Campbell Biology Chapter 41
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
The process where food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up
animal nutrition
Animals fall into three categories
Herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores
Most plants and animals are also
opportunistic feeders
An animals diet must provide 3 things
chemical energy for cellular processes, organic building blocks for macromolecules, and essential nutrients
Materials that an animal cannot assemble from simpler organic molecules are called
essential nutrients
There are four classes of essential nutrients
essential amino acids, essential fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals.
Animals require about _____ amino acids and can synthesize about half from molecules in their diet
20
The essential amino acids can be obtained from
food
Animals can synthesize most of the ______ they need
fatty acids
Essential fatty acids must be obtained from
diet
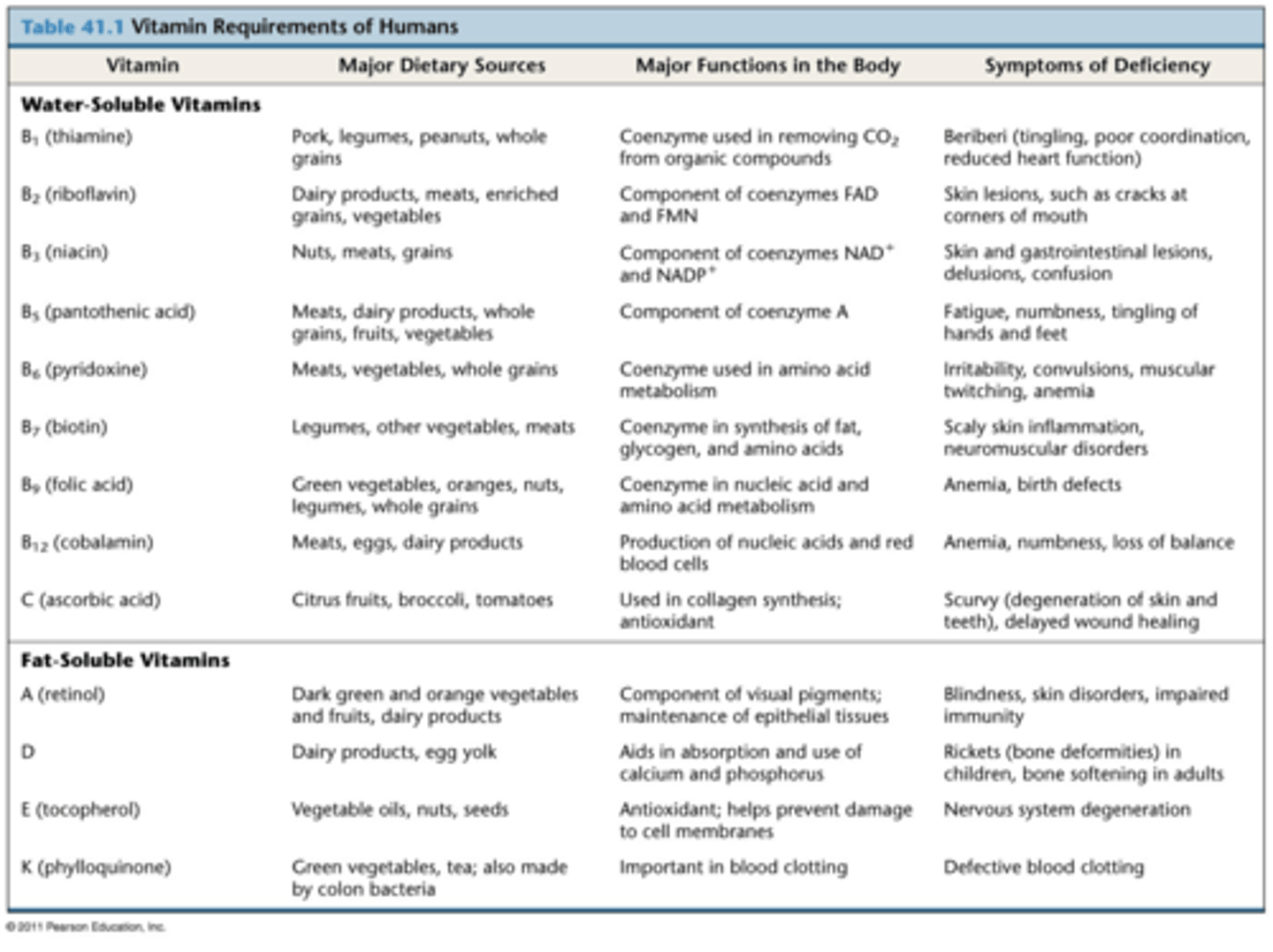
Vitamins
organic molecules required in the diet in very small amounts
how many vitamins are essential for humans
13
two categories of vitamins
fat-soluble and water-soluble
Vitamin requirements of humans
B2, b3, c, a ,d underlined on the slide.
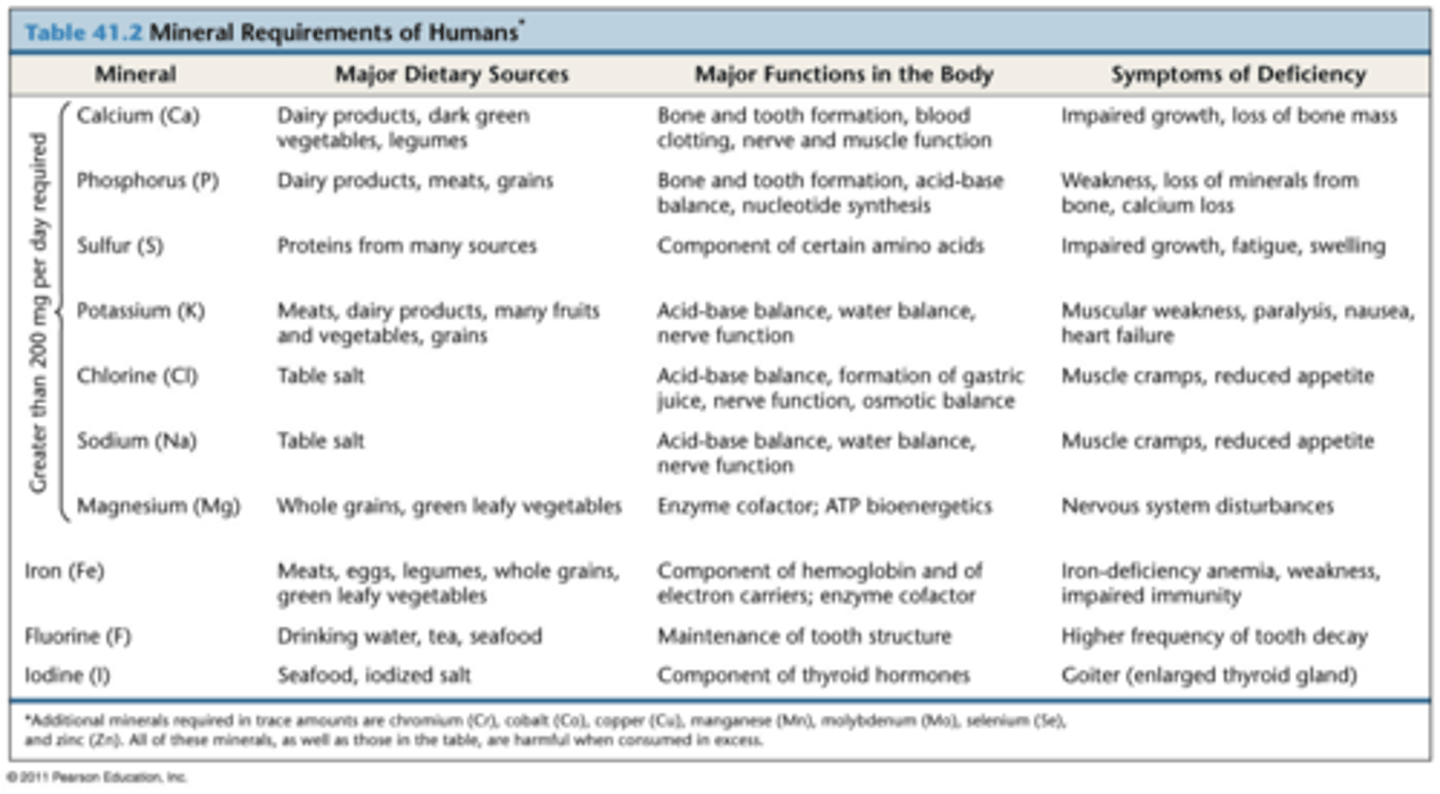
Minerals
simple inorganic nutrients, usually required in small amounts
Mineral requirements of humans
Ca, k, mg, fe, i
malnutrition
failure to obtain adequate nutrition
Undernutrition
diet does not provide enough chemical energy
An undernourished individual will
use up stored fat and carbs, break down its own protein, lose muscle mass, suffer protein deficiency of the brain, die or suffer irreversible damage
Epidemiology
the study of human health and disease in populations
Ingestion
the act of eating or feeding
4 steps of food processing
Ingestion, digestion, absorption, and excretion
Suspension feeders
sift small food particles from the water
Substrate feeders
animals that live in or on their food source
Fluid feeders
suck nutrient rich fluid from a living host
Bulk feeders
eat relatively large pieces of food
Digestion
the process of breaking food down into molecules small enough to absorb
Mechanical digestion
ie: chewing. increases the surface area of food
chemical digestions
splits food into small molecules that can pass through membranes, these are used to build larger molecules
absorption
uptake of nutrients by body cells
elimination
passage of undigested material out of the digestive system
In intracellular digestion food particles are engulfed by
phagocytosis
Complex animals have a digestive tube with two openings, a mouth and an anus
complete digestive tract or and alimentary canal
The mammalian digestive system consists of an _______ and ______ glands that secrete digestive juices through ducts
alimentary canal and accessory
Peristalsis
Rhythmic contractions of muscles in the wall of the canal
Sphincters
valves that regulate the movement of material between compartments
The human digestive system
human digestive system
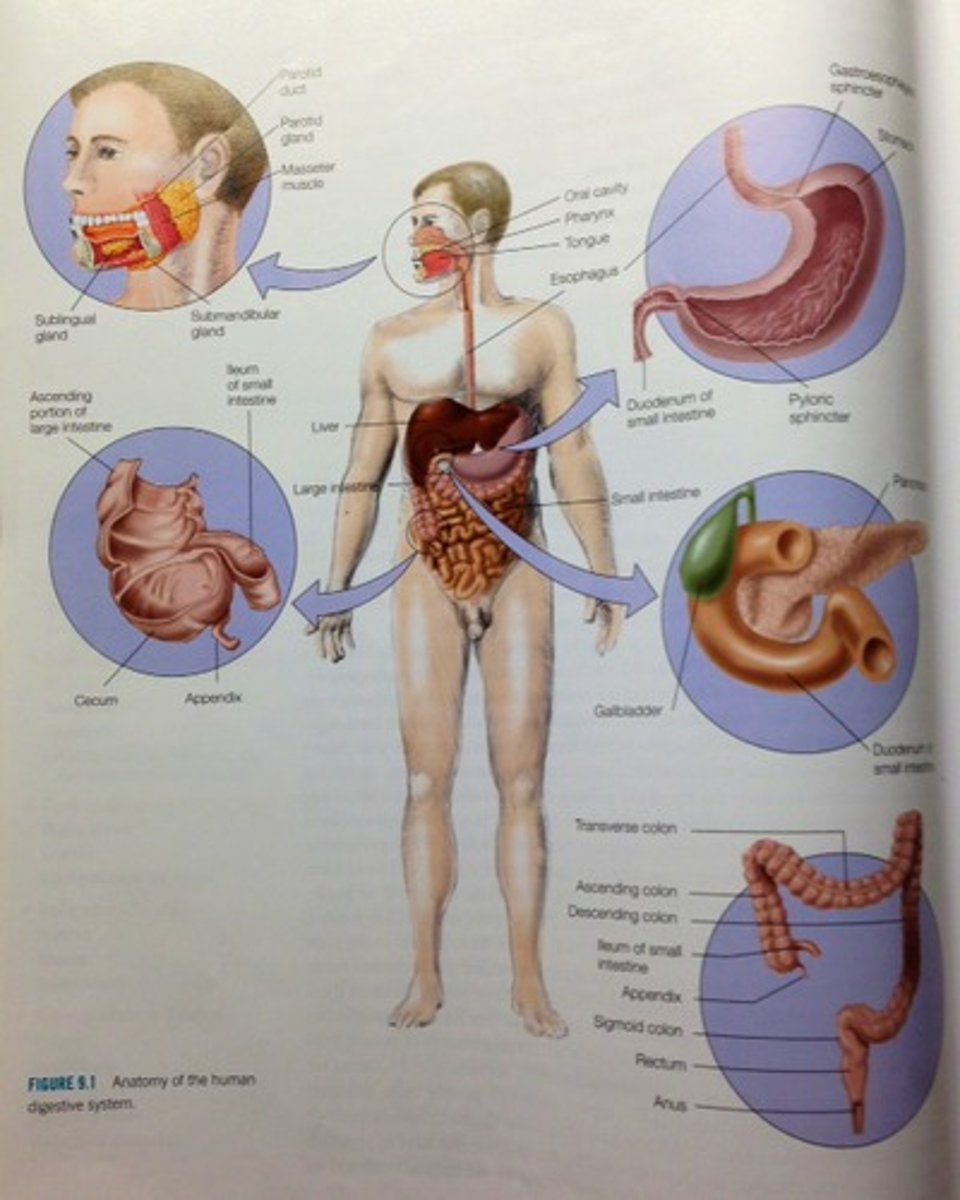
The first stage of digestion is mechanical and takes place in the
oral cavity
Salivary glands
deliver saliva to lubricate food
teeth chew food into smaller particles that are exposed to salivary
amylase
amylase
initiates breakdown of glucose polymers
Saliva also contains
mucus
mucus
a viscous mixture of water, salts, cells, and glycoproteins
The tongue shapes food into a _____ and provides help with swallowing
bolus
The throat, or _____ is the junction that opens to both the esophagus and the trachea
pharynx
The ______ connects to the stomach
esophagus
The ______ (windpipe) leads to the lungs
trachea
Swallowing causes the _____ to block entry to the trachea
epiglottis
The stomach
stores food and begins digestion of proteins
the stomach secretes ______ which converts a meal into ______
gastric juice and chyme
Gastric juice is made up of ______ and ______
Hydrochloric acid and pepsin
pepsin is a ______ or protein digesting enzyme that cleaves proteins into smaller peptides
protease
What cells secrete hydrogen and chloride ions separately into the lumen of the stomach
Parietal cells
_____ cells secret inactive pepsinogen
Chief
Pepsinogen
is activated to pepsin when mixed with HCl in the stomach
The longest compartment of the alimentary canal is the
small intestine
The first portion of the small intestine is the
duodenum
The duodenum mixes
chyme from the stomach with digestive juices from the pancreas, liver, gallbladder, and small intestine
Chemical Digestion
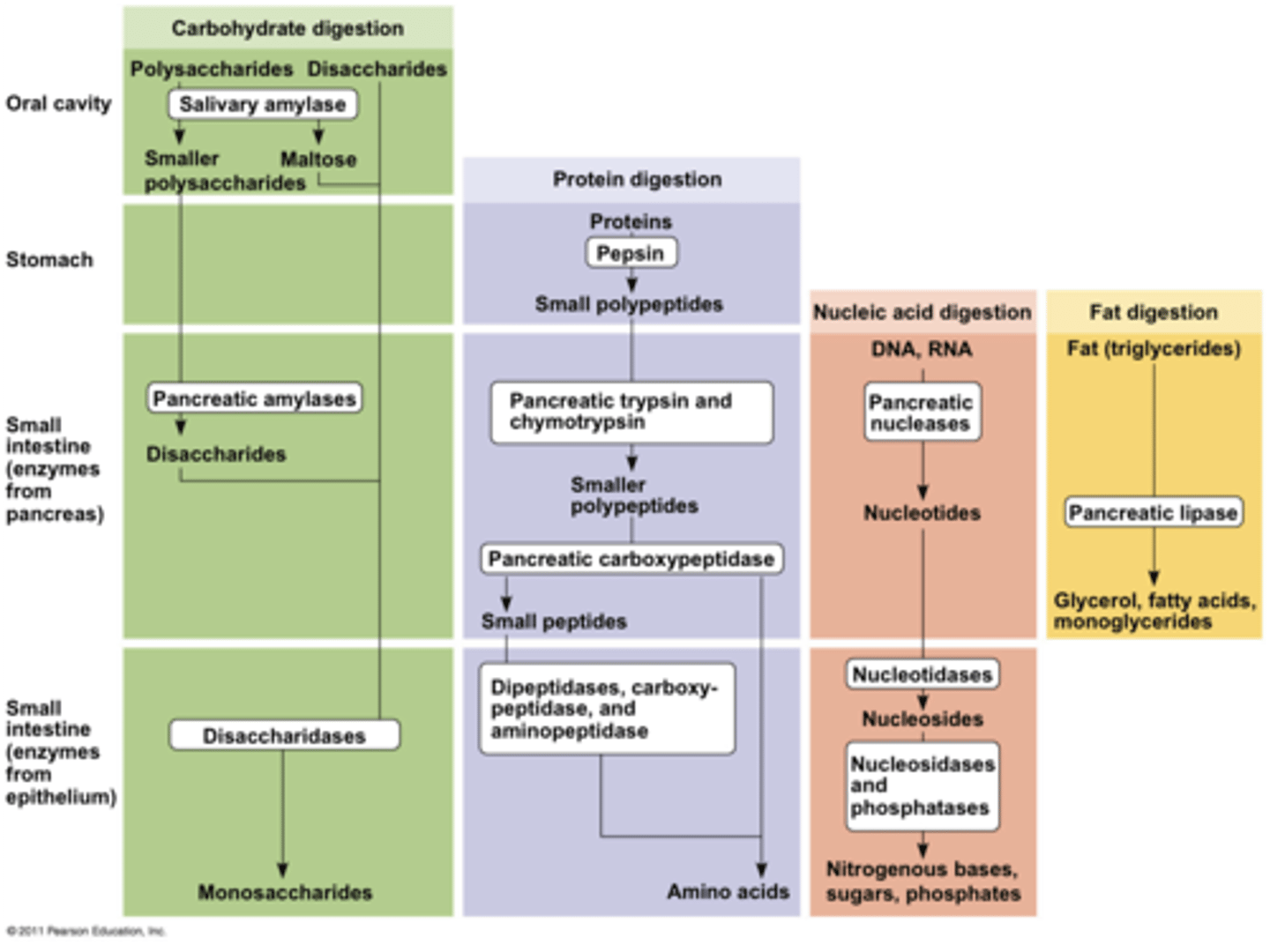
Pancreas produces
proteases called trypsin and chymotrypsin that are activated in the lumen
Bile
aids digestion and absorption of fats
Bile is made in the
liver
bile is stored in the
gallbladder
Most digestion occurs in the _______
duodenum
The small intestine has a huge surface area due to
villi and microvilli that are exposed to the intestinal lumen
Hepatic portal vein
carries nutrient rich blood from the capillaries of the villi to the liver, then to the heart
Fats that are coated with phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins that form water soluble
chylomicrons
Chylomicrons and transported into a _____
lacteal
lacteal
lymphatic vessel in each villus
Colon of the large intestine is connected to the
small intestine
The cecum aids in fermentation of _____ and connects where the small and large intestines meet
plant material
The human cecum has an extension called the
appendix
Feces
undigested material and bacteria, become more solid
Feces are stored in the
rectum
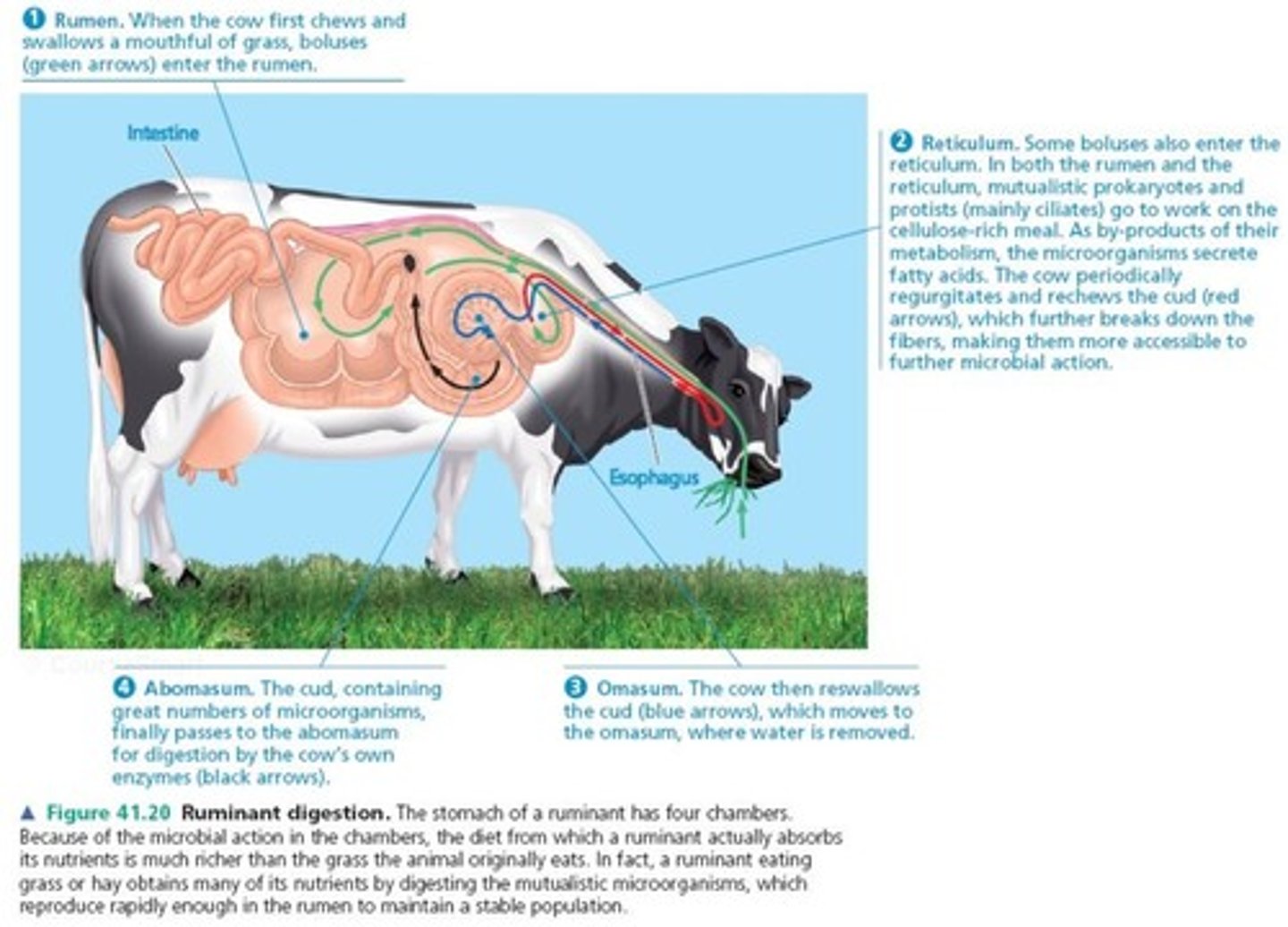
Ruminant digestion
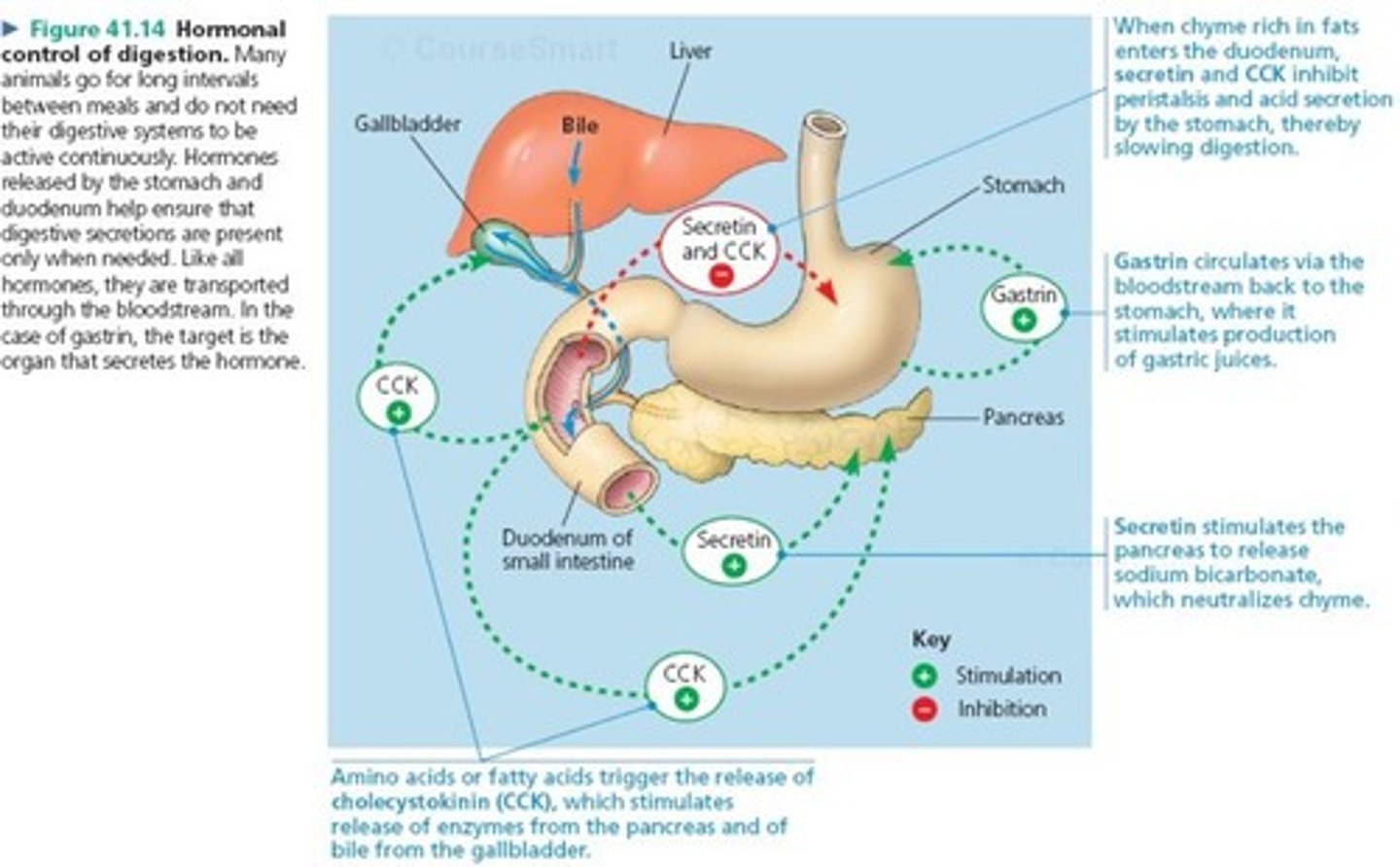
The endocrine system aslo
regulates digestion through the releases and transport of hormones
hormonal control of digestion
In humans, energy is stored first in the ____ and ____ cells in the polymer glycogen
liver and muscle
The hormones _____ and ______ regulate the breakdown of glycogen into glucose
insulin and glucagon
The _____ is the site for glucose homeostasis
liver
insulin acts on nearly all body cells to stimulate ____ uptake from blood
glucose
Glucagon and insulin are both produced in the islets of the ______
pancreas
alpha cells make
glucagon
beta cells make
insulin
Diabetes mellitus
caused by a deficiency of insulin or a decreased response to insulin in target tissues
Type 1 diabetes
autoimmune disorder in which the immune system destroys the beta cells of the pancreas
Type 2 diabetes
characterized by a failure of target cells to respond normally to insulin
Ghrelin
triggers hunger
Insulin and PYY
suppress appetite
Leptite
suppresses appetite and regulates body fat levels