Dentrifices, Mouthrinses, Chewing Gum and Product Safety Regulation
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Dentifrices Definition
Substances used to clean the teeth, commonly referred to as toothpastes
Mouthrinse definition
Used to flush food debris from the oral cavity, freshen breath, or if fluoridated, to deposit fluoride on the teeth
Chewing gum definition
A newer category of products with cosmetic claims and the ability to deliver therapeutic compounds
Mouth rinses
Available in liquid form, the traditional method for stabilizing and delivering many pharmaceutically active agents
•“fresh breath” or “clean feeling”
Mouthrinses are considered by consumers to have primarily cosmetic benefits
But it has therapeutic benefits as well
Mouthrinse components basics
Active ingredients
Astringents
Solvent
Mouthrinse active ingredients
• Quaternary ammonium compounds
• Phenolic compounds
• Sanguinarine
• Chlorhexidine
• Essential oils
• Fluoride
• Triclosan
Mouthrinse astringent ingredients
• Alum, zinc, stearate, zinc citrate, and acetic and citric acids
Mouthrinse solvent ingredients
alcohol
Pleasant sensation in mouthrinses are enhanced by which components of mouthrinse (active ingredient/astringents/solvent)
astringents
A solvent is a taste enhancer (true/false)
true
Alcohol mouthrinses that have the ADA seal of acceptance must have a child resistant cap and other safety measures (true/false)
true
Functions of mouthrinses basic
preventive-prevent caries, reduction of biofilm and gingivitis, desensitizing; Zinc sulfate reduces biofilm
cosmetic-remove extrinsic stain and halitosis; Zinc chloride reduces halitosis
therapeutic-remineralization, antimicrobial/antibacterial, reduces xerostomia; Oasis by Sensodyne, Biotene, Peridex
We get the most benefits of mouthrinses when we use it with
brushing and flossing
More successful in reducing plaque, gingivitis, and preventing caries
Cosmetic Mouthrinses
Halitosis:
• Caused by bacteria and plaque accumulation in oral cavity
• Tongue
• 10% from nonoral/systemic causes
Mask odors (no effect after 2-5 hours)
Zinc chloride:
• Neutralizing volatile sulfur compounds
• Kills gram – bacteria
Therapeutic mouthrinses
• Chlorohexidine Gluconate
• Essential Oils
• Quaternary Ammonium Compounds (cetylpyridinium chloride)
• Fluoride
• Triclosan
• Xerostomia
Chlorhexidine gluconate
Brand: Peridex (must be prescribed by dentist)
0.12% solution used in United States
Must be prescribed by dentist
Directions call for a twice-daily, 60-second rinse with one-half ounce.
Used for: inhibit bacterial colonization
• Pre-procedural rinse before aerosol procedures and etc
• Before, during, and after NSPT (non-surgical periodontal therapy)
• Disadvantage: causes some staining and altered taste
*Chlorhexidine has proven to be one of the most effective anti-plaque agents to date* due to substantivity (8-12 hours)
Substantivity
able to linger in the mouth for a longer period of time
Essential Oils
• Controlling plaque & gingivitis
• Disrupts cell wall of bacteria
• Due to alcohol content, may cause burning or irritation to tissue
• Listerine-Contraindications? Peeps with xerostomia, or alcohol abuse
Bacteria not resistant
Just rinsing won’t be effective in treating periodontal pockets since rinsing doesn’t reach depts of periodontal pockets
Quaternary Ammonium Compounds (CPC)
• Disrupts bacterial cell membrane
• Reduce plaque and gingivitis up to 12 hours
Examples:
• Crest Pro-Health
• Scope
• Rembrandt
No alcohol, claims no burning sensation and helps with halitosis
Fluoride
• Anticaries
• Sodium fluoride, Stannous fluoride, acidulated phosphofluorides
• Stannous and APF are NOT for weekly use!!!!!!! Only sodium fluoride
Recommended for:
• Moderate-High risk caries patients
• Ortho patients
• Patients with fixed appliances
• Patient receiving radiation therapy (decrease salivary flow=caries)
• NOT recommended for children under the age of 6 (upset stomach if they swallow it)
Ex) Act mouth rinses and pro health maybe
Triclosan
• Reduces biofilm and gingivitis
• Not marketed in the US
• Colgate total like colgate toothpaste
Xerostomia Mouthrinses
• Artificial saliva substitutes
• Moistens & lubricates mucous membrane
• Usually contains fluoride, calcium, and phosphate
Examples:
• Sensodyne: Oasis Mouthwash
• Biotene
• Orazyme Dry mouth mouthwash
Chewing gum
Have the potential to be used by the consumer for periods of 5-20 minutes several times a day
Enable delivery of a cosmetic or therapeutic agent for a longer time than with dentifrices or mouthrinses
Stimulate salivary flow
Mechanical removal of dental plaque and debris
Sugar free gum
Contain polyol sweeteners such as sorbitol or xylitol; these sweeteners are not broken down by plaque or oral microbes to produce acid
Xylitol is considered non-acidogenic and not fermentable by bacteria responsible for caries production
Xylitol (maintain neutral pH during and after chewing) is most effective, followed by sorbitol
Reducing plaque accumulation; reaching tooth surfaces commonly missed
Agents added to chewing gum
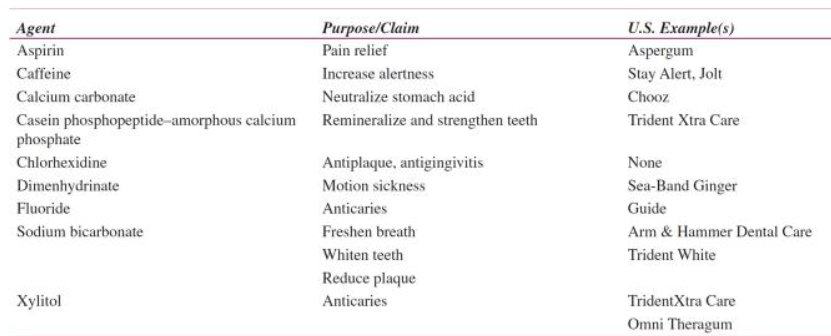
Chewing gum facts
FDA regularly tests the safety and efficacy of all chewing gums on a regular basis, holding to all rigid guidelines during testing
Chewing gums have not been approved by the FDA as having any therapeutic properties
Orbit and Extra the 1st sugar free gums to be awarded the ADA Seal of Acceptance
Product Regulation
FDA-safety, efficacy, and security of OTC and prescription drugs
Federal Trade Commission (FTC)-advertising of OTC and prescription drugs to protect consumers against false claims
Safety-potential to create no harm of discomfort to patients
Efficacy-ability to create a positive outcome
Stages of FDA Approval basic
1. Preclinical research and development by the manufacturer: Animal testing, lab testing, toxicity evaluation
2. FDA review of manufacturing information on the drug product: Submitted as part of an IND application (investigational new drug)
3. Clinical research conducted by the manufacturer after approval of the IND application
Investigate Process Phases
Phase 1:
• Study is limited in scope and uses 30-80 healthy volunteers to determine safe dose to humans
• Ingestion of dental products (injection or topical)
• Excessive topical applications to oral mucosa or teeth (2-4x daily to determine safe dose)
Phase 2:
• Several hundred subjects with the disease or condition
• Demonstrate the initial clinical efficacy of the drug (is it going to treat what is said to treat?)
• Define a dose range that is safe and efficacious
Phase 3:
• Several hundred to several thousands of people
• Expanded controlled and uncontrolled trials with “final” formulas
• Demonstrate long-term safety and efficacy
Duration of Investigate Process
Plaque and gingivitis-3-6 months
Caries-2-3 years
After investigate process
New drug application (NDA)-contains data from trials
FDA reviews and approves the NDA
Marketing begins-post-marketing surveillance of the product is mandatory
FDA requirements of products
Manufacturer must provide:
• Active ingredients and purpose
• Inactive ingredients
• Listed alphabetically
• Indicated objective of active ingredient must be on the label
• Proof must exist to make claim
Packaging and labeling guidelines
• Indication of the product (what it’s used for)
• The product’s use
• A warning
• Directions for use
ADA’s role
CSA: Council on Scientific Affairs
• Reviews dental products on a voluntary basis
• Study, evaluate, and disseminate information
• Consults with dental professional (not member of ADA)
ADA Seal of Acceptance: helps advertise products to the public
• Marketing tool
The ADA acceptance label is provided by the CSA or FDA
CSA