4.2 learning approaches: behaviourist
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Define the behaviourist approach
A way of explaining behaviour in terms of what is observable and in terms of learning
Define classical conditioning
Learning by association
Define operant conditioning
Learning by consequences
Define reinforcement
A consequence of behaviour that increases the likelihood of that behaviour being repeated
What behaviourist rejected introspection and why
John B Watson- because it involved too many concepts that were vague and difficult to measure
What type of studies do behaviourists carry out
Lab studies because they study observable and measurable behaviour
What did behaviourists identify as the two forms of learning
Classical conditioning and operant conditioning
Who did research to support classical conditioning
Pavlov (the dogs)
Who did research to support operant conditioning
Skinner (the rats)
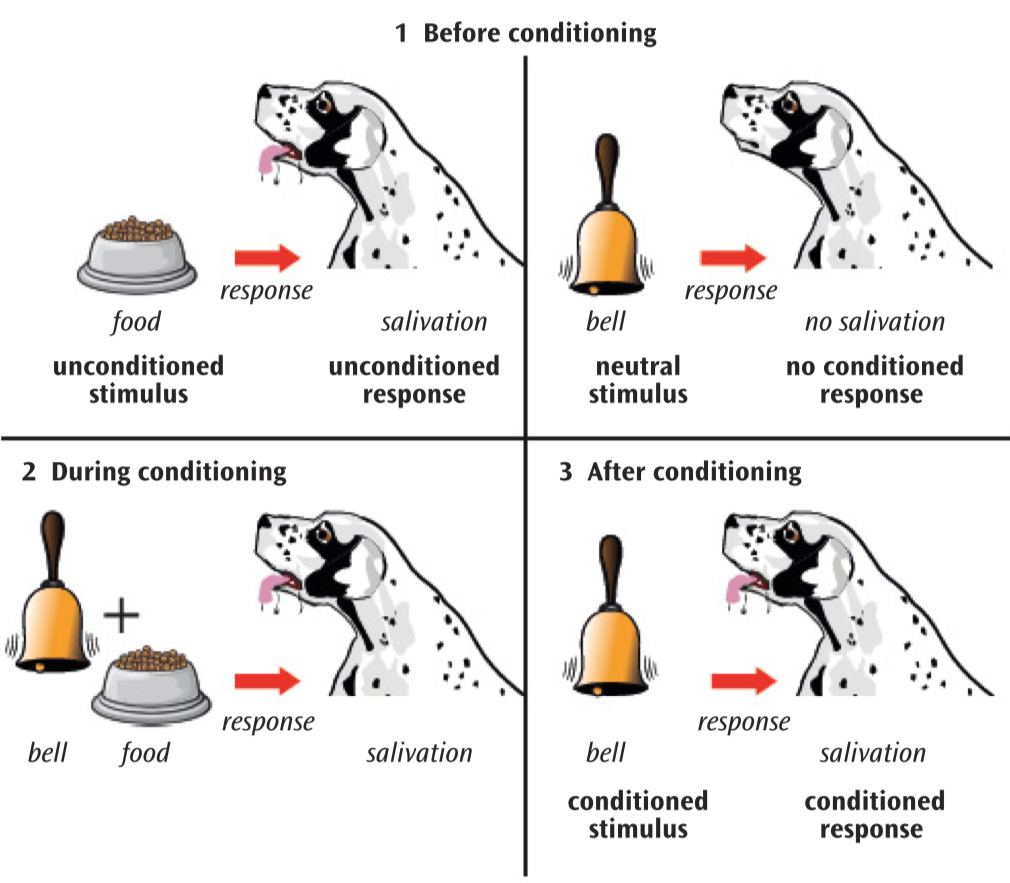
Explain Pavlovs research
Showed how dogs could be conditioned to salivate to the sound of the bell, if the bell was associated with food
Draw the 4 stages of Pavlovs dogs (before, during and after conditioning)
.
Operant conditioning- define positive reinforcement
Recieving a reward when a certain behaviour is performed
Operant conditioning- define negative reinforcement
Avoiding something unpleasant to have a positive outcome
Operant conditioning- define punishment
Unpleasant consequence of behaviours
Do positive and negative reinforcement increase or decrease the likelihood of behaviour being repeated
Increase
Does punishment increase or decrease the likelihood of behaviour being repeated
Decrease
Explain skinners rats for positive reinforcement
Every time the rat activated the lever, food was given
Explain skinners rats for negative reinforcement
The rat was electric shocked, but when the rat activated the lever the shocks would stop
Evaluation- well controlled research
highly controlled lab setting
All extraneous variables were removed allowing a cause and effect to be established
Suggesting that behaviourist experiments have scientific credibility
Counter- may be oversimplified, did not include human thought (like social learning and cognitive- focus on mental processes). Suggests that learning is more complex than observable behaviours alone
Evaluation- real world application
operant conditioning used in institutions- prisons and psychiatric wards
Classical conditioning has been applied to the treatment of phobias
Evaluation- environmental determinism
Ignores free will
says that our past conditioning determines the outcome
Define environmental determinism
Suggests that an individuals behaviour is solely caused by external environmental forces such as experiences, conditioning and social influences
Evaluation extra- ethical issues
animals were housed in harsh cramped conditions
They were deliberately kept below their natural weight so they were always hungry