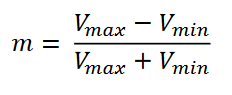Amplitude Modulation
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Modulation
Process of converting message data into signals to optimize transmission.
Amplitude Modulation (AM)
It is a modulation process focused on modulating or changing the signal's amplitude.
Carrier Signal
A steady waveform, constant in amplitude and frequency.
Modulating Signal
The message that must be transmitted.
Modulated Signal
The output after modulation, where amplitude varies based on the message signal.
Sidebands
Frequencies created above (Upper Sideband, 𝑓𝑈𝑆𝐵) and below (Lower Sideband, 𝑓𝐿𝑆𝐵) the carrier frequency.
Percentage of Modulation
𝑚 multiplied by 100 to get percentage.
Time domain signals
These illustrations show the variation of carrier amplitude concerning time and are to be in the time domain.
____ ______ _______ are voltage or current variations that occur over time and are displayed on an oscilloscope screen.
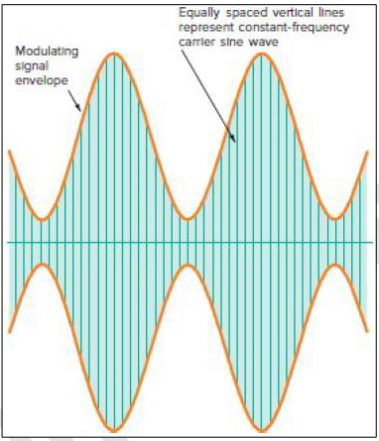
Envelope
Imaginary line connecting the positive and negative peaks of a carrier waveform.
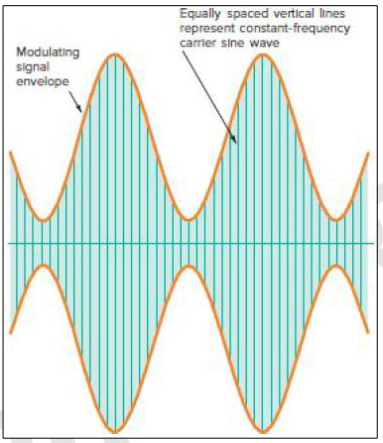
Modulation Index (m)
The ratio of the modulating signal's amplitude to the carrier's amplitude: m = Vm / Vc
Also referred to as the degree of modulation or modulating factor/coefficient.

Oscilloscope
Can be used to derive the modulation index (𝑚) by measuring the values of the modulation and carrier voltages and then calculating the ratio.
Percentage of Modulation
Modulation index (𝑚) × 100.
Bandwidth (BW)
𝐵𝑊 = 𝑓𝑈𝑆𝐵 − 𝑓𝐿𝑆𝐵 or 𝐵𝑊 = 2𝑓𝑚
Modulation
__________ is done to improve signals often unsuitable for the transmission device.
20 𝐻𝑧 - 20𝑘 𝐻𝑧
The frequency people hear is in the audio spectrum only ranging from _____ – ______. This makes sending audio signals wirelessly using radio frequency harder.
Amplitude Modulation
One way to get a high-frequency signal to carry a low-frequency signal is by _________ __________.
Transducer
A microphone acts as a __________ that receives the input signal in the form of audio frequency.
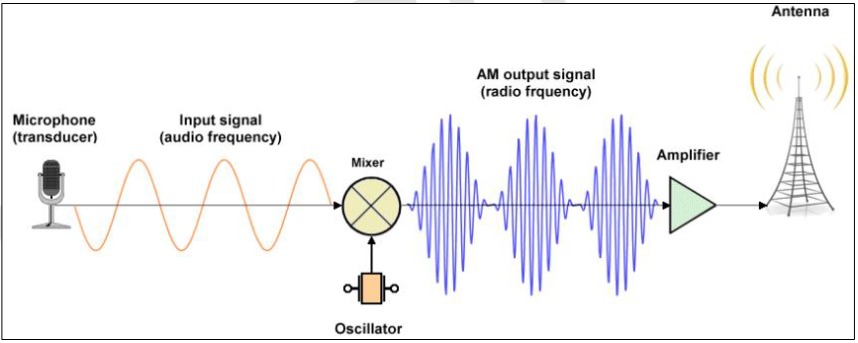
Carrier
This input signal will serve as the _______.
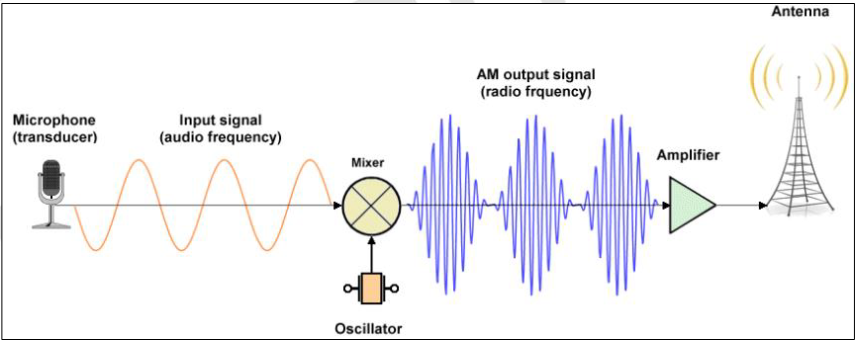
Mixer
It is only modulated by adding the input signal in a _____, turning it into a radio frequency acceptable for the transmission device.
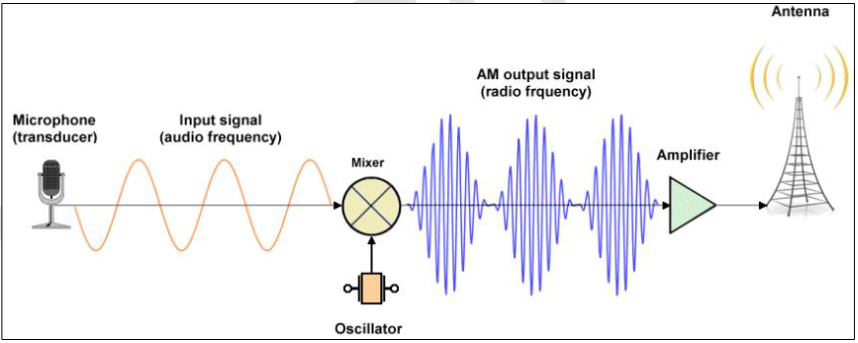
Device / Circuit
Can convert data into an electrical signal in an AM communications system. This signal, either the message or modulating signal, is then used to modify the amplitude of another signal.
Modulating signal
Modulated carrier
In Figure 4, (a) is the __________ ______, and (b) is the _________ _______.
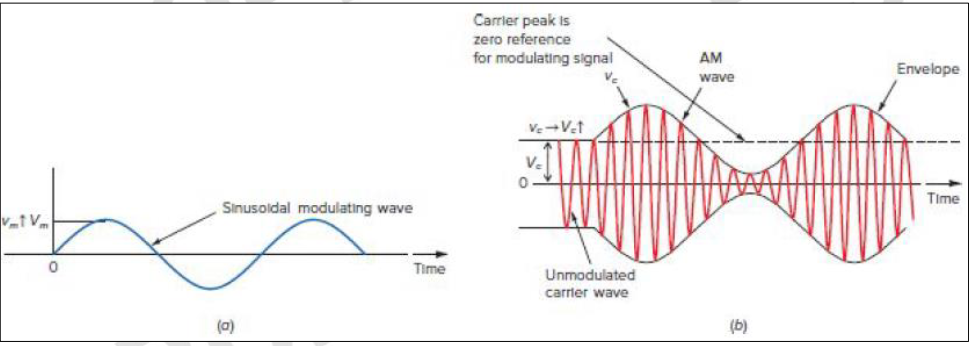
Carrier frequency
The _______ _________ stays constant during the modulation process, but its amplitude (height) changes based on the modulating signal.
Increases
An increase in the amplitude of the modulating signal _________the amplitude of the carrier.
Modulating signal
Changes in the positive and negative peaks of the carrier wave depends on the __________ ______.
Increase
Decrease
An increase/decrease in the amplitude of the modulating signal causes an ________ / ________ in the positive and negative peaks of the carrier amplitude.
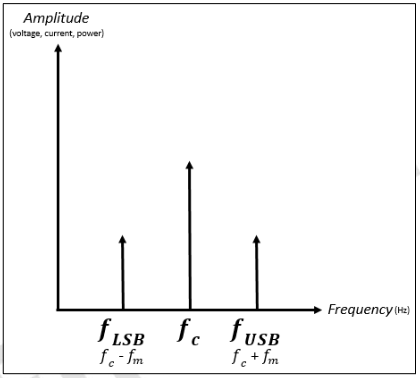
Sidebands / Side frequencies
During the modulation of a carrier wave by a modulating signal, new signals are generated at different frequencies as part of the process.
Frequency domain
It is preferred to show the AM signal in the _________ ______ rather than in the time domain if signals of more than one (1) frequency create a waveform.
Sidebands
_________ are the sum and difference of the carrier and modulating frequencies, such as :
𝑓𝑈𝑆𝐵 = 𝑓𝑐 + 𝑓𝑚
𝑓𝐿𝑆𝐵 = 𝑓𝑐 − 𝑓𝑚
Upper sideband
𝑓𝑈𝑆𝐵
Lower sideband
𝑓𝐿𝑆𝐵
Carrier Frequency
𝑓𝑐
Modulating Frequency
𝑓𝑚
Frequency domain
Sideband signals are illustrated in a _________ ______ where the horizontal axis represents frequency, and the vertical axis represents the signal’s magnitude, whether in voltage, current, or power amplitude.
Modulation index
𝑚
Peak values
𝑉𝑚 and 𝑉𝑐 are the ____ ______ of the signals, and the carrier voltage is the unmodulated value.
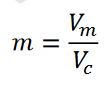
Oscilloscope
An ____________ can be used to derive the modulation index (𝑚) by measuring the values of the modulation and carrier voltages and then calculating the ratio.
Peak value of the modulating signal
𝑉𝑚
Peak
𝑉𝑚𝑎𝑥
Trough
𝑉𝑚𝑖𝑛
Peak value of the modulating signal
Vm
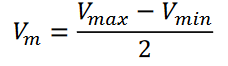
Ok
𝑉𝑚𝑎𝑥 is also one-half of the peak value of the AM signal, such as:
𝑉max(𝑝−𝑝)/2
The values for 𝑉max(𝑝−𝑝) and 𝑉min(𝑝−𝑝) can be obtained from an oscilloscope screen and be used to compute the modulation index. Additionally, the depth of AM is more expressed as the percentage of modulation than as a fractional value.
Press ok nalang. Di ko na alam.
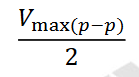
Peak
𝑽𝒎𝒂𝒙 is the ____ value of the signal during modulation.
Trough
𝑽𝒎𝒊𝒏 is the lowest, or the ______ of the modulated wave.
Peak value of the carrier signal
𝑉𝑐
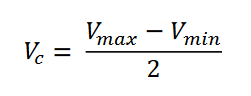
Peak-to-peak
Subtracting 𝑉𝑚𝑖𝑛 from 𝑉𝑚𝑎𝑥 gives the ____________ value of the modulating signal, wherein one-half is the peak value.
Vmax
Vmin
The peak value of the carrier signal 𝑉𝑐 is the average of the ____ and ____ values.
Modulation index