IB Geography Urban Environments
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
greenfield site
a piece of land that has not been built on before, but is now being considered for development
urban consolidation
the process of increasing the density of residential buildings in an urban area. Infilling gaps, bringing disused buildings back into productive use, etc.
suburbanisation
outward growth of towns and cities to engulf surrounding villages and rural areas.
suburb
residential areas within or just outside the boundaries of a city
decentralisation
when manufacturing industries and people relocate outwards from the urban center
gentrification
when middle class people move into run down inner city areas with the intention of renovating the old buildings
distance decay
as distance from the PLVI increases, land prices decrease... also reflecting this, building heights decrease.
Burgess Model
land uses are arranged around the CBD in concentric circles, with the profitable uses being found closest to the city center
Multiple Nuclei Model
Argues that land uses tend to be arranged in cells or patches throughout the city depending on the availability and the quality of land
bid rent theory
retailers can afford the highest rents, but they are not prepared to pay high prices if they are not in highly accessible areas
population density hollow
in the CBD residential land use is usually outbid by retailing and office space so the population of the CBD part of the city is low
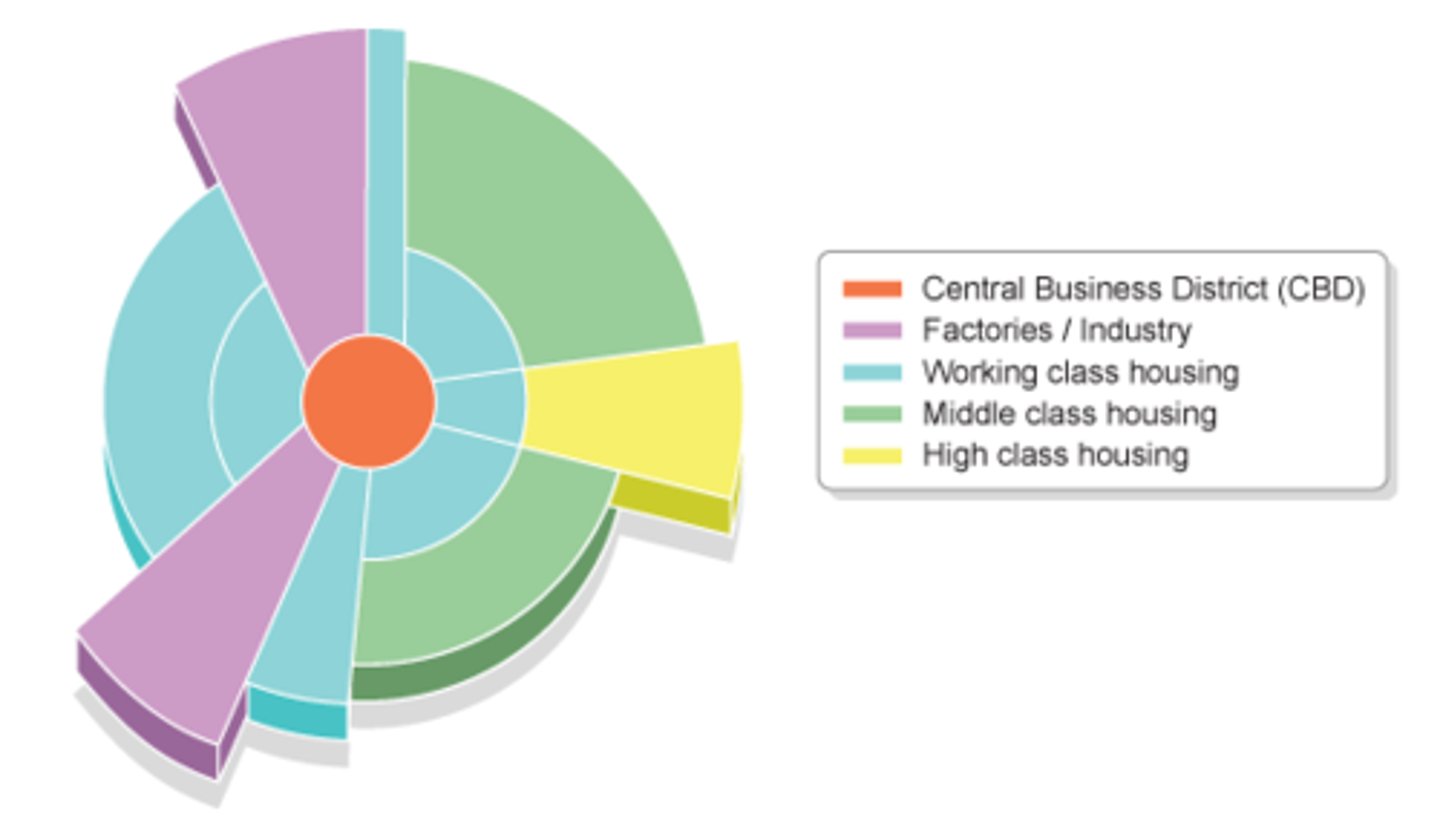
Hoyt (Sector) Model
based on the circles on the Burgess model, but adds sectors of similar land uses concentrated in parts of the city. Notice how some zones, eg the factories/industry zone, radiate out from the CBD.
Peak Land Value Intersection
the point of the highest land value often resulting from the intersection of communication routes
Megacity
A city with a population of at least 10 million people.
spatial exclusion
a process where wealthy residents become so concerned about their security and defending their luxury lifestyles that special access and freedom of movement becomes restricted
counter-urbanisation
movement of population away from inner urban areas to a new town, a new estate, a commuter town or a village on the edge or just beyond the city limits
ecological footprint
the theoretical measurement of the amount of land and water a population requires to produce the resources it consumes and to absorb its waste under prevailing technology
Brownfield Site
Abandoned or underused industrial buildings and land which may be contaminated but have potential to be redevelopment
Shanty Housing
'Homemade' housing using scavenged materials such as corrugated iron, cloth and plastic.
Squatters
People who have no legal title on the land they live on. The do not rent or own land and will build or live on vacant land, such as nearby railways or on steep slopes.
Urban Decay
Reflects the lack of inner-city demand. Many vacant blocks, derelict buildings, graffiti. It is not a source of employment, tax revenue or income.
Urban Dynamics
The processes operating in an urban area.
re-urbanization
development of activities to increase residential population densities within the existing built-up area of a city.
Urban Growth
Increase in size of an urban area or an increase in the number of people living in an urban area.
Urban Heat Island
Urban areas becoming warmer than their surroundings. Is done by cement retaining heat, car exhausts, pollution fumes, etc.
Urban Renewal
A governmental programme, converting run-down areas into attractive public areas. E.g. London Docklands in Sydney, Australia.
Urban Sprawl
Unplanned and uncontrolled physical expansion of a city into surrounding areas.
Urbanisation
An increasing percentage of a country's population moves into towns and cities. It can be due to migration or natural increase.
Centripetal movement
Movement toward the center. In this case, movement toward the city center.
Centrifugal movement
Movement away from the center. In this case, movement away from the city center.
Circular City System
Inputs come into the city and are recycled in order to reduce the amount of negative outputs like trash and pollution
Linear City System
Inputs come into the city such as people, natural resources and energy and products as well as waste, noise and congestion are the cities outputs.