolecule
Polymer: made up of identical monomers repeated; macromolecule: any group of monomers
What do condensation reactions usually make
Polymers
What kind of reaction turns monomers into polymers usually
Condensation
Why is a condensation reaction called that
Molecule of water is released
How would you break down a polymer back into monomers
Hydrolysis reaction
What is a hydrolysis reaction
Water molecules break down bonds between monomers in polymers, turn back into monomers
Glycosidic bond
-O-
Peptide bond
O=C-N-H
Ester bond
C-O-C=O
What kind of covalent bonds are formed to make proteins
Peptide
What kind of covalent bonds formed for carbohydrates
Glycosidic
What kind of covalent bonds formed for lipids
Ester bonds
Example of a hexose monosaccharide
Glucose
2 isomers of glucose
α-glucose, β-glucose
Chemical elements in carbohydrates
C,H,O
Chemical elements in lipids
C,H,O
Chemical elements in proteins
C,H,O,N,S
Chemical elements in nucleic acid
C,H,O,N,P
Difference between α-glucose and β-glucose
α-glucose has OH on c1 below ring; β-glucose has OH on c1 above ring
What is C5 bonded to on a glucose molecule
CH2OH on top; H on bottom
What is C2 bonded to in a glucose molecule
H on top; OH on bottom
What is in the top right of the hexagon of a glucose molecule
O atom
Polysaccharides containing only α-glucose
Starch, glycogen
Polysaccharide containing only β-glucose
Cellulose
What is difference between hexose and pentose sugars
Hexose has 6 C, pentose 5 C
Example of pentose sugars
Ribose, deoxyribose
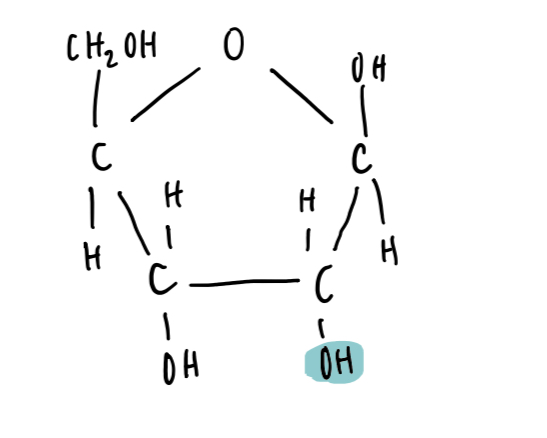
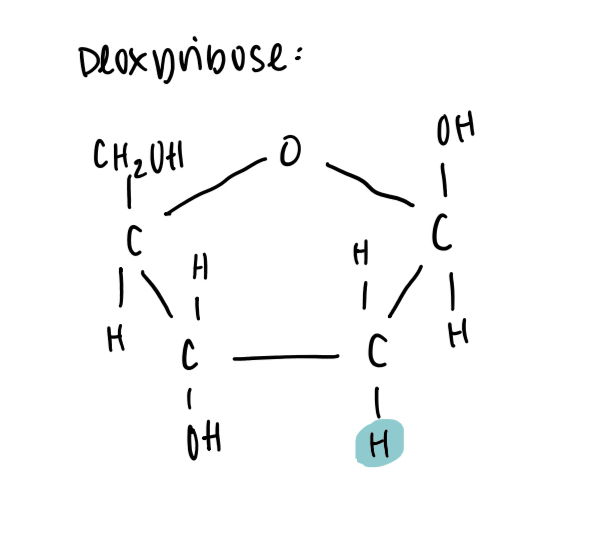
Ribose vs deoxyribose
Deoxyribose has C2 bonded to 2 H atoms, ribose has C2 bonded to H on top and OH on bottom
Ribose structure
Deoxyribose structure
How are glucose molecules joined together (what kind of bonds)
Glycosidic bonds
What is produced when a glycosidic bond is formed between glucose molecules
Polysaccharide + Water molecule
Properties of starch
Insoluble; mixture of amylose and amylopectin
What is starch used for
Main energy storage material in plants
What kind(s) of glucose does amylose contain
α-glucose
What kind(s) of glucose does amylopectin contain
α-glucose
How does insolubility of starch relate to its function
Won’t cause water to enter cell by osmosis
Describe structure of amylose
Unbranched helix chain; stabilised by h bonds within molecule
What kind of bonds are in amylose
α-1,4 glycosidic bonds
Describe how structure of amylose relates to its function
Angles of 1,4 glycosidic bonds => compact coiled structure; more can fit in small space; so good for storage
Describe bonds in amylopectin
In long chain: α-1, 4 glycosidic bonds; when branching off: α-1,6 glycosidic bonds
Describe structure of amylopectin
Long, branched chain of α-glucose
How does structure of amylopectin relate to its function
Enzymes which break it down can access glycosidic bonds more easily; so glucose can be released easily
What is glycogens main function
Main energy storage in animals
Glycogen vs amylopectin
Glycogen
How does glycogen’s structure relate to its function
Compact so good for storing lots of glucose; more branches for enzymes to easily access glycosidic bonds
What kind of bonds are in glycogen
α-1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds
Describe structure of cellulose
Long unbranched straight chains of β-glucose linked together by many hydrogen bonds to form strong fibres
How does structure of cellulose relate to its function
Strong fibres due to many hydrogen bonds provide structural support for plants
What is sucrose made of
A-glucose and fructose
What is maltose made out of
Alpha-glucose and alpha-glucose
What is lactose made up of
Glucose and galactose
How are fructose, galactose and glucose similar/different
Same molecular structure, different structural formula
What is a carbonyl group
C=O
What is a carboxyl group
OH
What is a reducing sugar
A sugar which can donate electrons (Can be oxidised)
Examples of reducing sugars
All monosaccharides; some disaccharides (maltose)
What is a non-reducing sugar
A sugar which cannot donate electrons (cannot be oxidised)
Which part of a sugar gets oxidised
Carbonyl group C=O loses O
How does Benedict’s test work
Sugar reduces soluble copper sulphate to insoluble copper oxide
What colour is copper (i) oxide formed in Benedict’s test
Brick-red
What is Benedict’s solution
Blue solution containing copper (I) sulfate ions
Is Benedict’s test quantitative or qualitative
Semi-quantitative; degree of colour change gives approximate indication of how much reducing sugar is present; not exact
Examples of non-reducing sugars
Sucrose
Test for non-reducing sugars
Add HCl; water bath; neutralise with sodium hydrogencarbonate (use indicator to identify when); add a little more to make slightly alkaline; then do Benedict’s
How does test for non-reducing sugars work
Acid hydrolyses glycosidic bonds; resulting monosaccharides will able to reduce the copper sulphate
How do you test for starch
Iodine test - add a few drops of orange/brown iodine in potassium iodide solution
How does iodine test work
Iodide ions interact with centre of starch molecules; resulting complex has blue-black colour
Why is iodine put in potassium iodide solution for starch test
Iodine is insoluble in water