AQA A-Level Chemistry Organic Mechanisms
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Name and outline the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of an alkane to a haloalkane.
[Free-radical substitution]
E.G.
1. Initiation, essential: UV light
Cl₂ --> 2Cl•
2. Propagation
CH₃CH₃ + Cl• --> HCl + CH₃CH₂•
CH₃CH₂• + Cl₂ --> CH₃CH₂Cl + Cl•
3. Termination
CH₃CH₂• + Cl• --> CH₃CH₂Cl
Name and outline the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of a haloalkane to an alkene.
[Elimination]
NaOH, ethanol, reflux
![<p>[Elimination]</p><p>NaOH, ethanol, reflux</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/47a26f4b-8c61-44a2-b367-0d927c5d7fb9.jpg)
Name and outline the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of a haloalkane to an alcohol.
[Nucleophilic substitution]
Warm NaOH(aq), reflux
![<p>[Nucleophilic substitution]</p><p>Warm NaOH(aq), reflux</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7d12669e-0c18-49f1-a201-84dbefce02da.jpg)
Name and outline the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of an alkene to a haloalkane.
[Electrophilic addition]
HBr, 20°C
![<p>[Electrophilic addition]</p><p>HBr, 20°C</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b1e3e4f6-58f7-4c73-8edc-85c30fd341ae.jpg)
Name and outline the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of an alkene to an alcohol. (1) (H+)
i.e. Hydration of an alkene
[Acid catalysed addition]
H₃PO₄ catalyst, steam, 300°C, 60atm
![<p>i.e. Hydration of an alkene</p><p>[Acid catalysed addition]</p><p>H₃PO₄ catalyst, steam, 300°C, 60atm</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a8788f0b-a917-4962-9791-c00d99a0d17b.jpg)
Name and outline the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of an alkene to an alcohol. (2) (H2SO4)
[Electrophilic addition]
H₂O, H₂SO₄ catalyst
![<p>[Electrophilic addition]</p><p>H₂O, H₂SO₄ catalyst</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fe44a17c-c3e8-429b-9d43-05efab120865.png)
Name and outline the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of an alcohol to an alkene.
[Acid-catalysed elimination]
Conc. H₂SO₄ or H₃PO₄, reflux
![<p>[Acid-catalysed elimination]</p><p>Conc. H₂SO₄ or H₃PO₄, reflux</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/93cb30a9-4bb8-443f-99de-2baac3a96014.png)
Name and outline the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of an alkene to a dribomoalkane.
[Electrophilic addition]
Br₂, 20°C
![<p>[Electrophilic addition]</p><p>Br₂, 20°C</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3d97595b-f58b-4b09-b401-ac8c2bb0a7d7.png)
Name and outline the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of a haloalkane to a nitrile.
[Nucleophilic substitution]
KCN(aq) in ethanol, reflux
![<p>[Nucleophilic substitution]</p><p>KCN(aq) in ethanol, reflux</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c83c3573-6c6e-4212-b9ed-98ddd75d346d.png)
Name the reaction, reagents and conditions for the conversion of a nitrile to a primary amine.
Reduction - LiAlH₄ in ether, dilute H₂SO₄
OR
Hydrogenation - H₂, Ni catalyst
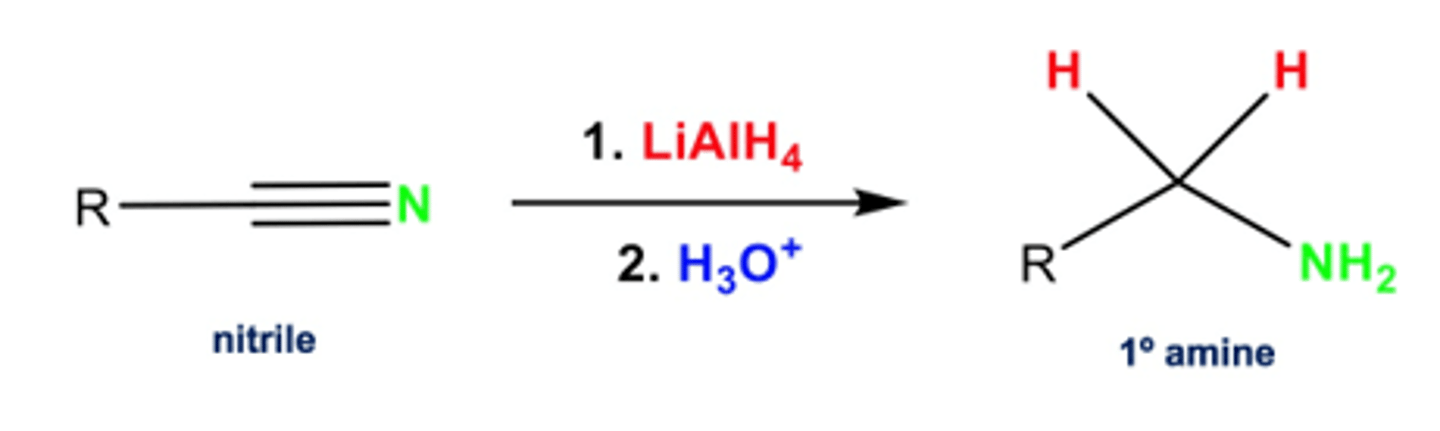
Name and outline the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of a haloalkane to a primary amine.
[Nucleophilic substitution]
Excess NH₃, heat
Product = Ethylamine
![<p>[Nucleophilic substitution]</p><p>Excess NH₃, heat</p><p>Product = Ethylamine</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cad96e1b-ef03-4828-b874-b98d307e4867.jpg)
Name the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of a haloalkane to a secondary amine.
[Nucleophilic substitution]
Primary amine (e.g. CH₃CH₂NH₂), heat
Name the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of a haloalkane to a tertiary amine.
[Nucleophilic substitution]
Secondary amine (e.g. CH₃CH₂NHCH₂CH₃), heat
Name the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of a haloalkane to a quaternary ammonium ion.
[Nucleophilic substitution]
Tertiary amine (e.g. CH₃CH₂N(CH₂CH₃)CH₂CH₃), heat
Produces an ammonium ion
![<p>[Nucleophilic substitution]</p><p>Tertiary amine (e.g. CH₃CH₂N(CH₂CH₃)CH₂CH₃), heat</p><p>Produces an ammonium ion</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5dc53897-54d7-4433-9384-7906e3ce9486.jpg)
Name the reaction, reagents and conditions, for the conversion of an alcohol to an aldehyde/ketone.
Oxidation - K₂Cr₂O₇, H₂SO₄ ( i.e. K₂Cr₂O₇/H⁺) heat in distillation apparatus
Primary alcohol --> aldehyde
Secondary alcohol --> ketone
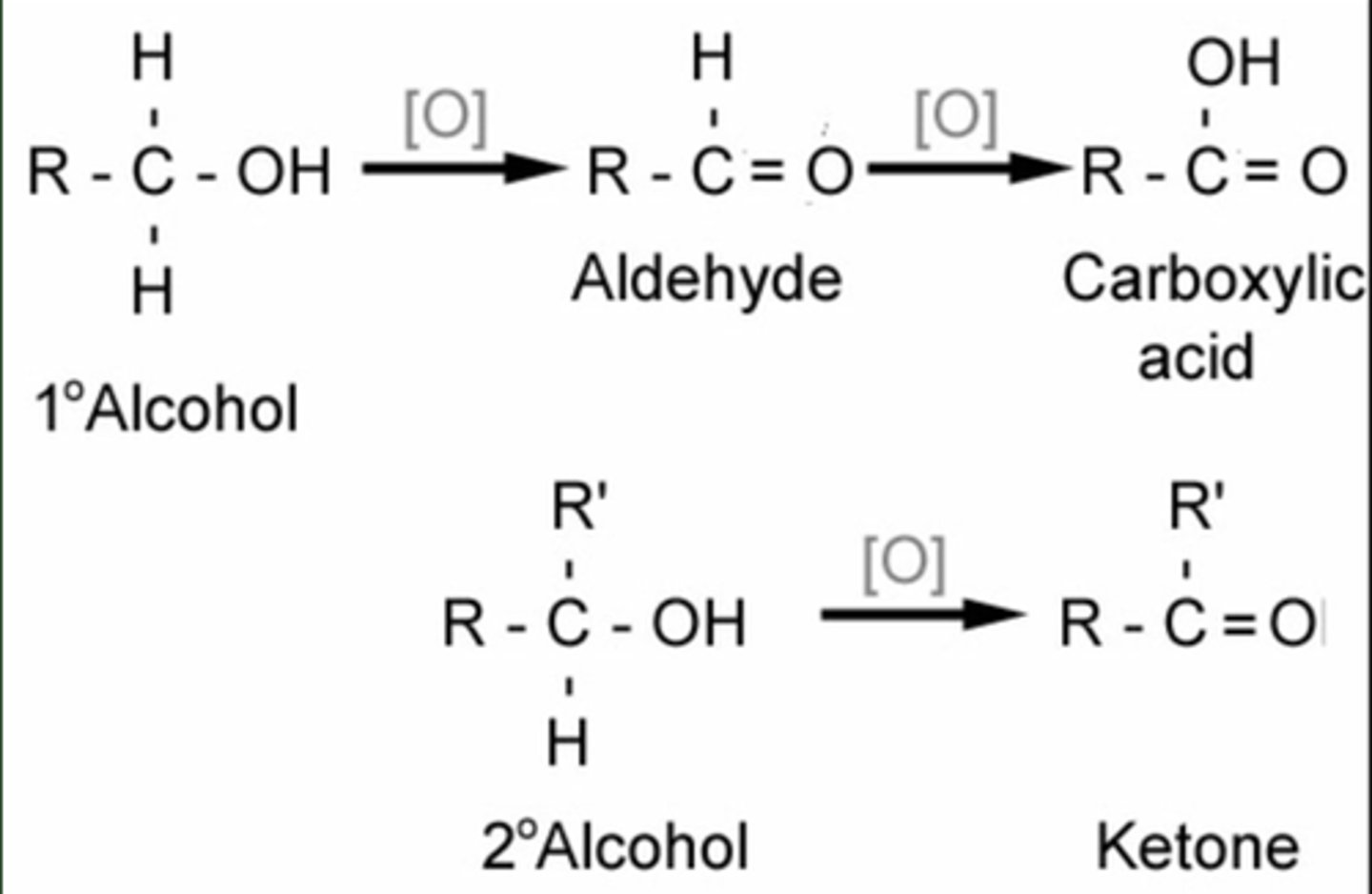
Name and outline the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of an aldehyde/ketone to an alcohol.
[Nucleophilic addition]
NaBH₄ in aqueous solution with methanol
Aldehydes produce primary alcohols.
Ketones produce secondary alcohols.
![<p>[Nucleophilic addition]</p><p>NaBH₄ in aqueous solution with methanol</p><p>Aldehydes produce primary alcohols.</p><p>Ketones produce secondary alcohols.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/05e6d299-a873-4929-9cb9-1f1857d725ff.jpg)
Name and outline the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of an aldehyde/ketone to a hydroxynitrile.
[Nucleophilic addition]
KCN(aq) or HCN(aq), H₂SO₄, 20°C
Product = 2-methylpropanenitrile (from a ketone)
![<p>[Nucleophilic addition]</p><p>KCN(aq) or HCN(aq), H₂SO₄, 20°C</p><p>Product = 2-methylpropanenitrile (from a ketone)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2d3cb8f1-a3af-4ad9-b98a-2f7a96aa2e17.jpg)
Name the reaction, reagents and conditions, for the conversion of an aldehyde to a carboxylic acid.
Oxidation - K₂Cr₂O₇, H₂SO₄ ( i.e. K₂Cr₂O₇/H⁺) reflux
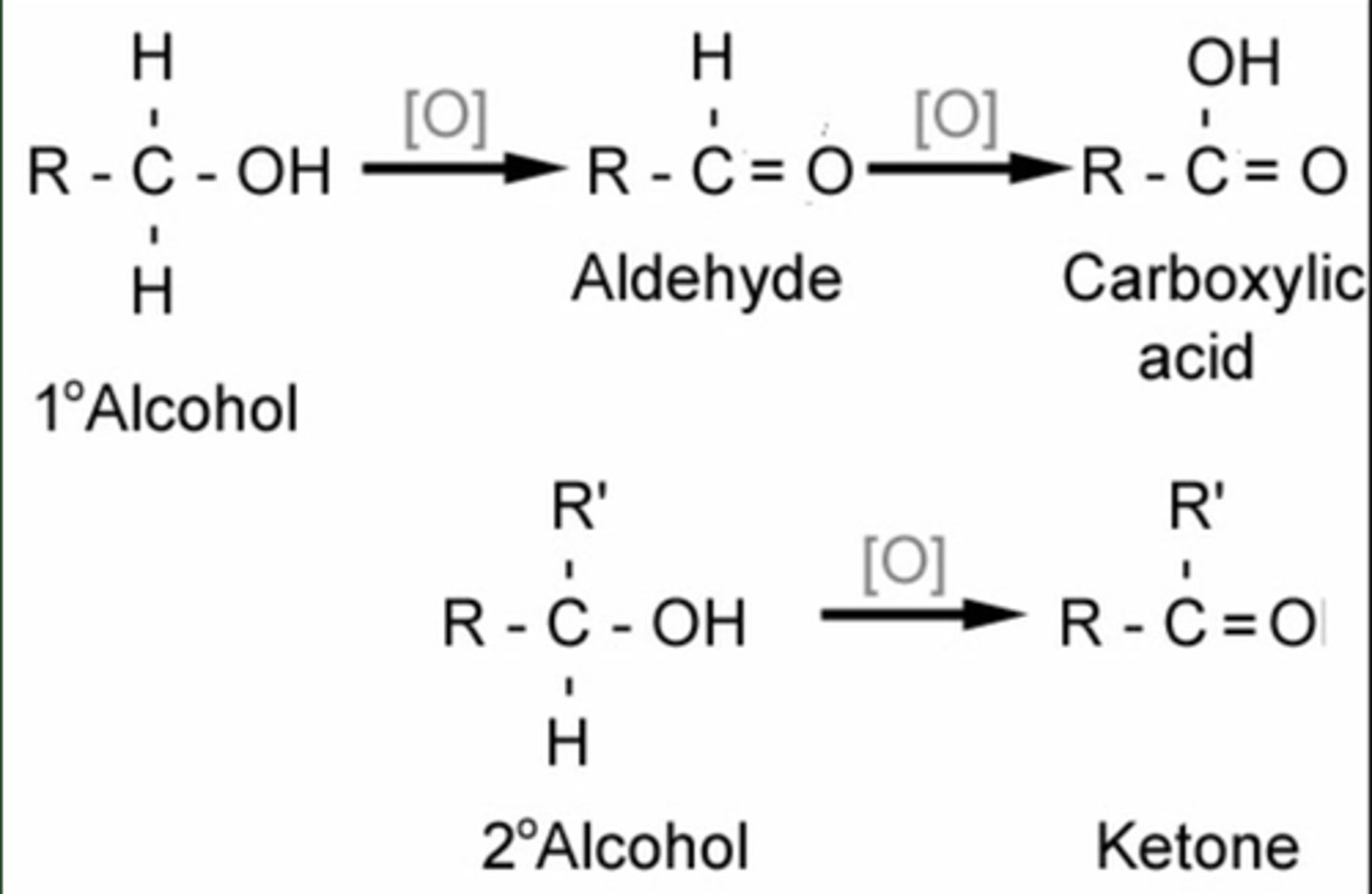
Name and outline the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of an acyl chloride to a primary amide.
[Nucleophilic addition-elimination]
NH₃, 20°C
Product = Ethanamide
![<p>[Nucleophilic addition-elimination]</p><p>NH₃, 20°C</p><p>Product = Ethanamide</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e314488f-5201-4e8a-9914-8134d9ef8380.jpg)
Name and outline the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of an acyl chloride to a N-substituted amide.
[Nucleophilic addition-elimination]
Amine, 20°C
Product = N-ethylethanamide
![<p>[Nucleophilic addition-elimination]</p><p>Amine, 20°C</p><p>Product = N-ethylethanamide</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1379881c-ec32-4111-a660-12b388890ae3.jpg)
Name and outline the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of an acyl chloride to an ester.
[Nucleophilic addition-elimination]
Alcohol, 20°C
Product = Ethylethanoate
![<p>[Nucleophilic addition-elimination]</p><p>Alcohol, 20°C</p><p>Product = Ethylethanoate</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b97588dc-56aa-4e7c-9c89-7c293aa40cd7.jpg)
Name and outline the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of an acyl chloride to a carboxylic acid.
[Nucleophilic addition-elimination]
H₂O, 20°C
![<p>[Nucleophilic addition-elimination]</p><p>H₂O, 20°C</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/185ff51b-e0bc-4662-8daa-aa6919a266c5.jpg)
Name the reaction, reagents and conditions, for the conversion of a carboxylic acid to an ester.
Esterification - Alcohol, conc. H₂SO₄ catalyst, heat
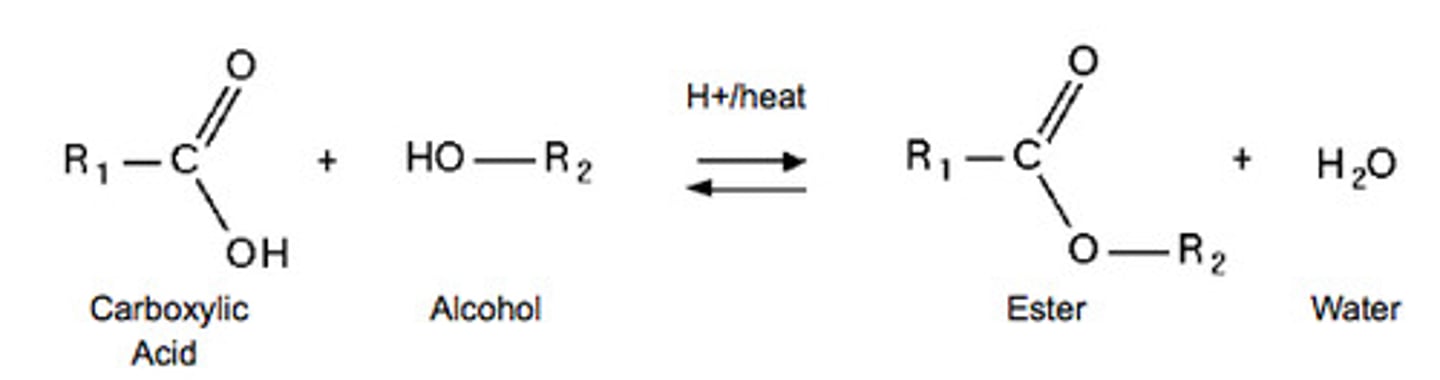
Name the reagents and conditions for the reaction of an ester to a carboxylic acid.
Dilute H₂SO₄ catalyst, H₂O, reflux
OR
Dilute NaOH(aq), reflux
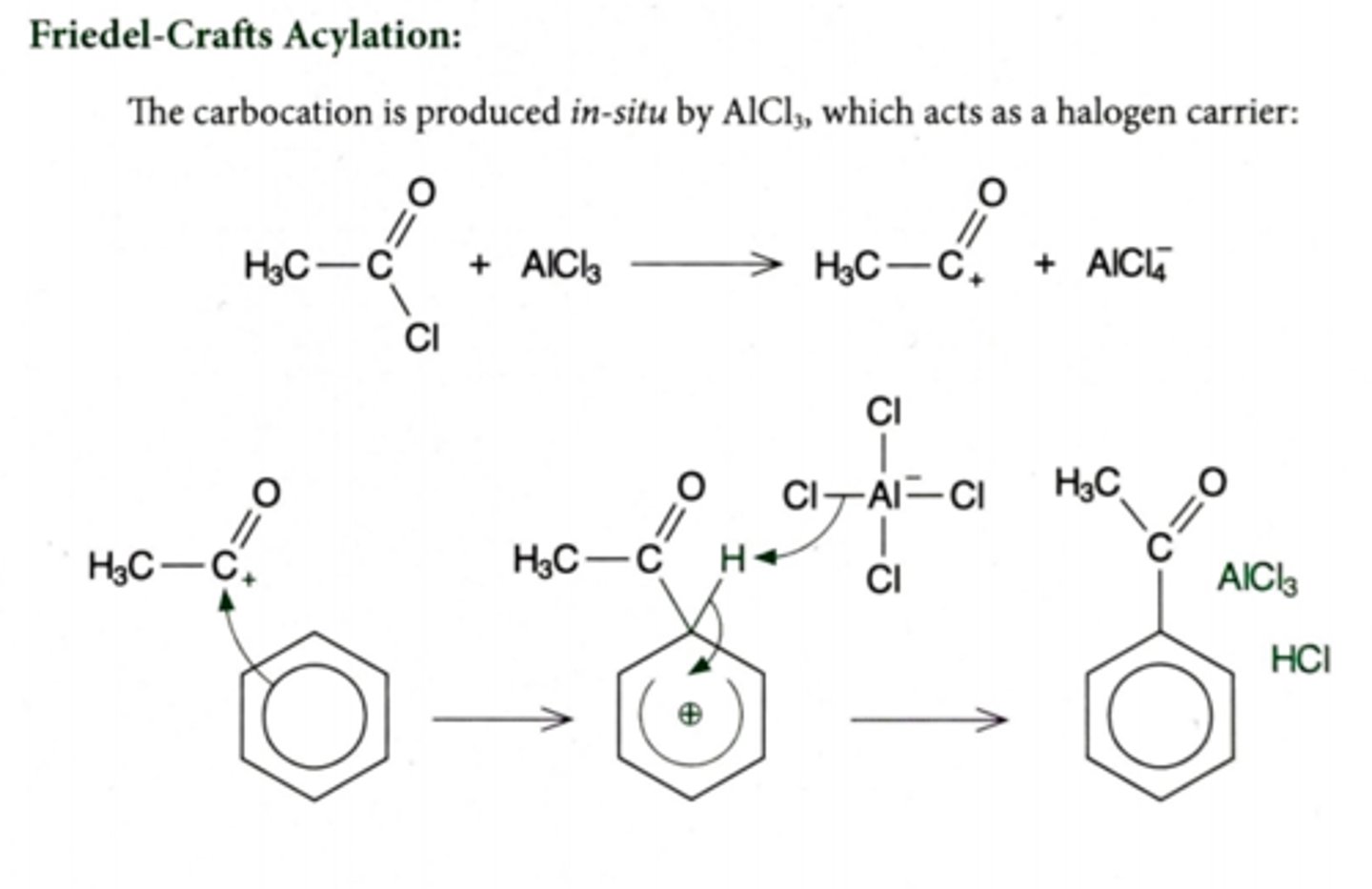
For the reaction of benzene to a phenylketone,
(i) write an equation for the formation of the reactive species
(ii) Name and outline the mechanism, reagents and conditions
(i) Formation of electrophile:
CH₃COCl + AlCl₃ --> CH₃CO⁺ + AlCl₄⁻
(RCOCl + AlCl₃ --> RCO⁺ + AlCl₄⁻)
Electrophile = CH₃CO⁺ (RCO⁺)
(ii) Electrophilic substitution
CH₃COCl (RCOCl), AlCl₃ catalyst, non-aqueous environment
Product = 1-phenylethanone / methyl phenyl ketone
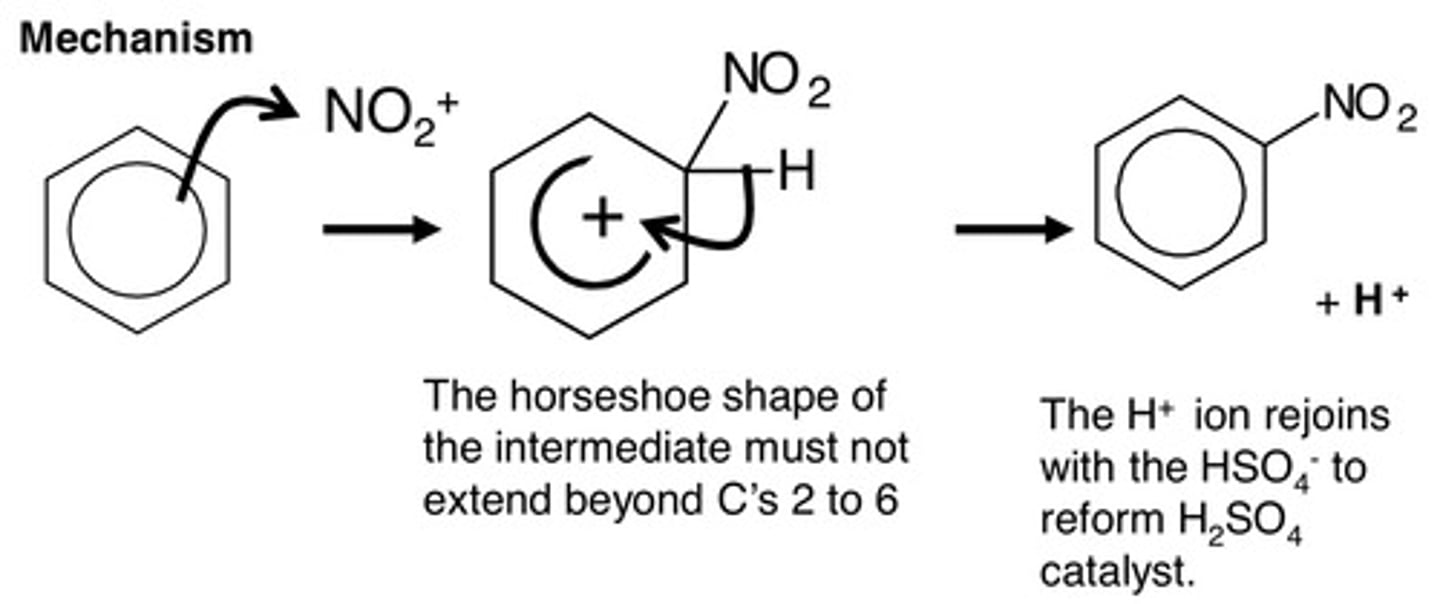
For the reaction of benzene to nitrobenzene,
(i) write an equation for the formation of the reactive species
(ii) Name and outline the mechanism, reagents and conditions
(i) Formation of electrophile:
HNO₃ + 2H₂SO₄ --> NO₂⁺ + 2HSO₄⁻ + H₃O⁺
Electrophile = NO₂⁺
(ii) Electrophilic substitution
Conc. H₂SO₄, conc. HNO₃, below 55°C
For the conversion of nitrobenzene to phenylamine,
(i) Name the reaction, reagents and conditions
(ii) Write an equation for this reaction, using [H] to represent the appropriate agent.
(i) Reduction - Sn, conc. HCL, reflux, NaOH(aq)
(ii) [H] to represent the reducing agent.
C₆H₅NO₂ + 6[H] --> C₆H₅NH₂ +2H₂O
Name and outline the mechanism, reagents and conditions, for the reaction of phenylamine to a N-phenylethanamide.
[Nucleophilic addition-elimination]
CH₃COCl
![<p>[Nucleophilic addition-elimination]</p><p>CH₃COCl</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b0df6bbc-8f7f-4c56-b7c9-be0f57d3ced2.png)