B1 Key Concepts
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
animal cells
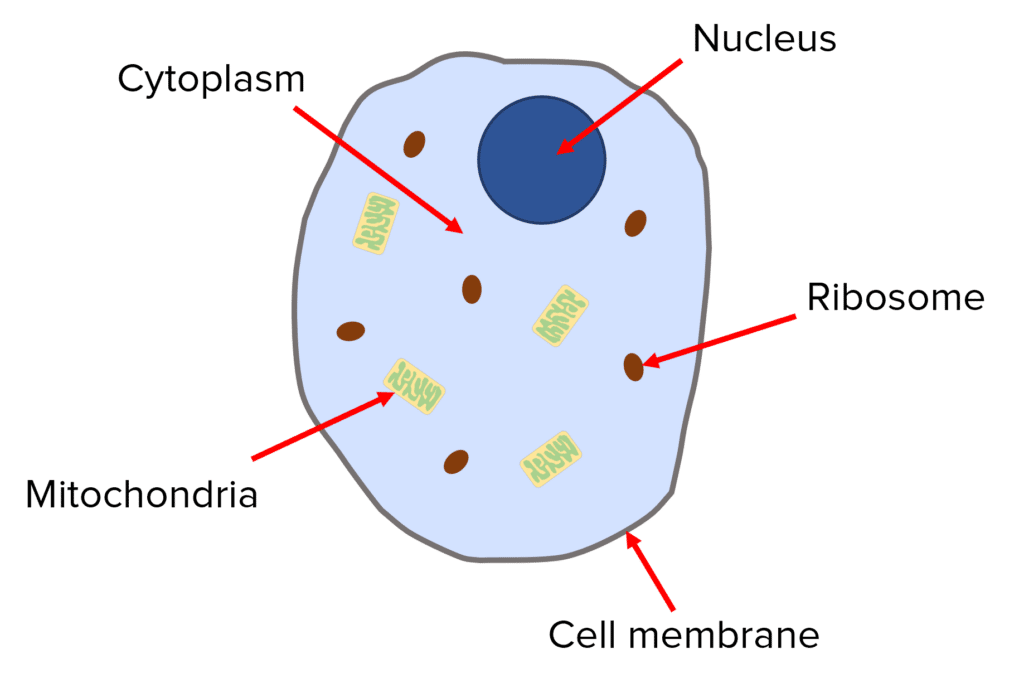
nucleas
contains genetic material
cytoplasm
jelly like material, contains organelles, where chemical reactions happen
cell membrane
controls what substances go in and out of the cell
mitochondria
contains enzymes for respiration
ribosomes
where protein synthesis takes place
plant cells
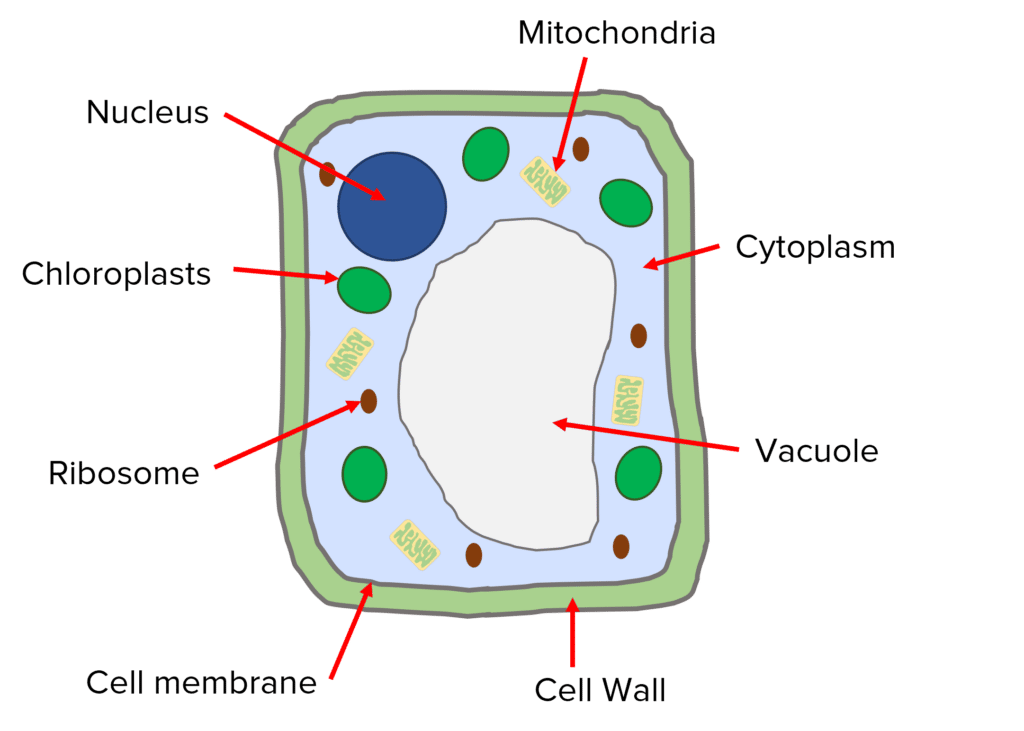
chloroplast
organelle that contains the green pigment chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis
cell wall
structure and protection for the plant, made from cellulose
permanent vacuole
filled with cell sap to help keep the cell swollen
Bacteria cell
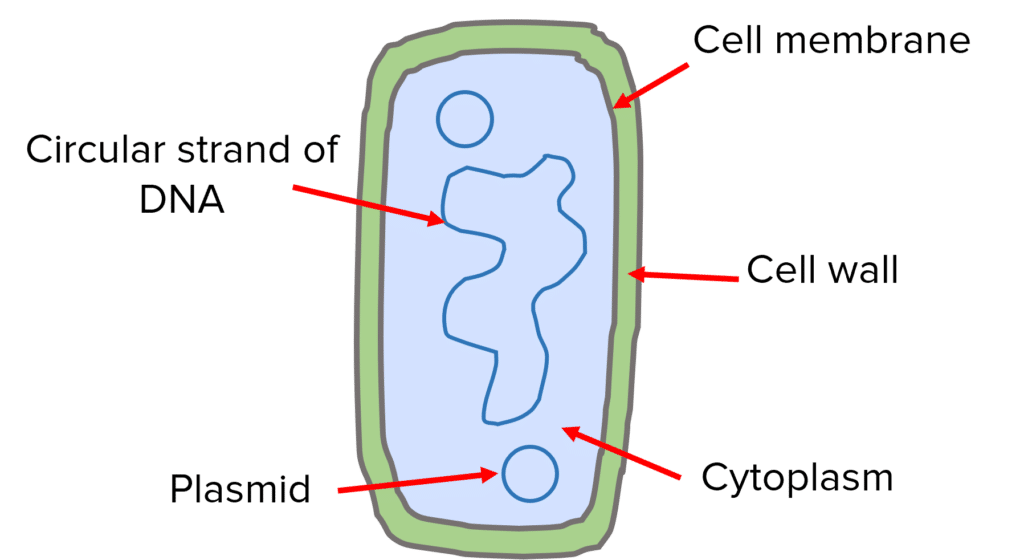
Chromosomal DNA
the DNA of bacterial cells is found loose in the cytoplasm
Plasmid DNA
bacterial also have small, closed - circles of DNA called plasmids present in the cytoplasm
Flagella
Bacteria can have one or more flagella, used for movement
Cell Wall
same as plant cells but not made from cellulose
why is a sperm cell adapted to its function
acrosome - contains enzymes so the sperm can penetrate the egg
haploid nucleas - contains the genetic material for fertilisation
mitochondria - to release energy needed to swim and fertilise an egg
tail - enables the sperm to swim
why is an egg cell adapted to its function
cytoplasm - contains nutrients for the growth of the early embryo
haploid nucleus - contains genetic material for fertilisation
The cell membrane changes after fertilisation by a single sperm so that no more sperm can enter
why is a ciliated epithelial cells adapted to its function
cilla on the surface beat to move fluids and particles up the trachea
microscopes
light microscopes
electron microscopes - uses beams of electron instead of light, this allows for much higher magnification and resolution than light microscopes.
Explain the mechanisms of enzymes action
The enzyme is lock the substate is the key. Just as a specific key fits into a specific lock, each enzyme is shaped to fit a specific substrate molecule.
When does an enzyme denature
extremes of Ph
high temperature
Core practical: Investigate the effect of Ph on enzyme activity
rate calculation for enzyme activity

Why are enzymes important in the synthesis and breakdown of biological molecules?
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up reactions in the body
They help build carbohydrates, proteins and lipid
They also help break down these molecules into smaller units
Carbohydrates into sugars
Proteins into amino acids
Lipids into fatty acids and glycerol
Test for starch
reagent = iodine solution
positive result = turns blue - black if starch is present
Test for reducing sugars
reagent = Benedict solution
method = heat the sample with Benedict solution
positive results - blue to brick red if reducing sugars are present
test for proteins
reagent = biuret solution
positive results = turns purple if proteins are present
test for fats (lipids)
reagent = ethanol and water
method = mix the sample with ethanol then add water
positive result = cloudy white emulsion forms if fats are present
diffusion
movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration
osmosis
high concentration to low concentration but through water
active transport
low concentration to high concentration which requires energy
Describe the method for the osmosis experiment using potato cylinders.
What is the aim of the experiment investigating osmosis in potato cylinders?
To investigate the effect of sucrose solutions on the mass of potato cylinders.
To determine the concentration of the cell sap in potato cells.
Variables in the osmosis experiment with potatoes?
Independent Variable: The concentration of sucrose solutions (0%, 20%, 30%, 40%, 60%, 80%, and 100%).
Dependent Variable: The change in mass of the potato cylinders.
Control Variable: each cylinder is left in the sucrose solution.
Calculate percentage gain and loss of mass in osmosis
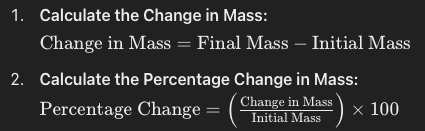
Calorimetry
Used to measure the energy content of food
small samples of material are placed in the machine which burns them the energy given off when the material burns is measured