Chemistry - 3 Structure and Bonding
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Particle theory
the concept that all matter is made of exceedingly small particles
How are particles arranged in a solid?
packed in a fixed arrangement and vibrate in place
How are particles arranged in a liquid?
close but irregularly arranged, particles can move over one another
How are particles arranged in a gas?
not packed, random arrangement, move freely in any direction
During a change of state, a substance will...
not heat up or cool down
Sharing electrons
covalent bonding
Transferring electrons
ionic bonding
Ions are only formed in ... bonding
ionic
What diagram can we use to represent the formation of ions?
dot and cross diagram
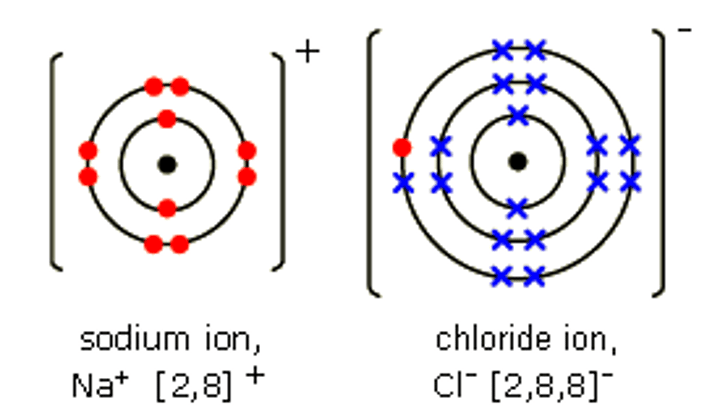
Ionic compounds are formed when ... react with ...
non-metals, metals
Metals in ionic compounds form ... ions
positive
Non-metals in ionic compounds form ... ions
negative
Ionic bonding
the electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions in an ionic substance
Giant structure/lattice
a huge network of ions
- Group 1 form:
- Group 2 form:
- Group 3 form:
- 1+ ions
- 2+ ions
- 3+ ions
- Group 4 form:
no ions except tin and lead
- Group 5 form:
- Group 6 form:
- Group 7 form:
- 3- ions
- 2- ions
- 1- ions
Polymers have ... melting and boiling points as they are ...
higher, larger
Giant ionic lattice
a three-dimensional structure of oppositely charged ions, bonded together by strong ionic bonds
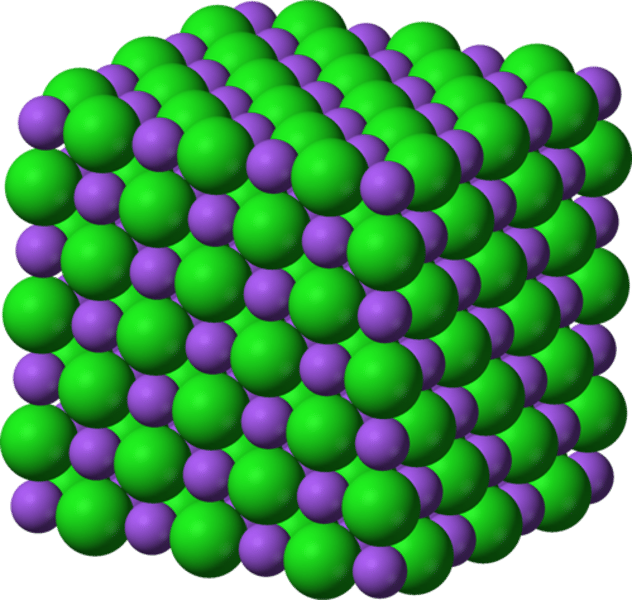
Ionic compounds have ... melting and boiling points
high
Why do ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points? [3]
- there are strong electrostatic forces of attraction acting in all directions
- (called ionic bonds)
- a lot of energy is needed to overcome these forces
Electrical conductivity in ionic compounds [2]:
- when solid, they cannot conduct electricity as the ions cannot move
- when dissolved or aqueous they can conduct electricity as the ions can move around
... ionic compounds can dissolve in water
many, but not all
Covalent bonding is found in compounds formed when...
non-metals react together
Covalent bonding is
sharing electrons
Non-metals ... electrons to achieve stability
gain
Giant covalent structure
A huge network of covalently bonded atoms
Macromolecule
giant covalent structure
The ... forces in covalently bonded molecules are strong
intramolecular
The ... forces in covalently bonded molecules are weak
intermolecular
Why do covalently bonded substances often have low melting and boiling points?
the intermolecular forces are weak (between molecules)
3D ball and stick model
2D ball and stick model
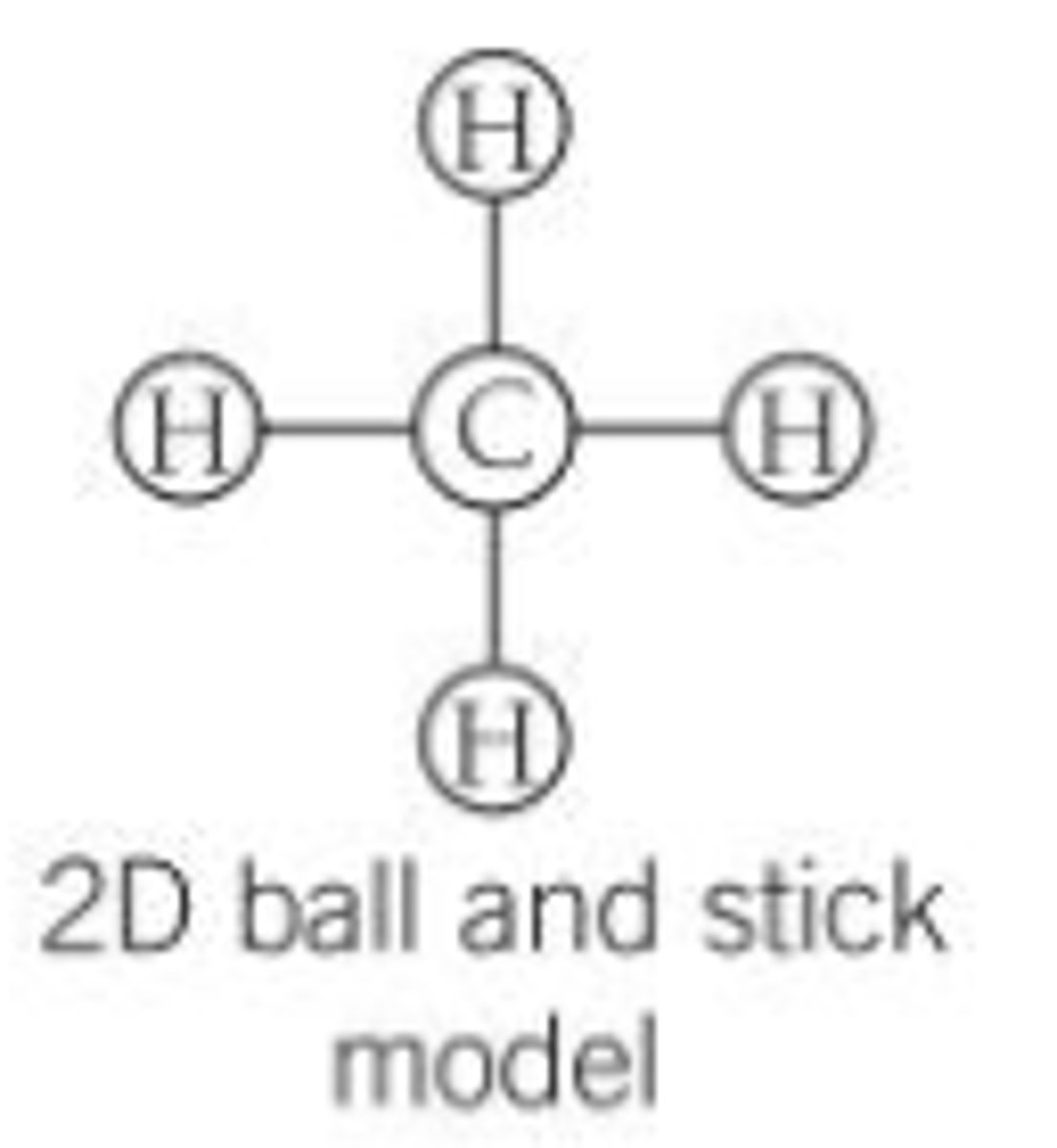
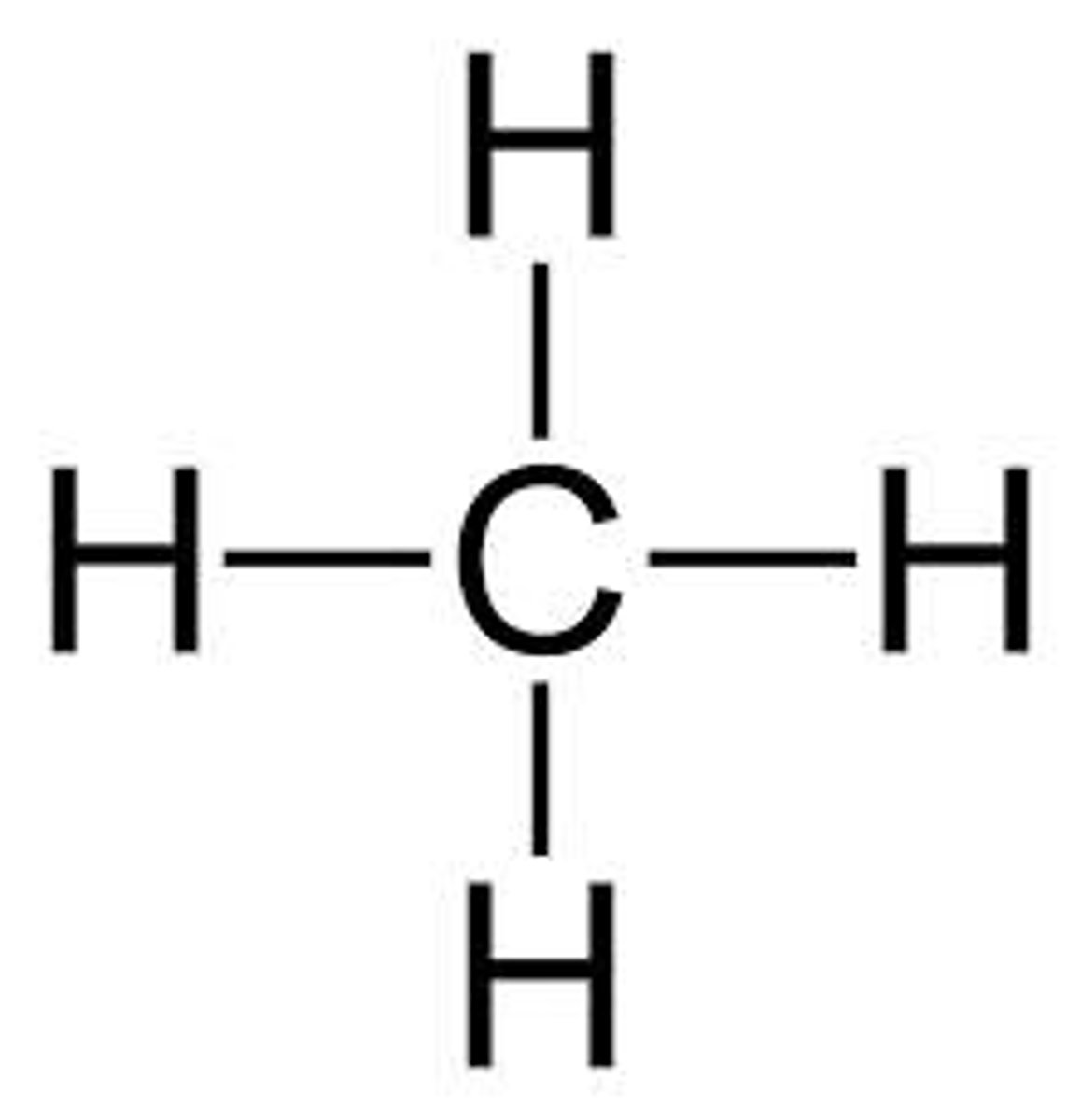
Displayed formula
Intermolecular forces ... with the ... of molecules
increase, size
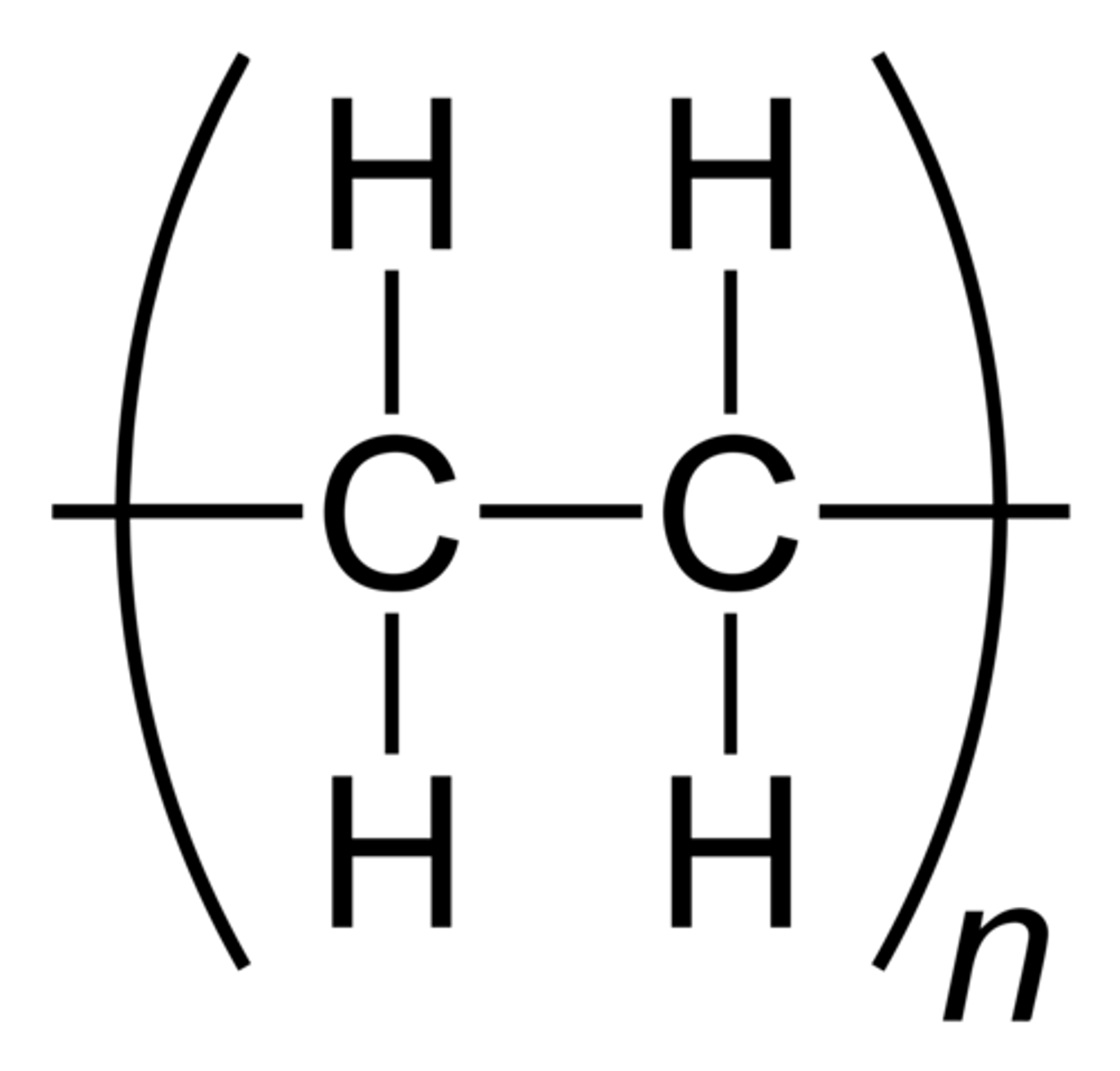
Polymers
large compound formed from combinations of many monomers
Representing polymer chains
we can put brackets around the repeating segment and use a subscript n to denote how many times this section repeats
Compounds made of simple molecules do not ... unless ...
conduct electricity, they react with water to form aqueous ions
why don't compounds made of simple molecules conduct electricity? [2]
- there is no overall charge on simple molecules
- their neutral molecules cannot carry electrical charge
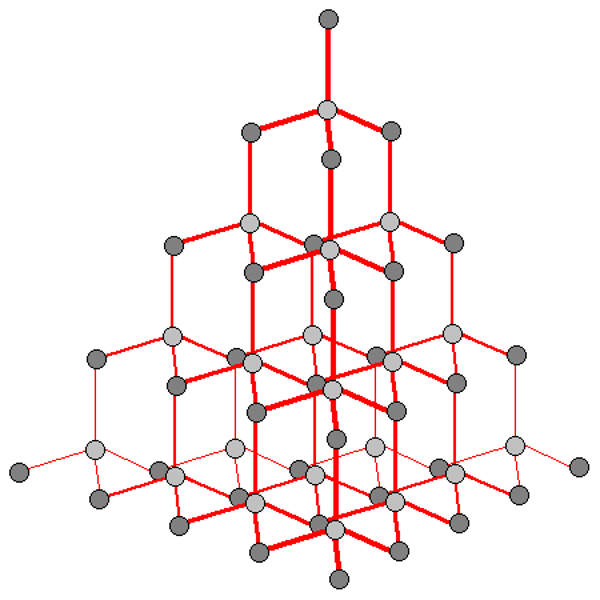
Diamond
formed by huge networks of covelently bonded carbon atoms, where each carbon atom is bonded to 4 others
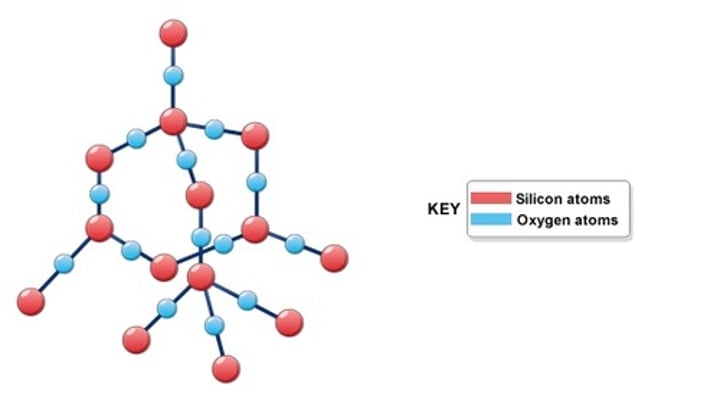
Silicon dioxide (SiO₂)
formed by huge networks of covalently bonded silicon and oxygen
Graphite
formed by huge networks of covalently bonded carbon atoms, where each carbon atom is bonded to 3 others
Properties of substances with a giant covalent structure [3]:
- very high melting and boiling points
- insoluble in water
- (apart from graphite) hard and do not conduct electricity
In graphite [3]:
- each carbon atom is bonded to 3 others
- they are arranged in hexagons
- they are arranged in layers without covalent bonds between them
Why does graphite conduct electricity (and thermal energy)? [5]
- each carbon atom is only bonded 3 times
- carbon atoms have 4 electrons in their other shell available for bonding
- this leaves 1 spare electron from each atom
- these electrons are delocalised and can move freely along the layers of graphite
- they can carry charges (and thermal energy)
Fullerene
a form of carbon that consists of atoms arranged in the shape of a hollow sphere
The structure of fullerenes is based on ... rings of carbon atoms
hexagonal, pentagonal or heptagonal
Carbon nanotubes
tiny, hollow tubes made of carbon atoms (cylindrical fullerenes)
First fullerene [3]
- 60 carbon atoms
- called 'buckminsterfullerene' or 'bucky-ball'
- named after Buckminster Fuller, a Canadian architect who built a similar-looking building
Useful properties of carbon nanotubes [2]:
- high tensile strength
- high electrical and thermal conductivity
Uses for carbon nanotubes [2]:
- tennis rackets
- electronics
Bucky-onion
a fullerene with a ball within a ball
How could fullerenes be used? [3]
- deliver drugs or radioactive atoms (cancer treatment) to specific locations in the body
- lubricants
- catalysts (due to large surface area to volume ratio of nanoparticles)
Graphene
a single layer of graphite, one atom thick
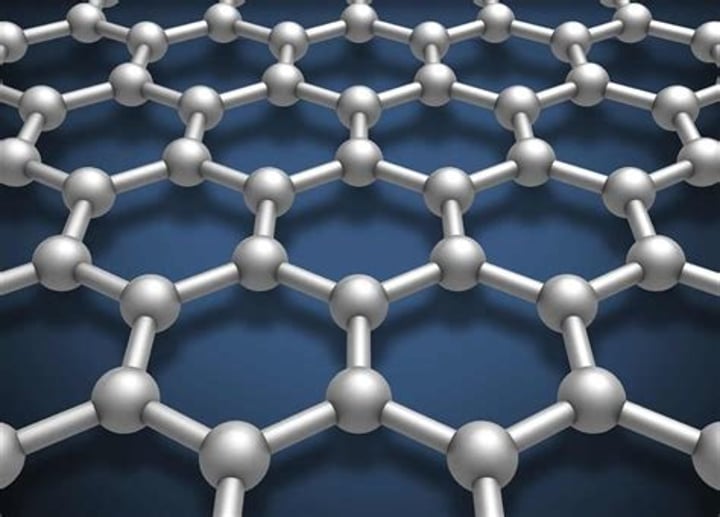
Properties of graphene [4]:
- excellent thermal and electrical conductor
- low density
- most reactive form of carbon
- incredibly strong
Metals form ...
crystals
Galvanised steel
applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron to prevent rusting
Metallic bonding [4]
- metal ions are arranged in fixed layers
- their electrons are free to move between them
- these electrons are delocalised and flow freely among the ions
- the strong electrostatic attraction between the positive ions and negative electrons hold the metal together
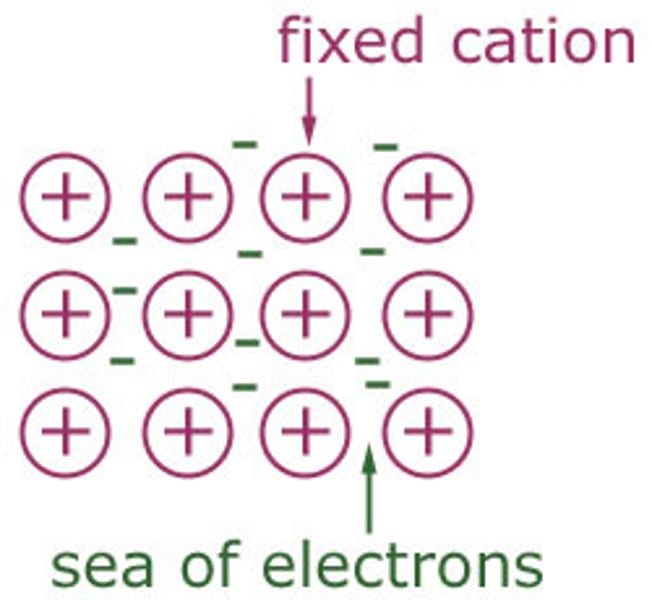
Properties of metals
- ductile
- malleable
- good thermal and electrical conductors
Alloy
a mixture of two or more metals
Why are alloys harder than pure metals? [3]
- different sized atoms of metals distort layers
- the layers cannot slide over one another as easily
- it is more difficult to change their shape
Why are metals malleable?
the layers of ions can slide over one another without breaking up the structure, as they are held together by delocalised electrons
Why are metals ductile?
layers of atoms can slide over each other
Why do metals have high melting and boiling points? [3]
- the electrostatic forces of attraction extend in all directions
- because electrons move freely
- it takes a lot of energy to overcome these forces
Why are metals good thermal and electrical conductors?
their delocalised electrons can flow and carry charges through the metallic lattice
Nano-
one billionth
Nanoscience
the study of molecules and nanostructures whose size ranges from 1 to 100 nanometers (one billionth of a meter).
What is the range of sizes a structure can be to be within nanoscience?
1-100 nm
For larger particles in the air, the unit used is
micrometres (μm)
Micro-
one millionth
These larger airborne particles are called
particulate matter (PM)
Coarse particles
particles with a diameter of 2.5-10 μm (PM₂.₅-PM₁₀)
Fine particles
particles with a diameter of 0.1-2.5 μm (PM₀.₁-PM₂.₅)
0.1 μm in nm
100 nm
1 nm in μm
0.001 μm
Nanoparticles have a high...
SA:V ratio, meaning a large proportion of their atoms are exposed at the surface
As the side of a cube decreases in size by a factor of 10,
its surface area to volume ratio increases by 10
The exposure of a large percentage of atoms at the surface of nanoparticles makes them
highly reactive
Why could nanoparticles be more sustainable? [2]
- they are more reactive
- less material is needed
Glass [3]
- coated with titanium oxide nanoparticles
- sun triggers chemical reaction that breaks down dirt on the glass
- when it rains, water spread evenly on the surface so broken-down dirt is rinsed off
Sunscreen [3]
- titanium oxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles used
- can be coated with silica
- more effective at blocking UV than conventional UV absorbers
Cosmetics industry [1]
- nanoparticles are absored deeper into skin
Medicine [4]
- gold nanocages used to deliver drugs
- small enough to enter tumours but not healthy blood vessels
- when a laser is directed at the tumour, the nanocages are heated and they heat the tumour whilst barely warming surrounding tissue
- they can also carry cancer-fighting drugs
Sport [3]
- nanotubes are light yet strong
- they can be used in sports equipment
- such as tennis rackets
Antimicrobial coating [4]
- silver nanoparticles constantly release a low level of silver ions
- these protect against bacteria
- they can be used to coat items and give them protection
- e.g. fridges, keyboards, wound dressings
Electronics [3]
- nanotubes used as nanowires
- to construct small electrical circuits
- improve the speed and memory capacity of computers
Sensors [2]
- nanotubes can make very sensitive sensors
- can detect traces of a gas in breath before asthma attack
Protection [4]
- nanotech suits, thin but bulletproof
- recieve aerial views of battlefield from satellite and transmit into soldier's brain
- built-in air conditioning
- nano-biosensors report on condition of soldier
Risks [3]
- large surface are makes great catalysts, which makes them dangerous if they cone into contact with a spark
- they could get into the environment and into our lungs, bloodstream and cells
- accumulate in organisms over time