FIX THIS Official ICVT intro. Final Exam Flashcard set
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
Types of acute coronary syndrome
just the names
Unstable angina
non predictable
Stable angina
predictable
ST-elevation Myocardial infarction (STEMI)
complete occlusion (100%)
Non ST-elevation Myocardial infarction (NSTEMI)
Sub-occlusive (97-99%)
counterpulsation or IABP que es
IABP Intra-aortic balloon pump
assist heart in pumping blood (reduce workload)
intracorporeal in relation to cardiac assist devices
they refer to mechanical devices implanted within body.
relation to cardiac assist these devices augment the hearts ability to pump blood
what are extracorporeal devices in relation to cardiac assist devices
mechanical systems that support heart function outside of body,
blood can be pumped outside the body and return to pt.
heart to weak to pump.
cardiogenic shock
what cardiac assist devices are intracorporeal
IABP
impella CP
PHP+
What is special about ECMO as a cardiac assist device
not only does it function to provide cardiac support but it also provides respiratory support by acting as a artificial lung
important during cardiogenic shock
what volume of blood does the IABP balloon displace
25-50 ml
what cardiac assist devices are extracorporeal
Tandem heart
VA-ECMO
Inflation during IABP does what and during when
augments diastolic pressure
^ art pressure which support hemodynamics
more importantly
displacement of blood retrograde in aorta to help perfuse coronary arteries
occurs during diastole
when does deflation of the IABP occur on an ECG
Onset of systole
peak of R wave
Tandem heart
short term extracorporeal centrifugal flow punmp
Impella
short term percutaneous catheter with a microaxial continuous non pulsatile pump
extracorporeal membranous oxygenaton ECMO
provides short-term full cardiopulmonary support for pt in sever shock
when does inflation of the IABP occur on an ECG
beginning of diastole
T wave on ECG
types of foreign body retrieval devices
Amplatz goose neck snare
EN Snare endovascular snare system
Forceps
what occurs during diastole in relation to IABP
IABP inflates helping increase hemodynamics
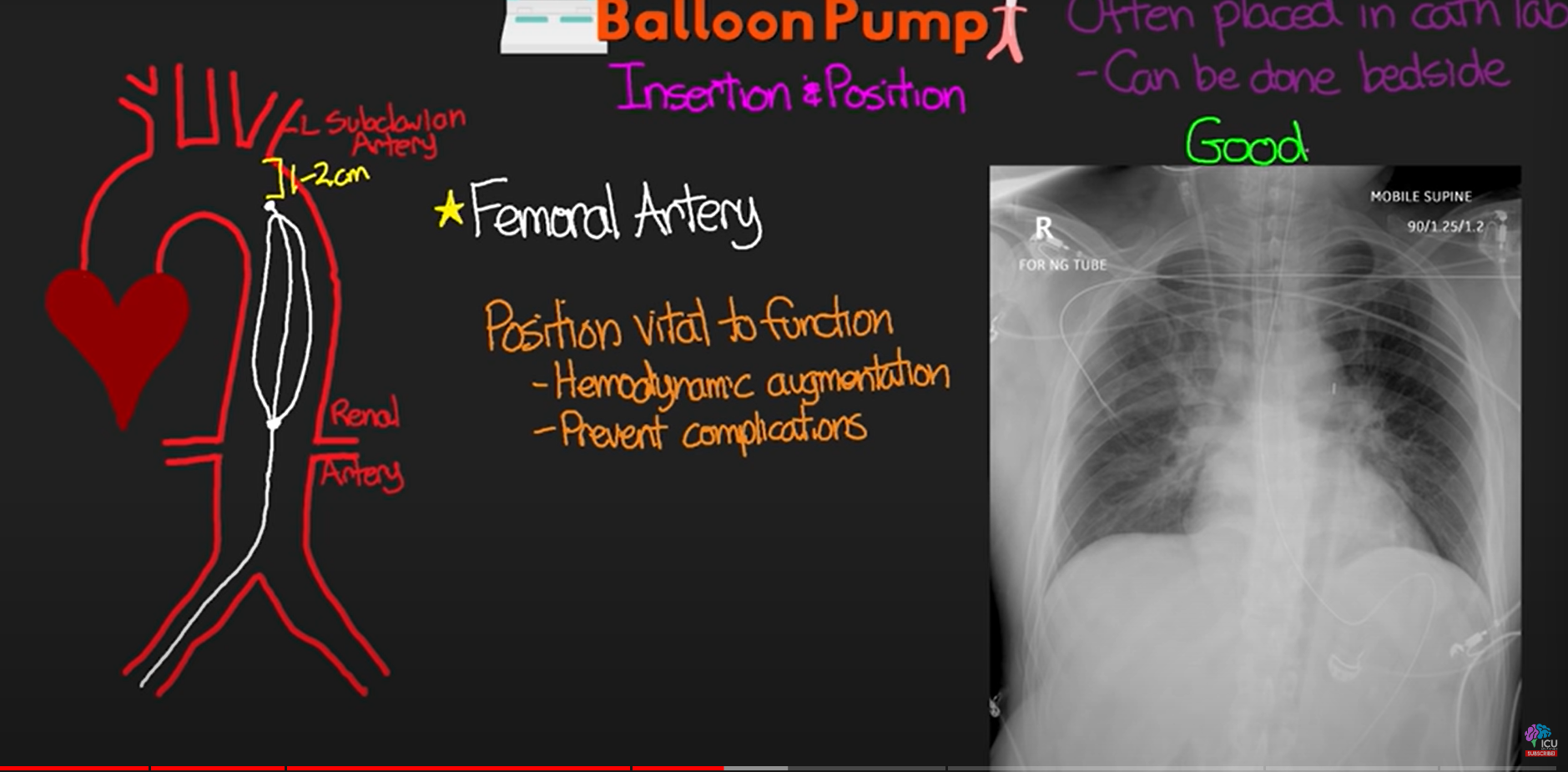
insertion of IABP occurs where
Left or right femoral artery
IABP location
tip of balloon resting just before aortic arch, 1-3 cm distal to left subclavian artery
bottom of balloon
just above the renal arteries
Type of gas used to pump balloon in IABP
helium
what is necessary during the consideration of IABP in a pt
a moderately functioning ventricle. The IABP only assists in hemodynamics.
deflation during IABP does what and during when
4 things
OCCURS DURING ISOVOLUMETRIC CONTRACT
lowers central aortic pressure
decreases afterload- decrease workload- dec. myocard. o2 demand. - contract greater amount of blood- augment hemod.
decreases myocardial oxygen demand
when does the IABP deflation occur
deflation occurs during isovolumetric contraction
when the heart begins to contract but the heart has not overcome the pressure which has not opened the AV valve. deflation lowers that central aortic pressure. (vacuum)
Unstable Angina
minimal exertion
usually more sever and prolonged
indicates significant risk of heart attack soon
Stable angina
predictable
pains is reproducible and felt as mild discomfort
dyspnea
nausea
sweating
lightheadedness
STEMI means
ST Elivated Myocard Infarc.
complete vessel occlusion
sever form of heart attack
muscle being deprived of oxygen
results in ST-segment elevation on an ECG & is associated with extensive heart damage
what is NSTEMI
Non-ST segment elevation Myocard. Infarction
decreased flow to part of heart muscle
leads to damage to heart muscle
indicated by ^ cardiac biomarkers but no persistent ST segment elevation
Lethal arrhythmias
asystole
V-fib
V-tach (pulseless) heart beating fast/disorganized, inadequate blood circulation
Coronary arteries
Blood vessels that supply the heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients.
sterile vs non sterile
non sterile does not eliminate most pathogens therefor non sterile products are administired to regions of human body that have a high density of natural microbial flora, physical/immunological barriers to infection.
sterile- no organisms
What does Pascal’s law states that…
pressure applied to a liquid at any point is transmitted equally in all directions.
Types of temporary pacing
Transcutaneous
Transvenous
Transcoronary
Transesophageal
Transthoracic epicardial
Pacing terminology
Capture
successful cardiac muscle depolarization triggered by cardiac pacing
Pacing terminology
Current (output)
The strength of the electrical impulse created by the pacemaker generator
Pacing terminology
Sensitivity
The ability of the generator to detect and analyze the heart’s intrinsic electrical activity
Pacing terminology
Threshold
Minimum amount of energy required to stimulate cardiac muscle depolarization
Pacing terminology
Pulse generator
the battery and control of the console of the pacemaker
Pacing terminology
Pacing rate
rate of impulses sent to stimulate the cardiac muscle
Placement of transcutaneous pacing pads
Right pec. & left lateral mid axillary
R. upper right torso, mid clav. line btx nip & clavicle
L. below left shoulder blade btx left subscapular area & left midaxillary line
What is a transducer in regards to a pressure measurement system
device used to convert one form or energy to another .convert mechanical pressure into an electrical signal to display the pressure within blood vessels.
What must be done to a transducer to get accurate readin levels.
leveling should be performed before balancing (zeroing)
leveling - same level as the tip of the IV catheter (important for right heart measurements & a carpenters leveler is rq’d, not always for left)
balancing - pressure measurement system btx trasnducer & the monitor. must be reset to local atmospheric pressure in room by stopcock near trasnducer.
transducer placement
phlebostatic axis
the 4th intercostal soace at the mid-anterior-posterior diameter of the chest wall
thrombectomy
operation where a clot (thrombi) is obstructing blood flow is removed to restore blood flow.
can occur in cerebral, coronary, peripheral lung renal, arteries ETC.
MINOR cath lab emergencies
UHBVBE
Urticaria
Hypotension
Bronchospasm
Vascular incidents
Bradycardia
Edema
Major complications in cath lab
VSSAAD
Vasospasm
Shock
Stroke
ACS
Arrythmias
Death
Moderate complications in the cath lab
HVFB
Headache
Vomiting
Facial edema
Bronchospasms mild
arrhythmias that occur during major complication
Pulseless VT
VF
Asystole
3rd degree heart block
JL4 Catheter
Angiographic catheter for coronary ostium
valves during systole
Open
AO & PA
closed
TV & MV
valves closed during systole
TV & MV
valves opened during diastole
open
TV & MV
valves during diastole
Open
TV &MV
closed
AO & PA
JR4 Catheter
Angiographic catheter for coronary ostium
Inherent rate of ventricle
40-20
Pigtail Catheter
Angiographic catheter for coronary ostium
Swan-Ganz Catheter
Flow-directed, balloon-tipped catheter for right heart pressures
Andreas Gruentzig
Performed 1st successful percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty
Heart Size
Roughly the size of a clenched fist
Heart Location
Slightly behind and to the left of the sternum
Blood Flow Path
Vena cava, RA, TV, RV, PA, lungs, PV, LA, MV, LV, AorticV, Ao
Vessel representing oxygen saturation, which ones have which
Depleted: venous; Rich: arterial
Heart Layers
Fibrous pericardium, parietal layer of serous pericardium, pericardial cavity, epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
Heart Valves
Semilunar (aortic & pulmonic), Atrioventricular (mitral & tricuspid)
Arterial Layers
Endothelium, elastic tissue, circular smooth muscle, connective tissue with elastic fibers
Coronary Arteries
Families, major coronaries, and location
SA Node
Inherent rate: 60 - 100 bpm
AV Node
Inherent rate: 60 - 40 bpm
Purkinje Fibers
Inherent rate: 40 - 20 bpm
Radiography Projections
RAO/LAO/Cra/Cau with specific hints for each
Radiation Safety
ALARA principle and 3 principles of radiation safety
Contrast Media
Radiopaque, radiolucent, filtration/metabolism, and contrast reactions/allergies
LHC vs RHC
Differences in measurements and procedures
IVUS vs OCT
Comparison of intravascular imaging techniques
iFR vs FFR
Comparison of functional assessment techniques for CAD
POBA vs Stenting
Comparison of angioplasty techniques
Access Site Hemostasis
Understanding of NAVL and manual compression hand placement
Endomyocardial Biopsy
Indications and location of myocardial samples retrieval
Angina
Chest pain or discomfort caused by reduced blood flow to the heart
RCIS
Registered Cardiovascular Invasive Specialist
ALARA
As low as reasonably achievable principle in radiation safety
PTCA
Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty
POBA
Plain old balloon angioplasty
LAD
Left anterior descending artery
CX
Circumflex artery
RCA
Right coronary artery
RAO/LAO/Cranial/Caudal
Different radiography projections
What does a LHC test for and where does it travel through
enters groin or wrist
assesses
coronary arteries
left ventricle
RHC enters and test for
through right side of the heart
assess
pressures within heart chambers
function of right ventricle
conditions
pulmonary hypertension
congenital heart disease
certain heart failures
iFR
Instantaneous wave free ratio
FFR
fractional flow reserve
ICE
Intracardiac echocardiagram
iVUS
resolution?
intravascular ultrasound
poor
OCT
resolution?
optical coherence tomography
good
NIRS
near infrared spectroscopy
IVUS, whats it do
uses catheters with ultrasound tech,
view and analyze vessel from inside out
What is IVUS optimal for
deep tissue penetration
vessel size
plaque morphology
extent of vessel narrowing
guide interventions such as stent placement
OCT uses
light waves, near infrared light
iVUS vs OCT what does what better
iVUS deeper tissue penetration
OCT superior image quality