Materials Test 2 Multiple Choice
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
6.8. The atoms surrounding a screw dislocation experience which kinds of strains: (a) tensile strains (b) shear strains (c) compressive strains (d) both (b) and (c)
(b) shear strains
6.9. Shape memory alloys have the following characteristics EXCEPT: (a) martensite transformation (b) original shape can be restored when heated above Af (austenite finish temperature) (c) deformation must occur above Ms (martensite start temperature) (d) deformation occurs by migration of twin boundaries
(c) deformation must occur above Ms (martensite start temperature)
6.10. A cylindrical rod of brass originally 10.2 mm in diameter is to be cold worked by drawing to the final diameter of 8.1 mm. The circular cross section will be maintained during deformation. What is the cold work percent from this drawing process? (a) 24.9 % (b) 28.9 % (c) 32.9 % (d) 36.9 %
(d) 36.9 %
6.11. A piece of chalk is twisted until it fractures. What is the angle of the fracture direction with respect to the chalk length direction? (a) 30deg (b) 45deg (c) 60deg (d) 90deg
(b) $45deg
6.1. Consider the total free energy change for nucleation for the case of a cubic nucleus of edge length a (instead of a sphere of radius r). Is the nucleation barrier for a cubic nucleus larger or smaller than that for a spherical nucleus? (a) larger (b) smaller (c) same (d) depends on temperature
(a) larger
6.2. Once a system is at a state of equilibrium, a shift from equilibrium may result by alteration of which of the following? (a) pressure (b) temperature (c) composition (d) all of these
(d) all of these
6.3. Yield strength of Al alloy was measured to be 280 MPa. The hardness of this alloy should be: (a) ~93 MPa (b) ~140 MPa (c) ~280 MPa (d) ~840 MPa
(d) ~840 MPa
6.4. Creep strain rate decreases with: (a) increasing grain size (b) increasing temperature (c) increasing applied stress (d) increasing voids
(a) increasing grain size
6.5. How can you improve fatigue life of a steel EXCEPT? (a) by removing stress concentrators (b) by imposing a tensile surface stress (c) by carburizing the surface (d) by applying the shot peening on the surface
(b) by imposing a tensile surface stress
6.6. What is KIc ? (a) fracture toughness that depends on specimen size (b) toughness under plane stress condition (c) critical value of stress intensity factor (d) ductility parameter
(c) critical value of stress intensity factor
6.7. Hot working takes place at a temperature above a metal's: (a) melting temperature (b) recrystallization temperature (c) eutectoid temperature (d) glass transition temperature
(b) recrystallization temperature
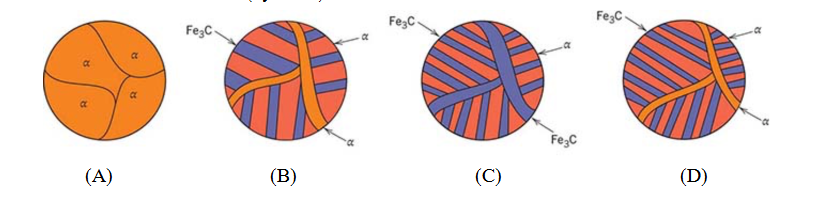
5.17. Schematic room-temperature microstructures for four iron-carbon alloys are as follows. Rank these microstructures (by letter) from the hardest to the softest. (a) B > D > C > A (b) D > B > C > A (c) C > B > D > A (d) C > D > B > A
(d) C > D > B > A
5.18. A peritectic reaction involves which of the following combinations of phase fields? (a) One liquid and one solid (b) One liquid and two solids (c) Two liquids and one solid (d) Three solids
(a) One liquid and one solid
5.9. The following statements about binary phase diagrams are true EXCEPT: (a) peritectic phase diagram is formed when melting temperatures are widely different (b) lowest melting temperature of an alloy can be obtained at a eutectic composition (c) eutectoid reaction is a congruent transformation (d) melting temperature increases when intermediate phase is formed
(c) eutectoid reaction is a congruent transformation
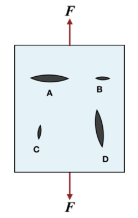
5.10. The figure right depicts a brittle material featuring four elliptical flaws, each featuring the same radius of curvature at their tips. Based on the loading type and the loading axis illustrated, which flaw is most likely to propagate first? (a) A (b) B (c) C (d) D
(a) A
5.11. At a eutectic point on a binary temperature-composition phase diagram, how many phases may be present when the system is at equilibrium? (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3
(d) 3
5.1. Consider the total free energy change for nucleation for the case of a cubic nucleus of edge length a (instead of a sphere of radius r). Is the nucleation barrier for a cubic nucleus larger or smaller than that for a spherical nucleus? (a) larger (b) smaller (c) same (d) depends on temperature
(a) larger
5.2. Once a system is at a state of equilibrium, a shift from equilibrium may result by alteration of which of the following? (a) pressure (b) temperature (c) composition (d) all of the above
(d) all of the above
5.3. Which type of the following alloying elements is the most effective in strengthening of alloys? (a) interstitial atoms (b) substitutional atoms (c) impurities with a similar atomic radius (d) impurities with a similar electronegativity
(a) interstitial atoms
5.4. The following materials are examples of metastable phases EXCEPT: (a) diamond (b) glass (c) martensite (d) quartz
(d) quartz
5.5. What is the driving force for the nucleation of a solid phase from a liquid state? (a) interfacial energy (b) undercooling (c) superheating (d) all of these
(b) undercooling
5.6. Based upon the Avrami rate equation, at what stage the growth rate is the fastest? (a) at the beginning (b) at the time when 50% of the transformation is complete (c) at the final stage (d) constant throughout the growth period
(b) at the time when 50% of the transformation is complete
5.7. Major elements of fracture mechanics are the following parameters EXCEPT: (a) sample size (b) crack length (c) resistance to cracking (d) applied stress
(a) sample size
5.8. Hot working takes place at a temperature above a metal's: (a) melting temperature (b) eutectoid temperature (c) recrystallization temperature (d) glass transition temperature
(c) recrystallization temperature
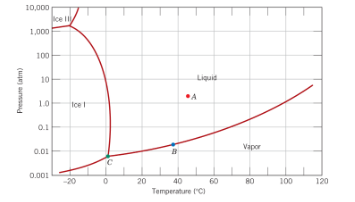
5.12. The pressure-temperature phase diagram for H2O is shown right. What is the number of degrees of freedom at point C? (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3
(a) 0

5.13. Microstructure shown on the right image (from US Steel Corporation) is obtained from a 1.4 wt.% C steel. What is the name of a phase indicated by an arrow A? (a) austenite (b) ferrite (c) cementite (d) pearlite
(d) pearlite
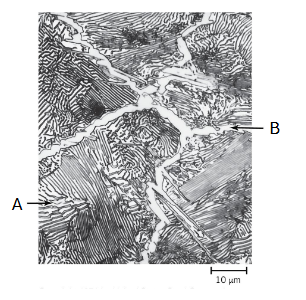
5.14. For the above problem (5.13), what is the name of a phase indicated by an arrow B? (a) austenite (b) ferrite (c) cementite (d) pearlite
(c) cementite
5.15. What is KIc? (a) fracture toughness that depends on specimen size (b) fracture toughness under plane strain condition (c) critical value of fracture strength (d) ductility parameter
(b) fracture toughness under plane strain condition

6.12. Many Liberty ships built during World War II have failed catastrophically as shown in the right image. The following factors contributed to such failure: (a) Temperature of water (b) Rivet joining failure (c) Brittle-to-ductile transition (d) Impact by a foreign object
(c) Brittle-to-ductile transition

6.13. The following metal specimen (right image) was tensile tested until failure. Which type of metal would experience this type of failure? (a) Very ductile (b) Indeterminate (c) Brittle (d) Moderately ductile
(d) Moderately ductile

6.14. Microstructure shown on the right image (from Republic Steel Corporation) is obtained from a 0.38 wt.% C steel. What is the name of a phase indicated by an arrow? (a) austenite (b) ferrite (c) pearlite (d) cementite
(c) pearlite