Circulatory System
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
What is circulatory System?
This is the body's transport system, which carries different substances around the body.
which organs are invloved in the circulatory system?
The heart
Blood
Blood vessels
Which gases are transported to and from the body's cells by the blood flowing in the circulatory system?
Oxygen & Carbon dioxide
- Oxygen is the gas needed for respiration and is transported to the body's cells.
- Carbon dioxide is the waste gas produced by respiration that must be carried away from the body's cells.
What are the 2 types of blood in the circulatory system?
Oxygen rich blood
Oxygen poor blood
Oxygen rich blood
-blood travelling to the body cells
-high oxygen content
-low carbon dioxide content
Oxygen poor blood
- blood travelling away from the body cells
-low oxygen content
-high carbon dioxide content
Do these 2 types of blood mix?
No
What is the heart?
The heart is the organ at the centre of the circulatory system. It pumps blood around the body.
The inside of the heart is divided into two sections, what are they?
The right side of the heart - Oxygen poor blood
The left side - Oxygen rich blood
How long does it take for blood to go around the body once?
30 seconds
Which type of blood does the left side of the heart pumps to the rest of the body?
Oxygen rich blood
Which type of blood supplies the body's cells with oxygen?
Oxygen rich blood
What gas does the blood pick up from the body's cells? And where does the blood go next?
Blood picks up carbon dioxide from the body's cells.
This oxygen-poor blood then travels back to the right side of the heart.
The oxygen-poor blood needs to lose the carbon dioxide and pick up more oxygen. How does it do this?
The right side of the heart pumps oxygen-poor blood
to the lungs.
In the lungs the blood gets rid of the waste carbon dioxide and collects more oxygen.
Where does this oxygen-rich blood then travel to?
The oxygen-rich blood then returns
to the left side of the heart.
This completes the blood's journey around the body.
Why is the journey
of blood through the circulatory system called a double circulation?
It is called double circulation because during one complete circuit of the body, blood passes through the heart twice.
The heart has two jobs to do and so the circulatory system involves a double circulation.
What is the heart made of?
The heart is made of muscle
What do the blood vessels on the outside of the heart do?
The blood vessels on the outside of the heart carry
oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle cells.
Oxygen-poor blood is then carried away from these cells by outer blood vessels and back into the heart.
what is each section in the heart called?
A chamber
How many chambers does the heart have?
4
what is the upper chamber called?
atrium (plural atria).
What is the lower chamber called?
ventricle.
What is the function of the right atrium?
bring blood to the lungs
What is the function of the left atrium?
bring blood to the body
What is the function of the right ventricle?
bring blood from the body
What is the function of the left ventricle?
bring blood from the lungs
Does blood flow in the same or different direction?
Same direction
What prevent blood from flowing in the wrong direction?
The chambers of the heart are separated by valves which prevent blood from flowing in the wrong direction.
What are the chambers of the heart separated by?
Valves
Where are the valves?
There are valves between the atria and the ventricles...
...and there are valves leading out of the ventricles.
What are the names of the valves ?
bicuspid/ Mitral valve, tricuspid valve, pulmonary semilunar valve, aortic semilunar valve
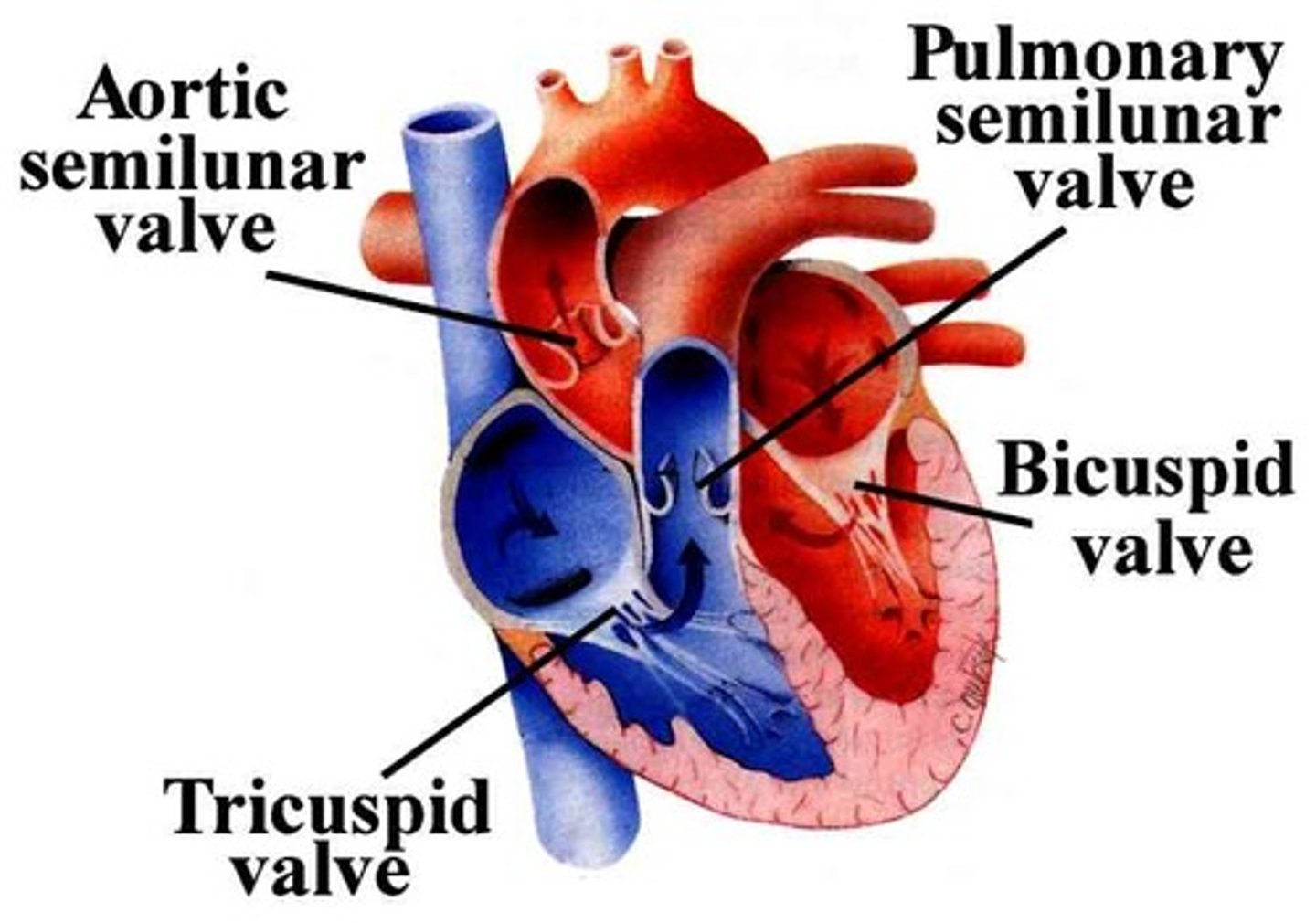
The valves between the atria and ventricles are connected to the inner walls of the heart by what?
The valves between the atria and ventricles are connected to the inner walls of the heart by tough tendons.
What is the purpose of the tendons?
The tendons allow the valves to close and hold the valve flaps in place. They prevent the valves from flipping up and turning inside out.
How does the heart produce enough force to keep doing
this 24 hours a day?
The heart can pump blood
because it is made of muscle.
Muscle tissue works by contracting (squeezing)
and relaxing.
How does blood move through the heart and is pumped to the lungs and the body?
All the parts of the heart on either side, work together in a repeated sequence.
The two atria contract and relax; then the two ventricles contract and relax.
What is One complete sequence of contraction and relaxation is called?
One complete sequence of contraction and relaxation is called a heartbeat.
How does a heartbeat start?
A heartbeat begins with the heart muscle relaxed and valves closed.
Describe stage 1 of the heartbeat
A heartbeat begins with the heart muscle relaxed and valves closed.
Blood flows into the two atria and both sides fill up with blood.
This blood has to be pushed through the valves to get into the ventricles.
What causes the valves leading to the ventricles to open?
The atria contract and the blood is squeezed which causes the valves leading to the ventricles to open.
Describe stage 2 of the heartbeat
The atria contract and the blood is squeezed which causes the valves leading to the ventricles to open.
Blood then flows from the atria into the ventricles.
The valves between the atria and the ventricles close.
This prevents any backflow.
What prevents backflow?
The valves between the atria and the ventricles close.
This prevents any backflow.
What happens to the open valves when the ventricles are empty?
When the ventricles are empty, the valves leading out of the heart close and the heart muscle relaxes
What forces open the valves leading out of the heart?
The pressure of the blood forces open the valves leading out of the heart.
Describe stage 3 of the heartbeat
Immediately, the ventricles contract and the blood is squeezed again.
The pressure of the blood forces open the valves leading out of the heart.
Blood is pumped out of the heart.
when the ventricles are empty, the valves leading out of the heart close and the heart muscle relaxes.
This completes the sequence of contraction and relaxation in one heartbeat.
The sound of the heartbeat is also the same as what?
The sound of a heartbeat is the sound of the heart valves.
What cause the "lub" sound?
The "lub" is caused by the closing of the valves leading to the ventricles.
What is the "dub" sound caused by?
The "dub" is caused by the closing of the valves
leading out of the heart.
How can you measure how fast your heart is beating?
You can measure how fast your heart is beating by taking your pulse.
How do you measure your pulse?
Place the fingertips of one hand on the opposite wrist, where an artery passes near the surface of the skin.
What causes the pulse you feel?
Each pulse that you feel is due to the pressure of
blood leaving the heart as the left ventricle contracts.
The flow of the blood
Superior and Inferior vena cava 🡺 right atrium 🡺 tricuspid valve 🡺 right ventricle 🡺 pulmonary valve 🡺 pulmonary artery 🡺 lungs (exchange of gases O2 & CO2) 🡺 pulmonary vein 🡺 left atrium 🡺 mitral valve 🡺 left ventricle 🡺 aortic valve 🡺 aorta 🡺 arteries 🡺 body systems
What are the types of blood circulation?
Pulmonary Circulation
Systemic Circulation
What are the SPECIAL types of circulation? ( special circuits )
Portal Circulation
Renal Circulation
Coronary Circulation
Pulmonary Circulation
Pulmonary Circulation - blood flows from the heart to the lungs to get O2 supply.
Systemic Circulation
Systemic Circulation - blood flows from the heart to the cells (distribute food and O2) and from the cells to the heart (carry wastes and to the heart CO2)
Portal Circulation
Portal Circulation - circulation of blood from the arteries to the digestive system.
Renal Circulation
Renal Circulation - circulation of blood from the arteries to the excretory system/kidneys
Coronary Circulation
Coronary Circulation - circulation of the blood within the heart.
What is blood?
Blood is the river of life. It carries oxygen and nutrients to the different body cells.
What does blood collect?
Blood collects body wastes and carbon dioxide.
What makes up our blood?
RBC- (erythrocytes)
WBC (leukocytes)
Platelets
Plasma
RBC- (erythrocytes)
RBC- (erythrocytes) - The blood cells that carry oxygen. Red cells contain hemoglobin and it is the hemoglobin which permits them to transport oxygen (and carbon dioxide). Hemoglobin, aside from being a transport molecule, is a pigment. It gives the cells their red color (and their name)
WBC (leukocytes)
WBC (leukocytes) - White blood cells are responsible for the defense system in the body. There are approximately 6,000 white blood cells per millimeter of blood or ½ a million white blood cells in every drop of human blood. White blood cells fight infections and protect our body from foreign particles, which includes harmful germs and bacteria.
Platelets
Platelets - Platelets help the blood clot. They are smaller than red or white blood cells.
Plasma
Plasma - is the liquid part of blood; it transports dissolved substances around the body and defends it against disease.
What are the blood types?
A+
o+
B+
AB+
A-
O-
B-
AB-
Almost what % of the population have O+ blood
40%
What is the universal blood type
Type O blood is the universal blood type and is the only blood type that can be transfused to patients with other blood types
About what % of the population have O-
7%
What blood type is the preferred type for accident victims and babies needing exchange transfusions?
Type O negative blood is the preferred type for accident victims and babies needing exchange transfusions
What are the 3 types of blood vessels?
Artery
Vein
Capillary
What is the largest artery?
Aorta
What is the smallest artery?
Arterioles
What is the smallest vein?
Venules
What is the largest vein?
Vena Cava
What is the function of the artery?
Arteries carry blood away from the heart.
What allows arteries to stretch under pressure?
the elastic fibres allow the artery to stretch under pressure
What is an artery made of?
thick muscle and elastic fibres
What is the purpose of the thick muscle?
the thick muscle can contract to push the blood along.
What is the function of the vein?
Veins carry blood back to the heart.
What does veins have?
veins have valves which act to stop the blood from going in the wrong direction.
What are veins made of?
thin muscle and elastic fibres
Why does body muscles surround the veins?
body muscles surround the veins so that when they contract to move the body, they also squeeze the veins and push the blood along the vessel.
What is the function of capillaries?
Capillaries link Arteries with Veins and they exchange materials between the blood and other body cells.
What are capillaries made of?
the wall of a capillary is only one thick cell
What can oly occur through the capillaries?
The exchange of materials between the blood and the body can only occur through capillaries.