HS 3150 - Chapter 8, 11, & 15
1/144
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 8: Diseases of Digestive system & Chapter 11: Diseases of Urinary system
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
Digestive system
digestive tract processes and transports the products of digestion
accessory organs manufacture and secrete endocrine and exocrine enzymes essential to digestive functions
Diseases of GI tract can
affect health and threaten life; interfere with:
ingestion and digestion of food
absorption of nutrients for metabolism
elimination of wastes
General categories of diseases
erosion of tissue, inflammation, and infection; benign/malignant tumors, obstruction, malnutrition, and malabsorption syndrome
diseases of oral cavity and jaws
function of teeth is to breakdown food into easily digestible pieces; decrease in saliva production can adversely affect the digestive process; there can be a connection between oral infections and cardiovascular diseases, respiratory diseases and diabetes
Xerostomia
dried mouth
Missing teeth (malocclusion)
can alter the bite (occlusion); malocclusion eventually leads to jaw pain called temporomandibular joint disease (TMD)
can lead to digestive disturbances and loss of nutrients
bolting: inadequate chewing
four main causes of malocclusion
dental decay
dental injury
congenitally missing
impacted
Impacted 3rd molar
wisdom tooth can become impacted and cause pain
usually no symptoms until they begin to emerge
decay much more often than other teeth
become impacted when they do not have enough room to erupt
Dental caries (cavities)
first appear as white spots (infection) on the tooth surface
major symptoms in the early stage is mild toothache, with hypersensitivity to sweets and extreme temps
eventually pulp of gums becomes inflamed, and pain is persistent; if untreated leaves bad taste in mouth, bad breath and affect taste of food
avoid this by brushing teeth and flossing, mouthwash
sugars can lead to cavities
Discolored teeth
colors range from a slight yellow to brown and gray
age causes yellowing, and smoking turns teeth brown
certain drugs can cause discoloration of enamel
things that can cause discoloration in teeth: blueberries, certain drugs, mouthwashes, coffee, tea, red wine
Treatment for discolored teeth
superficial treatment: polishing machine (on surface)
deep treatment: bleaching
Gingivitis
inflammation and swelling of the gums
gums are normally pale, pink and firm but become red, soft, and shiny…as well as bleed easily
can lead to periodontitis: destruction of gums and bone disease
Common cause is plaque {inflamed/swollen causes pocket formation}
Periodontitis
end result of gingivitis
Pockets form between the teeth and gums, gradually deepen and expose roots
Plaque develops and causes unpleasant tastes in the mouth, “offensive breath”
Tooth or teeth become extremely sensitive to extreme temperatures
Malocclusion (faulty bite)
signs include a protrusion or a recession of the jaw; teeth that are turned or twisted out of position because of crowding
generally results from genetics; crowing can result from the early loss of primary teeth or oral habits
keep fingers out of mouth
Temporomandibular joint disorder (TMD or TMJ)
when joints are inflamed or dieseased; jaw movement is markedly limited
patient reports hearing clicking sounds during chewing; experiences severe pain or aching in or around the ears and jaw joints made worse by chewing
pain and limitation are usually bilateral
Tooth Abscesses
a tooth abscess is a pus-filled sac that develops in the tissue surrounding the base or root
persistent ache or throbbing and can be extremely painful when biting/chewing food
forms when a tooth is decayed or dying or when tooth structure loss exposes the nerve to bacteria
mouth ulcers (2 most common types)
a ulcer in the mouth is a lesion on mucous membrane, exposing underlying sensitive tissue
can appear as pale-yellow spots with red borders
types: aphthous ulcer and traumatic ulcer
aphthous ulcer
also known as a canker sore; caused by stress, certain acidic foods, candy, illness
traumatic ulcer
caused by: injuries (braces, hot food, toothbrush, dentures)
should heal in 10 days; go to doctor if still present; not viral
treatment: mouthwash or salt water rinse
Herpes Simplex
a contagious, recurrent viral infection that affects the skin and mucous membranes
these blisters can develop on the lips and inside the mouth, producing painful ulcers
ulcers can form on the gums, causing them to become red and swollen
the types are based off the area located
herpes simplex type 1
generally in the mouth
herpes simplex type 2
generally genitals area
Thrush
candidiasis of oral mucosa, involving the mouth, tongue, palate, and gums; can happen to babies, elders, immunocompromised people
produces sore, slightly raised, pale yellow patches in the mouth sometimes the throat
fungus candida albicans causes mot cases of thrush; extended use of antibiotics can cause this
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GRED)
Clinical manifestations of regurgitation of stomach and duodenal contents into the esophagus
patient typically experiences belching with a burning sensation in the chest and mouth
chronic and frequent GERD:
difficulty swallowing and inflamed esophagus along with bleeding
causes: overeating, pregnancy, weight gain
Esophageal varices
superficial veins lining esophagus become dilated and twisted at the distal end
-maybe asymptomatic until a rupture
-result from increased pressure within the veins, develops when venous return to liver is obstructed
esophagitis
inflammation and tissue injury of the esophagus
main symptom is burning chest pain, which can make the patient believe that he or she is having a heart attack; onset of pain typically follows eating or drinking
corrosive esophagitis
severe inflammation resulting from the ingestion of a burning chemical
treatment: no hot, spicy foods, bland diet
Gastric ulcer
patient is asymptomatic, especially if caused by NSAID ingestion
some patient experience pain or a feeling of uncomfortable fullness after eating
common cause is helicovacter pylori infection
Duodenal ulcer
symptoms vary from subtle mid-epigastric pain and heartburn to intense pain in the upper abdomen
common cause is helicovacter pylori infection
Gastritis
stomach lining becomes inflamed the patient experiences epigastric pain, indigestion, and a feeling of fullness; when gastric mucosa is inflamed and swollen, it can bleed;
main cause is H. pylori, but alcohol, smoking, aspirin, & other anti-inflammatory drugs, & stress can lead to this
Acute appendicitis
Inflammation of the appendix
classic symptoms: abdominal pain, vague discomfort around the navel that localizes in the right side lower quadrant
obstruction of the narrow lumen initiates the clinical illness
surgical removal of the appendix is treatment & performed
Hiatal Hernia
defect in the diaphragm that permits a segment of the stomach to slide into the thoracic cavity
Symptoms: heartburn, chest pain, swallowing, difficulty swallowing
can be caused by a congenital defect in the diaphragm or a weakness due to old age, trauma, and obesity
Abdominal hernia
the condition in which an organ protrudes through an abnormal opening in abdominal wall
signs/symptoms: vary with size and location of the hernia
severe pain because hernia is trapped or strangulated
types of abdominal hernias (locations)
incisional: organ protrudes at site of previous surgery
umbilical: from belly button
indirect inguinal: at opening of inguinal ring
direct inguinal: near the opening of inguinal canal
epigastric: upper midline
Femoral: located on femoral canal
Crohn’s Disease
a chronic inflammatory disorder of the GI tract
all layers of the bowel wall are inflamed with edema
patients are accompanied with chronic diarrhea, or abdominal pain
any portion of the GI tract from mouth to anus can be affected
cause unknown
Ulcerative Colitis
a chronic inflammatory bowel disease affecting mucosa and submucosa of the rectum and colon; cause unknown
symptoms: intermittent episodes of bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramping, urgency to defecate, and stools with mucus
stools become looser and more frequent with cramping and rectal pressure
Gastroenteritis
Acute inflammation of the lining of the stomach, and intestines
stomach and intestines remain protected by normal bacteria flora and acid secretions and the motility of the GI tract
cause: can be result of infection, chronic consumption of acidic, caffeine, alcohol, spicy food, aspirin
Symptoms: increased motility, rapid fluid loss (aka travelers diarrhea
Intestinal Obstruction
mechanical or functional blockage of intestines
occurs when contents of the intestines cannot move because of partial or complete bowel blockage
sign: severe pain, nausea, vomiting, blocked abdomen without passage of stool/gas
functional blockage treatment is IV feed
Mechanical blockage vs functional blockage
mechanical is fecal impaction or tumor and functional is when muscles don’t work normally
Diverticulosis
diverticula (out pouches) of the mucosa that penetrate weak points in the muscular layer of the large intestine
characterized by defects in the muscular layer of large intestines
usually causes no symptoms
Diverticulitis
the inflammation of diverticula
Pseudomembranous Enterocolitis
in small and large intestine, you have dead tissue and plaque is sticking to dead tissue
marked by severe greenish, foul-smelling watery diarrhea
cause is long term use of antibiotics
Short bowel syndrome
insufficient function of the small bowel to absorb nutrients, fluid, vitamins, and minerals.
significant signs of malnutrition is noted and develops when the length of the small bowel has been altered by disease or surgery
diarrhea and abnormal stools occur
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Chronic abdominal pain, bloating, and discomfort and erratic dysfunction of bowel habits; cause unknown
classic symptoms include episodes of cramping or aching abdominal pain
Peritonitis
when irritated or infected, the peritoneum becomes hyperemic, meaning the fluid accumulates (edema)
Symptoms include: abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, weakness, and sweating
inflammatory process of peritonitis has potential to cause abscesses and adhesions
Hemorrhoids
Lump in rectal and anal area, could be painful or painless, if painful it may indicate thrombosis of external hemorrhoid
when symptomatic patient may experience rectal pain, itching, protrusion, or bleeding
veins in rectal and anal area become varicose, swollen, and tender as a result of blockage
caused by childbirth or straining due to constipation
Cirrhosis of the Liver
Chronic degenerative disease that is irreversible and involves slow deterioration of the liver, resulting in the replacement of normal liver cells with hard fibrous scar tissue; early stages of disease symptoms are vague
COMMON causes are alcoholism and exposure to chemicals
Wilson’s disease
the uncommon cause of cirrhosis of the liver; genetic disorder cause copper to build up in body which leads to cirrhosis of liver
Viral Hepatitis
most cases are by one of several viral agents
treatment is symptomatic in acute cases; some chronic cases respond to antiviral agents
Hepatitis A
common cause fecal to oral transmission; poor hygiene; highly contagious
Hepatitis B
blood/fluid borne; most common worldwide
Hepatitis C & D
blood/fluid borne
Hepatitis E
contaminated food and water
Cholelithiasis
Abnormal gallstones that form in bile, which lead to inflammation
may be asymptomatic until bile duct become obstructed by the stones; nausea and vomiting accompany the pain
Cholecystitis
acute or chronic inflammation of the gallbladder due to obstruction of the cystic duct
the patient can experience acute colicky pain localizes in upper right quadrant
Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis
can range from mild and self self-limiting to chronic, fatal destruction of pancreatic tissue
sudden onset of severe abdominal pain, which radiates to the back, along with nausea and vomiting
causes can include: alcoholism, trauma, infection, elevated calcium levels, structural anomalies, hemorrhage, hyperlipidemia
COMPONENTS OF A SUCCESSFUL WEIGHT LOSS PROGRAM
Patient self-control
Supportive Physician
Reduced-calorie diet
Nutritionally adequate diet
Increased physical activity
Do not focus on portion control alone
Malnutrition
Disrupts the body's metabolic processes, disturbing physical structure and biological function
Symptoms: decreased or increased appetite, loss of energy, diarrhea, skin lesions, hair loss, poor nails, edema
Causes: depriving yourself of food energy
not everyone who is slender is malnourished and weight/size does not determine malnourishment
Hypervitaminosis
Condition of toxicity resulting from an excess of any vitamin
four fat soluble vitamins: A, D, E, K
TOXICITY: Vitamins A,D,E,K,C
Facts of obesity
Overweight and obesity are identified objectively using BMI
A major correlation has been made between greater energy intake and output
Obesity and the regional distribution of fat have a strong genetic component
Malabsorption Syndrome
A group of disorders in which intestinal absorption of dietary nutrients is impaired; main cause of malabsorption syndrome is defective mucosal cells in the small intestine
symptoms: impaired digestion, inability to absorb fat or other components of diet
Celiac Disease
Disease of the small intestine that is characterized by malabsorption, gluten intolerance, and damage to the lining of the intestine
Symptoms: weight loss, anorexia, abdominal cramping and distention, diarrhea, intestinal bleeding
Cause may be a toxic or immunologic reaction to a component of gluten
Anorexia Nervosa
restriction of food intake leading to low body weight
Bulimia
eating or bingeing and then throwing up
Urinary system
is responsible for producing, storing, and excreting urine
responsible for also cleansing blood of waste products
regulating the water, salts, and acids in the body fluids ensures homeostasis
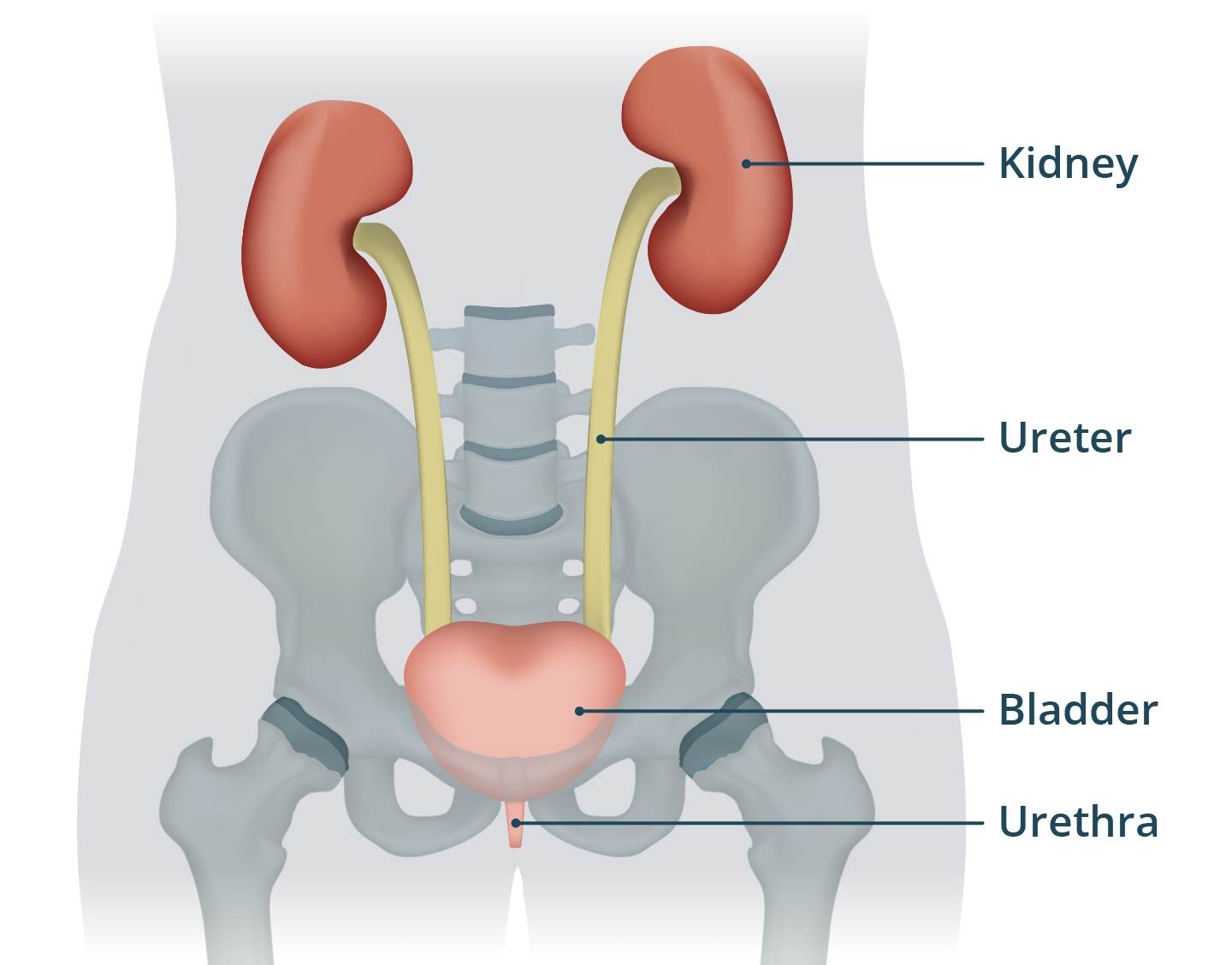
The kidneys
enable reabsorption of necessary nutrients, water and electrolytes
three regions: cortex, renal pelvis, and medulla
blood enters kidney by way of renal arteries and leaves through renal veins
Nephrons
each kidney is composed of about 1 million nephrons
urine transports from nephron to renal pelvis and then ureters
composed of: bowman’s capsule (glomerulus) and loop of Henle which are responsible for filtration, reabsorption and secretion of urine
Urea
waste product that passed through glomerulus
Types of disturbances in renal function
infection
scarring
toxic necrosis
trauma
congenital or acquired structural defects
Urinalysis
looking at the characteristics and constituent compounds of urine
color & clarity (normal is pale to dark yellow)
chemical nature (pH should be 6.5/slightly acidic)
odor (no fowl or fruity smell)
specific gravity (measurement of urine concentration)
constituent compounds & how much should be found in urine
glucose and ketones should not be present (if present is a sign of diabetes)
protein is acceptable from none to a trace (high level means kidney not functioning properly)
bile and bilirubin (should have no trace; if present something wrong with liver or gallbladder)
casts are particles in urine made of white/red blood cells or fat (should have none to small trace)
nitrogenous waste or urea
crystals are a result of minerals and salts in urine (none to very small trace)
fat droplets (none)
Culture and sensitivity of Urine
culture: urine specimen places in/on culture medium to identify pathogens
sensitivity: testing the pathogens against antibiotics to determine effective treatment
Renal Diagnostic Tests
clearance test: look at glomerulus filtration rate
concentration and dilution test: look at ability of renal tubes to retain and eliminate water
serum creatine and BUN: tells us how well protein is being metabolized
Protein in Urine Test: tells us how the glomerulus membranes are filtering and are they normal
Symptoms of urinary disease
Nausea and loss of appetite
fever
headache
edema
flank or lower back pain
decreased urinary output
hypertension
pruritus (itchy skin)
Acute glomerulonephritis
can be primary disease of kidneys or develop due to systemic disease
marked by proteinuria, edema, and decreased urine output
can be idiopathic or result from an immune trapping antibodies
Treatment: antibiotics, diuretic, steroid, limit salt intake
Chronic glomerulonephritis (CGN)
a progressive, non-infectious disease that leads to irreversible renal damage and eventually kidney failure
results in inflammation followed by progressive destruction of the glomeruli
leads to hypertension, hematuria, proteinuria, oliguria (decreased output) and edema
immune mechanisms suspected to be a major cause of CGN
Dialysis
filters out unwanted elements from the blood by diffusion across a semipermeable
the proper fluids, electrolytes, and acid-base balances are maintained in the body
Hemodialysis
removes impurities or wastes from patients blood by using an artificial kidney

Peritoneal dialysis
uses a dialysate solution and peritoneal membrane to filter out harmful toxins and excessive fluids
two types: CAPD or CCPD
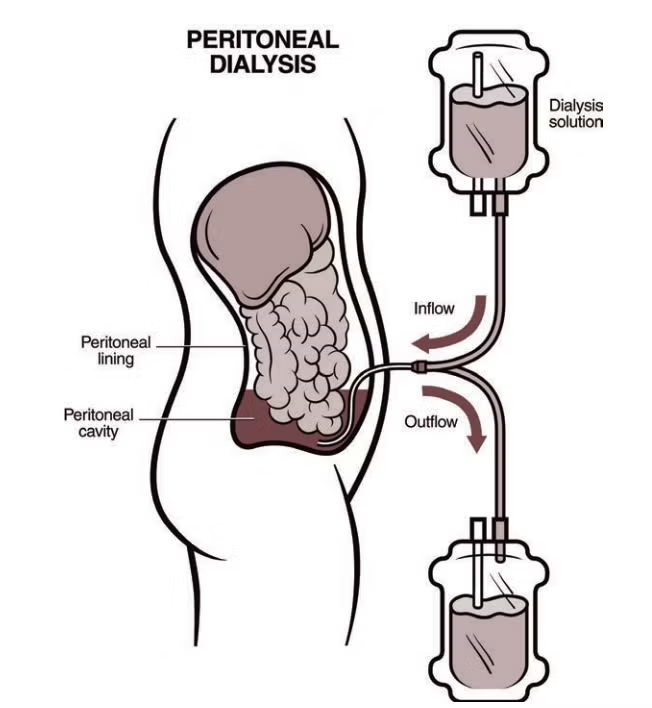
CAPD (continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis)
uses gravity to aid dialysate solution in filtering process, thereby draining waste into bag worn around the waist
takes about 15 minutes per session; repeated 3 too 4 times per day and once at night
CCPD (continuous cycling peritoneal dialysis)
uses a machine that continuous cycles the dialysate and extracts the waste; typically at night
Kidney Transplantation
surgical placement of a donor kidney into a patient with irreversible renal failure
immunosuppressive agents are used to prevent or treat rejection syndrome
evaluation of donor and the recipient to find good match offers the best chance for a good prognosis
Nephrotic syndrome (nephrosis)
a kidney disorder causing excessive protein (mainly albumin) loss in urine, leading to swelling due to retained water and sodium
sometimes referred to as protein-losing kidney
no cure; treatment is prevent further damage
caused by damage to glomeruli such as diabetes or an autoimmune disease
Nephrotoxic agents
solvents (chemicals)
heavy metals
pesticides
antibiotics
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
iodinated radiographic contrast media
antineoplastic agents (cancer meds)
poisonous mushrooms
Acute renal failure (ARF)
sudden and severe reduction in renal function; is reversible with quick treatment
symptoms: decreased urine output, gastrointestinal disturbances, headache, drowsiness
causes are classified: results is diminished blood flow to kidney; involve intrarenal damage or disease; result from mechanical obstruction of urine flow
Chronic renal failure (CRF)
results from the gradual and progressive loss of nephrons
patient feels tired and weak; retention of water causes hypertension and edema
The underlying cause must be treated
Treatment is dialysis and kidney transplant
Stages of CRF (glomerulus filtration rate)
1: 90 and up (eGFR) (normal function)
2: 60-89 (mild)
3a: 45-59 (mild to moderate)
3b: 30-44 (moderate to severe)
4: 15-29 (severe)
5: 15 and lower (kidneys are not working)
Pyelonephritis (Most common type of renal disease)
usually is caused by infection, pregnancy, or renal calculi
Pus collects in the renal pelvis, with the formation of abscess
Patient experiences rapid onset of fever, chills, nausea vomiting, and flank pain
Bacteria that ascend from the lower urinary tract to the kidneys usually cause pyelonephritis
Inflammation of the renal pelvis or 1 or both kidneys
Signs: fowl smelling urine
prevention: drink water
Hydronephrosis
abnormal dilation of the renal pelvis
usually chronic condition, with destruction of the kidneys without pain or symptoms
caused by buildup of pressure in the kidney because of an obstruction
treatment: depends on underlying cause of obstruction (cancer, calculi)
Renal Calculi
Kidney stones can be solitary or multiple and vary in size; Patient's symptoms vary with the degree of obstruction
With infection or blockage:
Patient experiences renal colic
Urinary urgency and other urinary symptoms
Nausea and vomiting, hematuria, fever, chills, and abdominal distention
Infection cystitis and Urethritis
Inflammation and infection usually caused by an ascending bacterial invasion of the urinary tract
Causes urinary urgency, and frequency, dysuria, and even incontinence
Treatment consists of organism-specific antibiotics or urinary antiseptic therapy
antibiotics kill bacteria but antiseptic prevents growth of bacteria
Diabetic Nephropathy
Clinical manifestations include urinary retention, hypertension, nausea, and protein in the urine
Diabetic glomerulosclerosis is a complication of diabetes mellitus
Lesions of the glomeruli eventually cause the filtration rate to decrease
Treatment plan must be individualized
Blood pressure control and the prolongation of proper kidney function
Polycystic Kidney disease
Slowly progressive and irreversible disorder in which normal tissue is replaced by grape-like cysts
Condition is bilateral, with cysts that form from dilated nephrons and collecting ducts
The kidneys become grossly enlarged, with compression of surrounding tissue leading to impaired renal function and renal failure
Patient experiences lumbar pain, abdominal pain and tenderness, hematuria, and systemic hypertension
two types: 1 is inherited and the 2 is someone who had CKD and long term dialysis
Urinary catherization
Involves the insertion of a catheter into the urinary bladder through the urethra for the withdrawal of urine for irrigation of the bladder with a therapeutic solution
Strict sterile technique is necessary to prevent cystitis
Neurogenic bladder
insult to brain, spinal cord. or the nerves supplying the lower urinary tract may result in the ability to empty the bladder of urine or to maintain continence
treatment: prevention of UTI and attempts to restore normal function
Classification of Neurogenic bladder (5 classifications )
Spastic (involuntary contractions, frequent urination, muscles become stiff)
Flaccid (weakening of bladder muscles)
Reflex (involuntary bladder contractions, frequent urinations)
Atonic (loss of muscle tone, bladder get distended)
Mixed (combination of above)
Urinary Incontinence
partial or total loss of voluntary control of the bladder with inability to retain urine
is sometimes experienced temporarily after childbirth due to stretching
neurologic damage may result in permeant incontinence
5 main types of incontinence
Stress incontinence: uncontrollable leakage of urine from the urinary bladder; occurs during physical exertion; caused by weakening of pelvic floor muscles; hormonal aging and menopause
Urge incontinence: sudden feeling to urinate but cant hold
Overflow Incontinence: bladder not completely empty
Functional incontinence: physical or mental disability
Mixed Incontinence: mix of multiple
Overactive Bladder
the uncontrollable urge can result in urinary incontinence with the accidental loss or leakage of small amounts of urine
the individual with this symptoms can never be sure when they will occur
the muscles transmit false signals to the brain before bladder is full
Trauma
causes: accidental, self-inflicted, violence
Effects:
Interfere with body to functions
Alter homeostasis of body