PD E2- lung and thorax
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
where is needle insertion for a tension pneumothorax?
2nd ICS
where is chest tube insertion?
4th or 5th ICS; literally/mid to anterior axillary
where is the lower margin of endotracheal tube placement?
T4
where are neurovascular structures?
under each rib
where are needles and tubes placed?
superior to rib margins
which ribs articulate w/ the sternum?
first 7 ribs
what ribs articulate w/ costal cartilage above?
8-10
what are the floating ribs?
11-12
Where is the apex?
2-4 cm above the ribs, sits above the clavicle anteriorly
where is the minor fissure?
parallels right 4th rib
where is oblique fissure?
spans T3- 6th rib MCL
How do you perform pulm exam if patient can’t sit up?
roll pt 45 degrees and abduct/flex arm
What is carina?
bifurcation of trachea; anterior - 3rd ICS, posterior- T4
Which bronchus is shorter and more horizontal?
right main bronchus
What can nitrofurantoin cause?
interstitial lung disease
what is consolidation?
occur when alveoli are not filled w/ air
no breath sounds
fremitus is inc
crackles- pulmonary edema, fibrosis, chronic bronchitis
pneumonia and bronchial obstruction- fever, dyspnea, cough
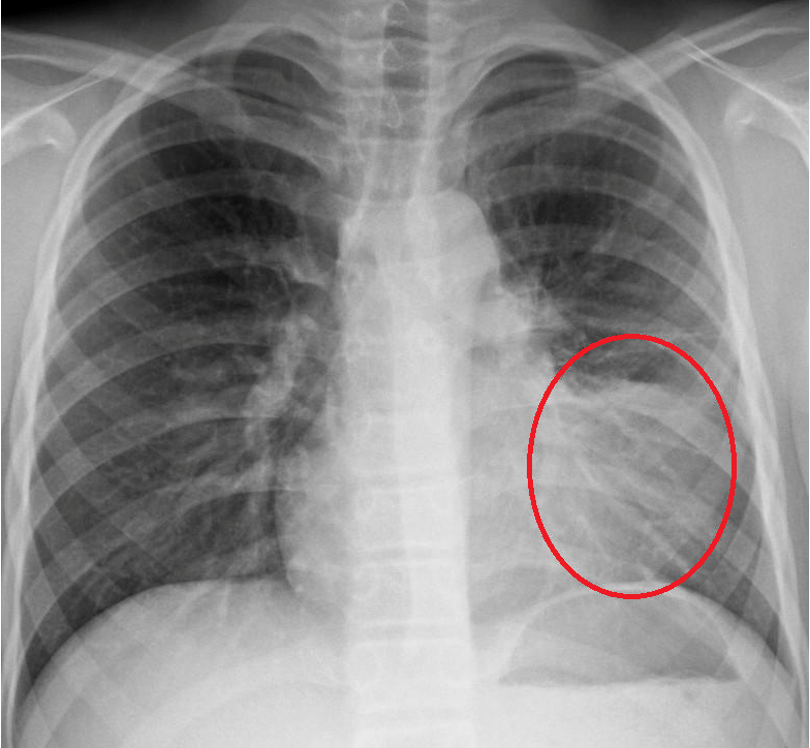
What is suspected w/ sx of community acquired pneumonia w/o signs of consolidation or negative CXR?
atypical pneumonia- mycoplasma, chlamydia, legionella
What should you encourage CAP patients to do?
ambulate, use incentive spirometer, take deep breaths and cough up sputum
what should you think of w/ frank blood in sputum?
TB or cancer
Who is hilar lymph node enlargement normal in?
children; NOT normal in adults
What is pleural effusion?
fluid build up bt pleural space and lungs
auscultation unable to hear sound → like putting head underwater at beach
dullness to percussion
absence of breath sounds
fremitus is absent
what is the order for the lung physical exam?
inspect, palpate, percuss, auscultate
what is normal cap refill?
< 2 s
what would you hear on auscultation w/ tracheal deviation?
stridor
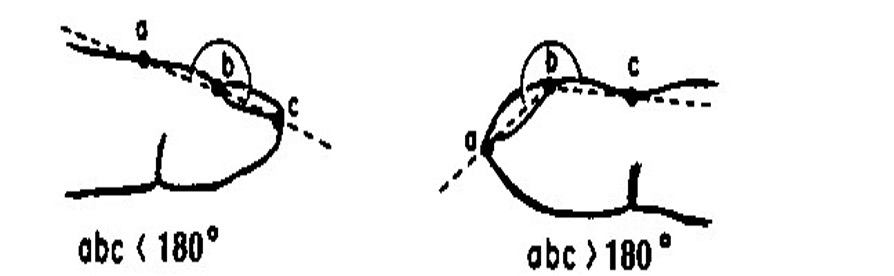
What is Oliver’s sign?
tracheal tug; downward displacement of cricoid cartilage w/ ventricular contraction → aortic arch aneurysm
what is Campbells sign?
tracheal tug; downward displacement of cricoid cartilage during inspiration → COPD
Describe a tension pneumothorax
trachea deviation toward side AWAY from pain
tympany and dec breath sounds
STAT needle decompression
Describe massive pleural effusion
tracheal deviation toward side AWAY from pain
dullness and decreased breath sounds
emergent thoracotomy
describe obstructed bronchus w/ atelectasis
toward side of pain
dullness and decreased breath sounds
urgent/emergent
How do you check respiratory rate?
count while pretending to count the pulse; do NOT let pt be aware you are counting their respirations
What are examples of chest asymmetry abnormalities?
kyphoscoliosis
larger hemithorax- pneumothorax, pleural effusion
smaller hemithorax- atelectasis, pleural fibrosis, agenesis of lung
What are examples of conditions with increased pleural negative pressure?
unilateral: airway obstruction
bilateral: COPD/asthma; intercostal and supraclavicular fossa retraction, downward movement of trachea w/ quiet inspiration
What is normal chest expansion?
2.5” and symmetrical
how do you measure chest expansion?
measure at level of 10th rib
pt sit erect or stand with arms to side
grab lower hemithorax on either side of axilla and bring thumbs midline
pt slowly take deep breath and expire
watch for symmetry and feel expansion
repeat anteriorly
what are conditions that would have decreased chest expansion?
diffuse lung and pleural dz- emphysema
stiff thorax- ankylosing spondylitis
diaphragmatic paralysis
what conditions are seen w/ asymmetric chest expansion?
kyphoscoliosis
unilateral loss of lung volume- atelectasis, resection, pleural fibrosis
unilateral space occupying lesions- pneumothorax, pleural effusion, large mass
unilateral lung or pleural disease
what is a normal breathing pattern?
12-20 per minute resting w/ no apparent discomfort; chest wall and abdomen expand during inspiration and movement is symmetrical
What rate is considered bradypnea and what conditions might it be seen?
< 12
narcotics, elevated intracranial tension, myxedema
what rate is considered tachypnea and what conditions might it be seen?
> 20
interstitial and vascular dz, anxiety
What is orthopnea and what conditions might it be seen?
supine position worsens SOB
CHF, diaphragmatic paralysis, SVC syndrome, anterior mediastinal mass, body habitus
what is cheyne stokes breathing pattern?
progressively deeper and sometimes faster w/ gradual dec that results in temporary apnea
assoc w. dec level of consciousness and inc age
caused by CHF
what is kussmaul breathing pattern?
rapid deep breathing
assoc w/ ketones on breath
causes: DKA, metabolic acidosis, ketoacidosis, ethanol
what is Biot’s breathing pattern?
irregular w/ periodic apnea (no pattern)
assoc w/ dec level of consciousness
cause: CNS injury- brainstem
what is sighs breathing pattern?
periodic deep breathing
cause: anxiety
what is pursed lip breathing pattern?
lips pursed, controls expiration slowly
cause: obstruct lung dz
what is sleep apnea breathing pattern?
apnea w/ sleeping
assoc w/ morning HA, snoring, inc size of neck/tonsils
cause: obesity, retrosternal goiter
what is abdominal paradox breathing pattern?
abdomen retracts while chest expands
cause: diaphragmatic paralysis
what is thoracic paradox breathing pattern?
unstable chest wall side, hemithorax retracts while normal side expands w/ inspiration
assoc w/ trauma
cause: flail chest
describe breathing pattern w/ no abdominal component
no abd breathing
assoc w/ pain
cause: acute abdomen
describe breathing pattern w/ no thoracic component
no thoracic breathing
assoc w/ pain
cause: pleurisy, chest wall pain, ankylosing spondylitis
What are fremitus features associated w/ non obstructed consolidation?
increase fremitus over the area
what are fremitus features assoc w/ obstructed consolidation?
decreased or absent fremitus over the area
What are fremitus features associated w/ pleural effusion?
decreased fremitus at inferior part; thin rim of inc fremitus at superior rim
What are fremitus features associated w/ lobectomy and pneumonectomy?
absent
when does tactile fremitus increase?
when density of lung tissue increases
(pneumonia, neoplasm, solid mass)
when does tactile fremitus decrease?
when lung space is occupied w/ fluid/air
(pneumothorax, pleural effusion, COPD)
What is vocal fremitus?
patients voice heard through stethoscope (normally sounds indistinct)
what does abnormal vocal fremitus indicate?
consolidation
what is bronchophony?
99 stated by patient
what is egophony?
pt verbalizes letter E
what is whispered pectoriloquy?
99 whispered by pt
what is normally heard w/ percussion?
resonance
What is diaphragmatic excursion?
measures descent of diaphragm w/ respiration; normal- 3-5.5cm
what is consolidated lung disease?
solid mass (like sponge soaked w/ maple syrup) inflammation due to bacteria filling alveolar spaces
what is effusion?
fluid bt lung and chest wall; compresses normal lung → no sounds over effusion
what is obstructive lung disease?
bronchioles become degraded and floppy; air trapped w/ exhalation due to positive pressure causing bronchioles to close (blebs)
what is pneumothorax?
if chest wall puncture or if one of alveoli pop, air is introduced in between chest wall and lungs, air is trapped there and will accumulate
what conditions are dull w/ percussion?
consolidated lung disease and effusionw
what conditions are hyper resonant w/ percussion?
obstructive lung disease and pneumothorax
describe vesicular sounds
heard in periphery of lungs (lung tissue)
inspiration is long
expiration almost not audible, no pause bt inspiration and expiration
I:E ratio is 1:3-1:5
gentle signing or gentle rustling
describe bronchial sounds
heard over tracheobronchial tree
loud and high pitched
normal when heard over manubrium
if present in periphery → may mean consolidation or pneumonia
sound of air blowing through hallow pipe
describe bronchovesicular sounds
heard over large central airways
pitch bt tracheal and vesicular
normal when auscultated near mainstream bronchi in 1st-2nd ICS and posteriorly bt scapula
if heard elsewhere, consider atelectasis or early consolidation
what is a wheeze?
high pitched hissing or shrill; continuous and musical
what is a rhonchi?
low pitched, snoring quality; continuous and musical; clears w/ coughing
what adventitious sounds are continuous?
wheezes and rhonchi
** longer than crackles, musical in nature
what adventitious breath sounds are discontinuous?
fine and course crackles
**intermittent, non musical and brief
what are fine crackles?
soft, high pitched and very brief; intermittent, non musical
sounds like crushing fine leaves, velcro, or crinkling
what are course crackles?
explosive loud, lower in pitch; intermittent, non musical, brief
sounds like hair being rubbed by the ear or salt crackling on a heated dish
what conditions are wheezes assoc w/?
asthma, COPD, bronchitis
CHF
CF
vocal cord dysfunction
FB aspiration
tumor
infections- croup, laryngitis
what conditions are assoc w/ rhonchi?
seen in young and elderly
caused by secretions in large airways
adults- pneumonia or chronic bronchitis
kids- RSV
what causes crackles?
caused by air bubbling through secretions or sudden explosive openings of airways
describe early inspiratory crackles
clears w/ cough; doesn’t change w/ posture
seen in COPD or bronchitis
describe late inspiratory crackles
doesn’t clear w/ cough; may change w/ posture; heard in bases and inferior regions
seen in pneumonia, pulmonary hemorrhage, CHF
Describe pleural friction rub
sound of 2 inflamed surfaces sliding by each other;
loud, heard over a small area; sounds like a hand over a wet balloon
describe stridor
loud musical sound heard at a distance; obstruction of trachea or larynx
seen in aspirations, URI, tracheomalacia, whooping cough, epiglottitis, croup
How does chronic bronchitis typically present?
rough sounds
airway obstruction
breath sounds are loud due to obstructions
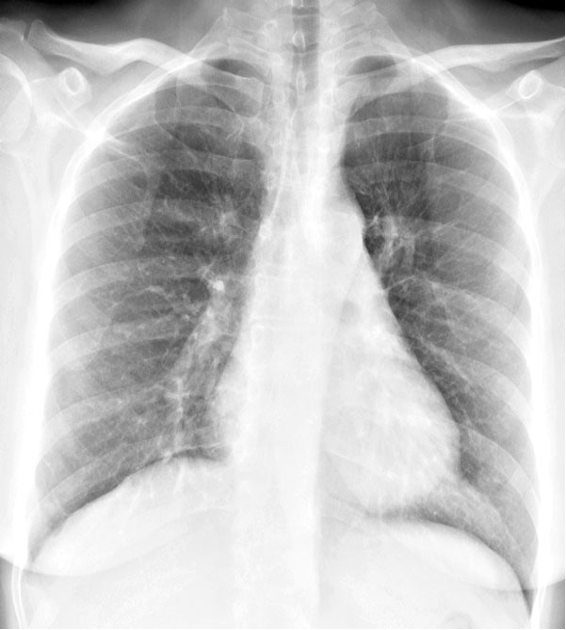
How does lobar pneumonia typically present?
bronchial nature of sounds
affects large continuous area of a lobe
palpation- increased fremitus
percussion- dull over the dense, airless lung
auscultation- bronchial breath sounds, crackles, egophony, whispered pectoriloquy, and ronchi heard
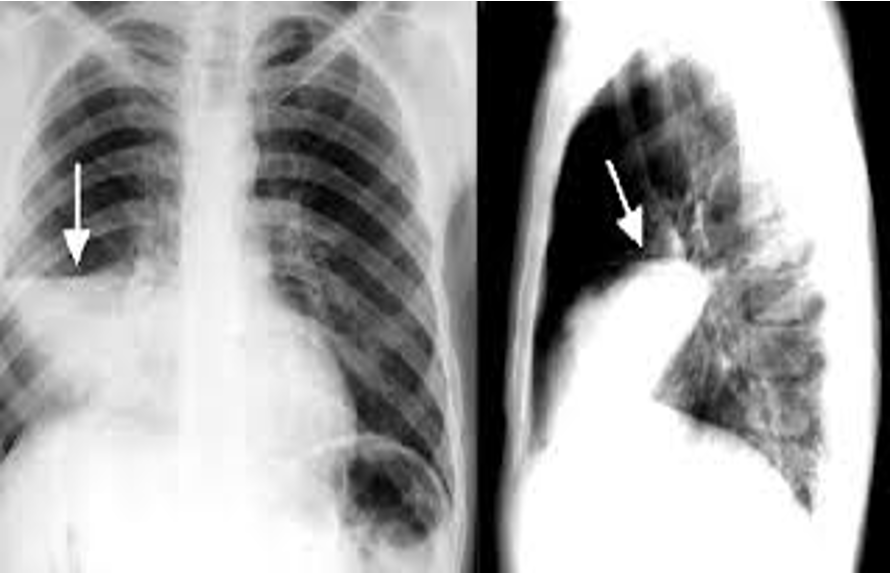
how does a pneumothorax present?
inspection- possible tracheal deviation to opposite side
palpation- absent fremitus
percussion- hyper resonant
auscultation- absent breath sounds
what is terminal congestion / death rattle?
secretions in airway → produces crackles
if profuse, can be heard in mouth as well as chest
What are causes of pseudo cyanosis?
amiodarone, methemoglobinemia
what is clubbing?
peripheral trapping of large immature platelets and platelet clumps in capillary beds; promotes angiogenesis and bone growth; determine w/ lovibond’s angle at base of nail and surrounding skin