ngna william
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
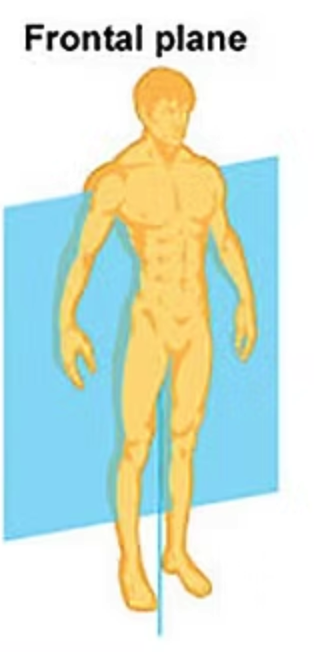
frontal plane
an imaginary vertical plane that divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) sections
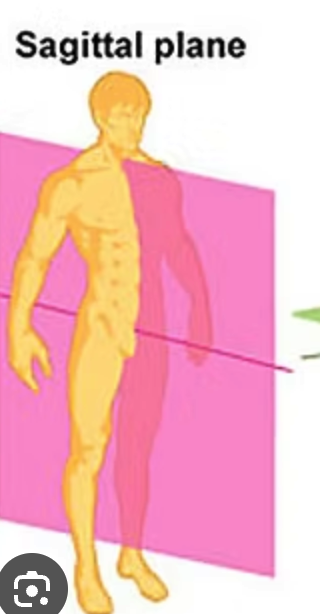
saggital plane
an imaginary vertical plane that divides the human body into left and right sections
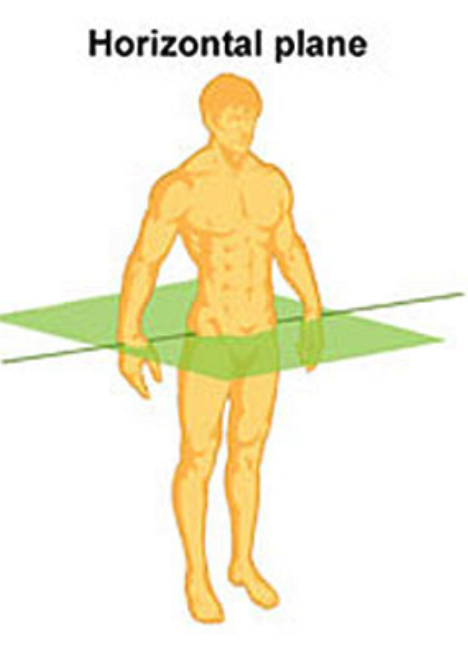
transverse plane
It divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) sections.
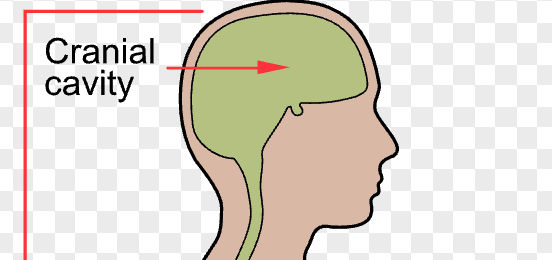
cranial cavity
a hollow space within the skull that houses and protects the brain
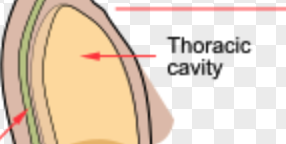
thoracic cavity
a bony and muscular enclosure in the upper torso that houses and protects vital organs.
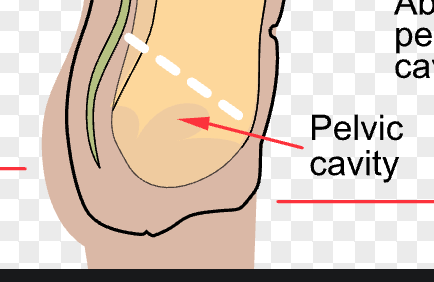
pelvic cavity
a bowl-shaped space located in the lower part of the abdomen, below the pelvic brim
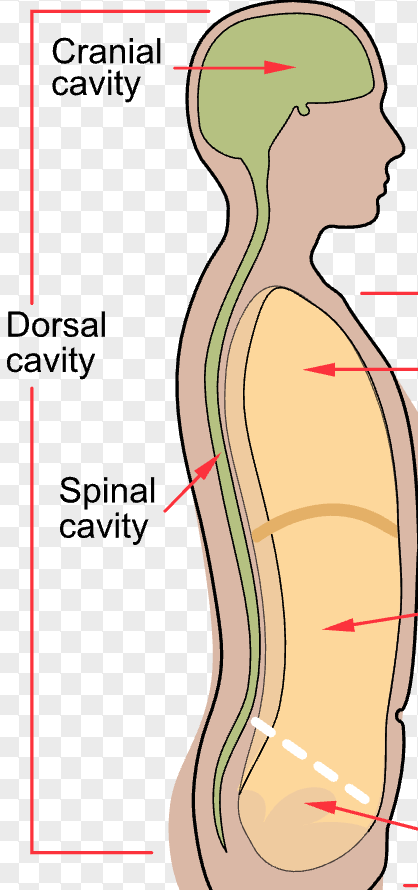
spinal cavity
a cylindrical space located within the vertebral column (backbone) that houses and protects the spinal cord
The Liver is located mainly in what quadrant?
RUQ
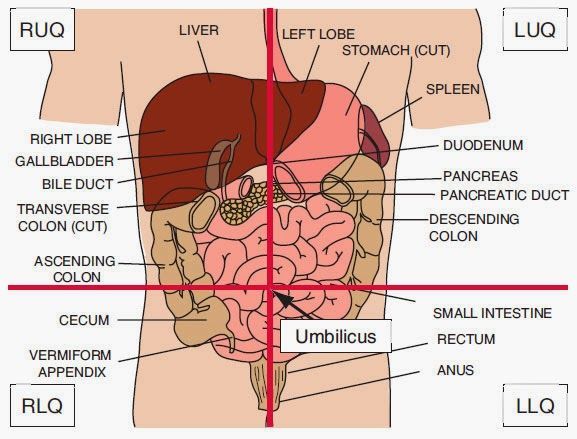
If the patient is complaining of RLQ pain with nausea, vomiting and fever. You might suspect what?
Appendicitis
This is the largest organ in the body and is the first line of defense against pathogens.
Integumentary system
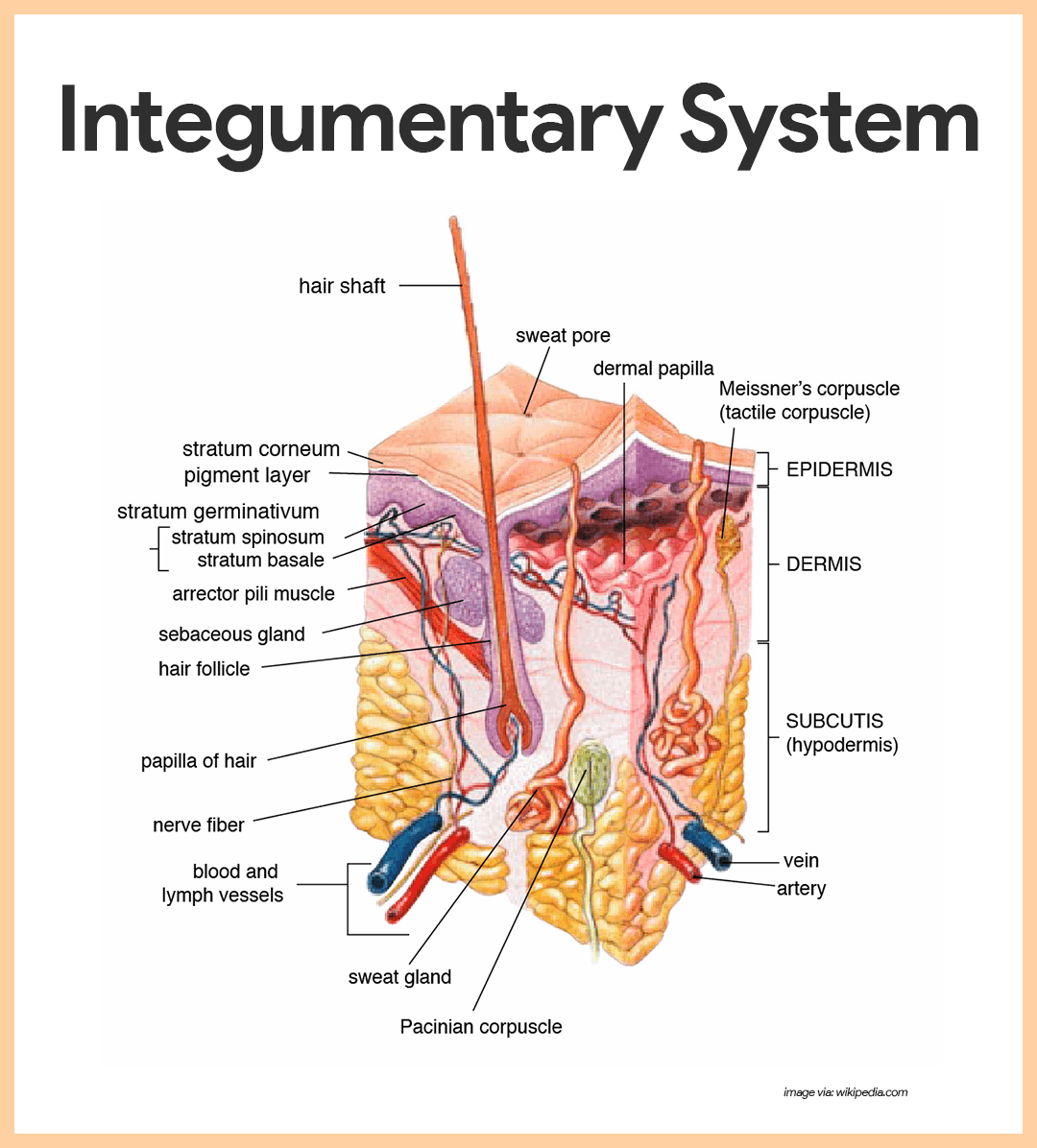
Your patient is pointing to the upper, center of their abdominal just below the diaphragm area, how would you chart this location?
Epigastric region
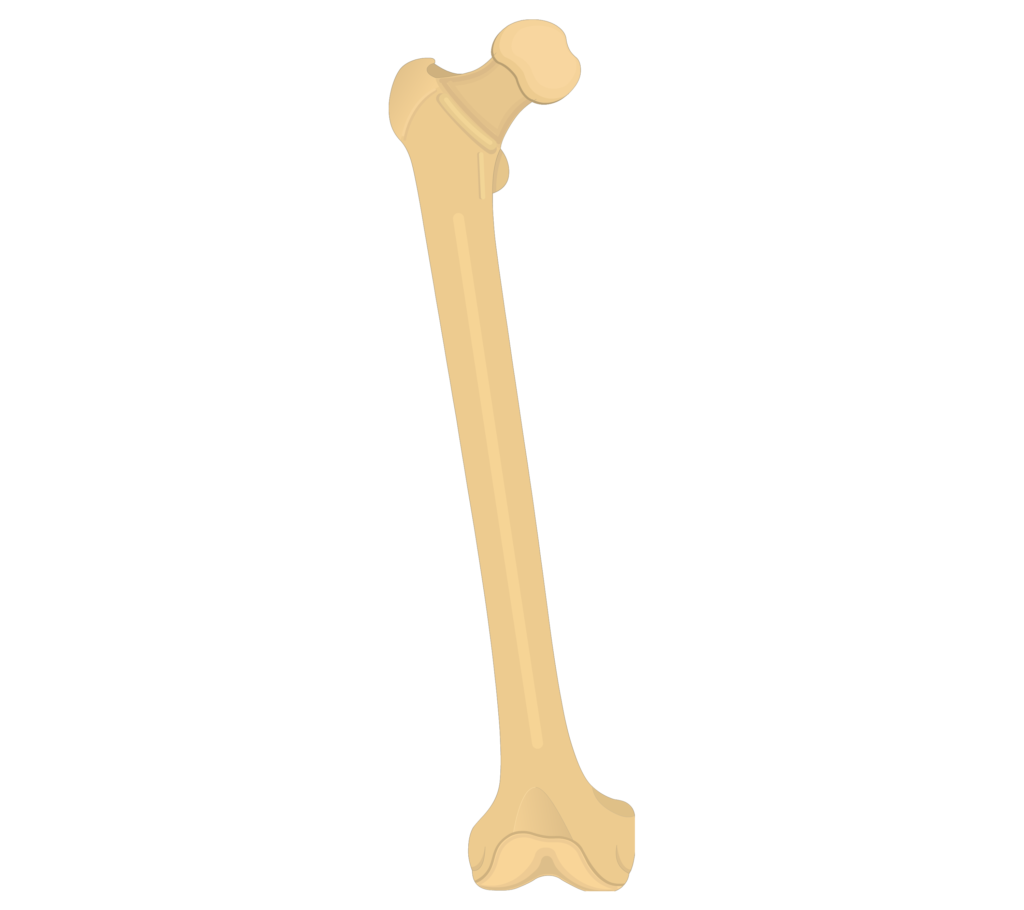
longest, strongest bone in your body
femur
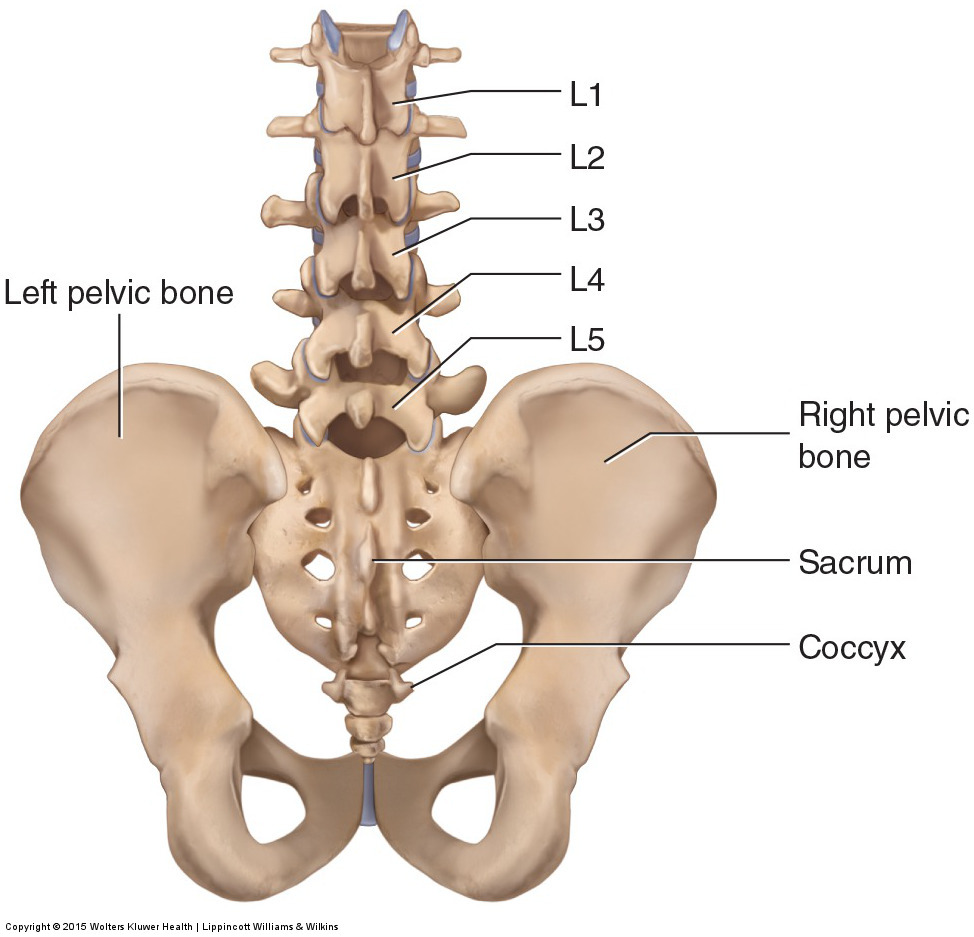
Irregular bones
pelvis, vertebrae
short bones
Carpals, tarsals, bones found in the wrist
FLAT BONES
Skull or ribs
Patella
another name for the knee cap / a Sesamoid bone
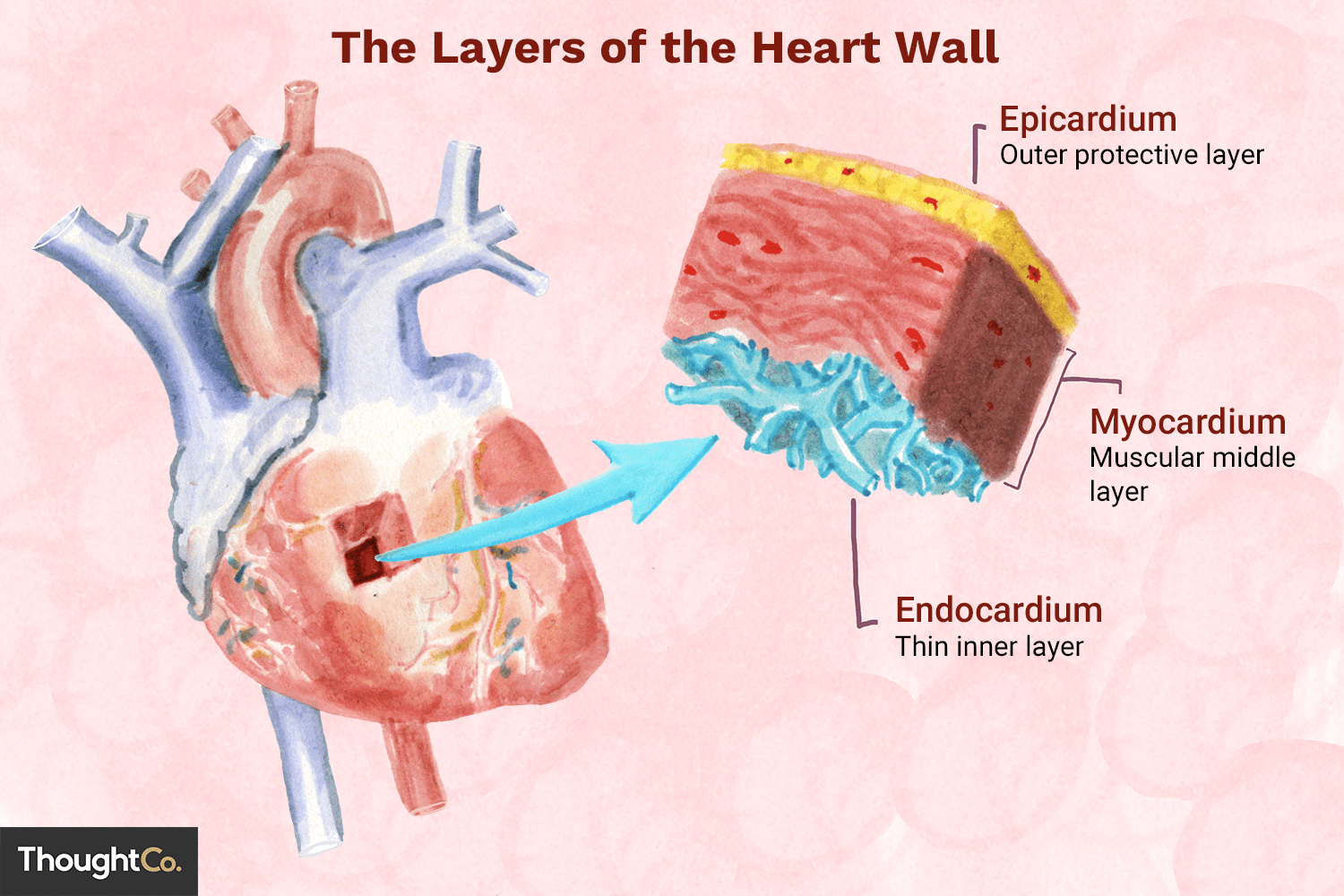
Epicardium
outermost layer of the heart
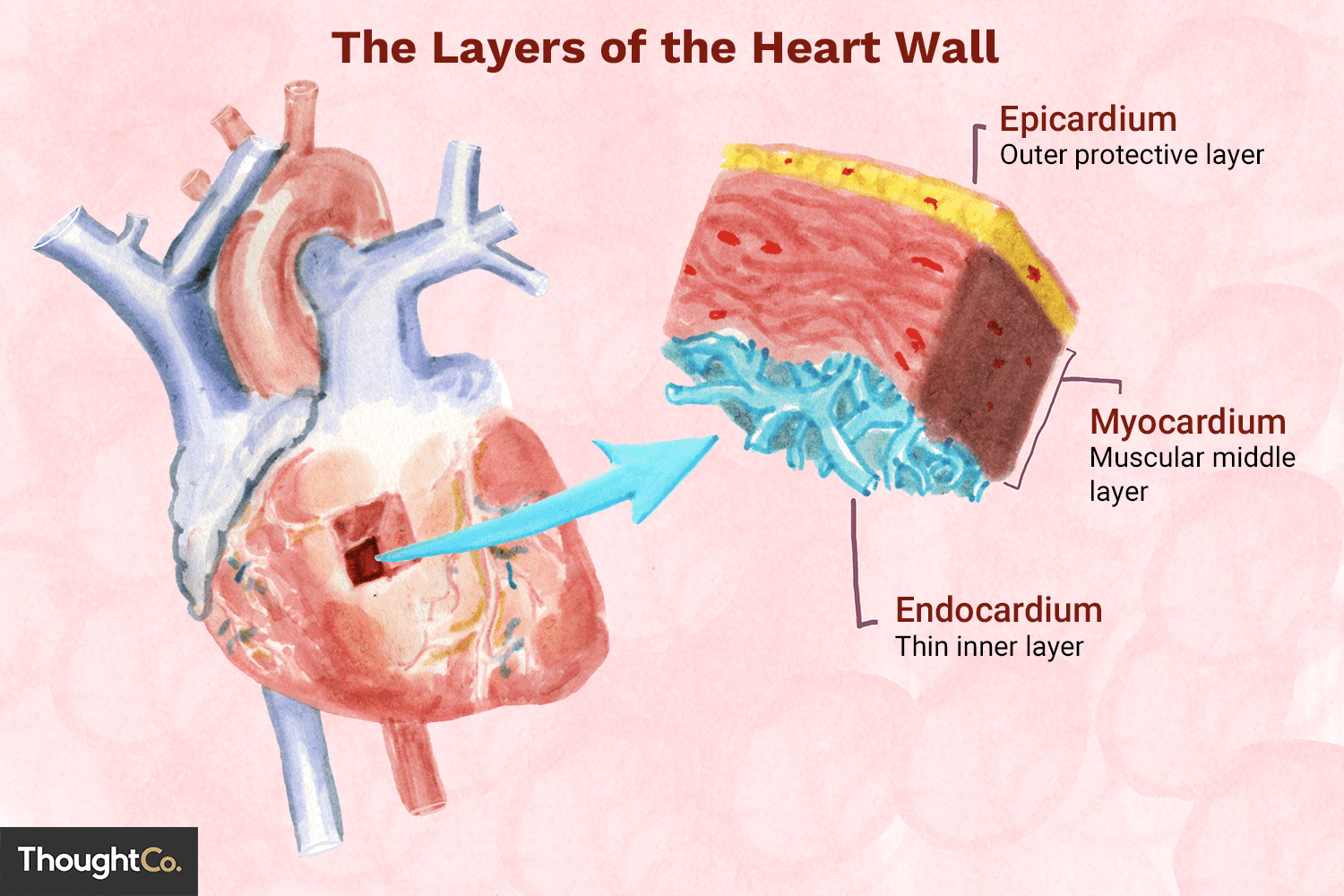
Myocardium
middle layer, muscle and thickest
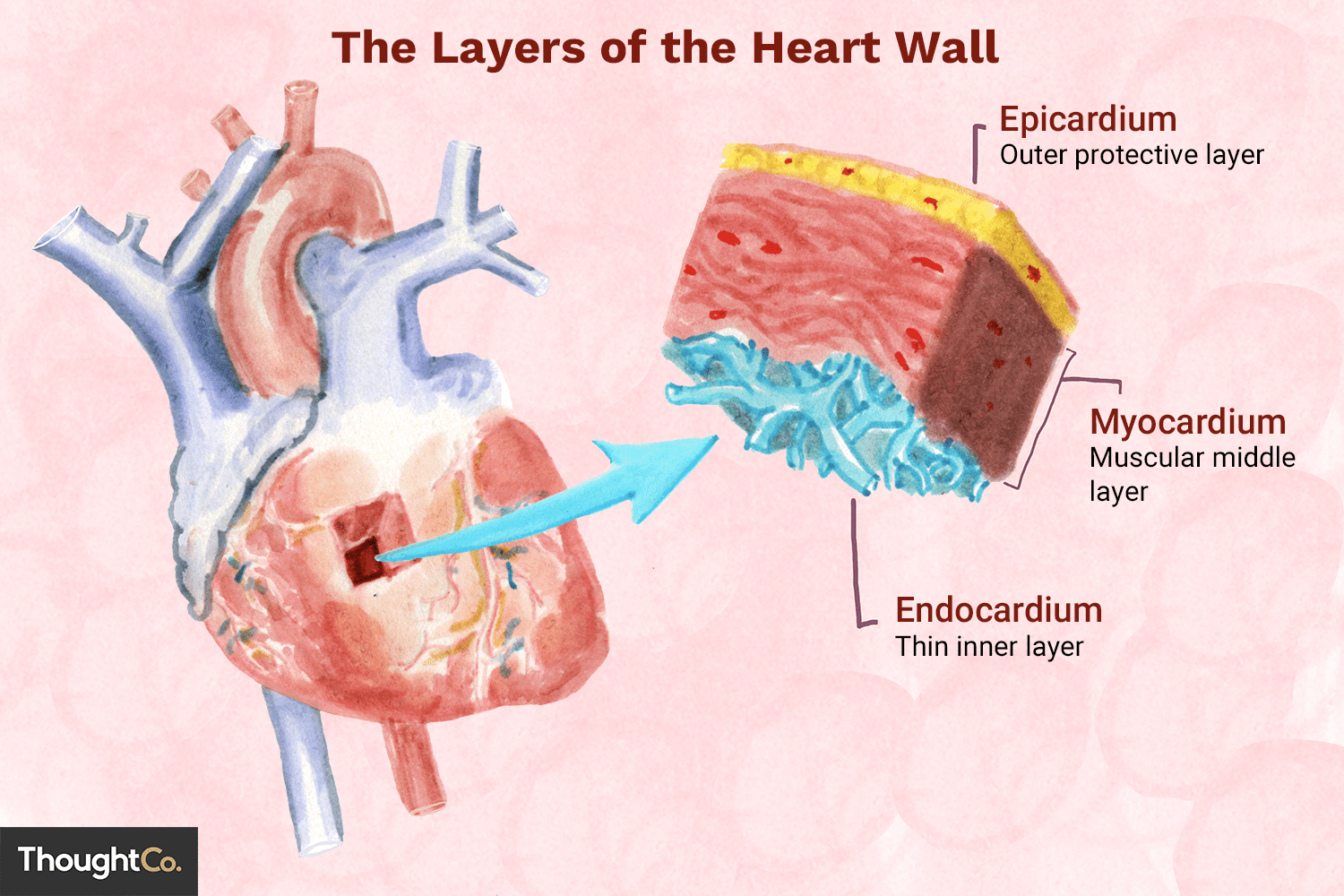
Endocardium
Inner layer, lining the atria, ventricles and valves
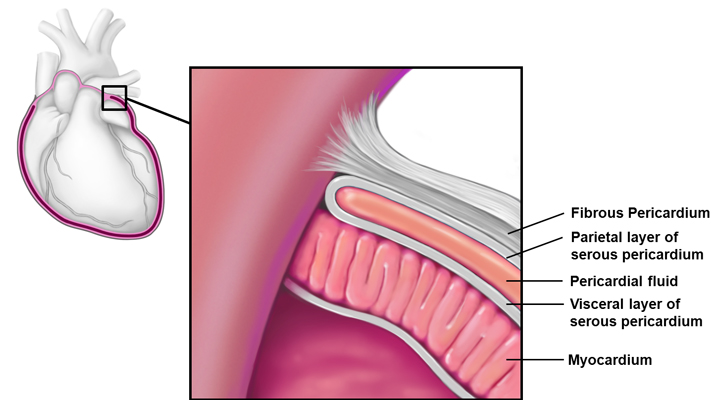
Pericardium
membrane that surrounds the heart
The primary organ of the cardiovascular system is the heart. The heart is a muscle made up of three layers and has 4 chambers. The 2 upper chambers are the ventricles and the 2 lower chambers are the atria
false
Chambers of the heart:
2 upper are right and left Atria
2 lower are right and left ventricles
The circulatory system is considered to a closed circuit.
true
the pathway for a complete electrical conduction system.
SA Node, AV Node, Bundle of His, Bundle Branches, Purkinje Fibers
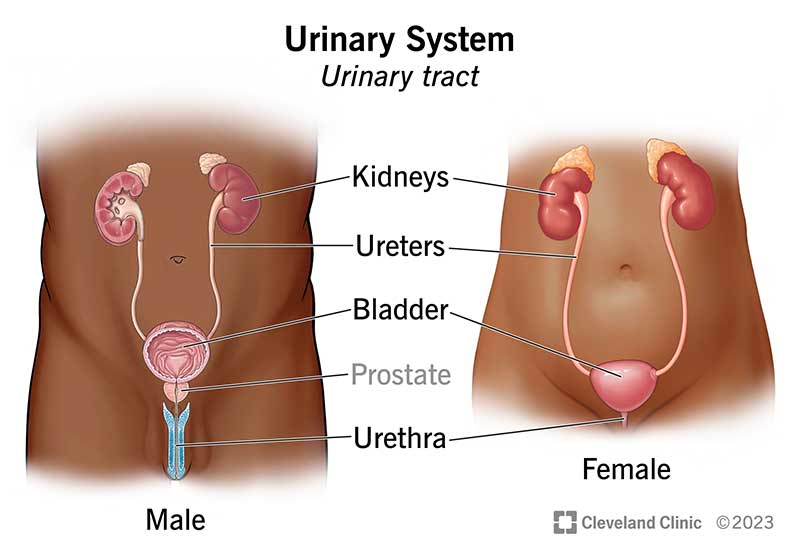
kidney
kidney
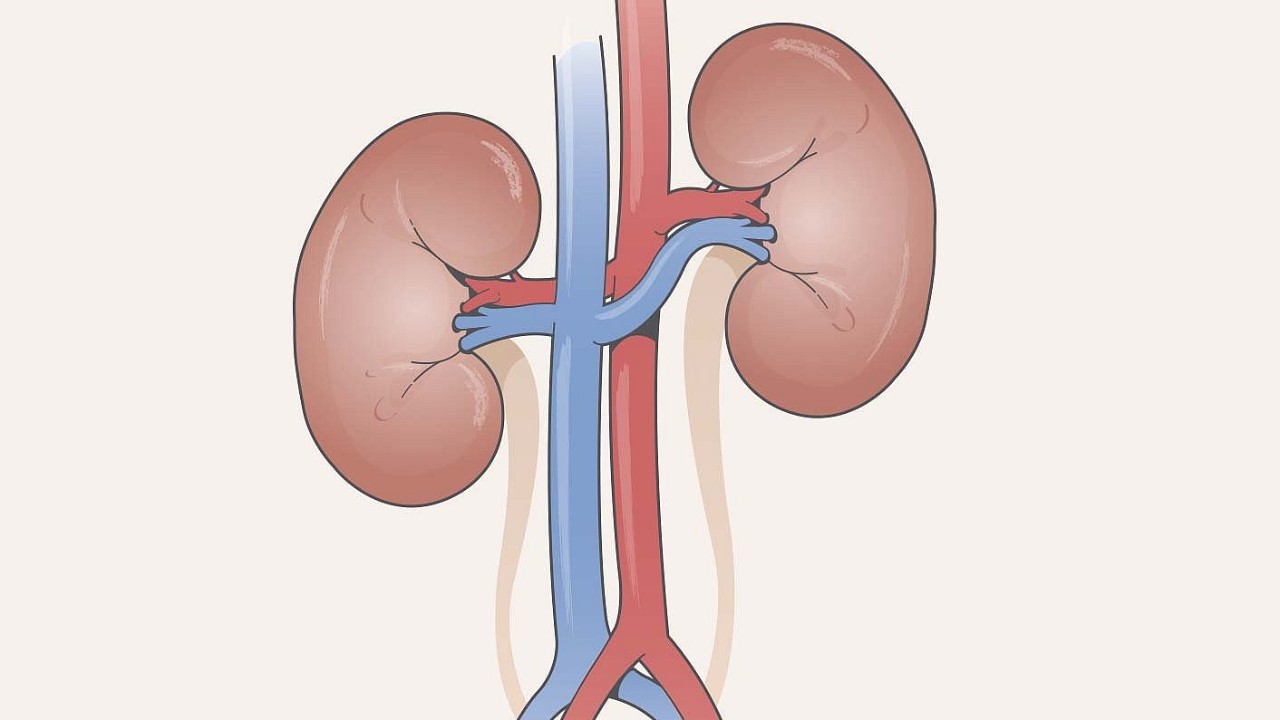
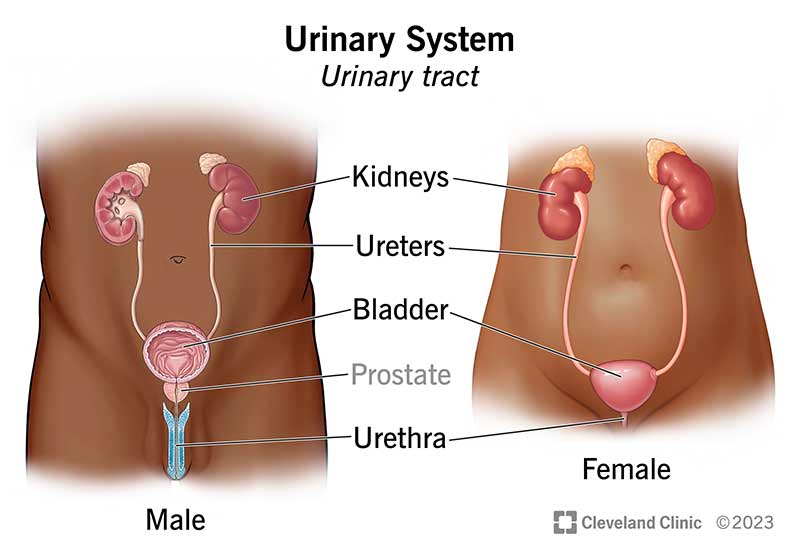
ureters
ureters
bladder
bladder
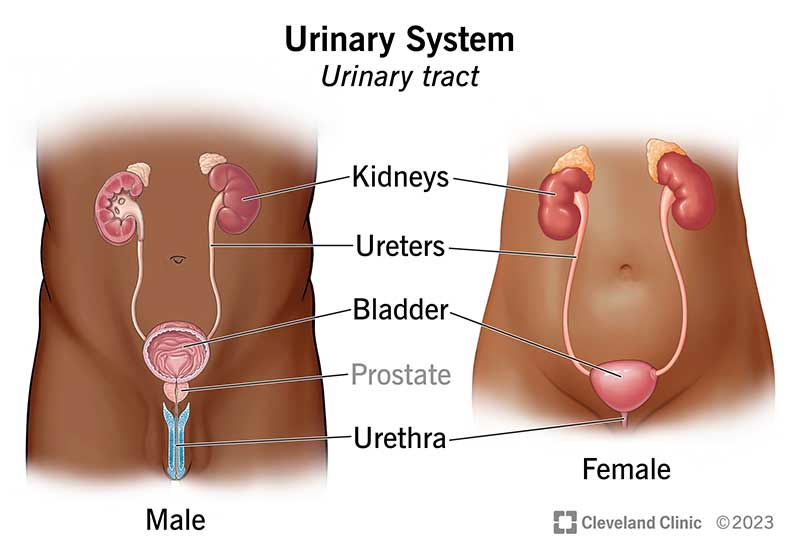
urethra
urethra
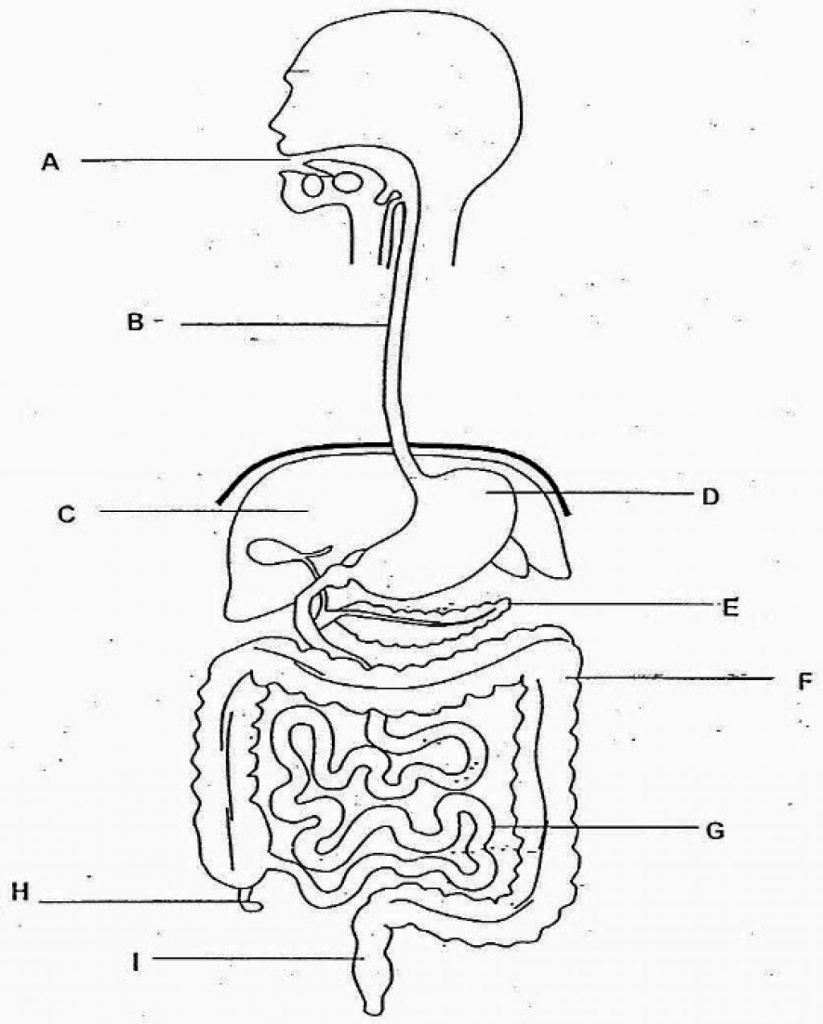
This organ is a part of the gastrointestinal and respiratory system.
pharynx
The adult Axial skeleton has _______ bones while the adult Appendicular skeleton has _________ bones.
80, 126
Which of the following describe what smooth and cardiac muscles have in common.
they are both involuntary muscles and work independently
The Thymus is located behind the sternum. How would this be documented?
the thymus is posterior to the sternum
The most abundant and active sex hormones in males is the ________ and in females it is the ________
Testosterone, Estradiol
esophagus
B
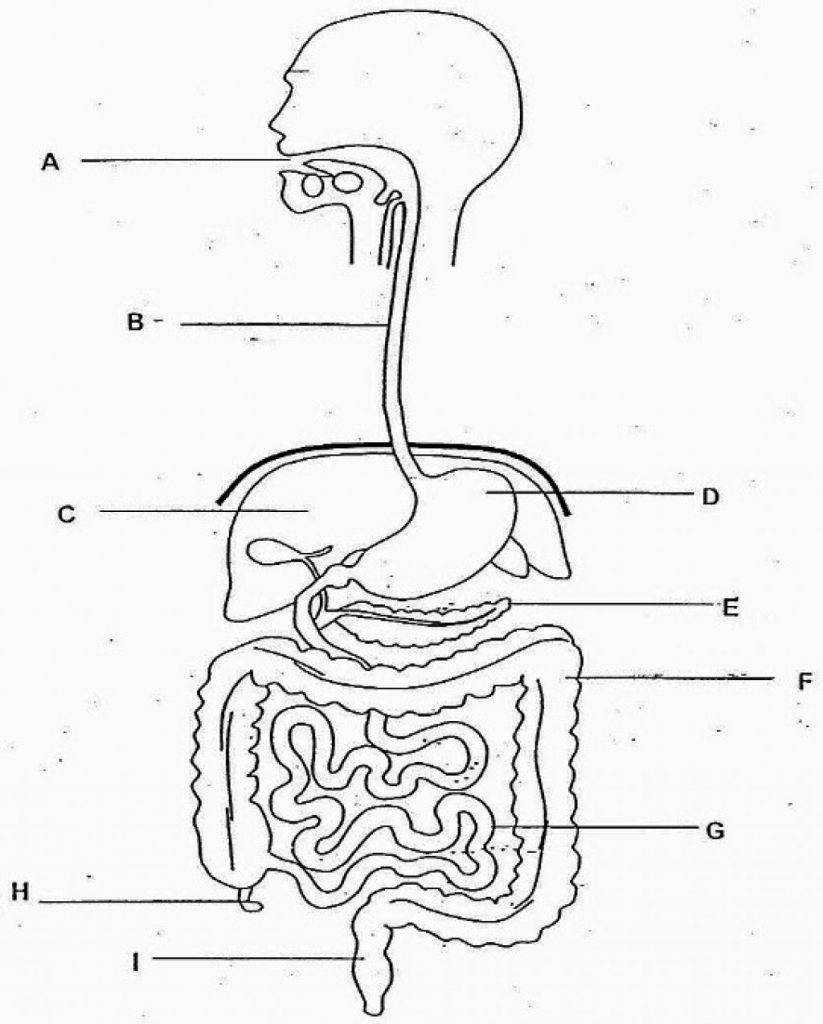
liver
C
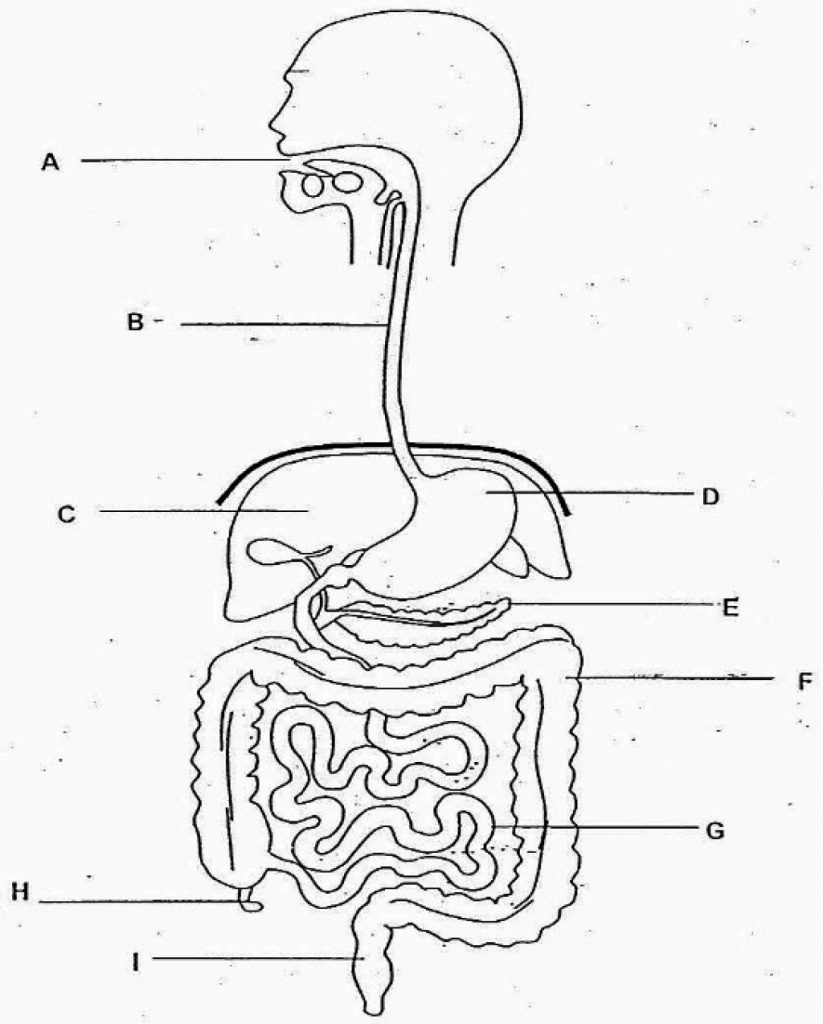
stomach
D

large intestine
F
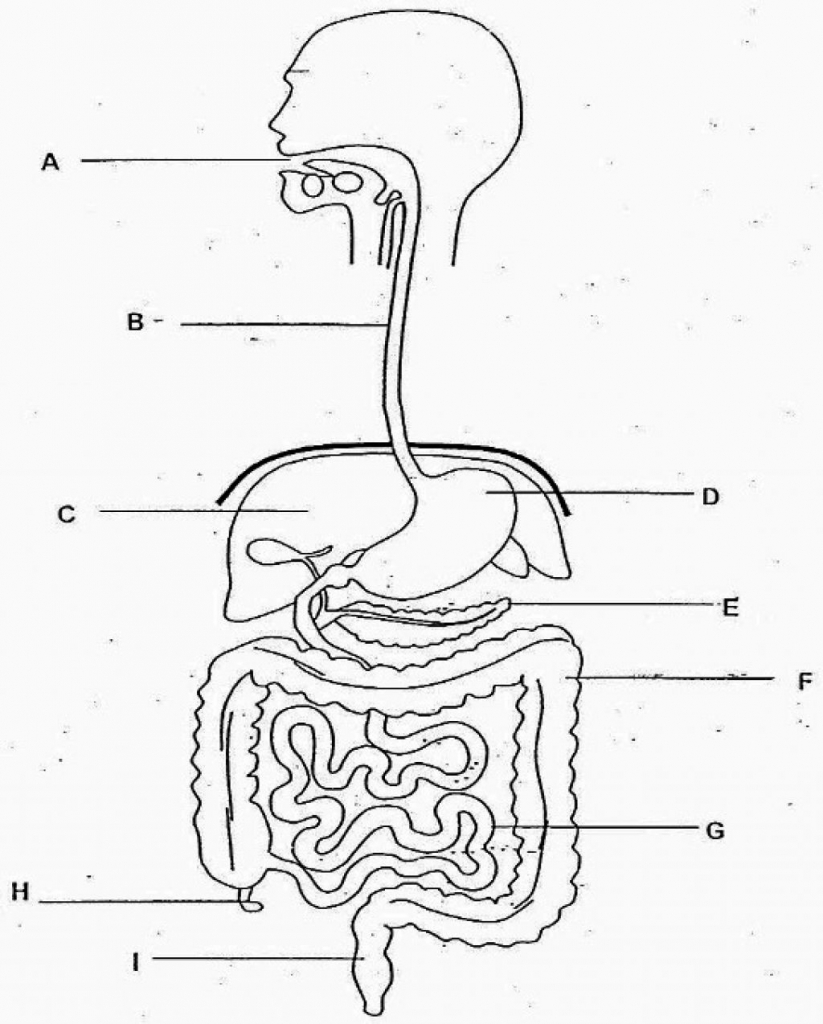
small intestine
G
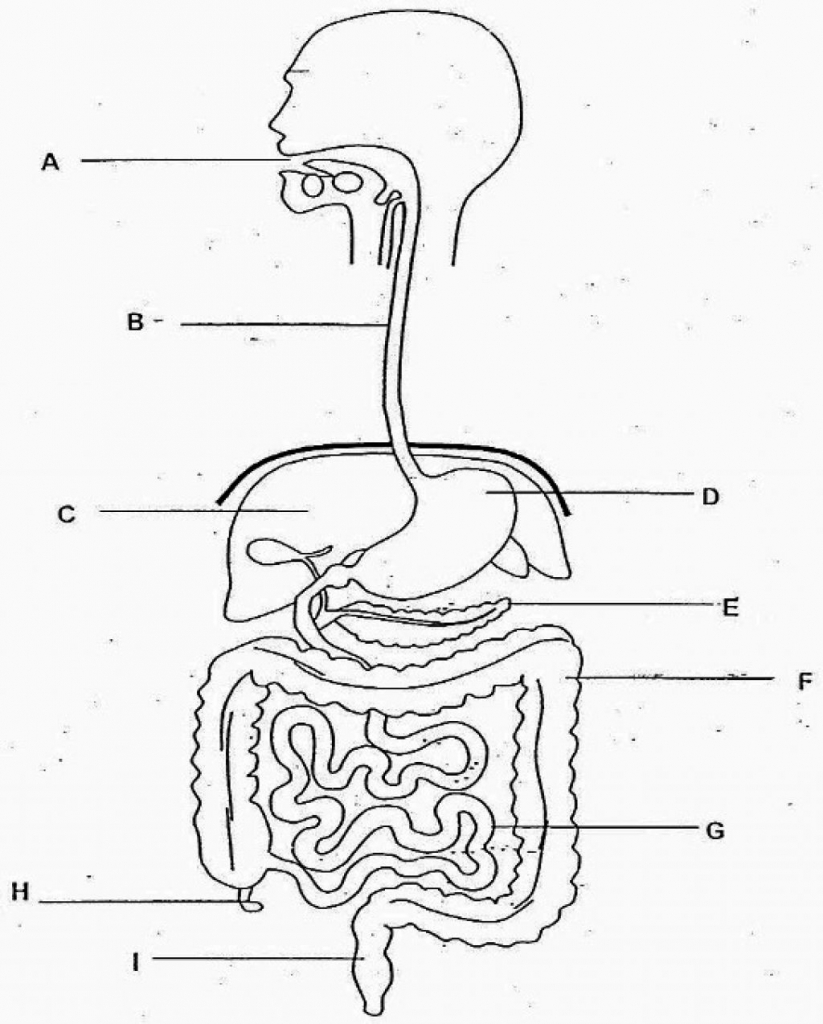
rectum
I
Skeletal System
provides structure and posture
Immune System
Protects the body from diseases and pathogens
Respiratory System
Moves air in and out of the lungs / removes CO2 and brings in O2
Gastrointestinal System
Facilitates Digestion
Cardiovascular System
Delivers blood to the whole body
Your patient is complaining of a red rash, with itching and burning on their arm. You know most likely the Dr. will dx the patient with what?
dermatitis
Myalgia is a disease of what system?
muscular system
A patient is having acute chest pain, nausea, vomiting, profuse sweating might be actually having a what?
myocardial infarction (MI)
Diabetes type 2 is usually only presented during adulthood and can be reversed or lessened in severity with proper diet, exercise and medication.
true
Your patient is dx with thrombophlebitis. What does this mean?
Your patient has a blood clot causing inflammation in the vein
hypertension
high or above normal blood pressure
tachycardia
fast heart rate >over 100
dyspnea
labored or difficulty breathing
syncope
fainting or feeling faint
bradycardia
slow heart rate < less than 60
hypotension
low or below normal blood pressure
ac
before meals
pc
after meals
asap
as soon as possible
cc
chief complaint
bx
biopsy
cpr
cardiopulmonary resuscitation
c/o
complaints of
dx
diagnosis
fx
fracture
sx
signs/symptoms
proximal
closer to the trunk
distal
further away from the trunk
abduct
away from the body
adduct
toward the body
anterior
front of the body or part
posterior
behind / back or the body or part
superior
above or toward the head
inferior
below or toward the feet
medial
toward the midline
lateral
sides / either side of something
dorsal recumbent
lying on your back with knees bent and feet flat
fowlers
sitting up at 90 degrees
semi-fowlers
sitting up at 45 degrees
lithotomy
lying on back, knees flexed and feet in stirrups / for gyn and pelvic exams
prone
lying on your abdomen
supine
lying on your spine
sims
lying on your left side with knee bent / rectal exams
trendelenburg
feet and legs raised above heart level, used to get circulation back to vital organs.
ectomy
surgical removal
algia
pain
emesis
vomiting
itis
inflammation of
ology
study of
ologist
one who specializes
cardi/a
heart
my
muscle
peri
around
phleb
vein
thromb
clot
plasty
surgical repair
hypotensions
low or abnormally low blood pressure
phlebitis
inflammation of the vein
athroplasty
surgical repair of a joint
hypertension
high or above normal blood pressure
cardiomyopathy
Disease of heart muscle
angina
chest pain