Food Tech: Provenance
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Where do different sweeteners come from?
Sugar - Sugar cane / sugar beet
Honey - Bees make it from nectar
Maple syrup - Sap of maple tree
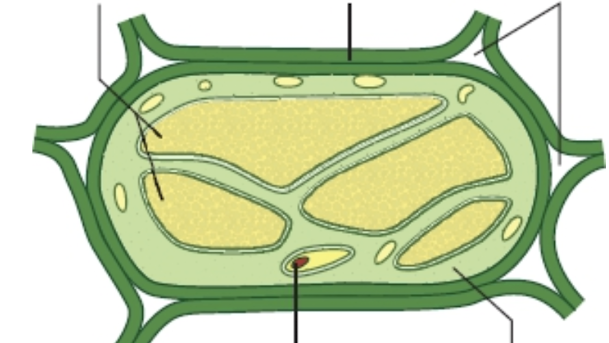
Label a fruit cell
Vacuole - sap, sugar, pigments, salts
Cytoplasm - Jelly, pigments, fat
Cell wall - cellulose (NSP)
What are the categories of fruits and some examples?
Category | Examples |
Citrus | Lemon, orange, limes |
Soft / Berries | Black currents, blue berries |
Hard | Apples, pears |
No category | Bananas, melon, kiwi |
What causes colour in vegetables?
Chlorophyll - green
Carotenoids - orange / yellow
Anthocyanins - Blue / Red (beetroot)
What are the categories of vegetables and examples?
Leaves | Cabbage, spinach, lettuce |
Fruit | Cucumber, aubergine, peppers |
Roots | Carrot, beetroot, swede |
Flowers | Broccoli, cauliflower, artichoke |
Bulbs | Onions, leeks, shallots |
Stems | Celery |
Tubers | Potatoes, yams |
Seeds / Pods | Peans, runner beans, broad beans |
Advantages and disadvantages of locally produces fruit and veg
Fresher | Less choice |
Less food miles | Different sizes |
Less energy for transport | More expensive |
Supporting local farmers |
What benefits do green/glass houses have?
Control and monitor conditions
Increase yield
Grow foods out of season
What are the categories of meat and examples?
Offal | Kidney, liver, tongue |
Poultry | Chicken, turkey, goose, duck |
Game | Venison, rabbit, pheasant |
Meat | Beef, lamb, pork |
How is CHicken reared?
Barn cage
Laying cage systems / enriches colony cages
Free range
Organic
What does the red tractor logo mean?
The food comes from farms and food companies that meet industry standards for food safety & hygiene, animal welfare and environmental protection.
What is intensive farming of crops?
Uses chemicals and pesticides to increase yield → (Concerns about long term health affects on us & environment)
Also called factory farming
What is intensive farming of animals?
Kept indoors to control their diet, movement, breeding and disease control
This maximises yeild
What is organic farming? Why do people choose it?
Grown without chemicals or artificial fertilisers or pesticides
Animals raised without growth hormones or antibiotics.
No genetically engineered ingredients
Certified by the soil association
Tastes nicer, respects environment and wildlife, concerned about health affects of chemicals.

How are fish caught? 10 methods
Trawling | Common. Nets, pulled along sea bed |
Dredging | Metal cages pulled across sea bed |
Gill netting | Curtains of net suspended in sea |
Harpooning | Lunge a long metal pole into fish |
Jigging | Grappling hoot attached to line targets fish |
Long lining | Lines for miles, strung with bait |
Pole & line | Fishing pole and bait targets fish |
Purse seining | Large net around school of fish |
Traps and pots | Wire cages with bait put on sea floor |
Cyanide | Explosive stun or kill fish so easier to catch |
What are the categories of fish and examples?
White (round) | Cod, haddock |
White (Flat) | Plaice, dover sole |
Oily | Tuna, salmon, sardines, herring |
Shellfish, molluscs | Oysters, scallops, mussels |
Shellfish, crustaceans | Lobster, crab, prawns |
What does sustainable fish supply mean?
Farmed or caught with minimal damage to the marine environment and other wildlife.
Marine Stewardship logo confirms sustainable fishing.
What can be done to make catching fish more sustainable?
Larger holes in nets to let smaller fish out
Releasing unwated species if accidentally caught
Sinking long lines deeper to reduce bycatch
Set up marine reserves to allow stocks to recover
What are the three groups of fish farming?
Farming - Whole process is in captivity
Sea rearing - Young fish caught in wild, grown in controlled environment
Sea ranching - Young fish bread in captivity then released into the wild.
What are the advantages of fish farming?
Less transport - grown near to market
Produce higher quantities
Doesn’t reduce wild fish stock
Protected from weather changes
Cannot escape
Protected from predators
What are the disadvantages of fish farming?
Expensive to run
Fed fish which would be food for wild fish
Use pesticides and antibiotics
Drugs pollute surrounding water
Waste is polluting
Spread disease quickly
What is primary processing?
Processing raw materials into ingredients
Milling wheat into flour
Heat-treating milk
Extracting oil from crops
How is flour processed?
Wheat grain removes from plants
Processed through milling
Cleaned to remove stones
Conditioned - water softens outer layer, so easy to remove floury endosperm
Gristing - blended to make different kinds of flour
Grains are crushed
Wholemeal flour ahas all layers of wheat
Brown has some layers removed
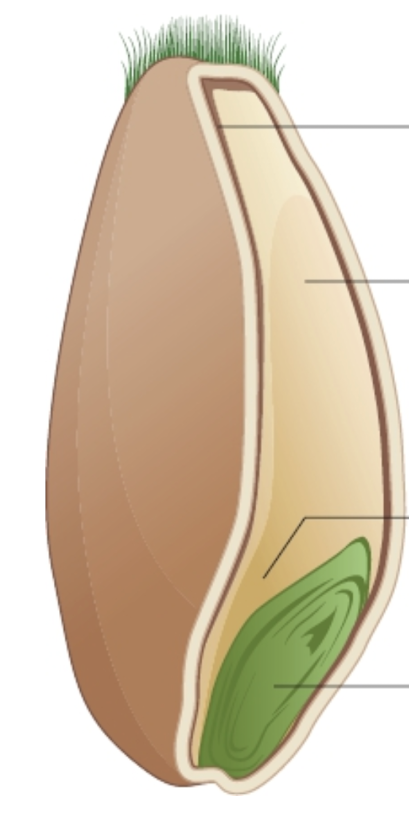
Label a wheat grain
How is milk processed?
Milk is an emulsion (mostly water with fat globules)
The milk is homogenised (forced at high pressure through small holes)
This break up the fat and evenly disperses it through the milk
Cream doesn’t sit on top
What methods of heat treatment are used on milk?
Pasteurised - Heated to 72ºc for 15 secs. Quickly cooled below 6º (destroys pathogenic micro-organisms. Stores for short time)
Sterilised - Heated to 104ºc for 40 mins. Cooled quickly (destroys nearly all micro-organisms & enzymes. Extends storage.)
UHT - Heated to 135ºc for 1 sec. Put in sterile, sealed containers (Extend storage up to 6 months unopened
Canning - Packed in aseptic cans, sterilised. (Double seam / hermetic seal)
What are Low temp methods of treating milk?
Cold temp slows bacteria growth (don’t destroy). Freezing temp (-18ºc) makes it dormant
Chilling - Fridge 0-5º
Blast Chilling - Reduces to below 3º in under 90 mins
Cook-chill - Short-term preservation. 4-5 days Cooked to 70º, portioned, chilled within 30 mins. Reduced to 3º in 90mins. Must be heated immediately once out of fridge.
Advantages of cook-chill
No skill to prepare
Max quality fresh food for long time
Save energy at home
Available in single portions
Little waste
Consistent quality
Doesn’t destroy nutrients
What is the danger zone?
The temp at which micro-organisms can replicate quickly
5º - 63º
How is flour made into bread?
Ingredients delivered to bakery
Mix ingredients at high speed. Dough is divide. Passes along conveyor belt and left to prove
Continuously kneaded for 2 mins. Dropped into pre-greased baking tins.
Second proving for about 50 mins
Bake in oven for 20 mins at 230º
Removed from the pan and cooled for up to 1.5 hours. Passed down conveyor for slicing and to be bagged.
What is milk made into?
Butter - Churning cream to remove liquid
Yoghurt - Fermenting milk with harmless bacteria (Milk pasteurised, homogenised, incubated with bacteria, left to set to reach correct acidity, add flavours)
Cheese
How is cheese made?
Milk pasteurised, cooled to 30º
started culture of bacteria added
Rennet added and left to set
Curd is cut so whey is released (soft → whey drains naturally, hard → curd heated and put on top of each other to release more whey)
Cheese is milled, pressed into moulds
Left to ripen
What is clarified butter?
Melt butter and use the fat that rises to the top.
Ghee is a form of clarified butter
What are the different types of cheese?
Hard | Cheddar, Parmesan |
Semi-hard | Cheshire |
Soft ripened or bloomy rind | Brie |
Blue | Blue stilton |
Washed rind | Stinking Bishop |
Fresh | Mozzarella, cottage cheese |
What are the advantages of preserving?
Lasts longer, shop less, longer shelf life
Buy products when out of season, more rnage of foods
Prevents micro-organisms multiplying
What are the disadvantages of preserving?
Contains lots of fat, sugar and/or salt
Not much fibre
Lose nutrients during processing
Additives to restore colour lost in processing
More expensive
Why are frozen food products increasing?
More choice
Saves time
Extends shelf life
More consumer demand
Lack of cooking skills
What are some methods of Freezing?
Blast - -30º / -40º cold air circulates.
Fluidised bed - freeze small fruits and veg so they don’t stick together. Air causes food to float above conveyer
Plate - between 2 cold plates
Cryogenic freezing - liquid nitrogen -190º
Ways of dehydrating foods
Cheaper, easier to transport, long shelf life
Sunlight - slow evaporation: raisins
Fluidised bed drying - Clump dry particles into granules: potato, coffee
Accelerated freeze-drying AFD - quick frozen, then placed in vacuum under pressure. Heat vaporises ice to steam
Oven-drying - warm oven: herbs, teas, veg
Spray drying - foods which may be damaged by too much heat: milk, coffee
Roller drying: baby foods, mash potato
Methods of Chemical preservation
Smoking - over wood, gives flavour
Add acids, salt, sugar
Vinegar - bacteria can’t survive in low pH
Salt - ham / bacon / fish like tuna in brine (salt and water solution) Reduce water via osmosis
Sugar - Reduces water, so no bacteria. Preserves. candied fruits.
Methods of Modified / controlled atmosphere packaging MAP / CAP
Slows bacteria growth, lack of oxygen, longer shelf life (bananas/cheese)
Package fresh foods in peak condition. ‘Gas flushing’ O2 N CO2 Sealed with hermetic seal
Vaccum packing - remove air (anaerobic), prevent bacteria growth, maintains taste and flavour