Anatomy 3 exam
1/139
Earn XP
Description and Tags
gg your even more cooked than before the fries are actually in the bag now
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
Pathway of Bloodflow
Arteries, arterole, Capillary, venule, Vein
3 layers of blood vessels
There are 3 tunics
Tunica intima
Tunica media
tunica adventitia or externa.
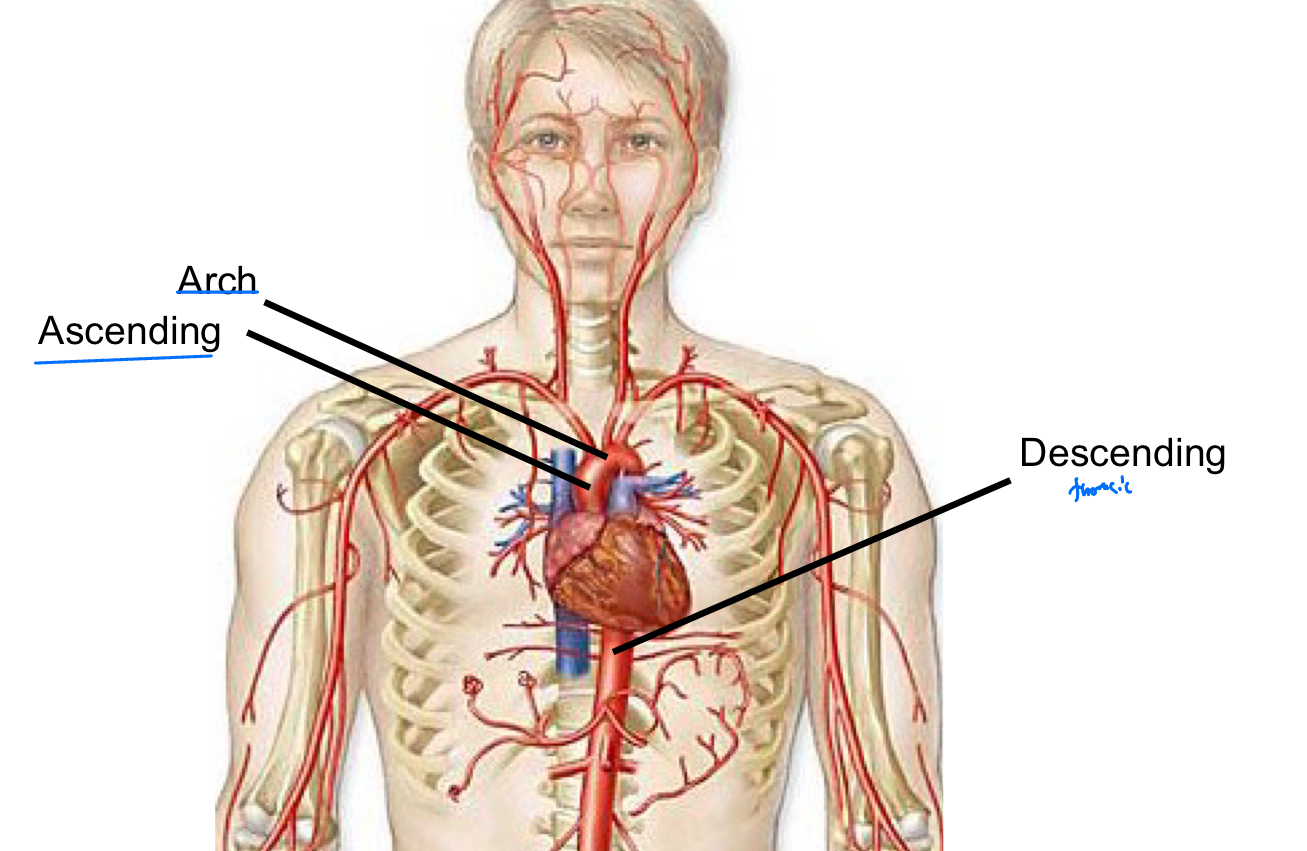
Parts of the aorta
Ascending aorta
Arch of aorta
Descending aorta
Major Arteries – Abdomen and Pelvis (first)
Descending aorta > abdominal aorta
Major Arteries – Abdomen and Pelvis 2
Abdominal aorta > left and right common iliac arteries
Major Arteries – Abdomen and Pelvis 3
Common iliac arteries > internal and external iliac arteries
Arterial Supply to the Upper Extremity
Subclavean> axillary> brachial and deep brachial> radial and ulnar arteries> palmar arches
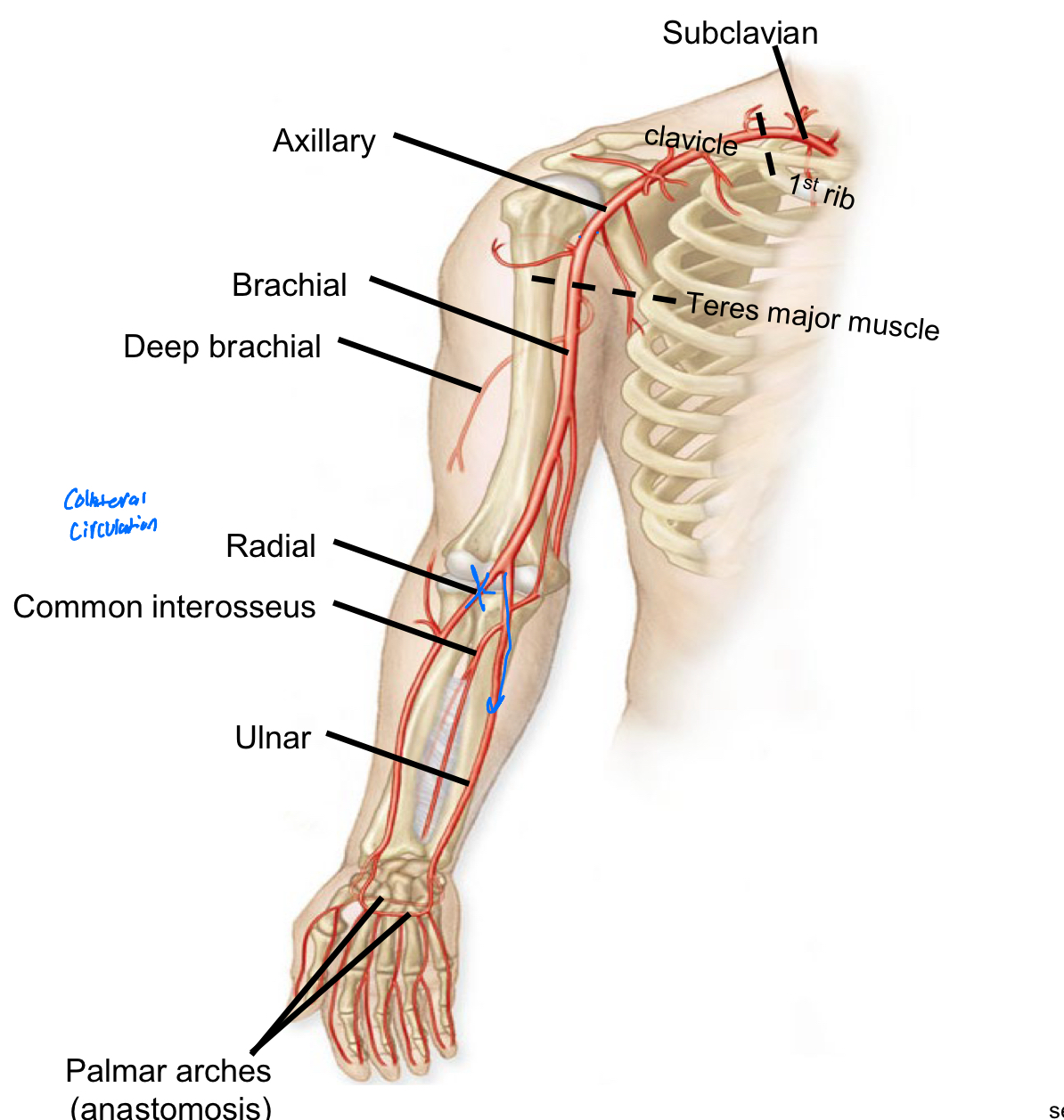
Deep Brachial Artery
Supplies blood to the triceps brachii muscles collateral to radial and ulnar arteries
Arterial supply to the Head 1
Common carotid artery> external and internal carotid arteries
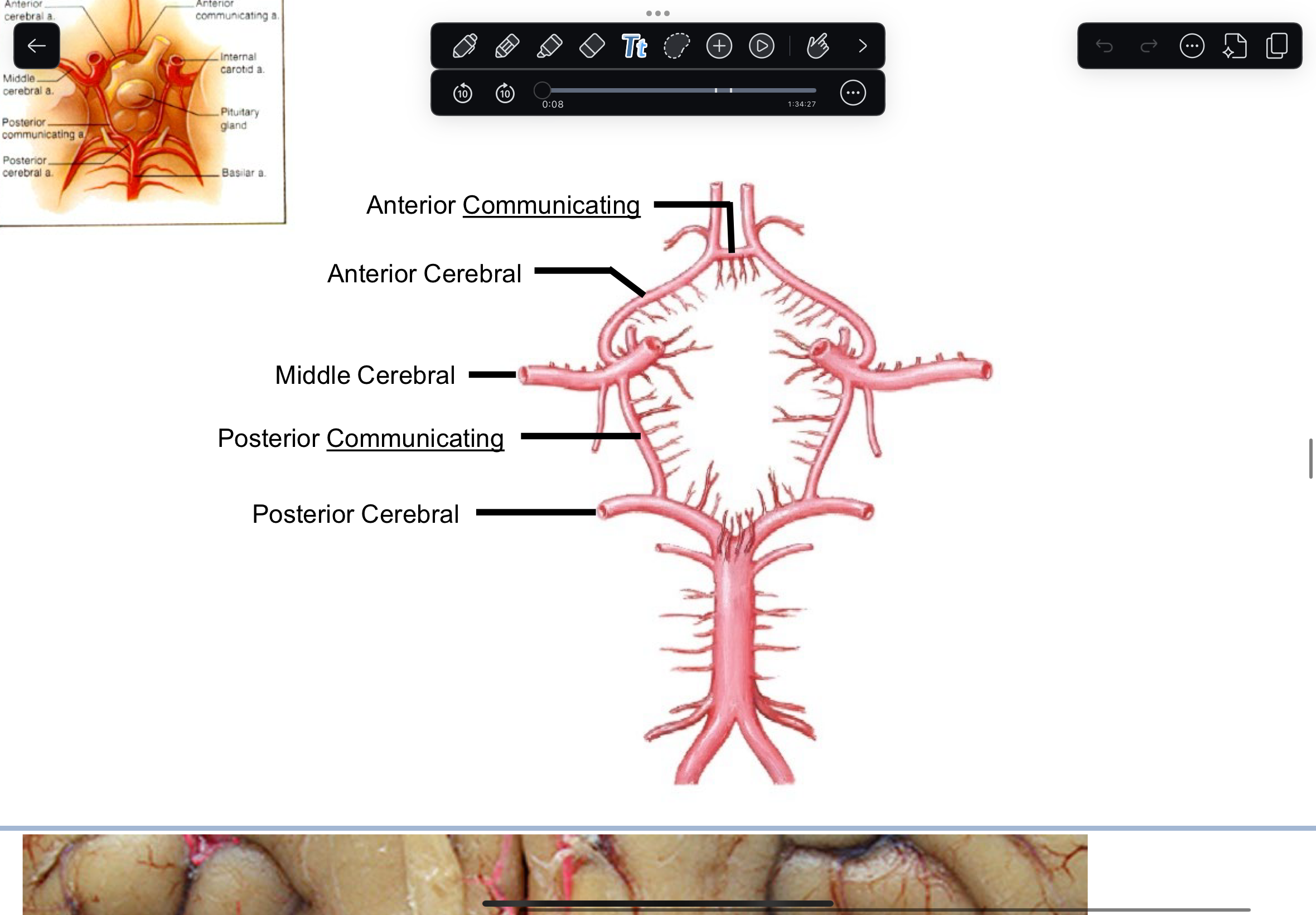
How blood is supplied to circle of Willis
Internal carotid artery Carotid canal Foramen Lacerum middle cranial fossa Vertebral artery Transverse foramina Foramen Magnum Basilar artery posterior cranial fossa
Circle of Willis
Internal Carotid Artery >Anterior & Middle Cerebral Arteries > Anterior Cerebral > R & L Vertebral arteries > Basilar artery > R & L Posterior Cerebral Arteries > Middle Cerebral > Posterior Communicating >. Posterior Cerebral
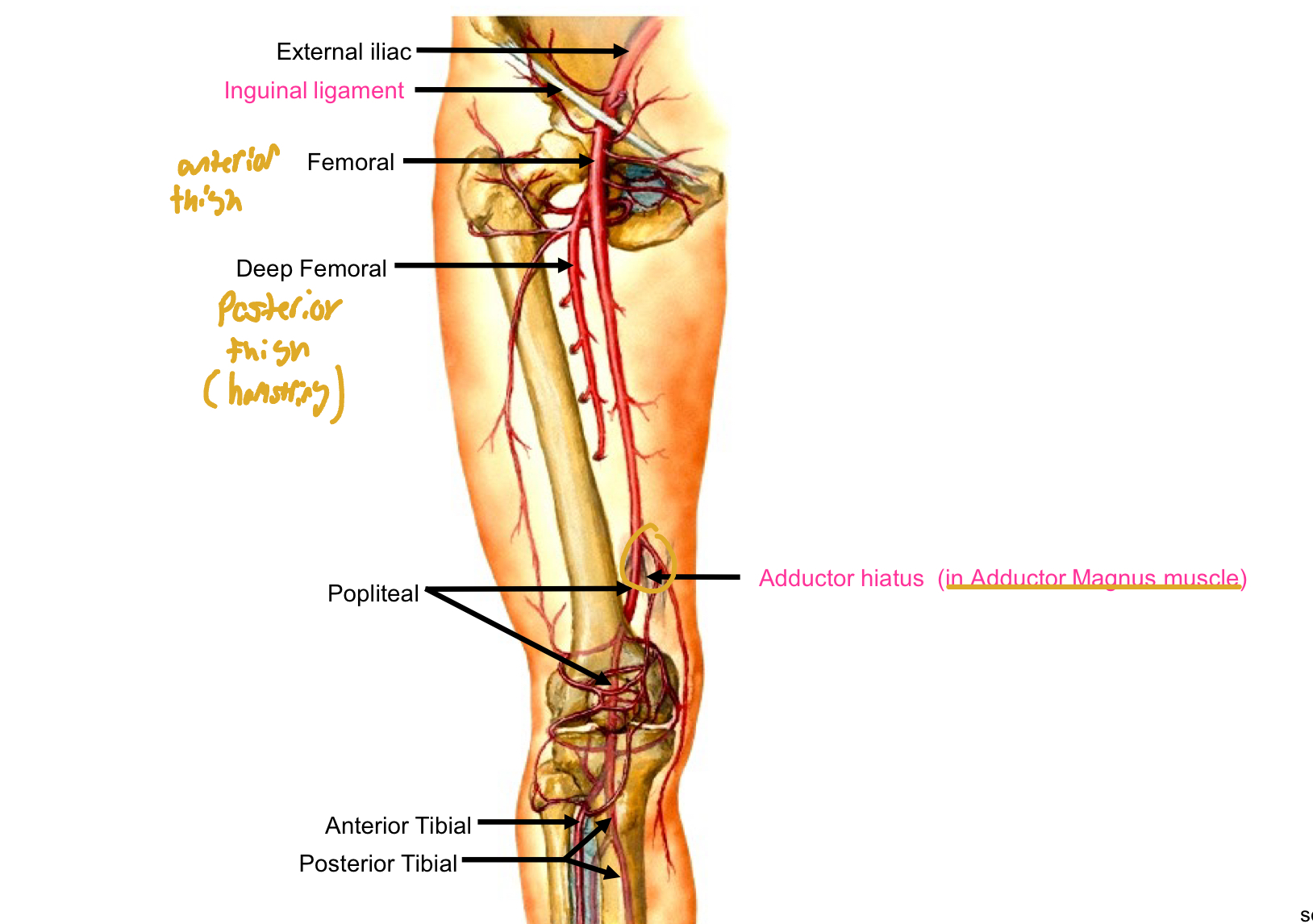
Arterial Supply to the Lower Extremity 1
Abdominal Aorta bifurcates to form the Left & Right Common Iliac arteries
Arterial Supply to the Lower Extremity 2
External iliac > Femoral >Popliteal >Anterior & Posterior Tibial
Arterial Supply to the Lower Extremity Genicular arteries
Genicular arteries = Collateral Circulation around the Knee
Fibular Arteries supply
(to Fibularis longus and brevis muscles)
Posterior Tibial artery Supply
arterial supply to the Plantar foot
Anterior tibial artery supply
Muscles of the Anterior compartment of leg and Dorsum of foot
Arterial Supply to the Lower Extremity Of the foot
Anterior Tibial >medial malleolus > Dorsalis Pedis > Arcuate artery
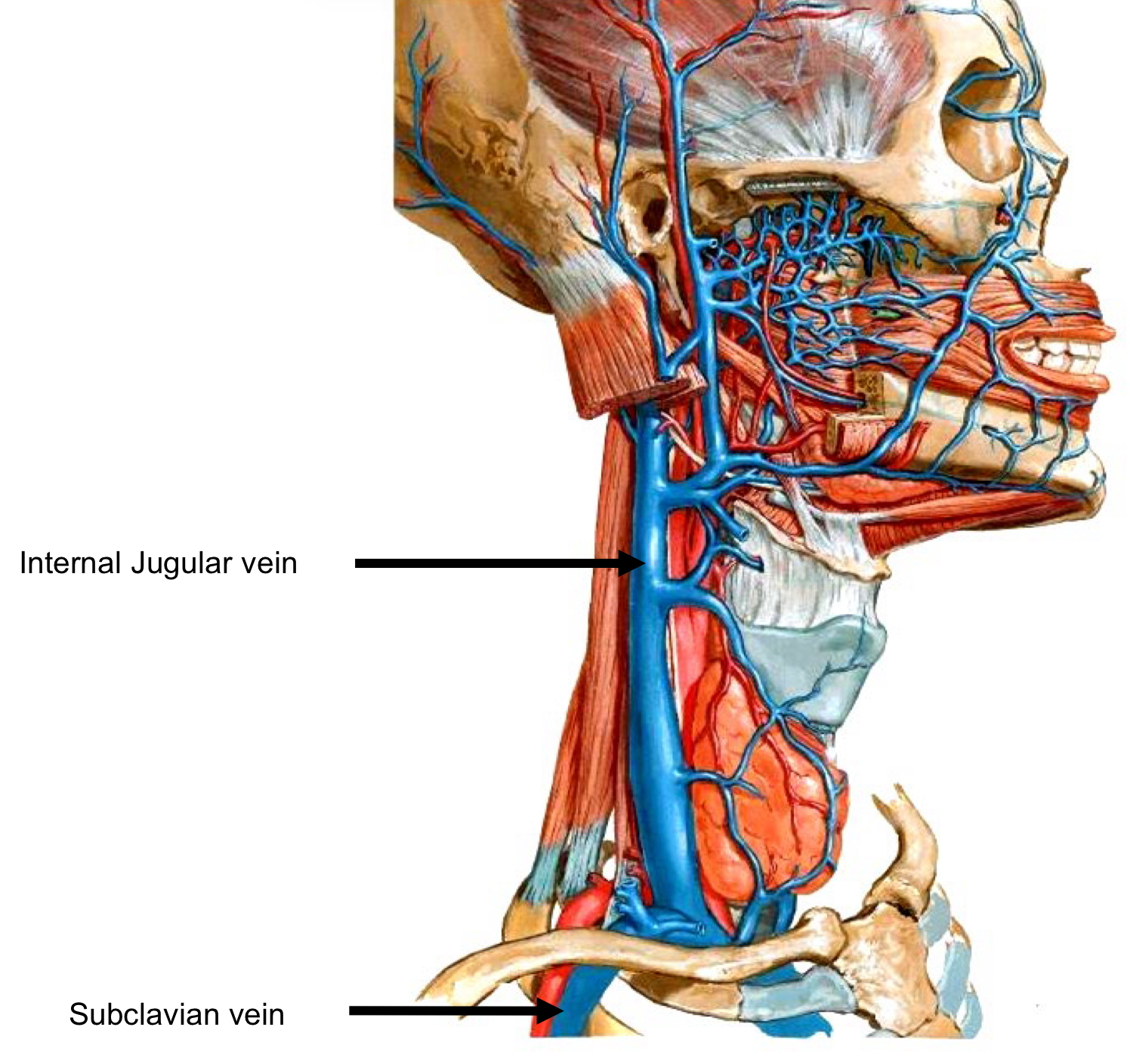
Veins of head and neck
The Internal Jugular joins the Subclavian Vein.
Collateral supply of foot
Arcuate artery Anterior Tibial anastomosis with Posterior Tibial artery to form collateral circulation to the foot.
Arterial Supply to the Thorax 1
Arterial supply to Intercostal muscles of respiration
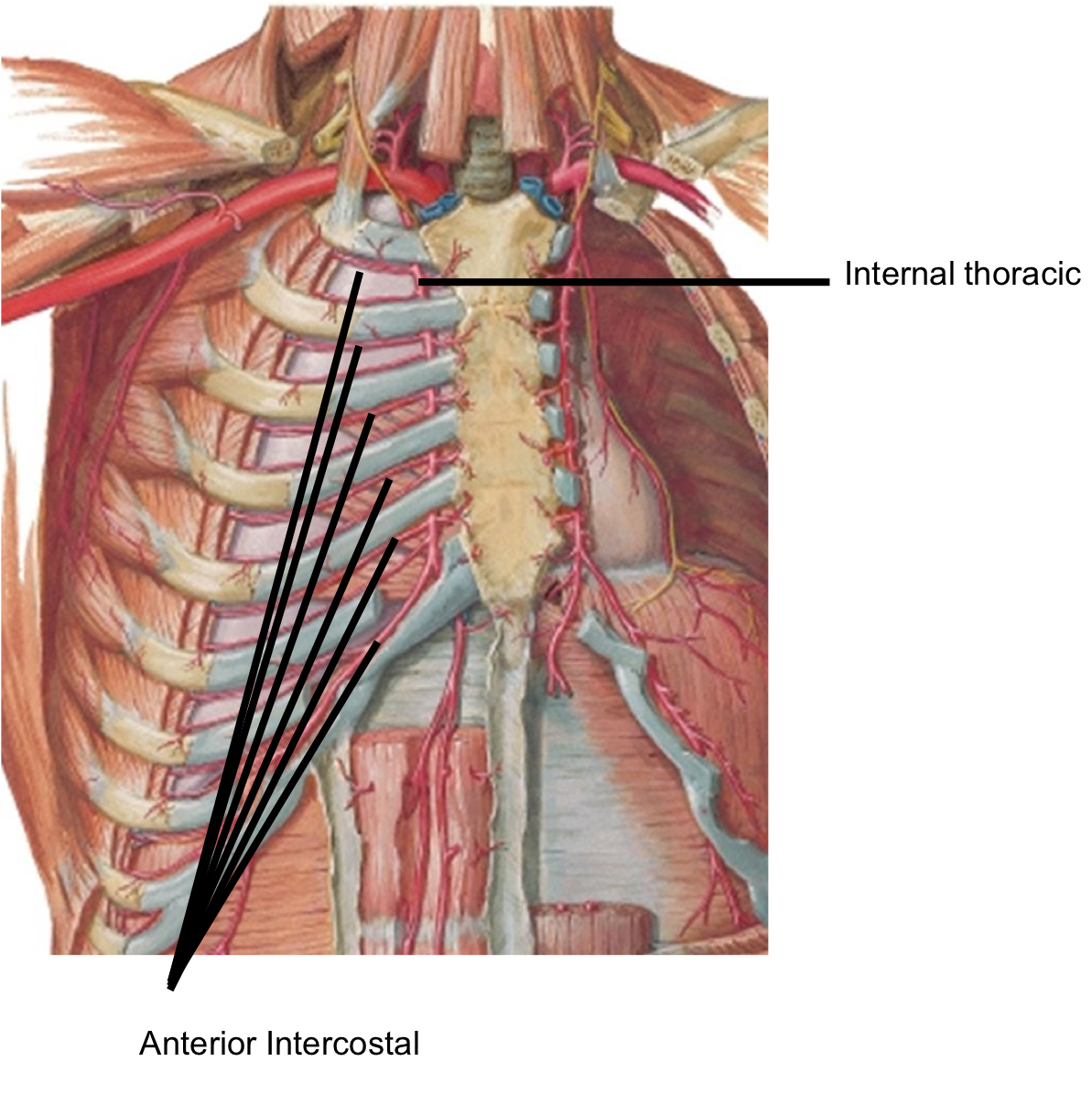
Arterial Supply to the Thorax
Internal Thoracic artery >Respiratory Diaphragm
Arterial Supply to the Thorax 3
Internal Thoracic artery > Anterior Intercostal arteries
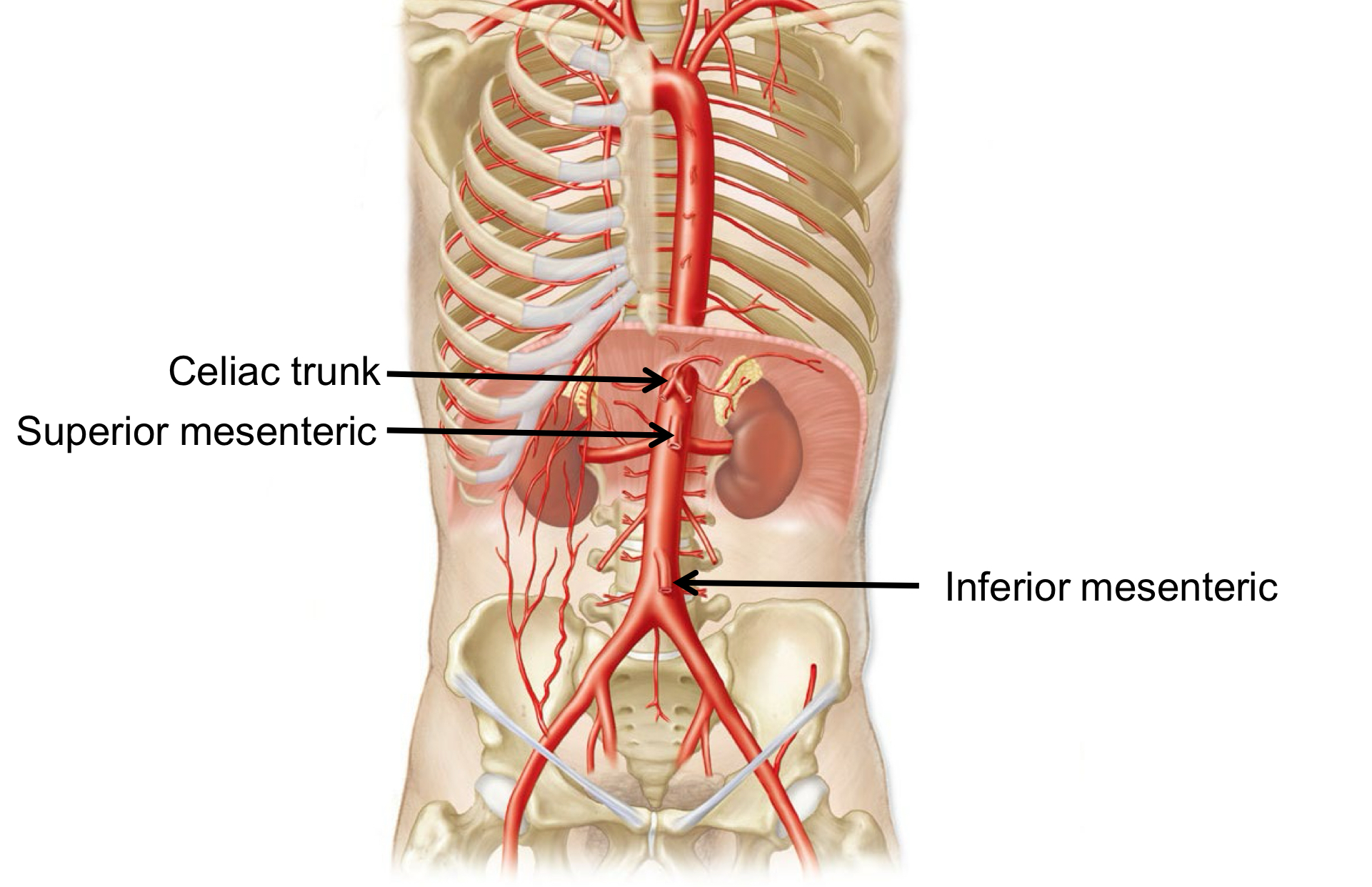
Arterial supply to the Abdomen
Abdominal aorta> Celiac trunk >Superior mesenteric > Inferior mesenteric
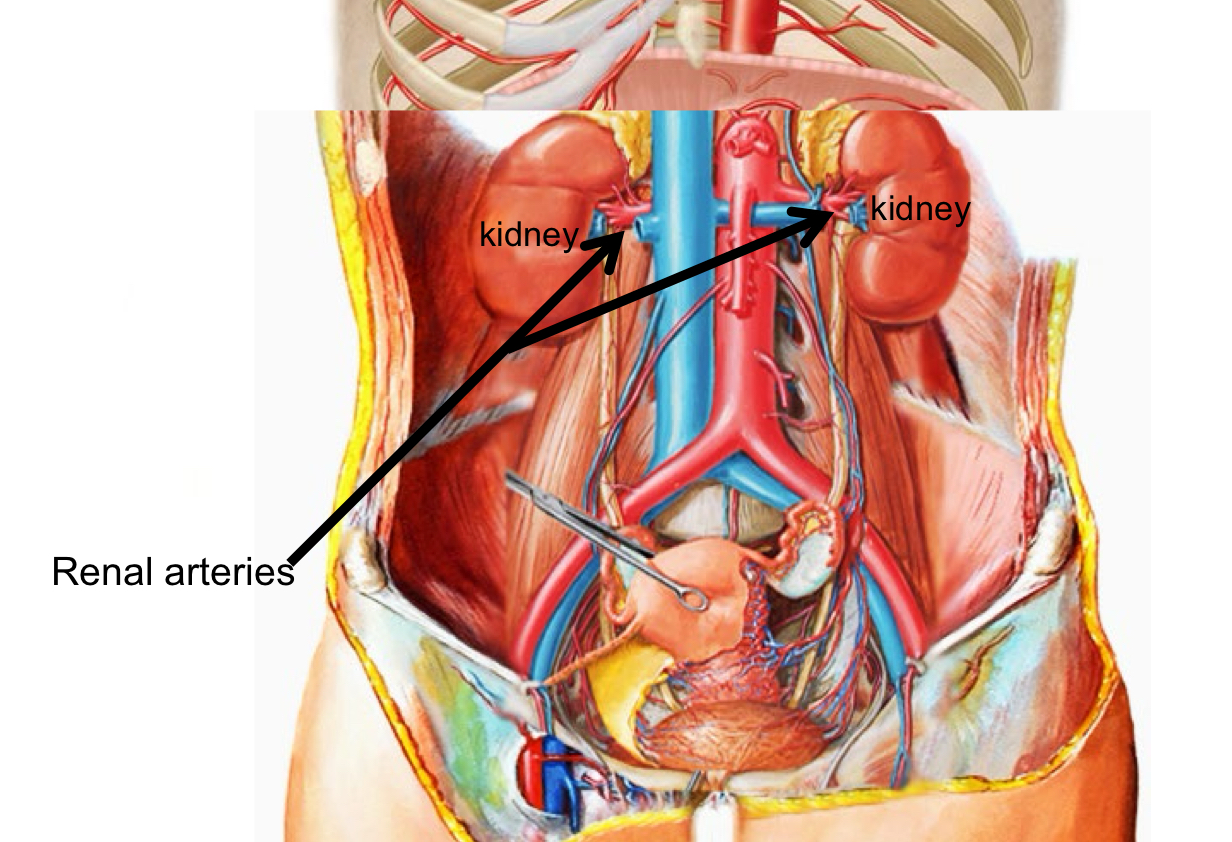
Arteries of the Abdomen 2
Renal arteries
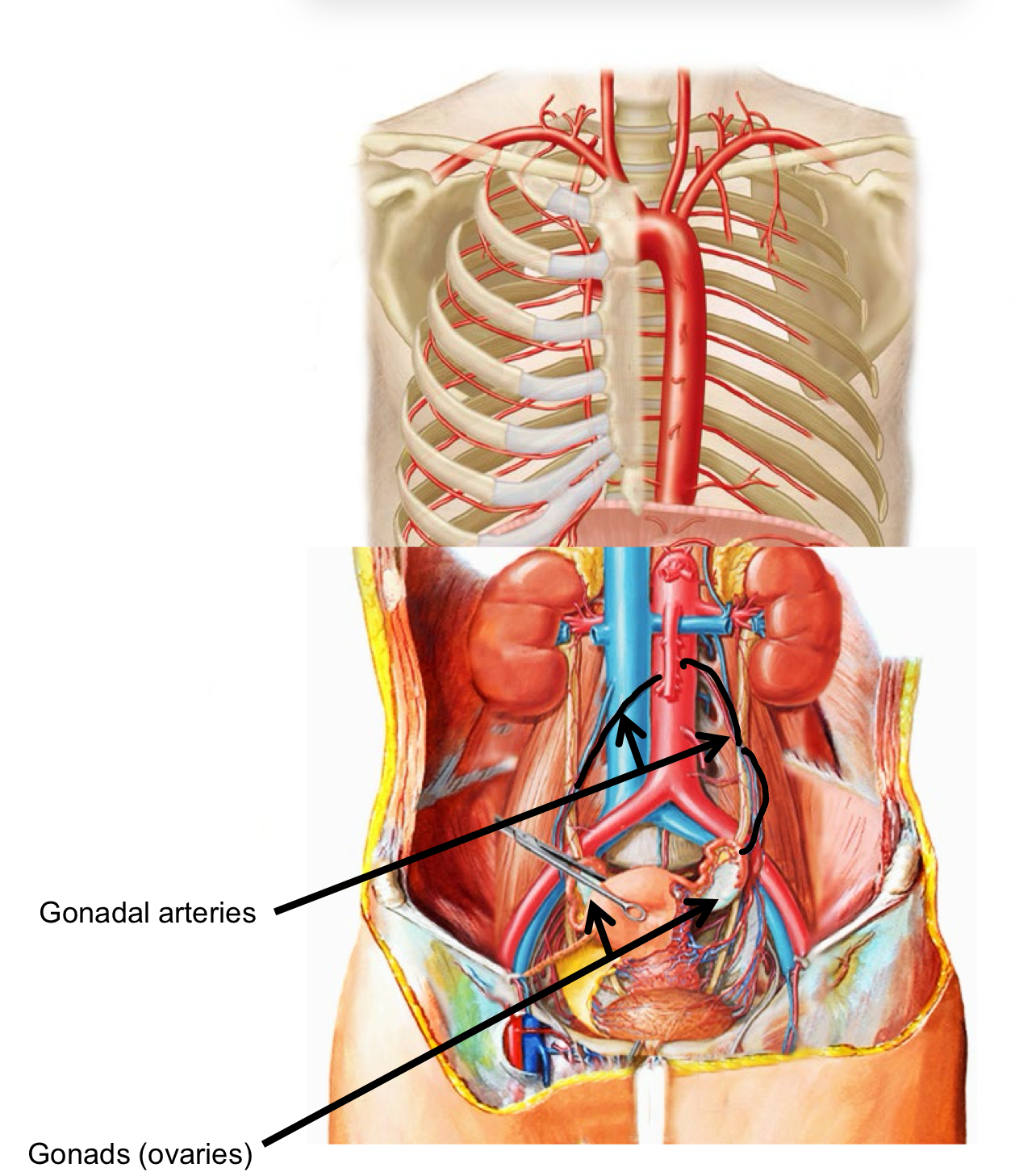
Arteries of the Abdomen 3
Gonadal arteries
Gonads (ovaries) or testes
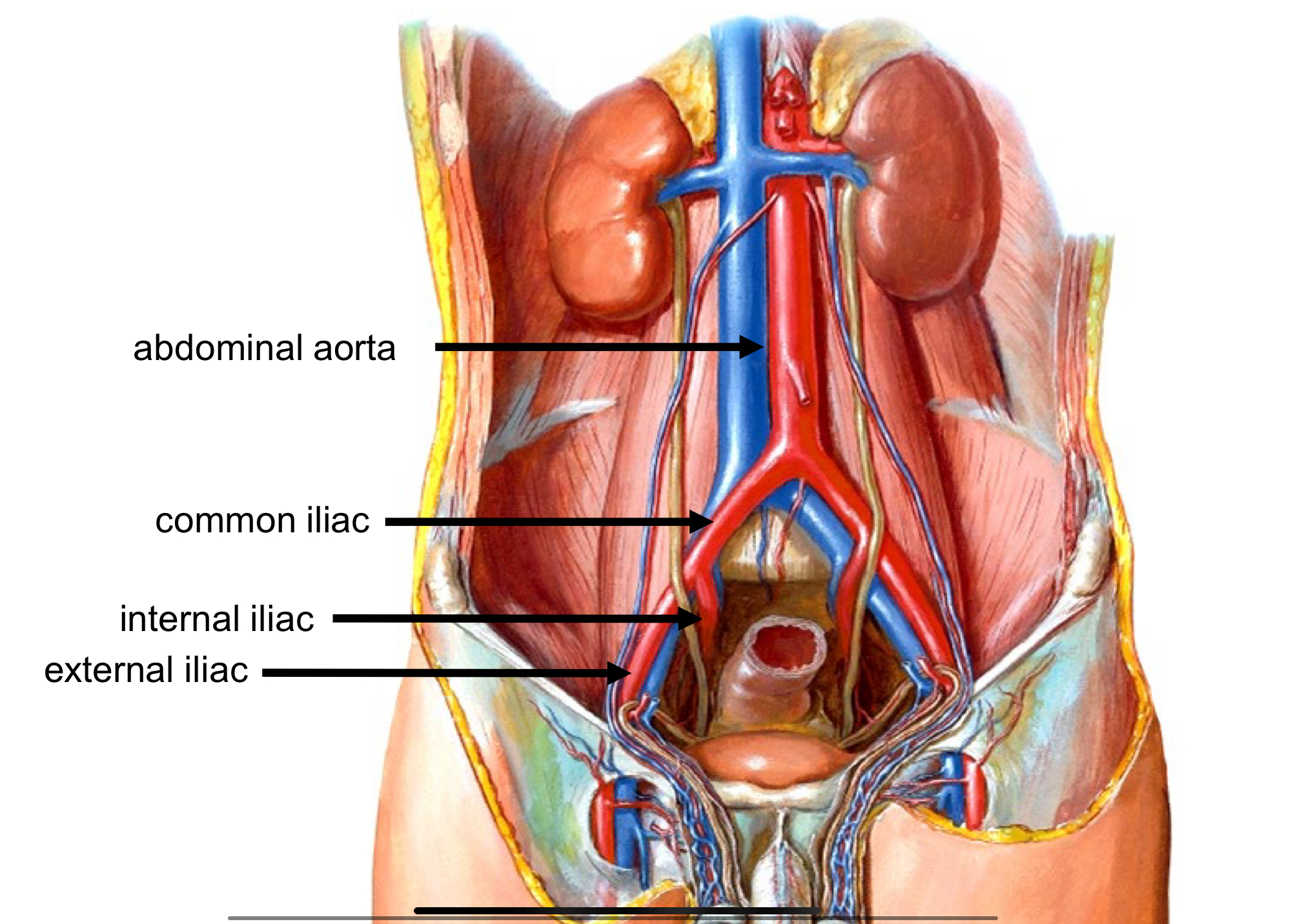
Arterial Supply to the Pelvis and Gluteal region
Common iliac > internal + external iliac
Arterial Supply to the Pelvis and Gluteal region 2
Pelvic organs> Internal iliac > bladder uterus vagina rectum and gluteal muscles
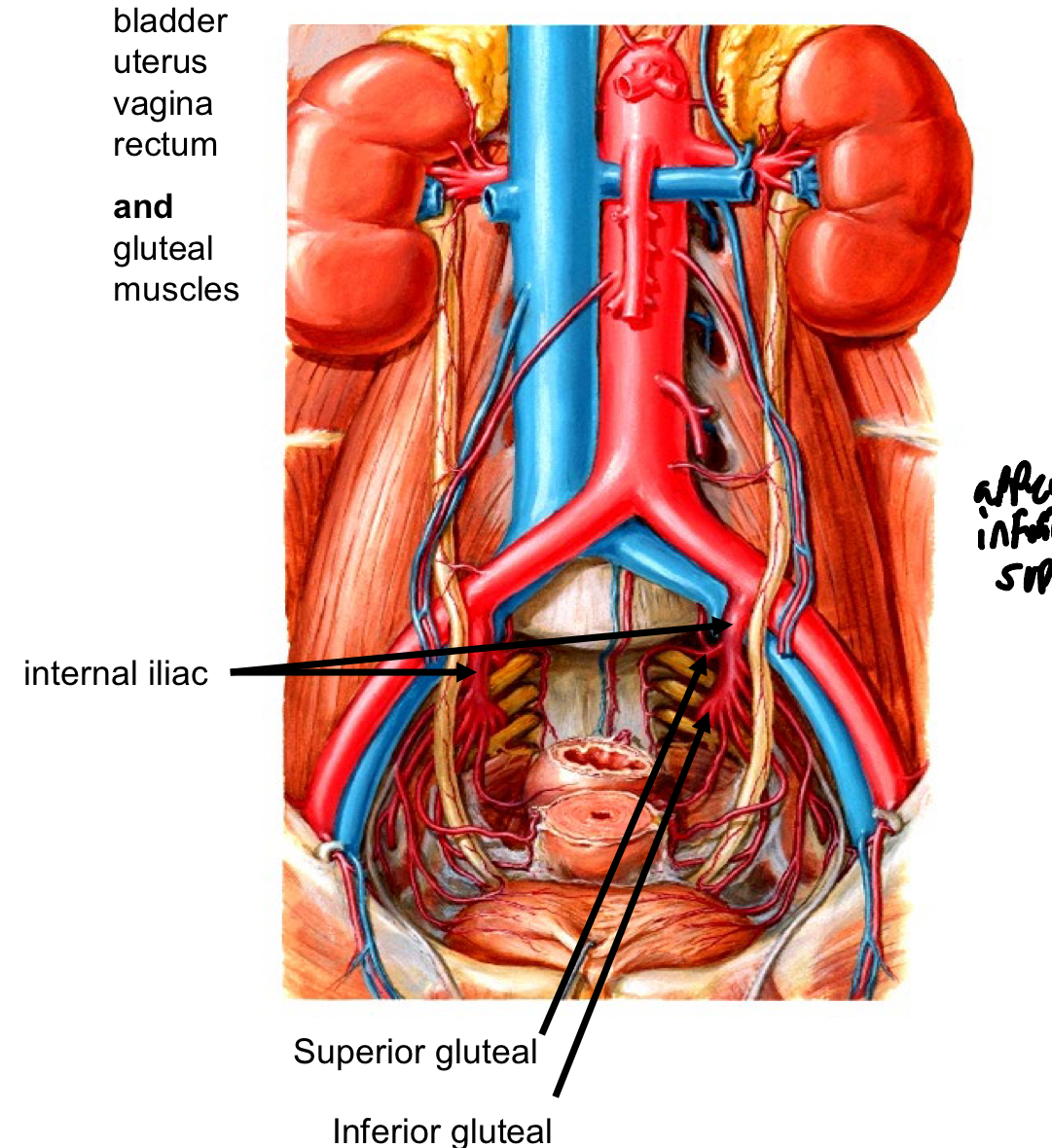
Internal iliac supply
Internal iliac Superior Gluteal Artery Gluteus Medius, Gluteus Minimus, and Tensor Fascia Lata muscles Inferior Gluteal artery Gluteus Maximus muscle
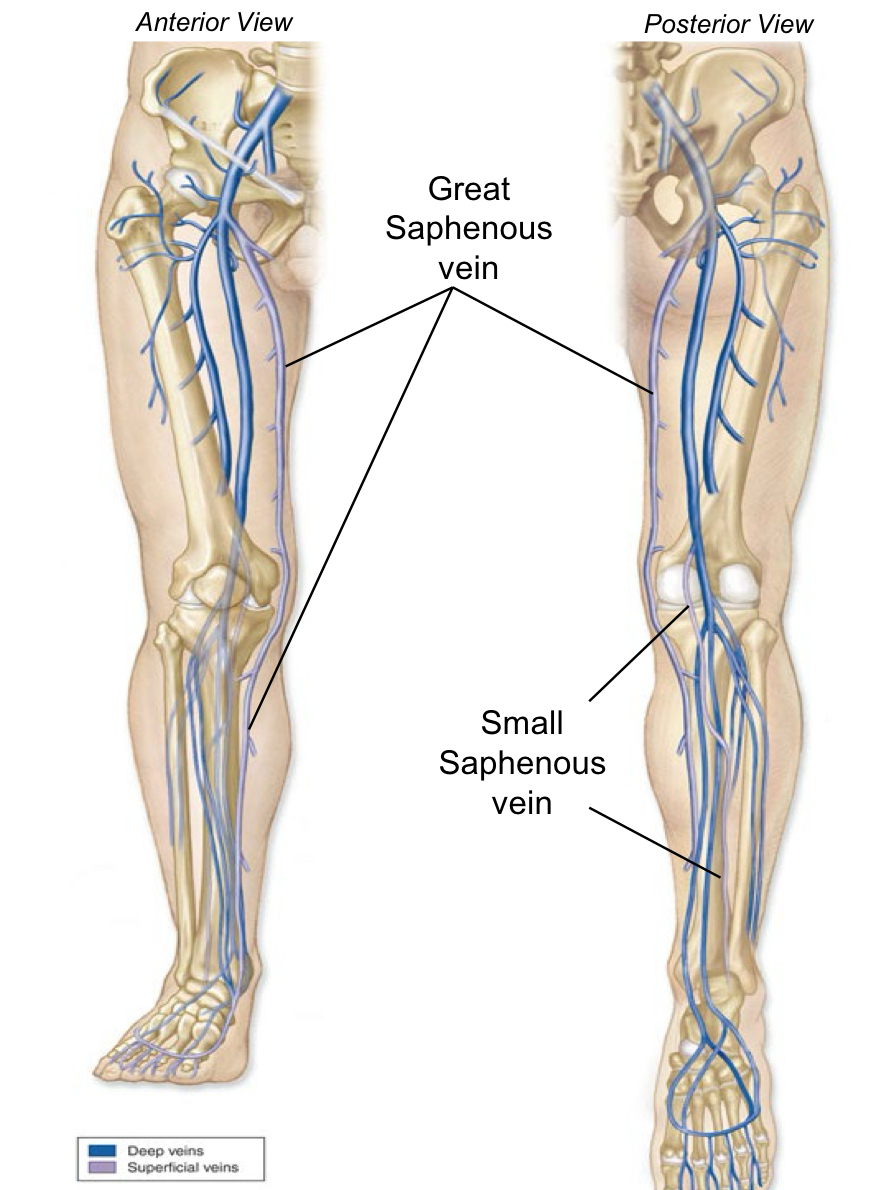
Superficial Veins of the Lower Extremity Superficial veins are in the Superficial fascia or Hypodermis.
Great Saphenous vein And Small Saphenous vein
During inhalation or inspiration:
Respiratory Diaphragm contracts and flattens to increase volume of thorax
Innervation: Phrenic Nerve Intercostal muscles contract to elevate ribs and increase volume of thorax
Innervation: Intercostal Nerve
During exhalation or expiration:
Diaphragm relaxes to a dome shape which decreases the volume of the thorax Intercostal muscles relax to allow ribs to return to depress to a lower position and decrease the volume of the thorax Abdominal muscles can assist to depress the sternum and ribs and decrease the volume of the thorax
Control of Ventilation
Medulla Oblongata sets a baseline ventilatory rate
Increase in ventilation rate:
Stretch receptors in the smooth muscle of BronchoPulmonary
segments
Increased lung inflation
chemoreceptors respond to decreases in O2, or pH in the blood
Conduction Zone
Conducting = Ventilation, breathing, airway
Respiratory Zone = O2 / CO2 exchange
Respiratory = exchange of Oxygen (O2) and Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
External Respiration = exchange between air and blood (in Lungs)
Internal Respiration = exchange between blood and tissues
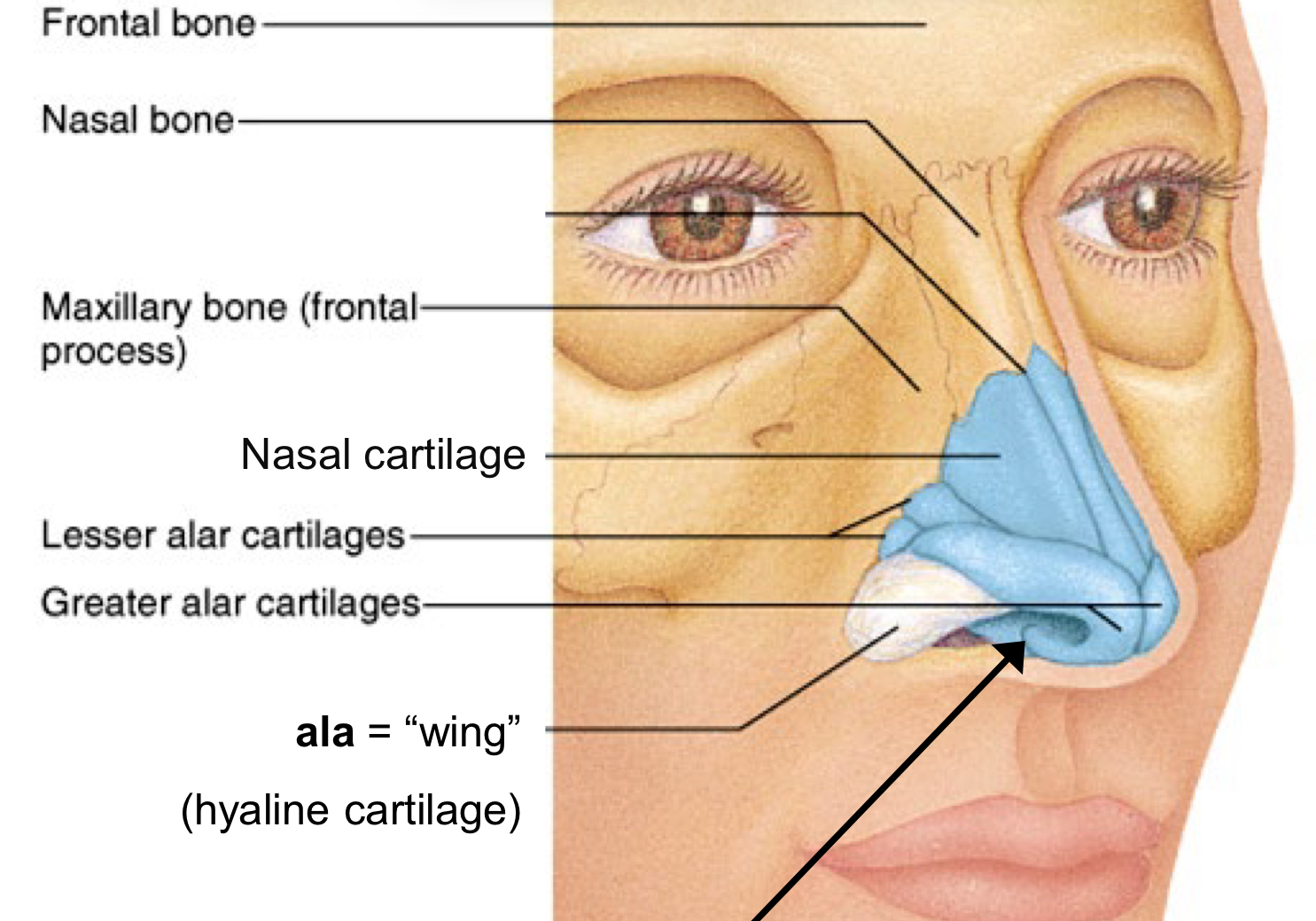
Ala
Wing
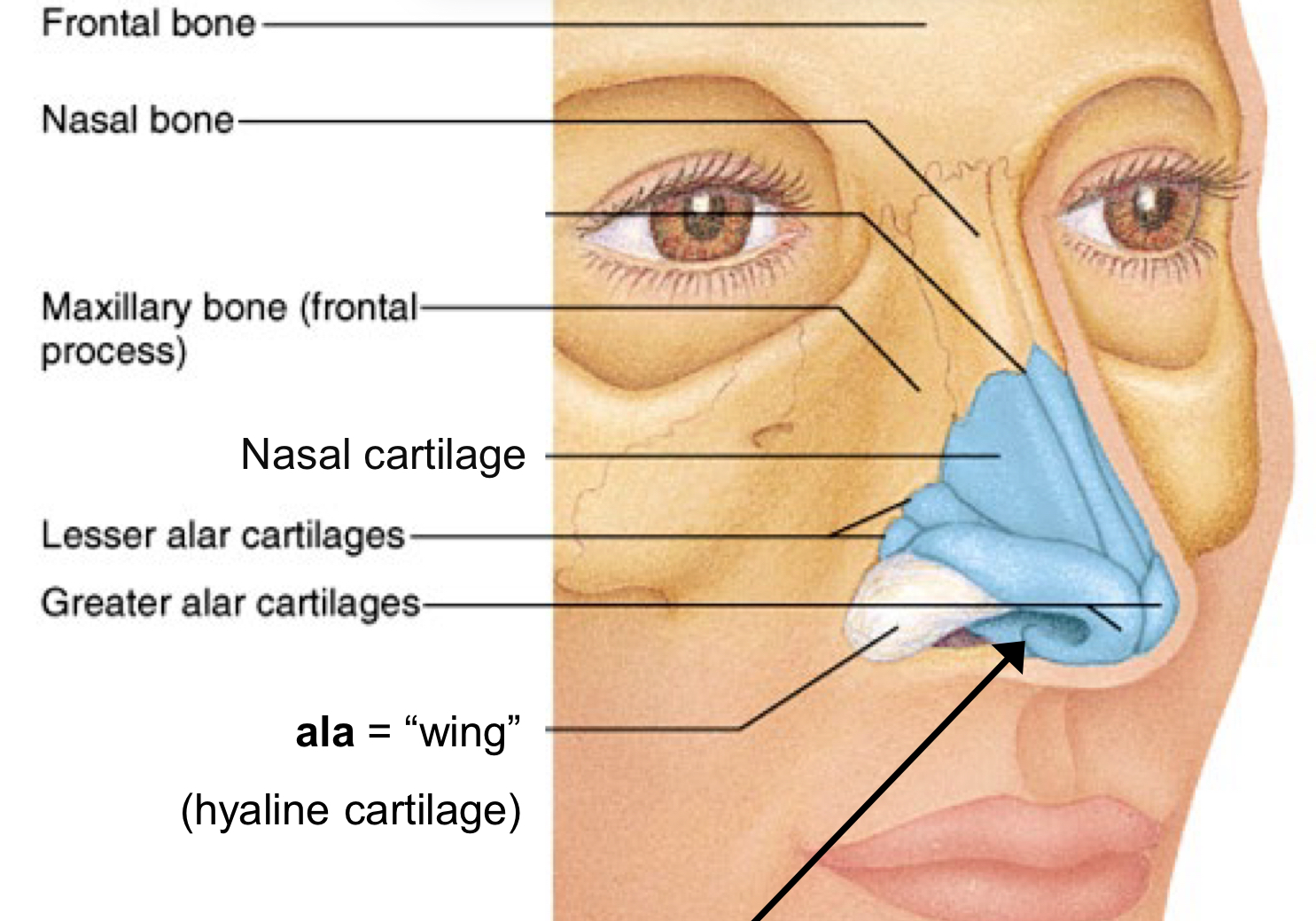
External Nare also called nostril
Vestibule = “entrance” or “atrium”
Vibrissae = “nose hairs”
(skin = stratified squamous epithelium)
What is the Upper Respiratory System lined by
Respiratory Mucosa
Internal Nare or Choana
Channels to the throat behind nasal conchae
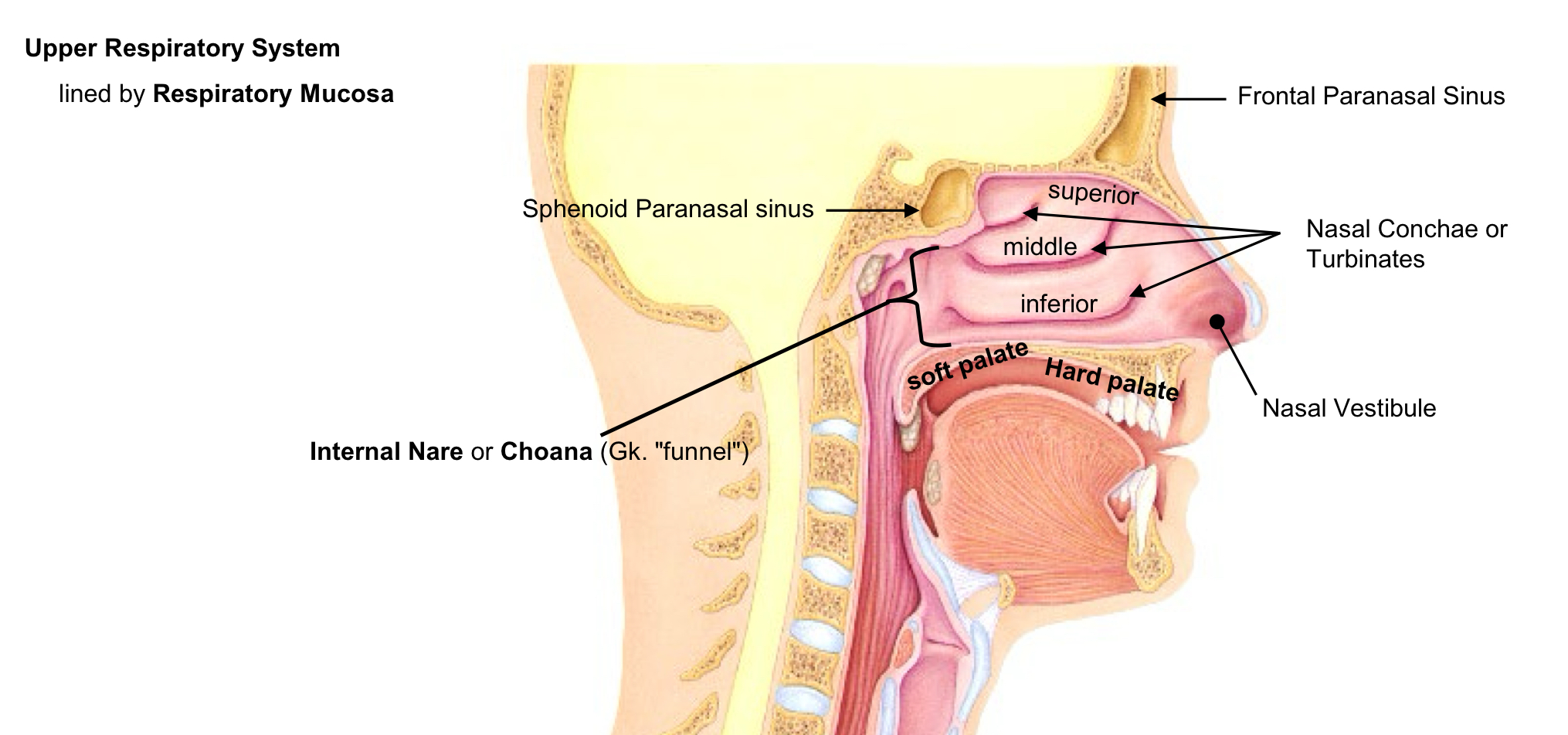
Hard palate
Anterior front room of mouth made of maxilla and palatine bones
Soft palate
Forms the posterior roof of the mouth more flexible and mobile
Nasal Septum
Perpendicular Plate of ethmoid bone and the Vomer
Nasal Conchae
3 layers
Superior (ethmoid bone)
Middle (ethmoid bone)
Inferior (a cranial bone)
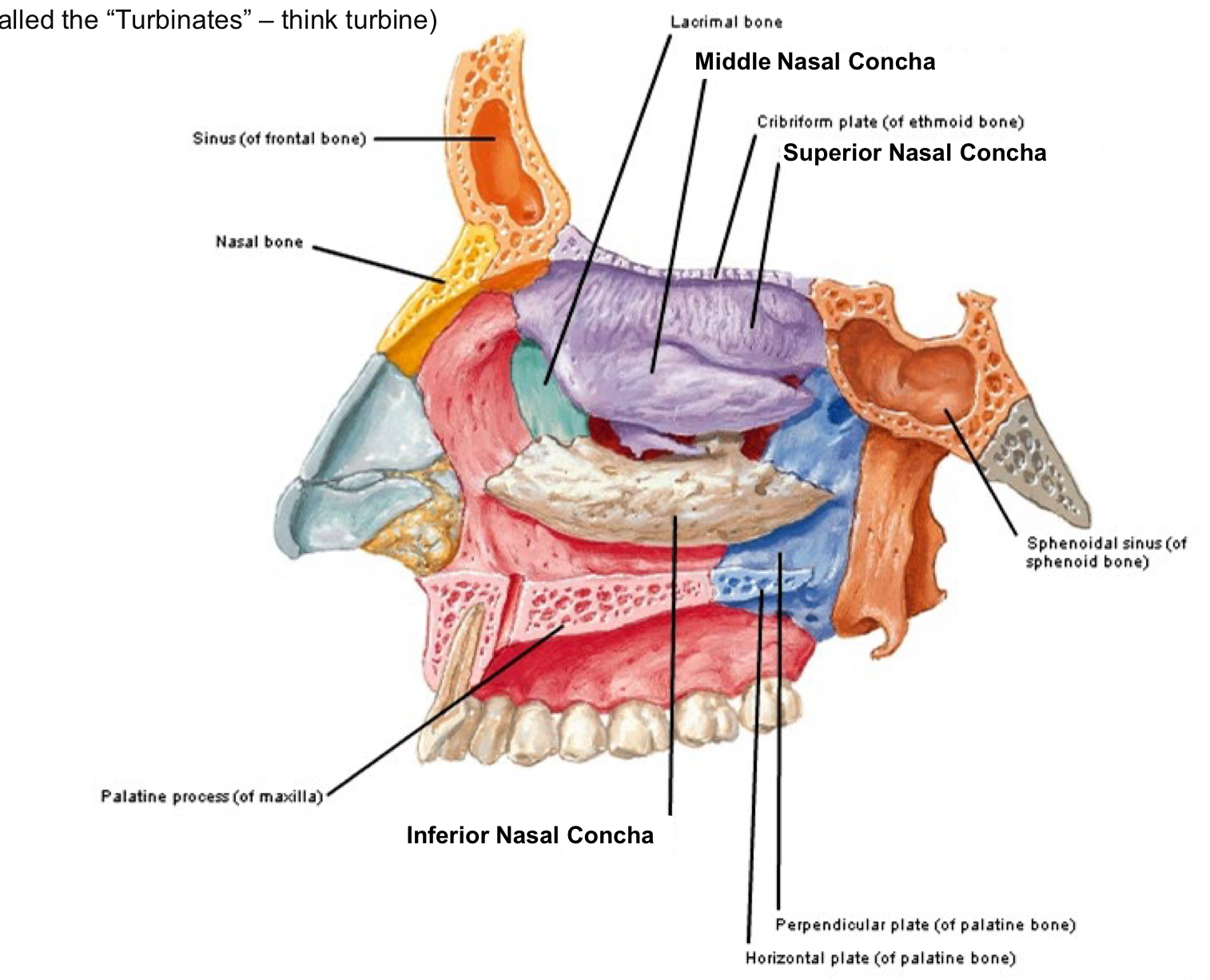
Meatus of the nasal cavities
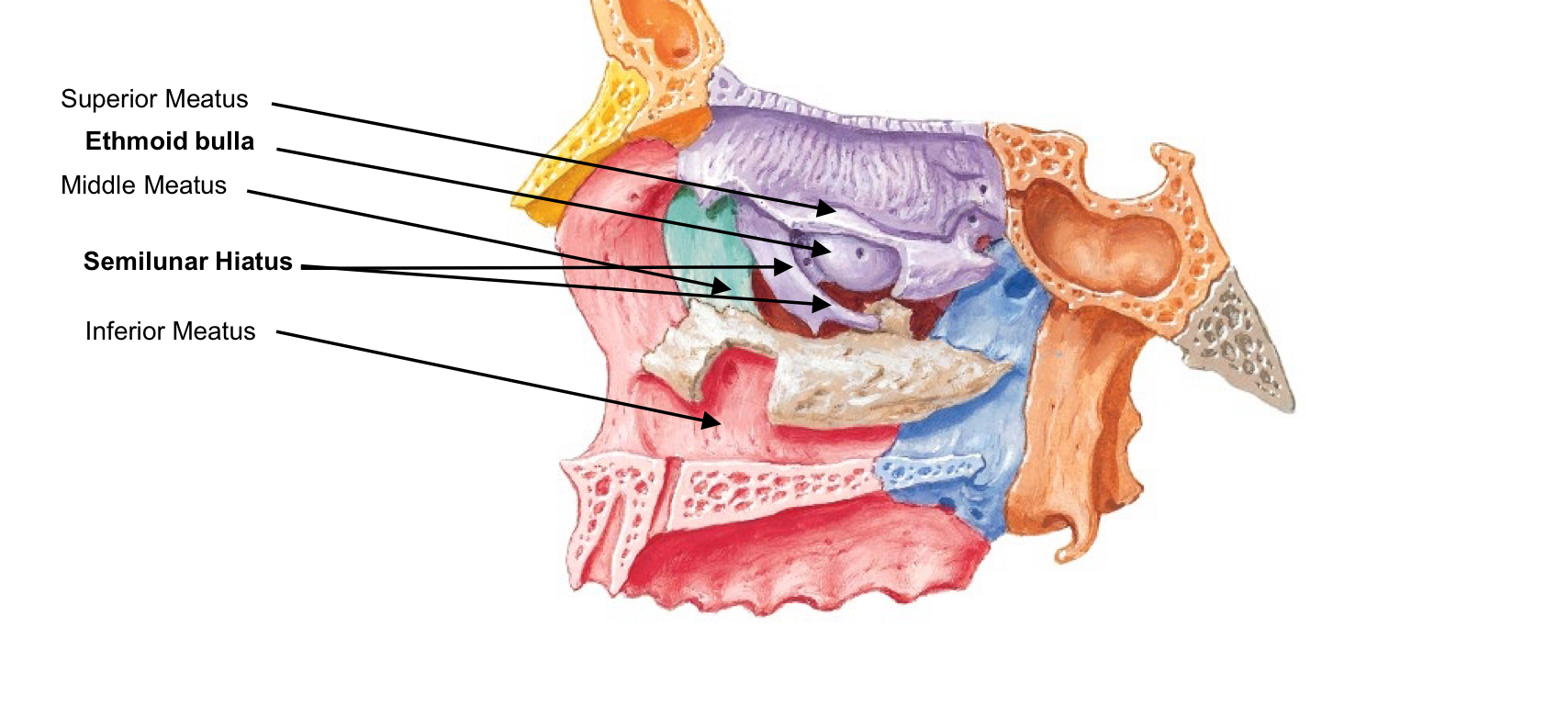
canal” or “channel”, located between Conchae The middle meatus also contains: Openings into the paranasal sinuses
Ethmoid bulla
Semilunar hiatus
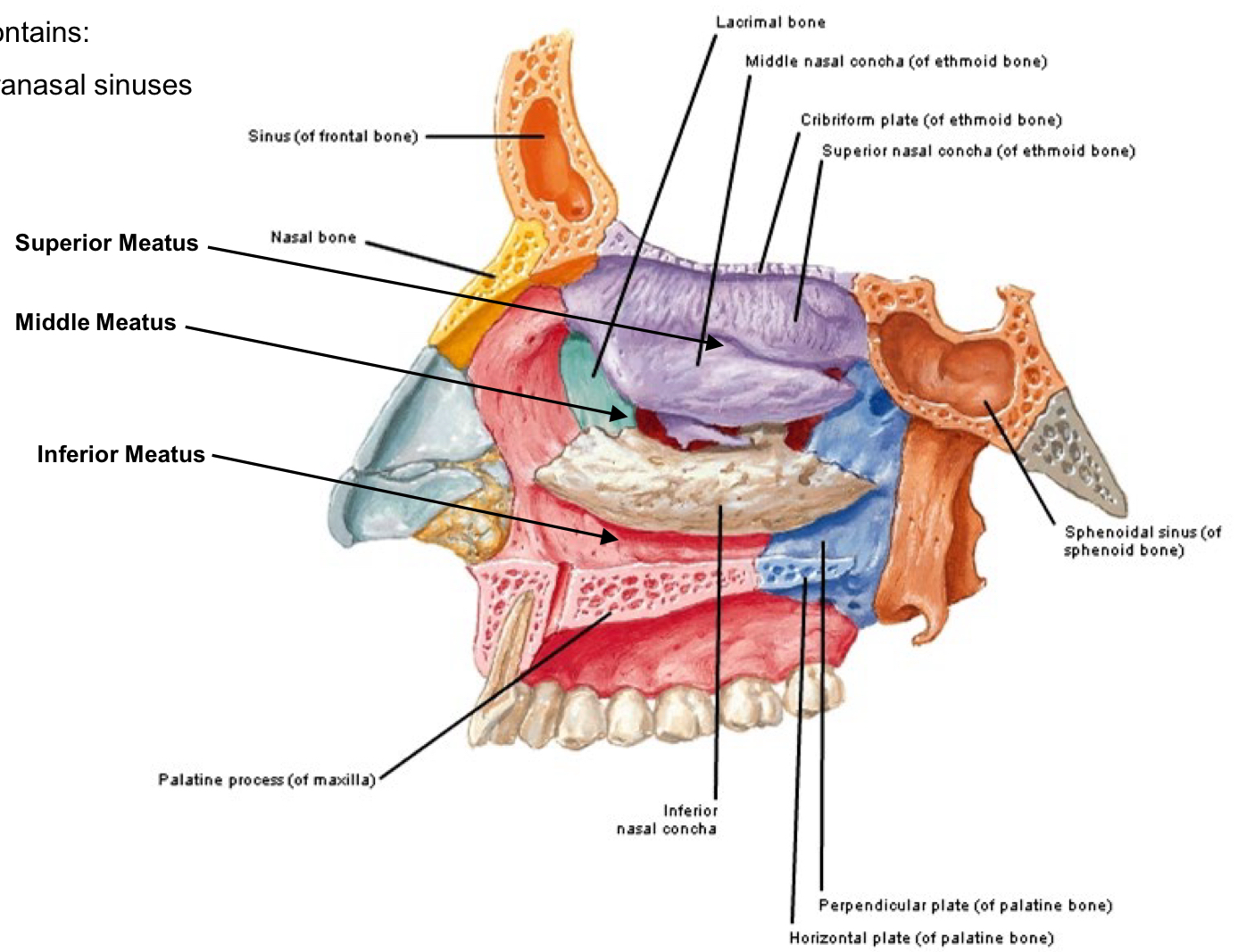
middle meatus Openings into the paranasal sinuses
Ethmoid bulla
Semilunar hiatus
Respiratory Epithelium
Epithelium = Ciliated Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium and Goblet cells
Function of mucosa
Secretion of mucus, protection, and absorption (in some areas)
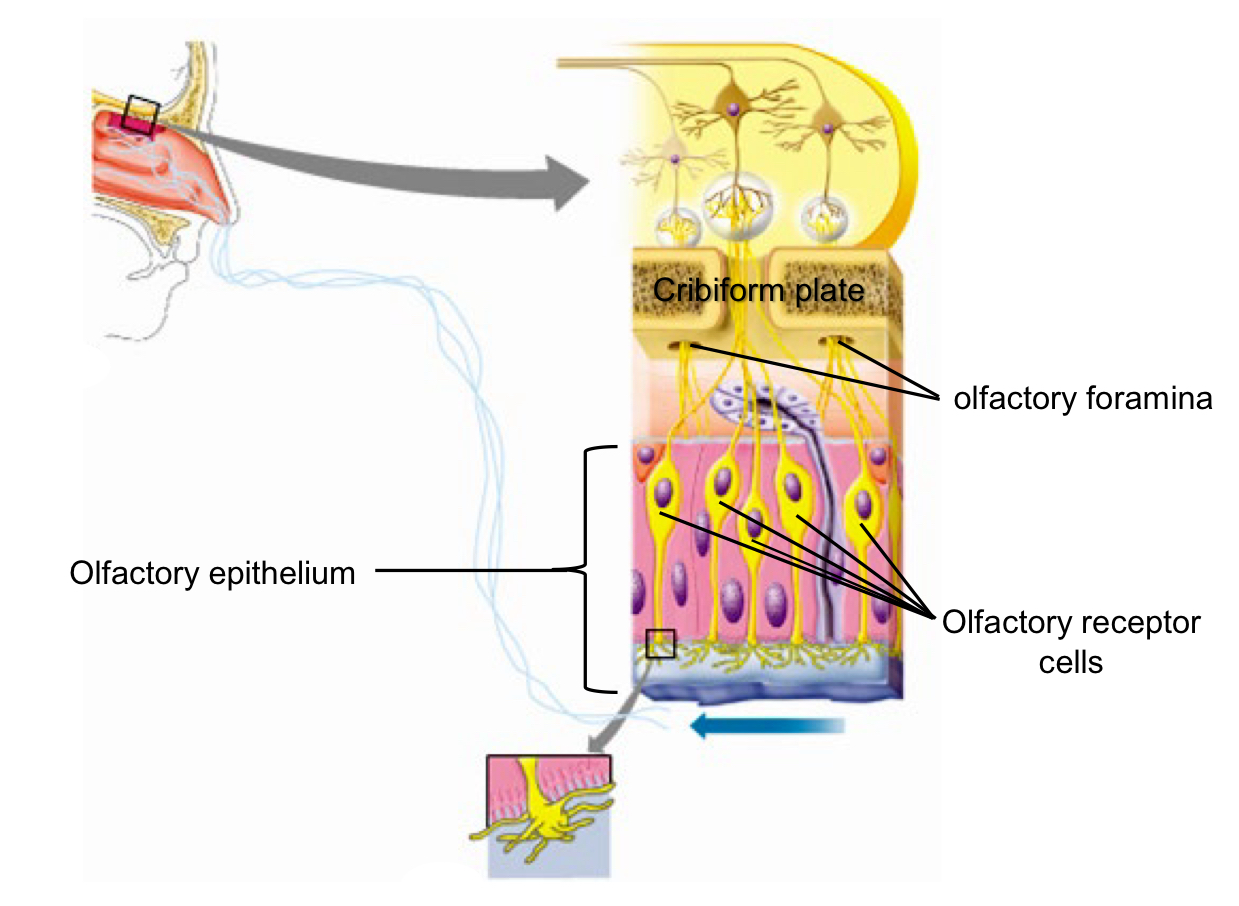
Olfactory Epithelium
specialized supporting cells and glands + Olfactory Receptor Cells Olfactory epithelium is located in the Nasal Cavity, below cribriform plate
Let’s you smell
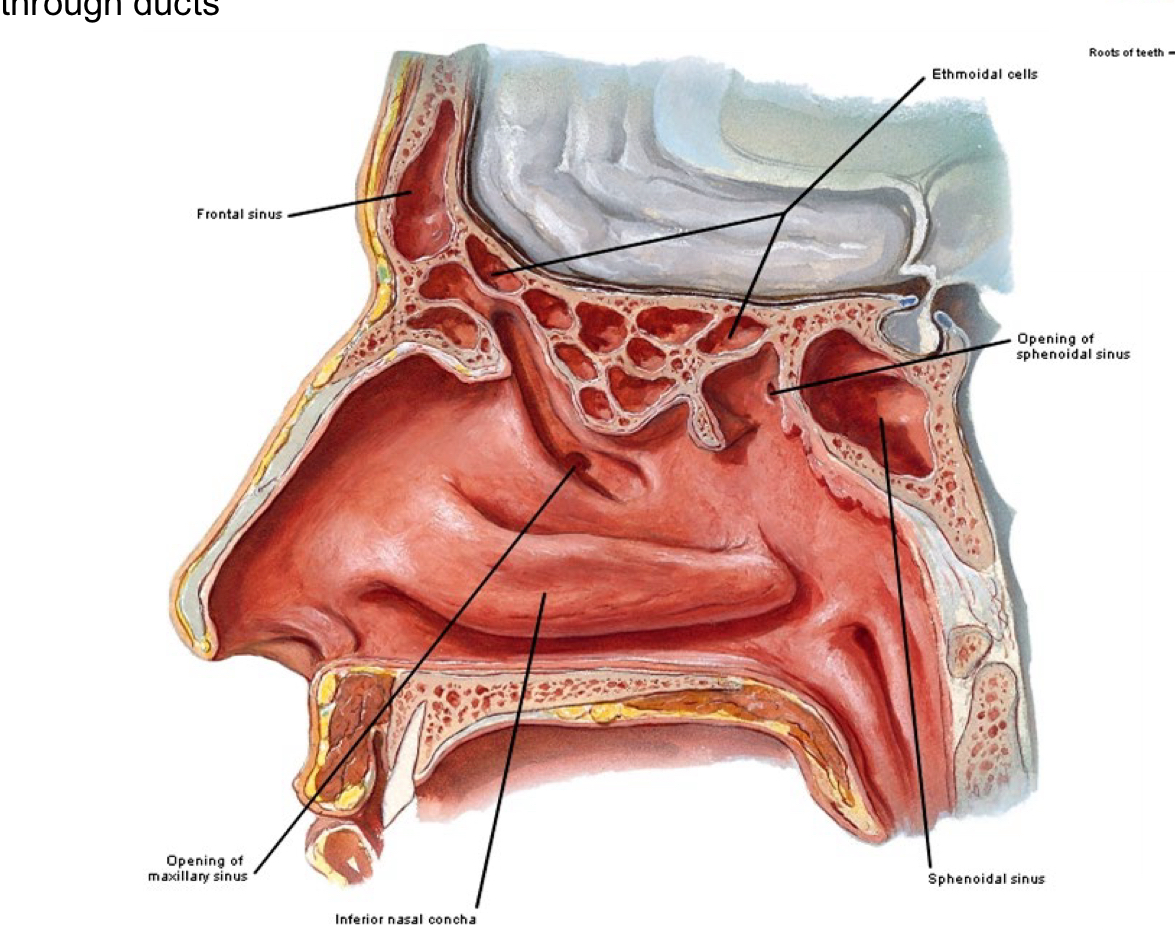
Paranasal Sinuses are named for the bones in-which they are housed
Frontal
Ethmoidal
Sphenoidal
Maxillary
Pharynx is composed of 3 parts:
(1) naso-pharynx (behind nasal cavity and above soft palate)
(2) oro-pharynx (behind oral cavity soft palate to the top of the epiglottis)
(3) laryngo-pharynx( epiglottis to the esophagus)
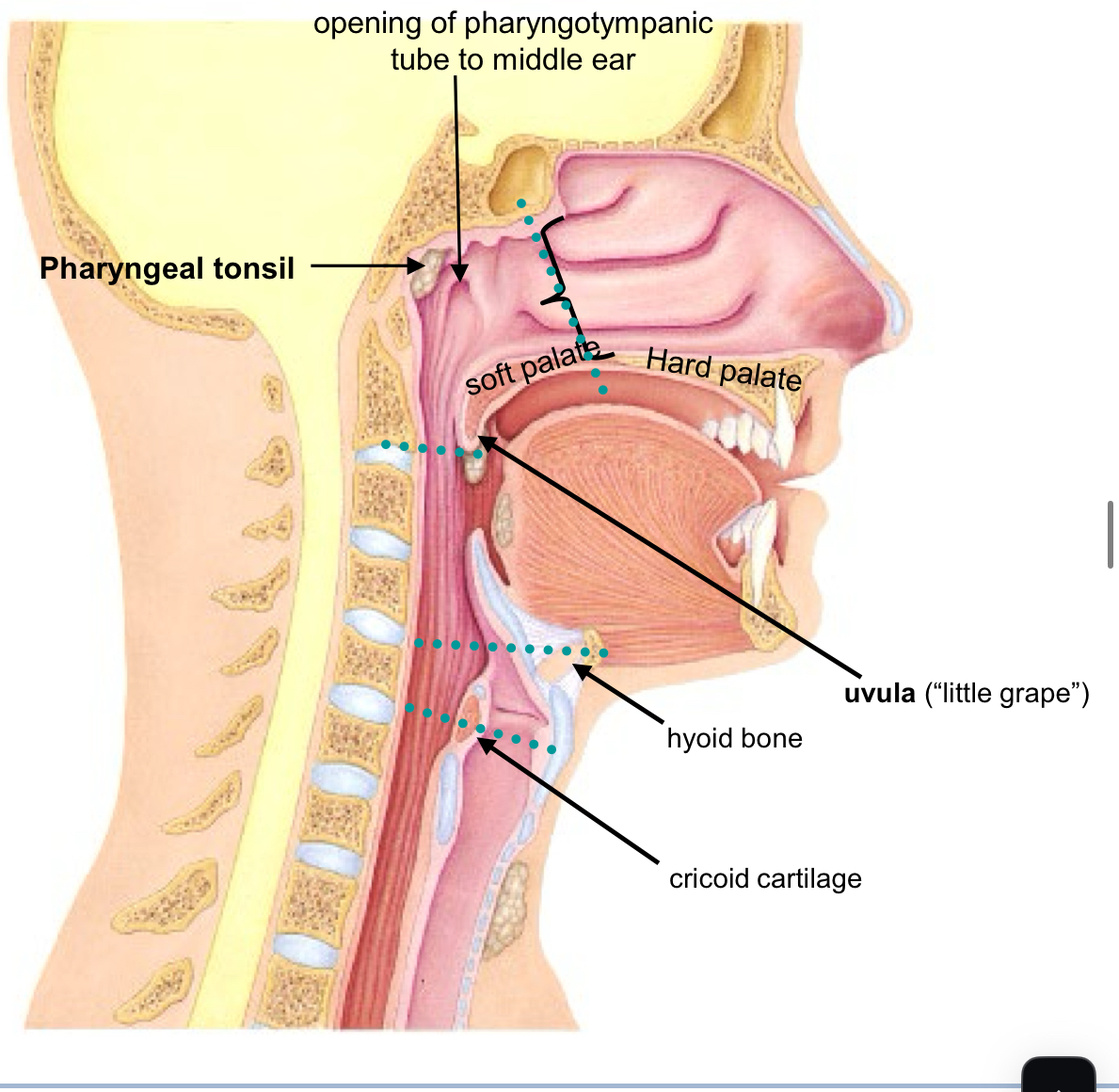
naso-pharynx
Posterior to Nasal Cavity Passage way for air Contains the following structures: Opening of Pharyngotympanic or Auditory Tube Pharyngeal Tonsil (lymphatic tissue) Lined by Respiratory Epithelium
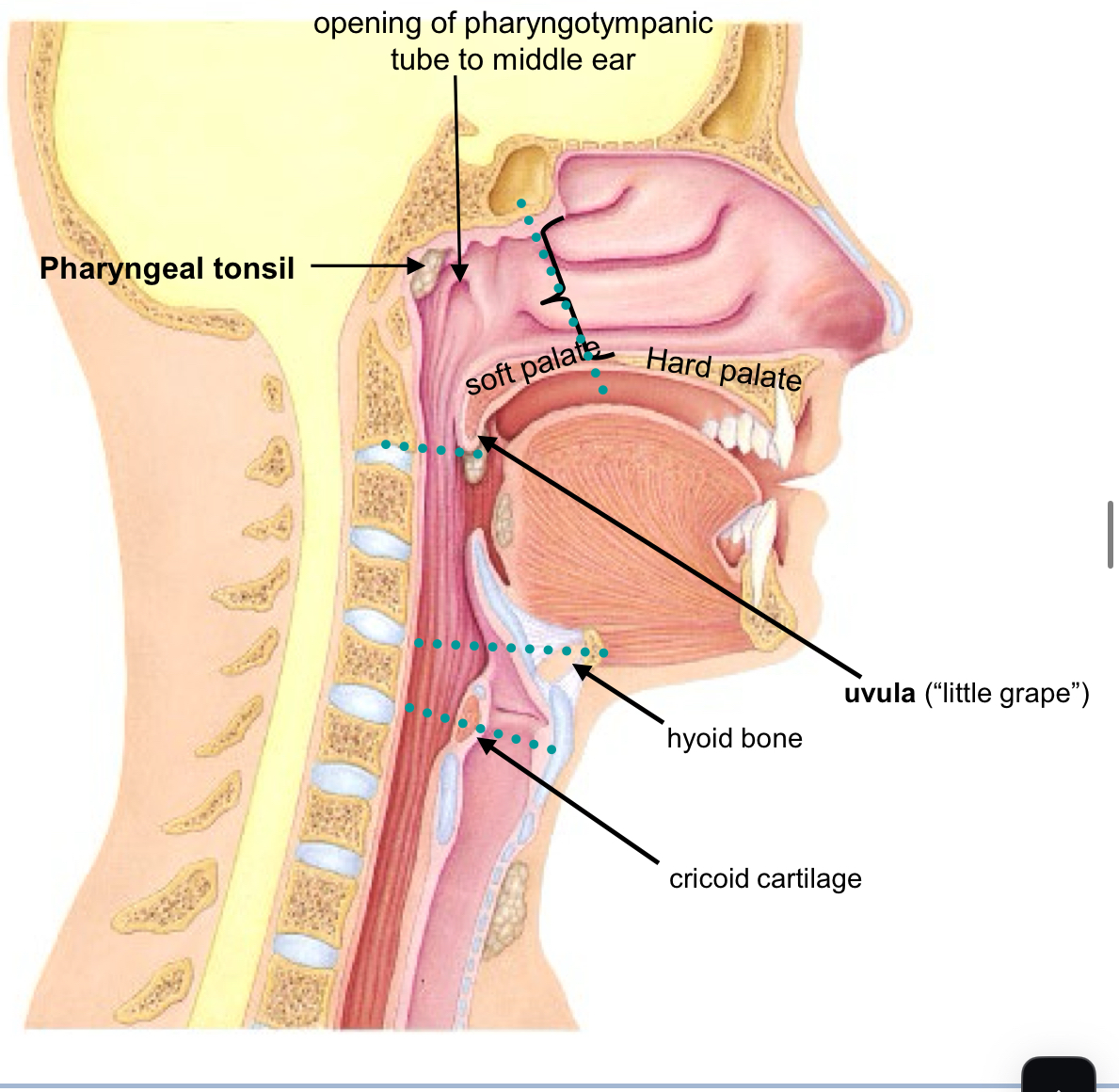
oro-pharynx
from Fauces to uvula & hyoid bone
Posterior to Oral Cavity Contains the following structures:
Palatine Tonsil (lymphatic tissue)
Lingual Tonsil (lymphatic tissue)
Epiglottis (elastic cartilage) Passage for both air and food Lined by stratified squamous epithelium (same as oral cavity)
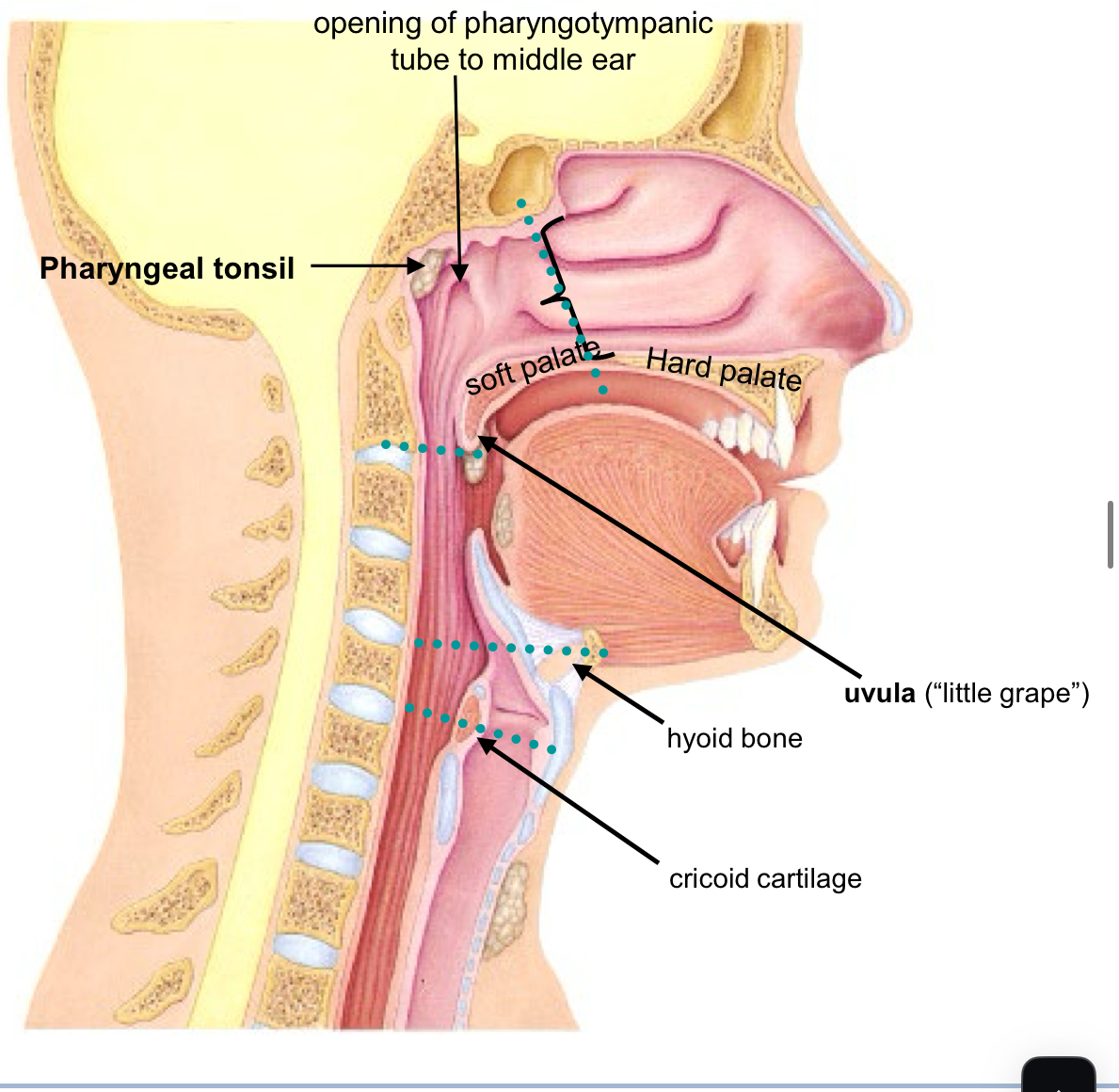
laryngo-pharynx
From level of hyoid bone to level of cricoid cartilage of trachea Posterior to Larynx Passage for both air and food
Contains the following structures:
Opening into the Larynx (“voice-box”)
Lined by stratified squamous epithelium (same as oral cavity)
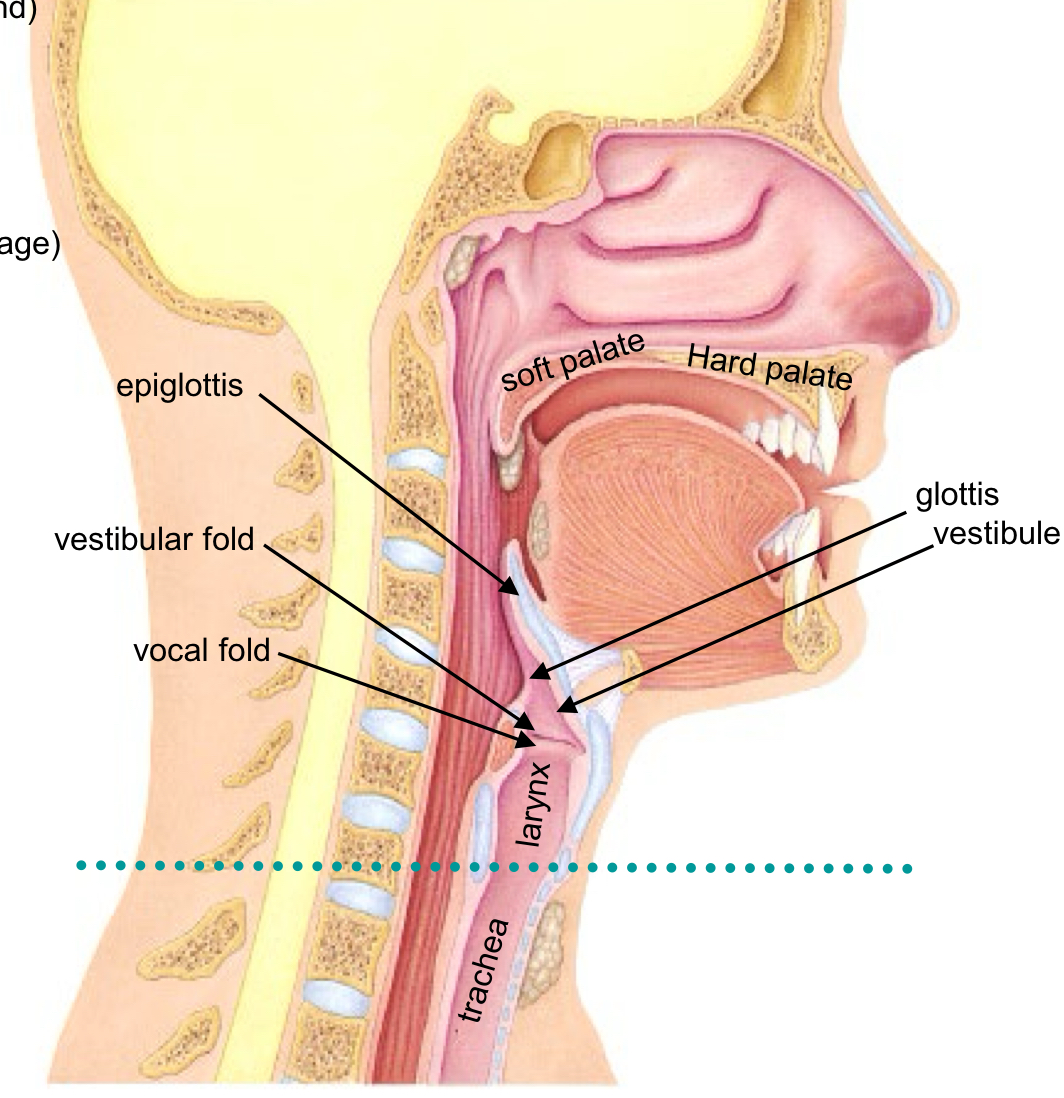
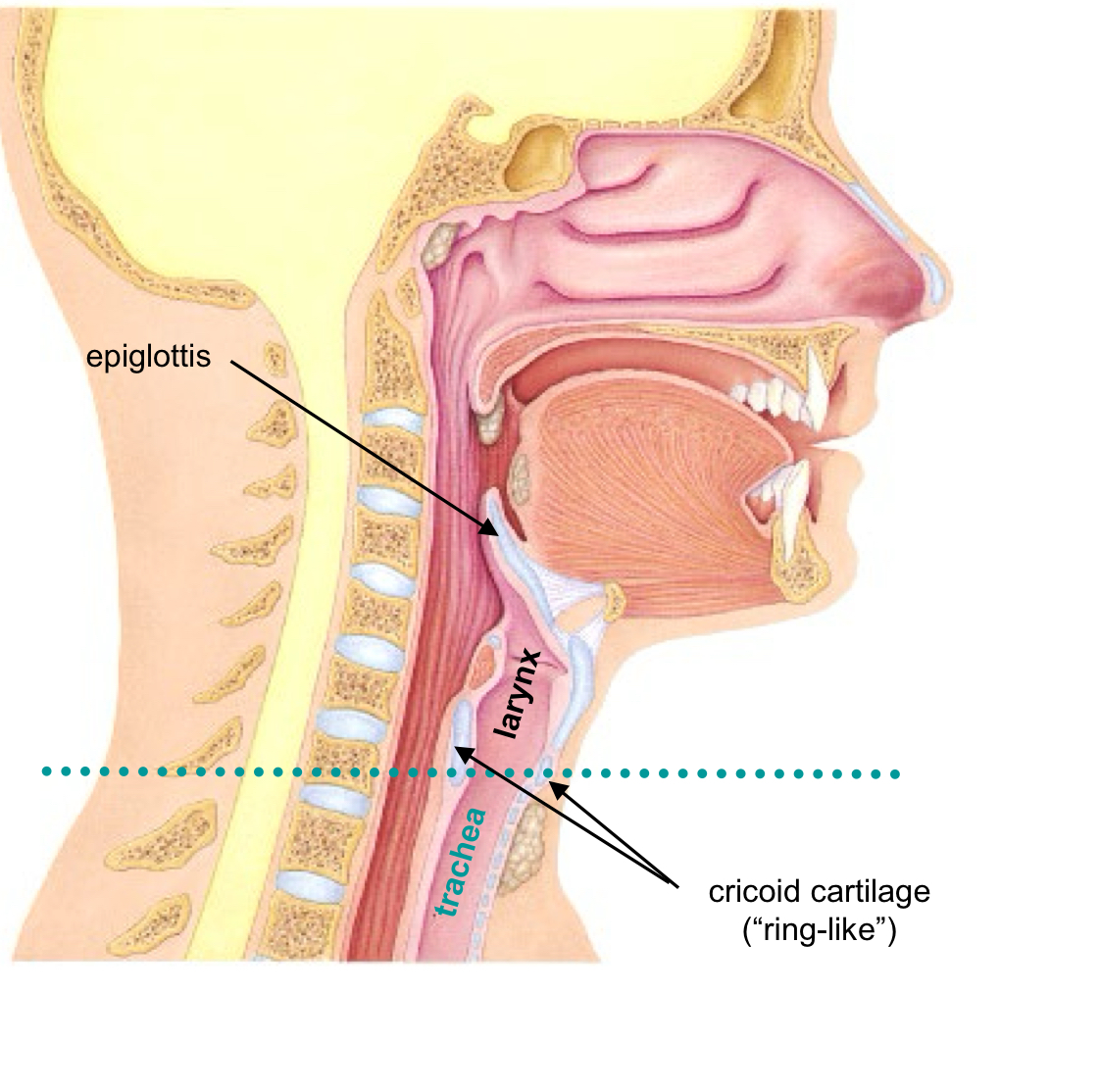
Larynx
is often called the “voice-box” Passage for air (ventilation) and for vocalization (producing sound)
Larynx becomes Trachea at Cricoid Cartilage
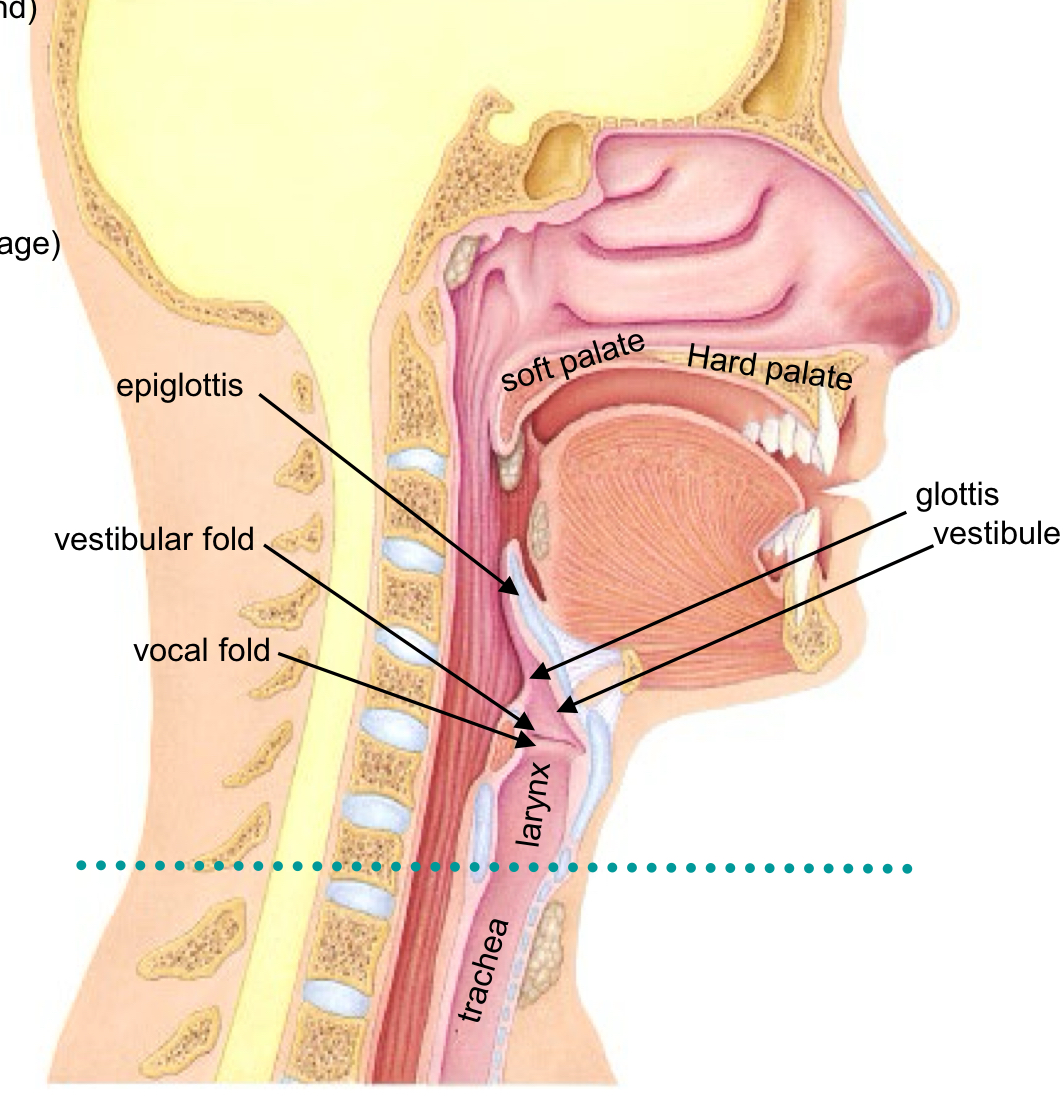
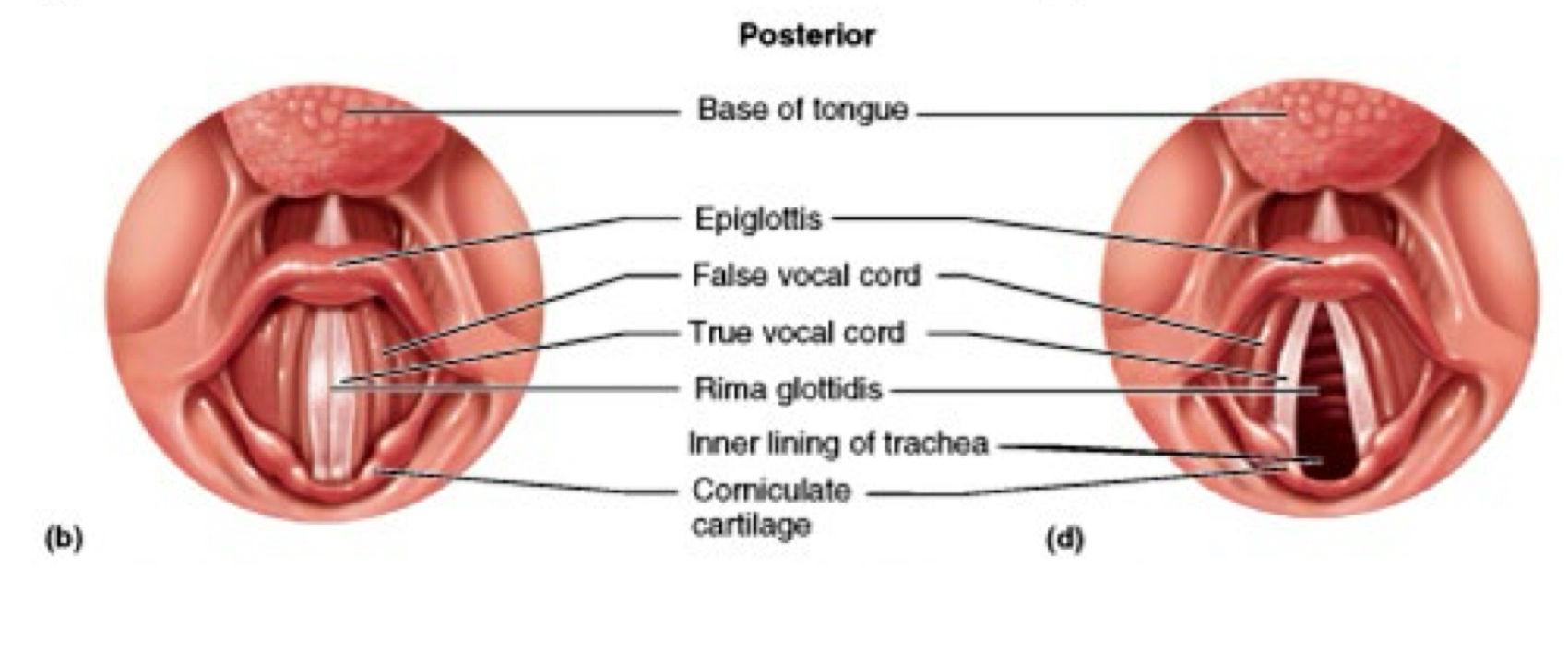
Glottis, Rima Glottidis, Epiglottis
opening into larynx
“rim around the glottis” or the ring-shape
a flap that bends to close the opening (elastic cartilage)
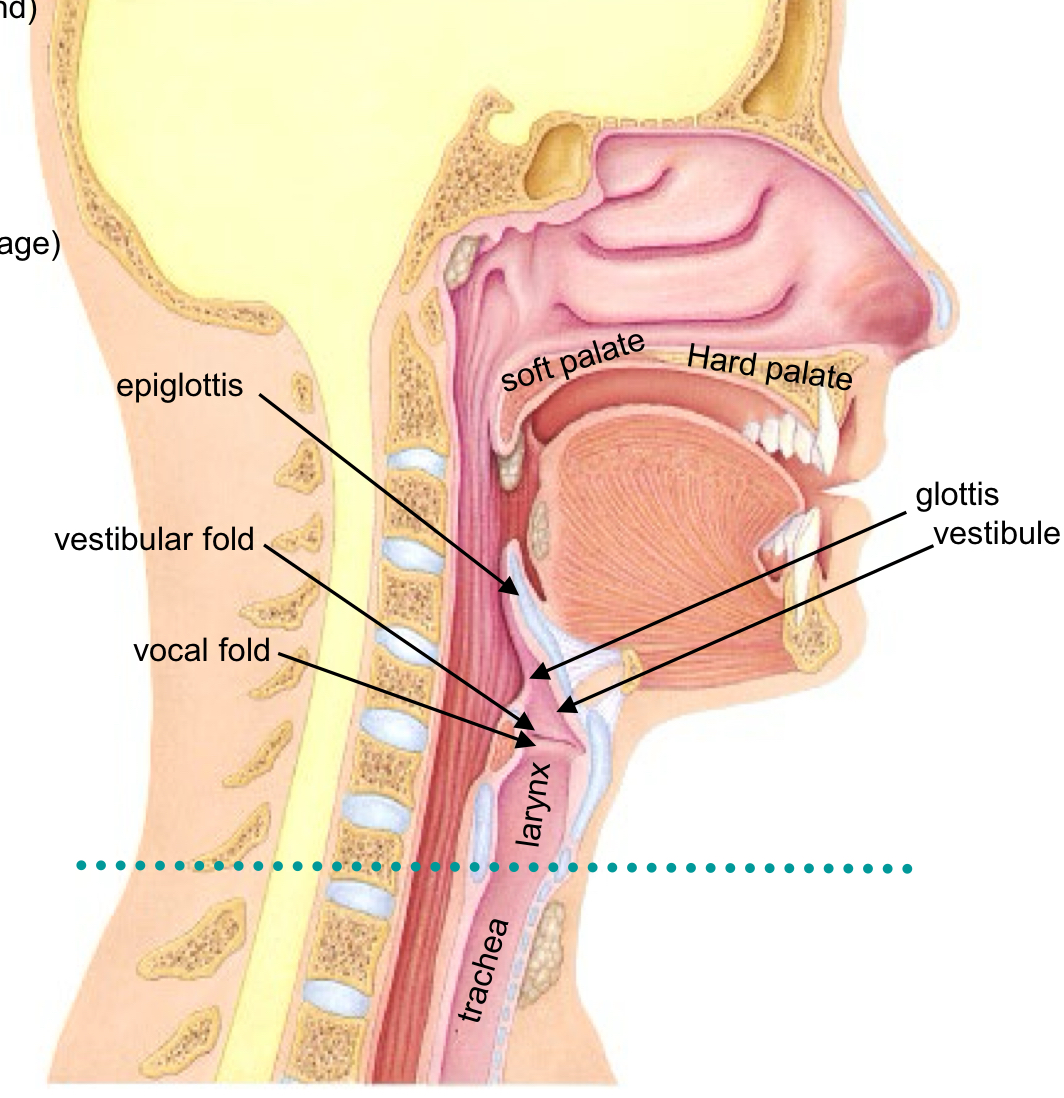
Vestibule
entrance of the Larynx
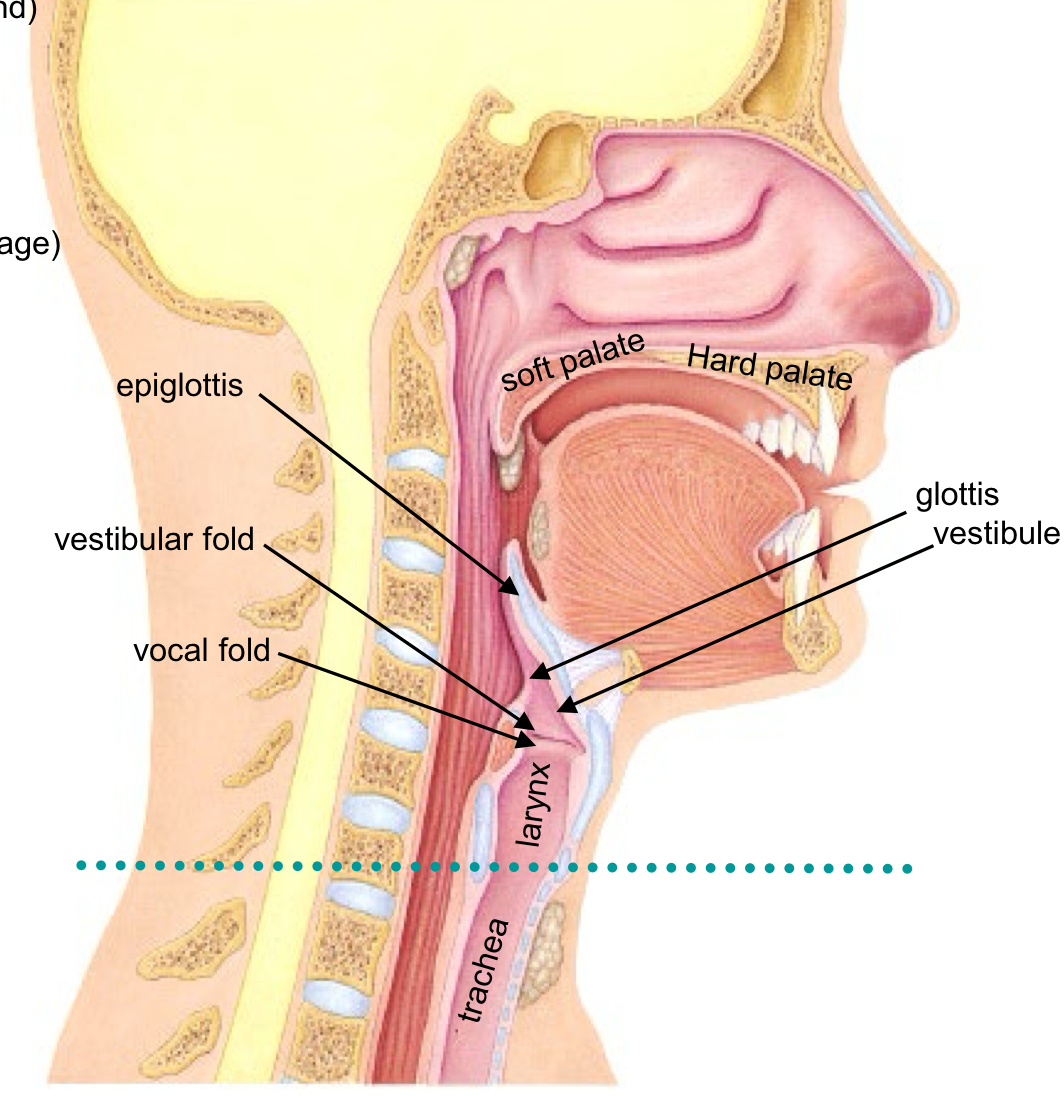
Vestibular fold or false vocal-cord function
Protection
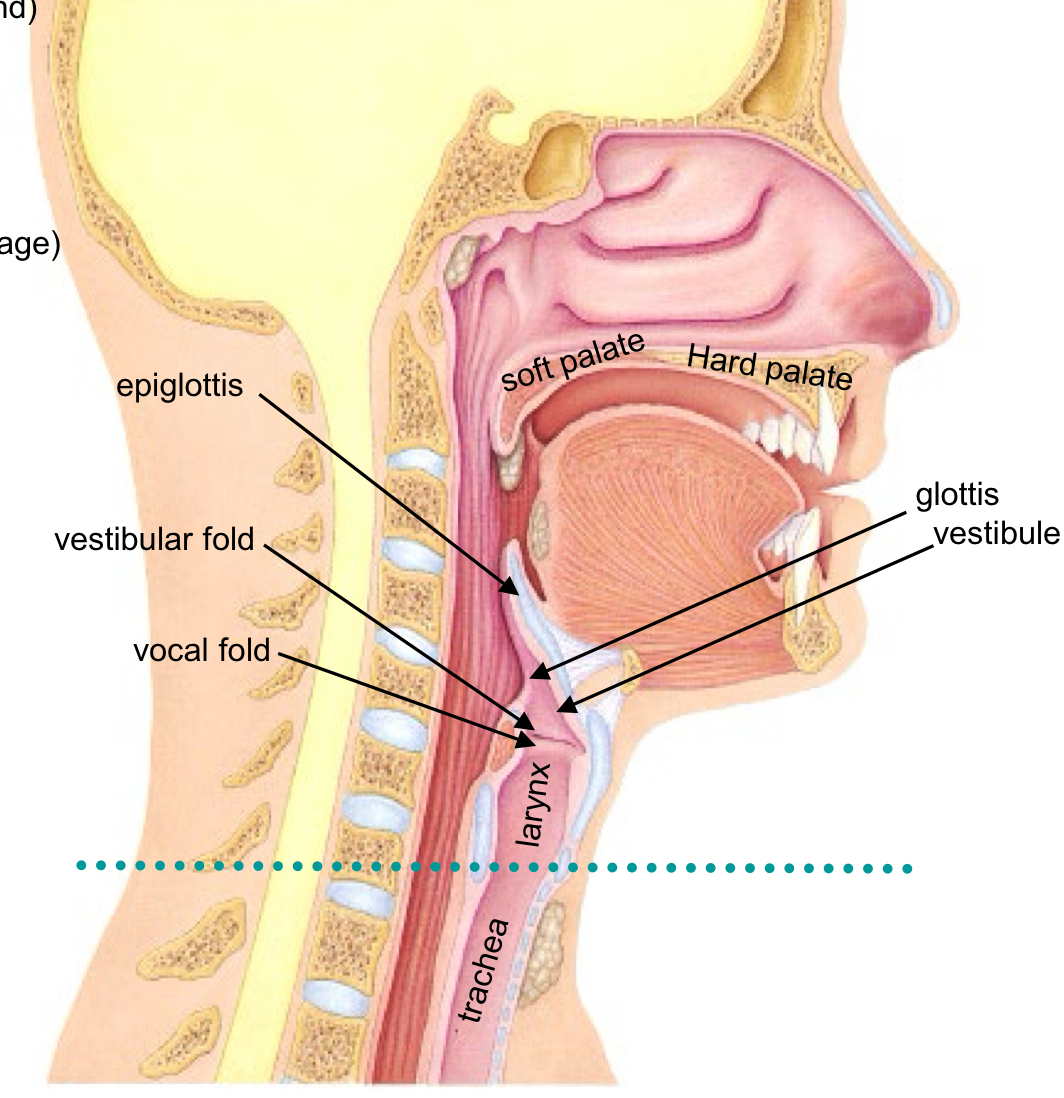
Vocal fold or true vocal-cord
Sound protection
There are 4 cartilages which support the Larynx
Thyroid = “shield-shape”
Arytenoid = “resembles a pitcher”
Cricoid = “ring-shaped”
Corniculate = “horn-shaped”
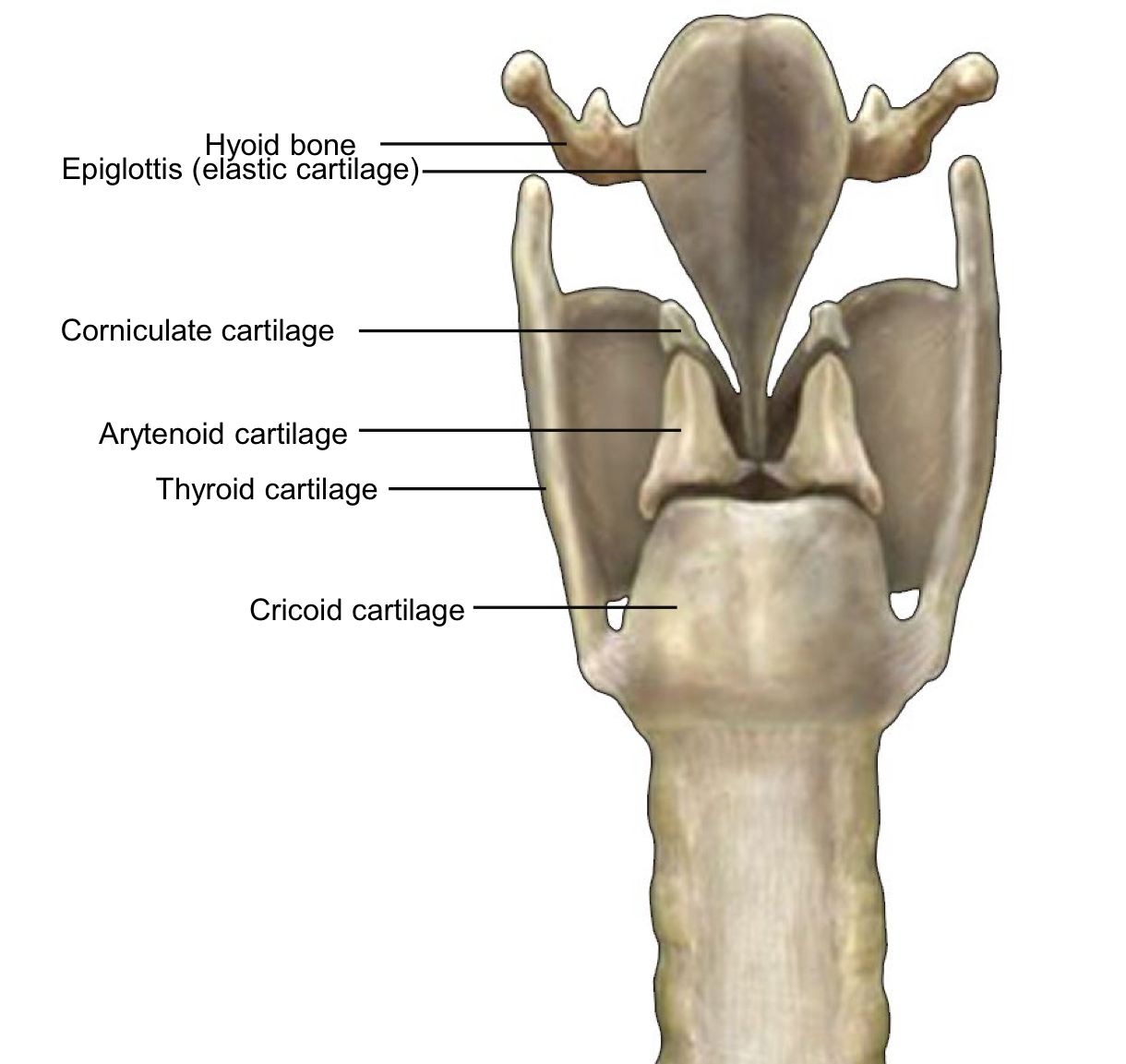
Vocal Cords = Vocal Ligament + mucosa (“Fold”)
Vocal ligament extends from thryroid cartilage to arytenoid cartilage Laryngitis or Laryngeal Inflammation is caused by inflamed vocal cords
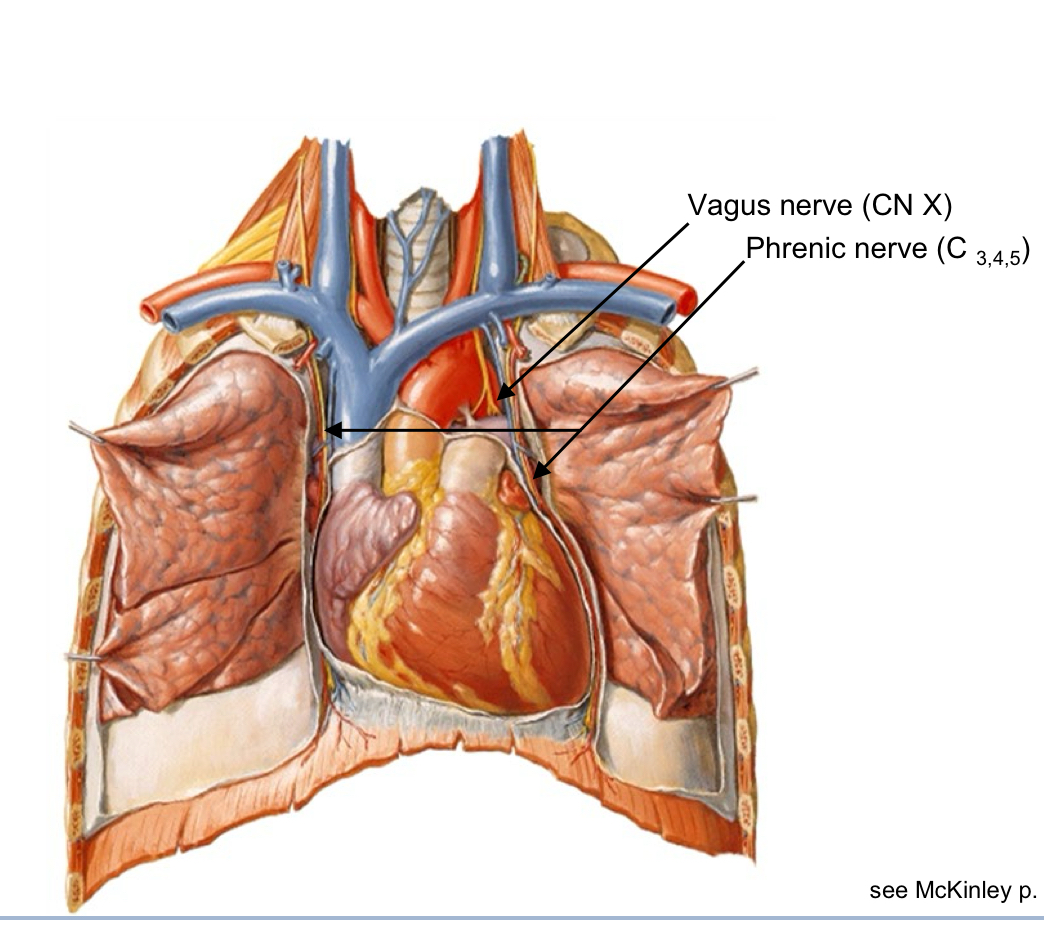
The Vagus nerve (CN X)
Motor innervation to muscles of vocalization Sensory to Larynx
Cartilages of the Larynx
Epiglottis = elastic cartilage
All laryngeal cartilages = hyaline Trachea
(“C”-shaped rings) = hyaline
The Trachea
Begins inferior to Larynx at the Cricoid Cartilage
Lined by Respiratory Epithelium or Respiratory Mucosa
Held open by “C”-shaped Cartilaginous Rings (hyaline cartilage)
Posterior side is soft – in contact with Esophagus
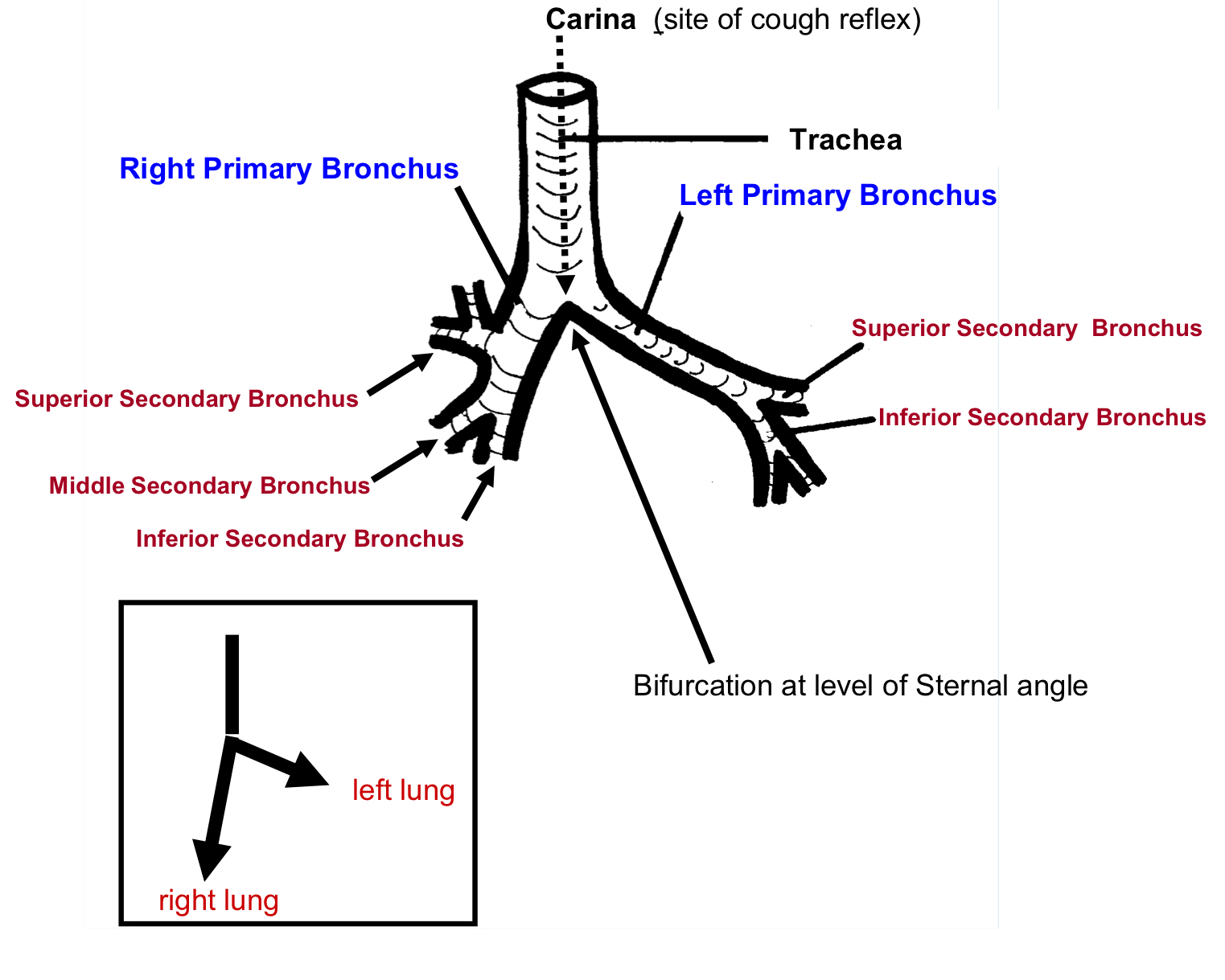
The Trachea Bifurcates
Bifurcates into Right and Left Primary Bronchi
Ridge at bifurcation called Carina (“shaped like the keel of a boat”)(highly innervated)
An asymmetrical bifurcation pattern
Surface Landmark of bifurcation is the Sternal Angle
Primary Bronchi bifurcate to form Secondary Bronchi 3 secondary bronchi on right side Right Primary Bronchus 2 secondary bronchi on left side
The Lungs Lobes
Right lung = 3 lobes
Left lung = 2 lobes (heart)
Right lung features
Right lung = 3 lobes
Oblique fissure and Horizontal Fissure
Left lung features
2 lobes (heart)
Oblique fissure
Cardiac impression
Cardiac notch
CardioPulmonary (“Heart” – “Lung”) Circulation
Heart >Lungs Lungs > Heart
Circulate between systematic circulation at the end.
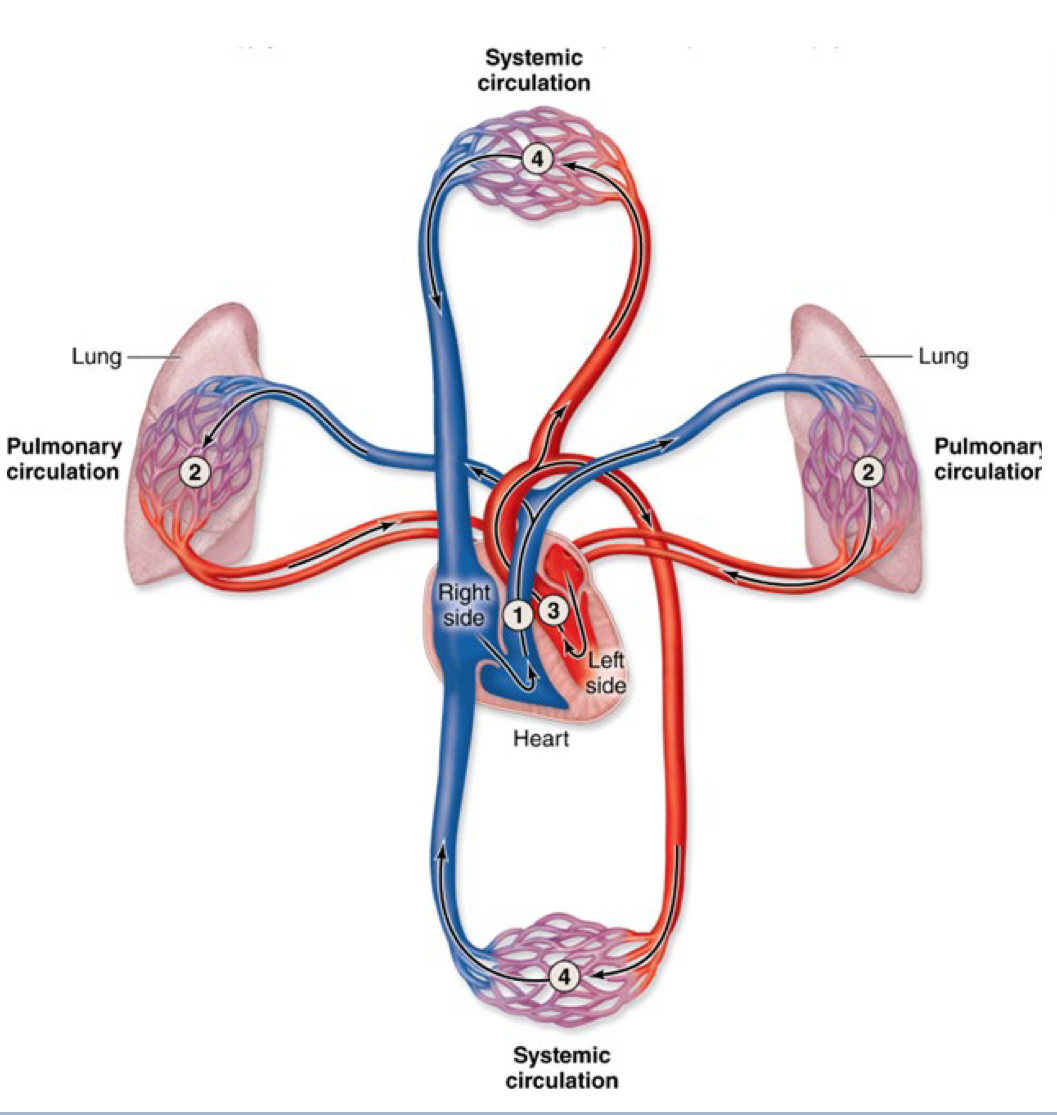
CardioPulmonary (“Heart” – “Lung”) Circulation
Blood Flows from Heart Lungs and Lungs Heart
External Respiration
Gas exchange occurs between blood vessels (capillaries) and Lung (alveolus)
How oxygen gets to the lungs
Pulmonary arteries – carry deoxygenated blood to Lungs
Pulmonary veins – return oxygenated blood to Heart
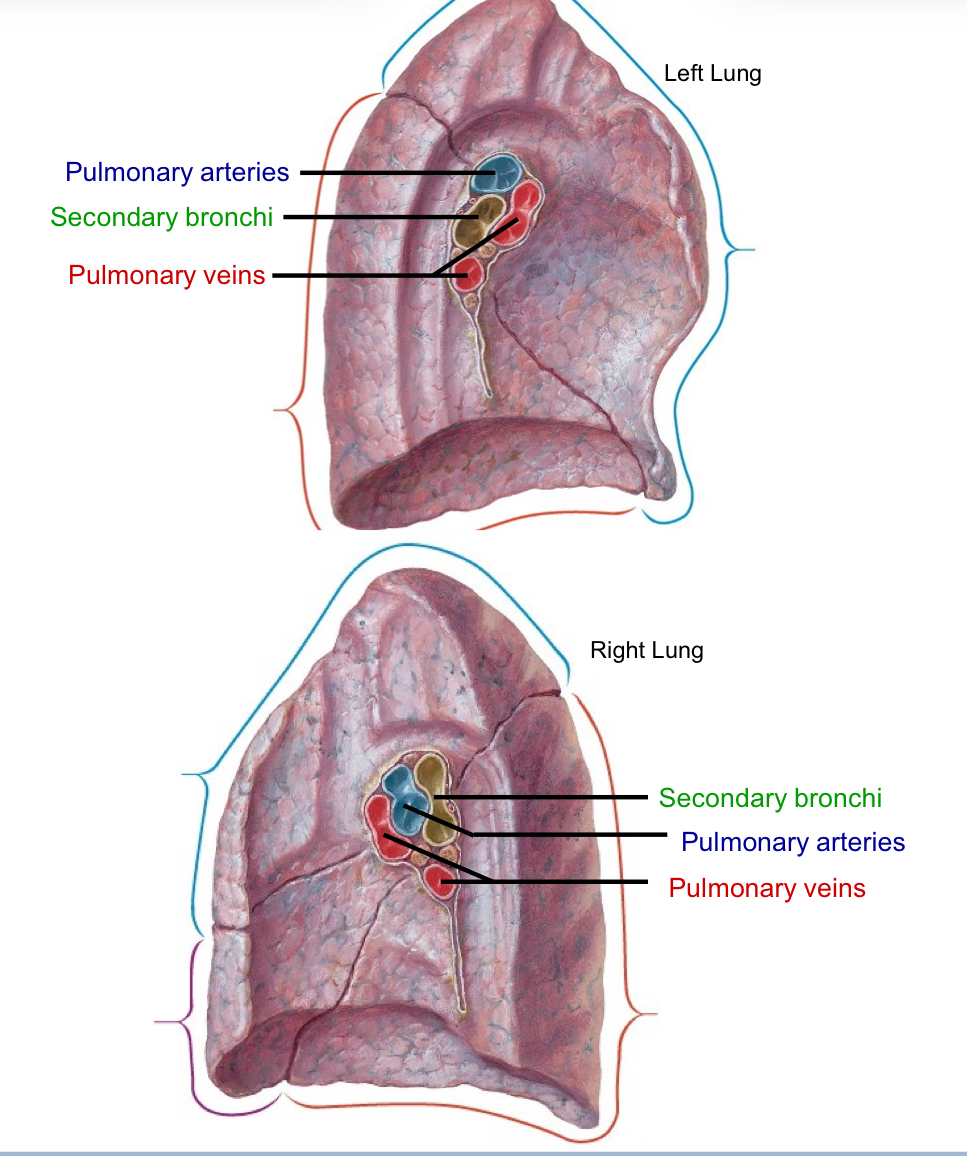
Root of the Lung
Note the difference between the right and left root
Structures from superior to inferior
Right lung: Bronchi Arteries Veins
Left lung: Arteries Bronchi veins
Root of the Lung nerves
The Vagus and Phrenic nerves descend side-by-side through the neck They can be distinguished distally as ………
the Phrenic nerve travels over the root of the lung the Vagus nerve travels deep to the root of the lung
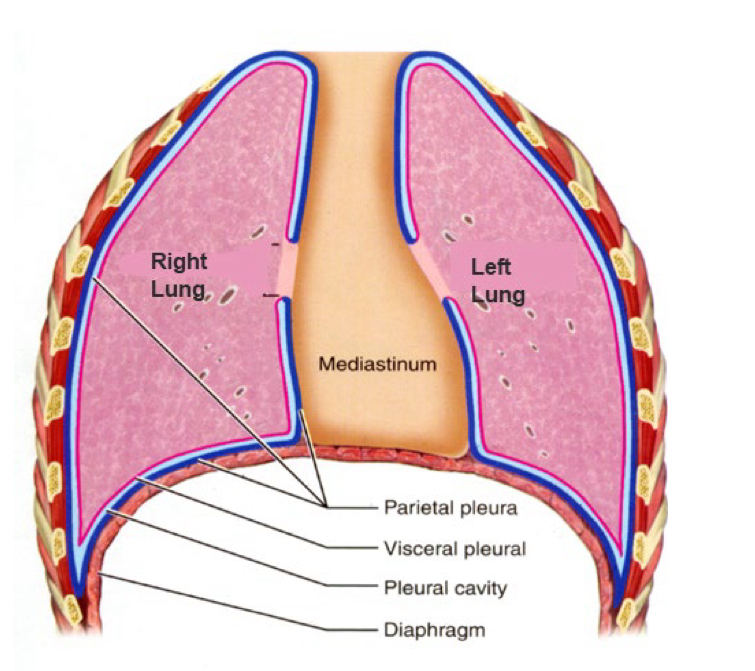
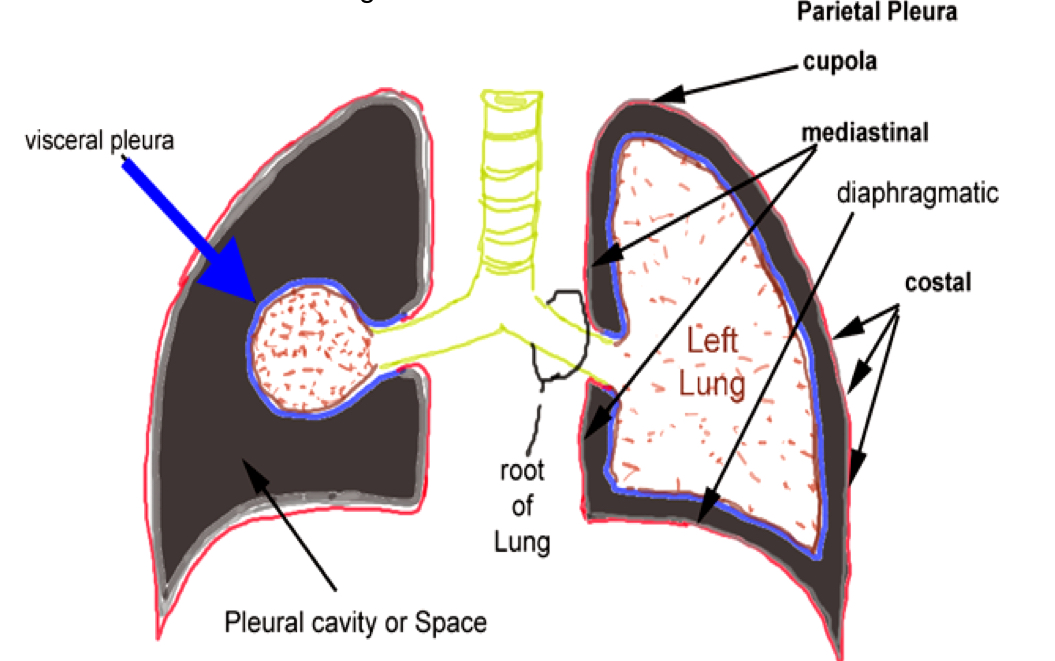
Pleura
The Serous Membrane that surrounds the Lungs
Two components = Visceral Pleura (touching viscera/ “organ”) & Parietal Pleura (touching the thoracic “wall”)
Serous Membrane
simple squamous epithelium producing lubricating serous fluid
Structures of the parietal pleura
Parietal Pleura has many regions = Cupola (“dome”),
Costal (“rib”). Diaphragmatic (diaphragm),
Mediastinal (“in the middle”)
Conduction Zone Of the lungs
Trachea & Primary Bronchus
• respiratory epithelium
2. Secondary Bronchus also called Lobar Bronchus
3. Bronchiole
4. Terminal Bronchiole (smallest bronchiole) • simple cuboidal epithelium
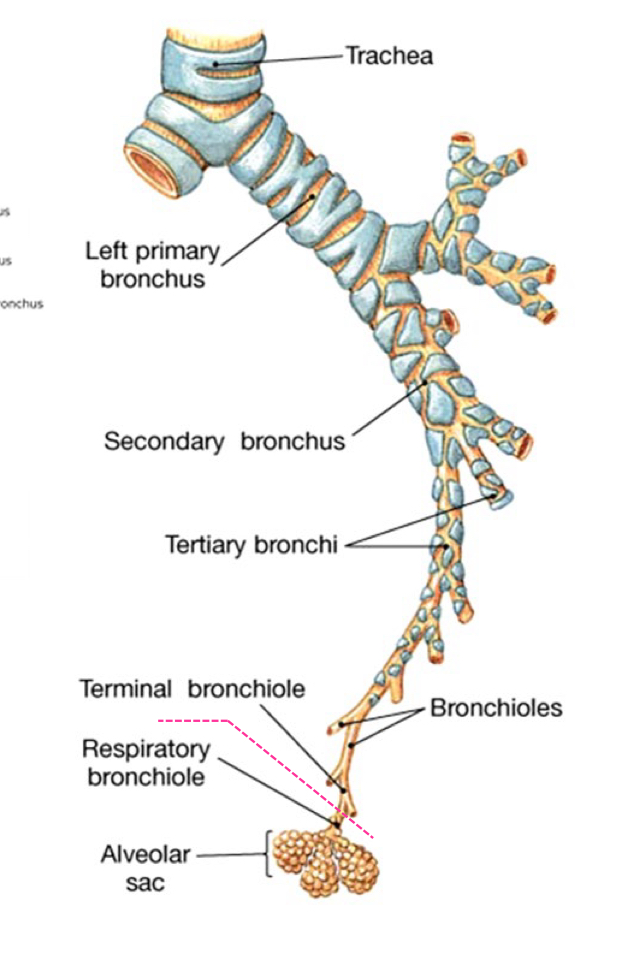
Trachea & Primary Bronchus
* respiratory epithelium
• Cartilagenous Rings
Secondary Bronchus
Cartilagenous Plates
Bronchiole
absence of Cartilage
Terminal Bronchiole
simple cuboidal epithelium
Respiratory Zone
Oxygen & CO2 exchange
• Respiratory bronchioles
• contain alveoli
• Alveolar Sacs
• terminal clusters of alveoli
• Alveolus (gas-filled air-exchange chamber)
• most of lung volume
• simple squamous cells form chambers
• these cells are also called “Type-I cells”
Alveolus
(gas-filled air-exchange chamber)
• most of lung volume
• simple squamous cells form chambers
• these cells are also called Type-I cells
Type-I cells = simple squamous cells that form chambers
• Type-II cells = surfactant secreting simple cuboidal cells
• Alveolar macrophages also called Dust cells (macrophages)
Respiratory membrane
“Air-blood barrier”
Alveolus (squamous epithelium) + Capillary (squamous epithelium)
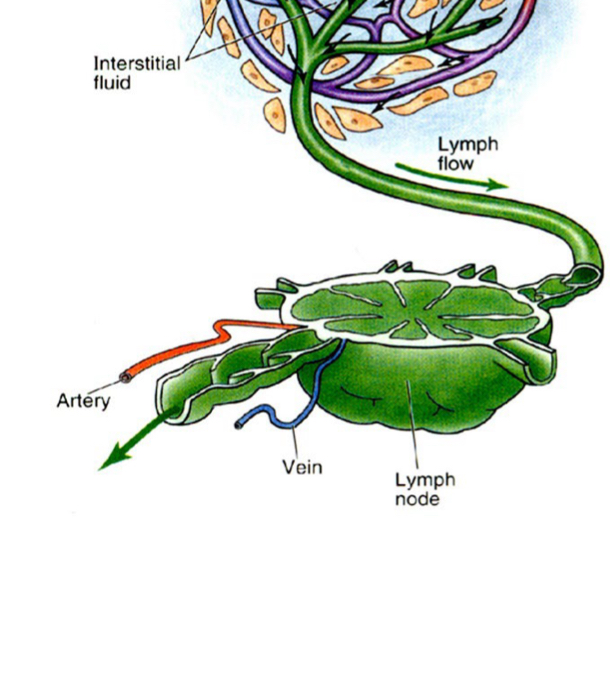
The Lymphatic system Hierarchy
Cells lymphoid cells = lymphocytes lymphatic capillaries, vessels, and ducts
Tissues “aggregate lymph tissue” superficial fascia >> extracellular or lymphatic fluid
Organs Bone marrow, thymus, spleen, lymph node
Functions of the Lymphatic system
Return extracellular fluid back to circulatory system
Returns 3L per day
Transports nutrients hormones and waste
Functions of the Lymphatic system #2
#2
Provides sophisticated defense (“Immunosurveillance”)
Chemotaxis = chemical signal produced from WBCs
Diapedesis = "through" + "walking"
Out of capillaries >> into interstitial space >> into lymph capillary Fight infection
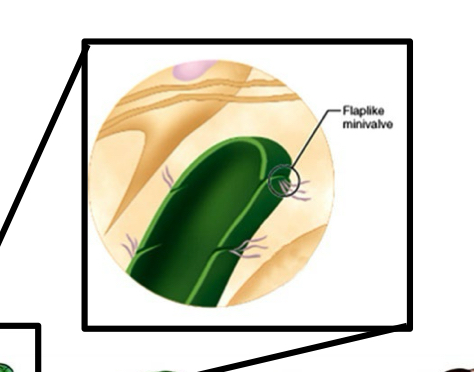
Lymphatic Capillary Flap
opens for uptake of Fluid and Cells
Lymphatic system versus Circulatory system
Relies on valves there is no pump unlike in the circulatory system
Lymph Nodes
filter Lymph Fluid
Lymphatic Vessels Function
absorb lipid (fat) from the Small Intestine Transportation of lipid = Lacteal Duct (lymphatic) into circulator system
Lymphoid Cells
Two types of LYMPHOCYTES =
T-lymphocytes (these cells mature in the “Thymus")
and
B-lymphocytes (these cells mature in the “Bone Marrow")
T-lymphocytes
Cell-mediated“ or “Stabbing” killers
B-lymphocytes
Humoral mediated attack”
(immunoglobulins or antibodies) Produce and release antibodies into the bloodstream
LYMPH NODULES
germinal center of nodule - one dividing B-cell
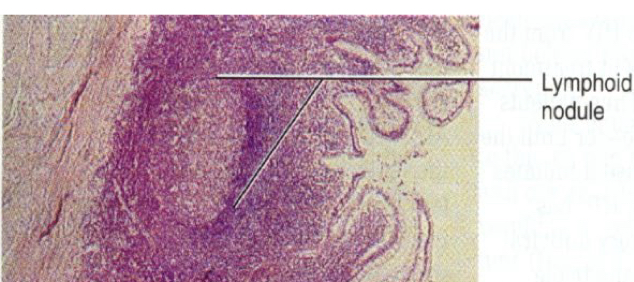
Aggregate lymph Tissue
Does not have a capsule Lymph nodule with Germinal Center These are dividing B-lymphocytes.
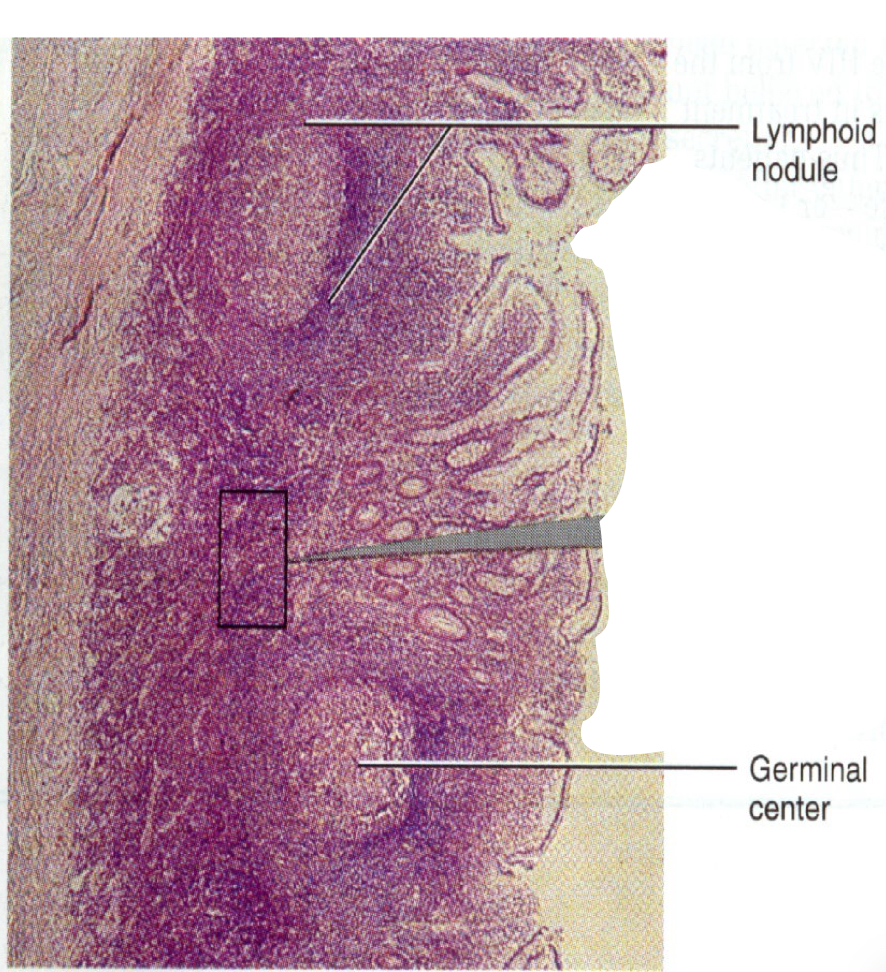
Tonsils
They do not have a capsule
They are not glands
They are aggregate lymph tissue
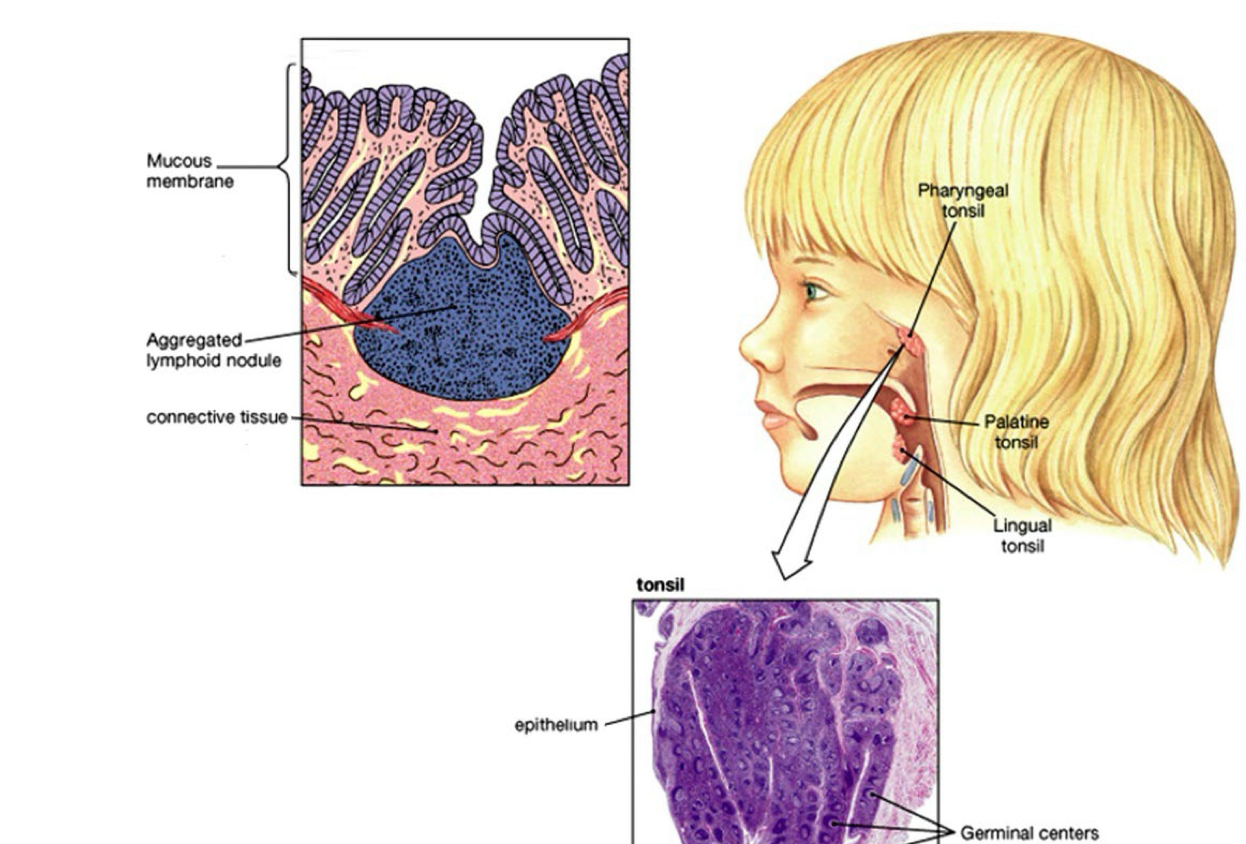
Peyer's Patches and Tonsils
Aggregate lymph tissue
No capsule Mucosa
Associated Lymph Tissue or MALT Found only in the mucosa of the small intestine
Central organs
Can’t fight infection
(a) bone marrow
Hematopoeisis & matures B-lymphocytes
(b) Thymus
Site where newly formed T-cells (Thymocytes) become mature or Immunocompetent
Peripheral organs
major defense sites
(c) lymph nodes
filter antigens from lymph vessels These are also lymphocyte activation sites
(d) spleen
Filters Red Blood Cells and foreign antigens out of the blood