Chapter 7.1 - Basic Structures of the Human Body
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Anatomy
The study of the structures of the body (heart, brain, etc…)
Physiology
The study of the functions or processes of the body (how the heart pumps blood, how the brain sends a message, etc…)
Pathophysiology
The study of how disease occurs and the body's response to it
Cytology
The study of cells
Histology
The study of tissues
Diagnosis
Identification of a disease
Prognosis
Prediction of the probable outcome of a disease
Etiology
Cause of a disease
Idiopathic
Unknown cause of disease
Congenital Disease
Occurs during development of the infant in the uterus; Examples are club foot, cleft lip, spina bifida
Inherited Disease
Transmitted from parents to child genetically; Examples are color blindness, cystic fibrosis and Down Syndrome
Infectious Disease
Caused by pathogens (germs) that enter the body; Examples are bacteria or viruses that cause the common cold, hepatitis and STI's
Degenerative Disease
Caused by a deterioration of the body; Examples are normal aging and osteoarthritis
Cell
Basic unit of structure in all living things
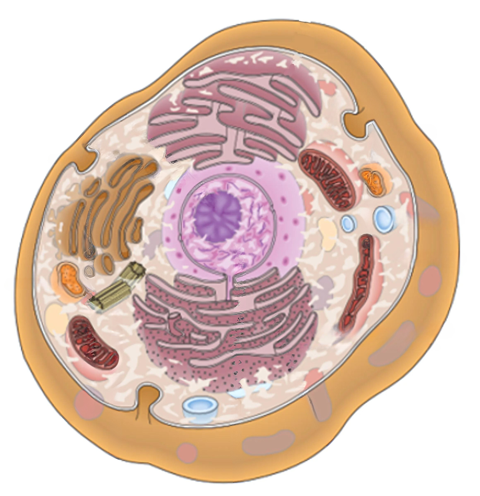
Organelles
Structures inside a cell that help it to function
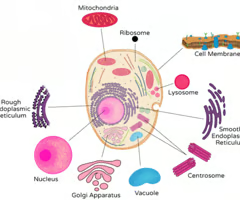
Cell Membrane
Outer protective, semi-permeable covering of a cell
Cytoplasm
Fluid inside a cell where chemical reactions take place; contains water, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, minerals, and salts
Nucleus
Control center of the cell; regulates cell activities; contains genetic information
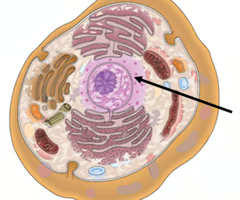
Nucleolus
Located inside the nucleus and is important in cell reproduction; manufactures ribosomes
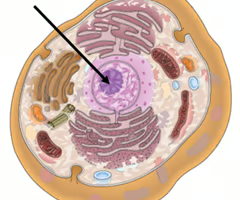
Ribosomes
Make proteins
Chromatin
Located in the nucleus; Made of DNA and protein; Condenses to form chromosomes during mitosis
Centrosome
Contains 2 centrioles; aids in cell division during mitosis
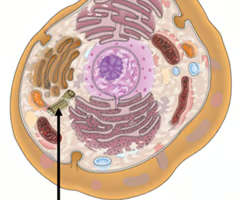
Mitochondria
Breaks down carbs, proteins and fats to produce energy in the form of ATP
Golgi Apparatus
Produces, stores and packages secretions for the cell
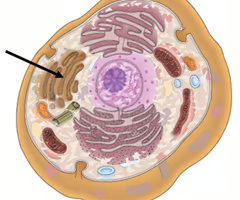
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Tubes that allow for transport into and out of the nucleus; Contains ribosomes
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Tubes that allow for transport into and out of the nucleus; Does NOT contain ribosomes; Makes cholesterol, metabolizes fat and detoxifies drugs
Vacuoles
Pouch-like structures filled with a watery substance, stored food or waste products
Lysosomes
Contains enzymes that digest and destroy old cells, bacteria and foreign material
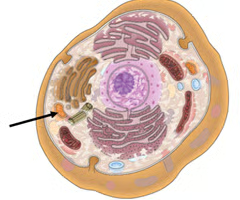
Pinocytic Vesicles
Pocket-like folds in the cell membrane; Allows large molecules like protein and fats to enter the cell
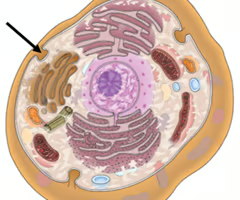
Mitosis
Process of cell division; a single cell divides to produce two identical cells
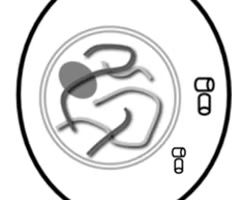
Interphase
Cell grows and develops, and carries out normal functions; Chromatin is in a loose state; DNA is copied
Prophase
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes; Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear; Centrosomes form spindle fibers
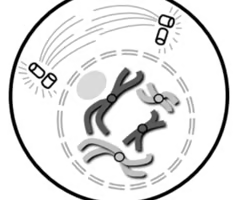
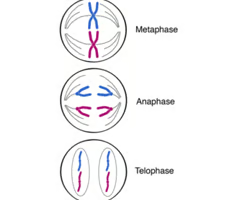
Metaphase
Spindle fibers attach to chromosomes and line them up along the middle of the cell
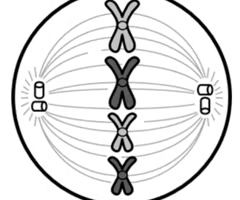
Anaphase
Chromosomes divide into two sets; Each half of the chromosome is pulled away to opposite sides of the cell
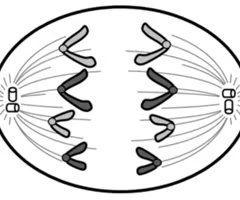
Telophase
Two nuclear membranes form; Cells begin to separate
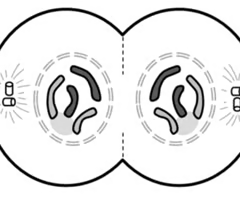
Cytokinesis
Cytoplasm divides; Chromosomes uncoil; Two cells with the same number of chromosomes are created
Tissue
Group of similar cells with the same size, shape and function that join together
Dehydration
Condition of insufficient (not enough) fluid
Edema
Swelling; Excess fluid in tissues
Epithelial Tissue
Tissue type that lines and covers body surfaces to protect and secret substances; Examples are the skin and lining of the intestinal, respiratory, circulatory and urinary tracts
Connective Tissue
Tissue type that supports/connects structures; Examples of types of connective tissue are hard, soft and vascular
Soft Connective Tissue
Adipose tissue and fibrous tissue
Adipose Tissue
Soft connective tissue found around internal organs; Stores fat to use for energy; Insulates the body
Fibrous Tissue
Soft connective tissue found in ligaments and tendons; Holds structures together
Hard Connective Tissue
Osseous Tissue and Cartilage
Osseous Tissue
Hard connective tissue; Bone; Provides skeletal framework of body
Cartilage
Hard connective tissue located between joints, end of bones, nose/ears; Cushions joint, acts as shock absorber
Vascular Connective Tissue
Blood and Lymph Fluid
Blood
Vascular connective tissue that carries nutrients, waste and fights infection
Lymph
Vascular connective tissue that carries tissue fluid and helps immune system
Muscle Tissue
Tissue type that contracts to produce power and movement
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Muscular tissue that connects to bones to produce movement
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Muscular tissue only found in the heart; pumps blood
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Muscular tissue found in internal organs, blood vessels, digestive and respiratory tracts; Contracts to control diameter of vessels or cause peristalsis
Nervous Tissue
Tissue type that controls and coordinates body activities by transmitting messages throughout the body
Organ
Formed when tissues with similar functions join together
Body System
Formed when organs with similar function join together