Pediatric Cancer Nursing: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Complications
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What percentage of all cancers does childhood cancer account for?
Approximately 1%
What is the leading cause of disease-related death in children?
Childhood cancer
What are the most common types of childhood cancer?
Leukemia (especially ALL), Brain and CNS tumors, Lymphomas, Wilms tumor, Neuroblastoma, and Bone tumors
What is the peak incidence age range for childhood cancer?
Ages 2-5 years
What is the survival rate for childhood cancer with early detection and multidisciplinary care?
Greater than 80%
What are some genetic predispositions associated with childhood cancer?
Down syndrome, neurofibromatosis, Li-Fraumeni syndrome
What are some environmental risk factors for childhood cancer?
Ionizing radiation, previous cancer treatment, immune system deficiency, viral infections
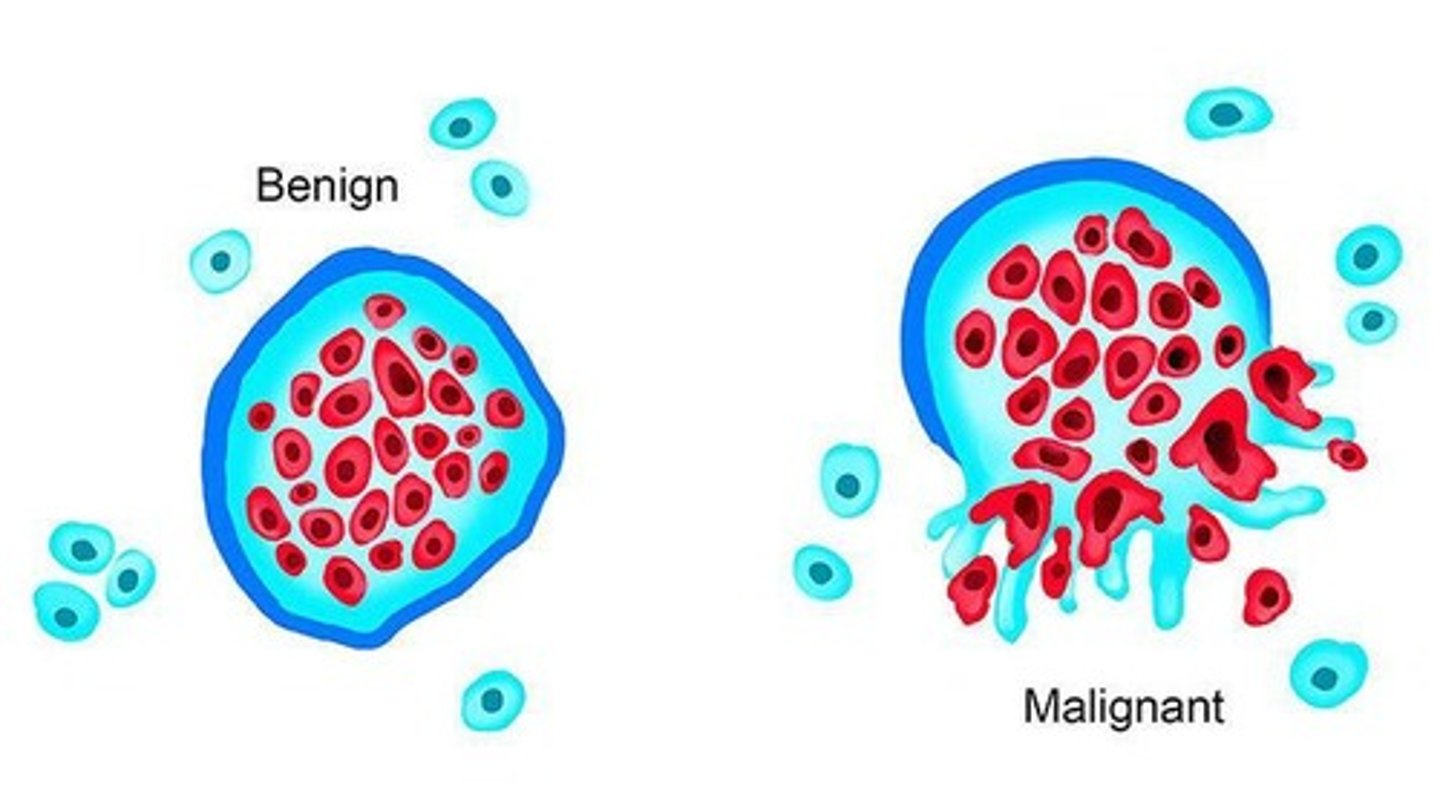
What is the pathophysiology of cancer in children?
Genetic mutations in normal cells lead to uncontrolled growth, impaired differentiation, and potential metastasis.
What is the primary purpose of chemotherapy in pediatric oncology?
To destroy rapidly dividing malignant cells and induce remission.
What are the phases of chemotherapy treatment for leukemia?
Induction, Consolidation, Maintenance
What are common side effects of chemotherapy in children?
Myelosuppression, mucositis, nausea, alopecia, fatigue
What is the goal of surgical management in pediatric cancer?
To obtain biopsy, remove localized tumors, or relieve complications.
What are common surgeries performed for pediatric cancer?
Wilms tumor nephrectomy, limb-sparing surgery for osteosarcoma, tumor debulking
What is the purpose of radiation therapy in pediatric cancer?
Local tumor control or as an adjuvant to surgery/chemotherapy.
What are the types of radiation therapy used in pediatric cancer?
External beam and Brachytherapy
What is the role of biologic/immunotherapy in pediatric cancer?
To enhance immune response and target tumor-specific molecules.
What are some side effects of immunotherapy?
Fever, chills, fatigue, hypotension, allergic reactions
What is the purpose of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant (HSCT)?
To replace diseased bone marrow after high-dose chemotherapy/radiation.
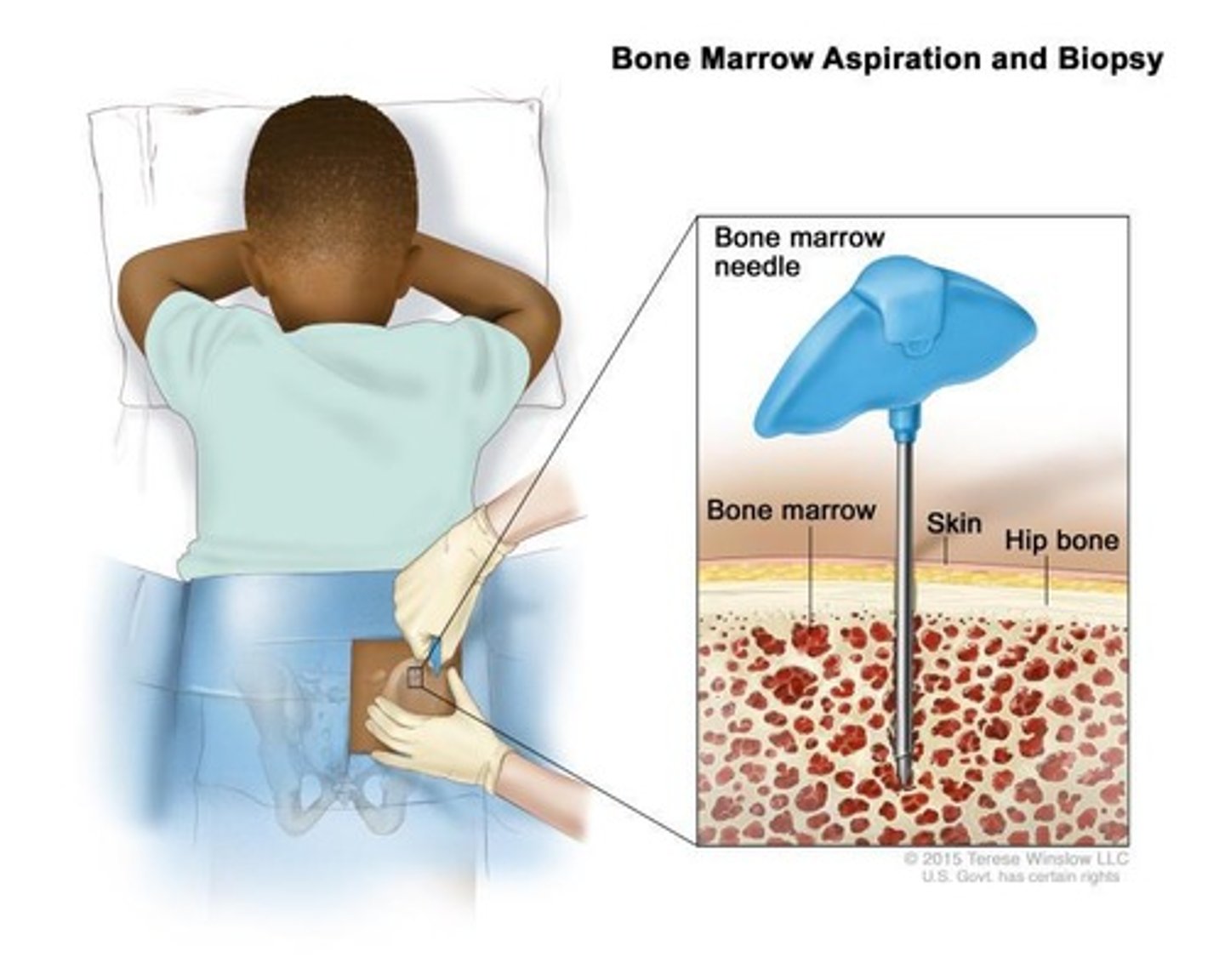
What are the two types of HSCT?
Allogeneic (from matched donor) and Autologous (from patient's own stored stem cells)
What is the significance of Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC) in pediatric oncology?
It indicates the risk of infection; severe neutropenia (<500/mm³) is a medical emergency.
What precautions should be taken for a child with neutropenia?
Private room, strict hand hygiene, no fresh flowers or raw foods, avoid crowds.
What are the critical values for thrombocytopenia that indicate bleeding precautions?
<50,000/mm³ for precautions, <20,000/mm³ for high risk of spontaneous bleeding.
What nursing actions should be taken for a child with thrombocytopenia?
Avoid IM injections, rectal temperatures, and suppositories.
What is a nursing alert for any fever in a neutropenic child?
It is considered a medical emergency.
What platelet count indicates the need for bleeding precautions?
<50,000/mm³
What platelet count indicates a high risk of spontaneous bleeding?
<20,000/mm³
List three bleeding precautions for patients with thrombocytopenia.
Avoid IM injections, use soft toothbrushes, apply pressure for ≥10 minutes after venipuncture.
What should families report regarding bleeding?
Any new bruises, bleeding gums, or nosebleeds.
What is the definition of Tumor Lysis Syndrome (TLS)?
Rapid destruction of malignant cells releases intracellular contents into the blood.
What are common conditions associated with Tumor Lysis Syndrome?
Leukemia, lymphoma, neuroblastoma.
What key lab findings are associated with Tumor Lysis Syndrome?
Increased potassium, phosphate, uric acid; decreased calcium.
What is the immediate nursing intervention for Tumor Lysis Syndrome?
Aggressive IV hydration before chemotherapy.
What are the signs of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)?
Oozing from IV sites, petechiae, hematuria, hypotension.
What triggers DIC?
Sepsis, leukemia, shock, massive tissue injury.
What nursing management is required for DIC?
Treat underlying cause, administer FFP, cryoprecipitate, and platelets as ordered.
What is the purpose of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT)?
To replace diseased bone marrow after high-dose chemotherapy or radiation.
What is a critical nursing alert for patients undergoing HSCT?
Protective isolation until engraftment (ANC > 500/mm³).
What are common long-term complications of pediatric cancer treatment?
Growth delay, infertility, organ dysfunction, secondary malignancies.
What are some common psychosocial changes in children undergoing cancer treatment?
Alopecia, weight loss, surgical scars, amputations.
What nursing support can be offered to children experiencing body image changes?
Prepare the child for changes, offer wigs or hats, encourage self-expression.
What is the recommended dietary approach for children with anemia?
Offer small, frequent, high-calorie meals and monitor hydration.
When are PRBC transfusions indicated?
When hemoglobin is ≤7-8 g/dL or hematocrit is ≤21-24%.
What is the nursing care focus for a child with anemia?
Encourage rest, monitor vital signs, and reassess after transfusion.
What should be monitored in patients with thrombocytopenia?
Petechiae, bruising, bleeding gums, epistaxis, hematuria.
What is a critical nursing alert regarding medication for patients with thrombocytopenia?
Never give aspirin or NSAIDs as they impair platelet function.
What are the signs of hyperleukocytosis?
WBC >100,000 leading to capillary obstruction and neurologic symptoms.
What nursing interventions are needed for Superior Vena Cava Syndrome?
Maintain airway, elevate head, administer corticosteroids, prepare for radiation.
What nursing care is required for spinal cord compression?
Administer corticosteroids, provide radiation, and implement safety measures.