6.3 (2.1.6) Meiosis
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
why is meiosis known as reduction division
each cell (gamete) formed contains half of the chromosome number of the parent cell
define homologous chromosomes
chromosome pairs, one from each parent, that are similar in length, gene position, and centromere location
define allele
different versions of the same gene
describe meiosis 1
reduction division when the pair of homologous chromosomes are separated into two haploid cells
describe meiosis 2
mitotic division in which the pairs of chromatids present in each daughter cell are separated to form two more cells. four haploid cells produced in total
describe prophase 1
1) chromosomes condense
2) nuclear envelope breaks down
3) nucleolus disappears
4) spindle fibres are formed
5) the homologous chromosomes pair up forming bivalents
6) crossing over occurs
describe metaphase 1
1) homologous pairs of chromosomes assemble along metaphase plate
2) independent assortment of chromosomes occur
define independent assortment
the random separation of homologous chromosomes in meiosis 1 that produces genetic variation
describe anaphase 1
homologous chromosomes are separated and the chromatids stay joined to each other
define chiasmata
the point at which chromatids break and rejoin
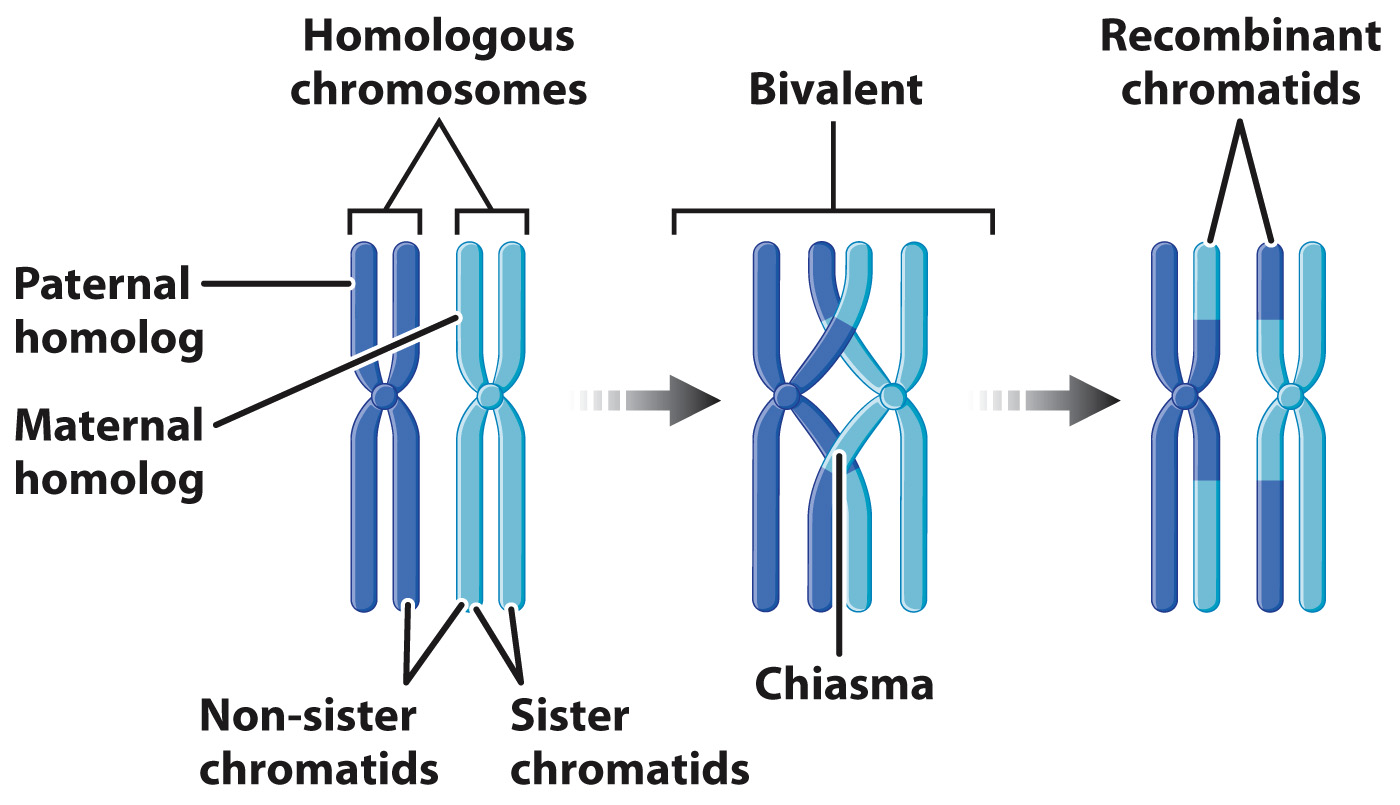
describe telophase 1
1) chromosomes assemble at each pole
2) nuclear membrane reforms
3) chromosomes uncoil
4) 2 new haploid daughter cells are formed
describe prophase 2
1) chromosomes condense and become visible
2) nuclear envelope breaks down and spindle formation begins
describe metaphase 2
1) individual chromosomes assemble on the metaphase plate
2) independent assortment occurs
describe anaphase 2
sister chromatids of the individual chromosomes pulled to opposite poles after division of centromere
describe telophase 2
1) chromatids assemble at opposite poles
2) chromosomes uncoil and form chromatin
3) nuclear envelope reforms and nucleolus becomes visible
4) in total 4 haploid non-identical daughter cells are formed