MCB 010 Topic 5: Regulation of Gene Expression
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
gene regulation makes cells different
-controls which genes are "turned on" (expressed)
-each cell type has a different set of active genes
-different patterns of gene expression make different proteins, which allow for cell specialization
How do cells decide what to express?
-cell type
-info from inside the cell: inherited proteins, damaged DNA, ATP
-info from outside the cell: chemical signals from other cells, mechanical signals, and nutrient levels
types of gene expression and regulation
-chromatin accessibility
-transcription
-RNA processing
-RNA stability
-translation
-protein activity
***main one is transcription
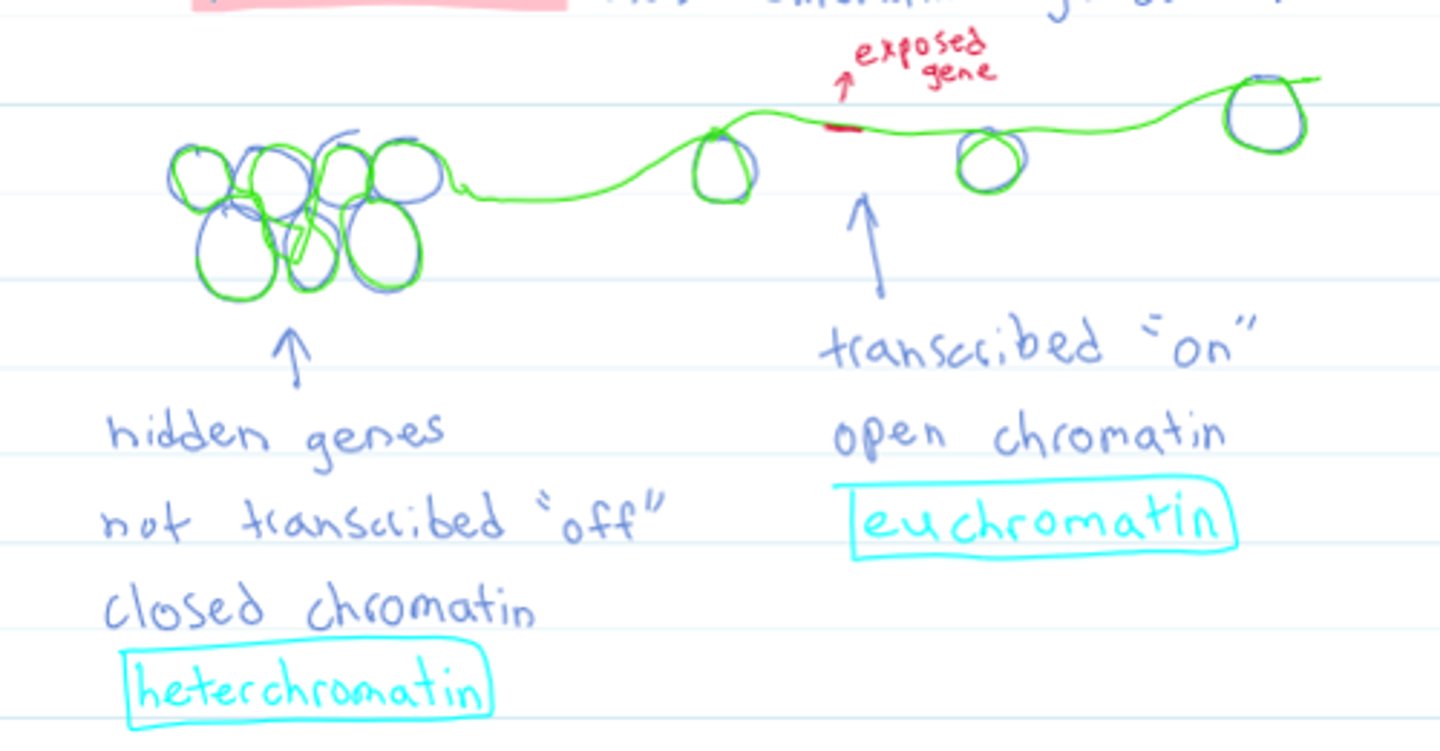
chromatin accessibility (gene expression & regulation)
the structure of chromatin can be regulated. More open or "relaxed" makes a gene more available for transcription.
-Euchromatin
-Heterochromatin
chromatin
-DNA wrapped around histone proteins
-state of DNA in humans (& other eukaryotic)
transcription (gene expression & regulation)
-regulating whether transcription initiation occurs
-most regulated step b/c the cell could potentially waste a lot of resources allowing transcription to happen
-chromatin (epigenetics)
-transcription factors
RNA processing (gene expression & regulation)
Can be regulated...
-splicing
-capping
-adding poly-A tail
-what exits the nucleus
-alternative splicing
RNA stability (gene expression & regulation)
the lifetime of a mRNA molecule in the cytosol affects how many proteins can be made from it. Small regulatory RNAs called miRNAs can bind to the target mRNAs and cause them to be chopped up
translation (gene expression & regulation)
can be increased or inhibited by regulators
-miRNAs block translation of target mRNAs
-amount of protein made
protein activity (gene expression & regulation)
variety of modifications--chopped up or tagged with chemical groups
-affect the activity or behavior of the protein
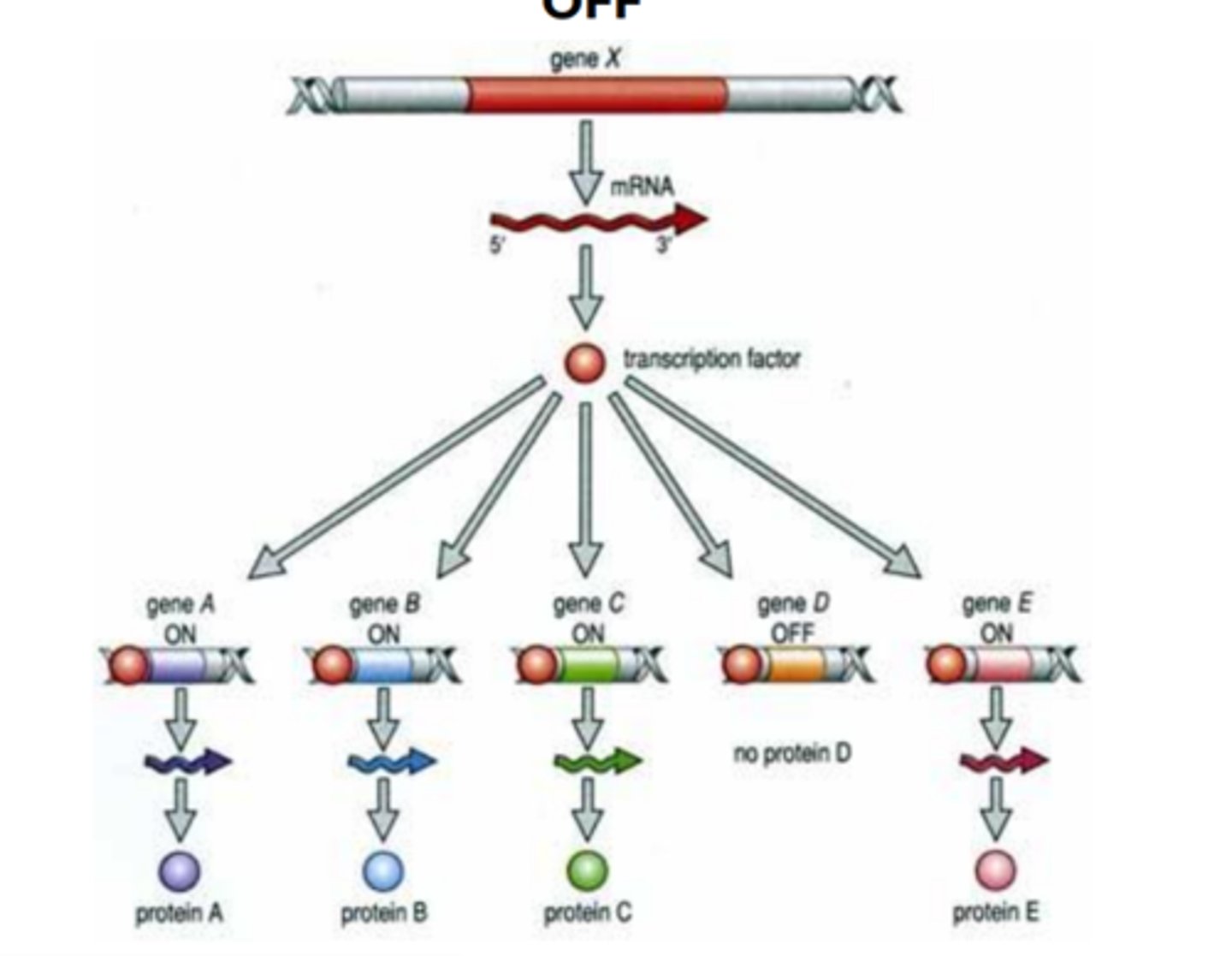
transcription factors
proteins that regulate the transcription of genes--that is their copying into RNA, on the way to making a protein
-ensures that the right genes are expressed at the right time
-bind to DNA (& other proteins) in a sequence specific manner (lock and key)
gene expression
when a gene is turned on & used to make the protein it specifies
-not all genes are on a the same time or in the same cells or parts of the body
What is the key on/off control point for many genes
transcription
-if a genes is not transcribed then it will not make a protein
-if it is transcribed then it will make a protein and it will be expressed
-the more a gene is transcribed the more protein is made
transcription factors and regulation
-transcription factors are necessary for RNA polymerase to attach to the DNA and start transcribing
-large class that controls the expression of specific, individual genes
How transcription factors regulate
-once a transcription factor binds to the DNA at the target sequence it makes it easier or harder for the RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter of the gen
-activators
-repressors
-binding sites
activators
activate transcription
-help general transcription factors and or RNA polymerase bind to the promoter
repressors
repress transcription
block general transcription factors and or RNA polymerase from binding to the promoter
binding sites
often close to gene's promoter. However they can also be found in other parts of the DNA, sometimes very far away from the promoter, and still affect the transcription of the gene
differences in _________________________ result in cellular diversity within an organism. Different cells have the same _____________ genes but different _____________ and _________.
gene expression
proteins, mRNA
gene expression
-transcription and translation of a gene
-producing mRNA and proteins of what the gene encodes
when a gene is "on"
-expressed
-transcription and translation
when a gene is "off"
-not expressed
-no transcription or no translation
-end product is not made
What determines a cell's identity/function?
the amount and types of mRNA (& the proteins made from it)
transcription factors (gene expression & regulation)
sets of transcription factor proteins bind to specific DNA sequences in or near a gene and promote or repress its transcription into an RNA
nucleosome
double stranded DNA wrapped around 8 histone proteins; basic unit of chromatin
Euchromatin
-"open chromatin"
-loosely packed nucleosomes
-genes on
-spacing of nucleosomes would make it more accessible
Heterochromatin
-"closed chromatin"
-genes off
general transciption factors (GTF)
-bind to promoter sequency (TATA) and help recruit RNA polymerase
-required for transciption to occur for all genes
-basal TFs
specific transcription factors
-bind to regulatory DNA sequences called either enhancer sequences or silencer sequences and function to activate or repress transcription initiation
-specific to a set of genes, cell type, tissue type, or development time
many transcription factors can regulate expression of the same gene
true
far away sequences can be close together in the 3D, especially when DNA is wrapped up
true

gene regulation cascade
master transcription factor
top of a gene regulation cascade to drive a developmental fate or differentiation
-Oct4, Sox2, Nanog
-repress differentiation
stem cell
special type of cell that has the ability to 1) replicate (mitosis) & make more cells 2) ability to differentiate into different cell types
-undifferentiated
what helps regulate differentiation
transcription factors
differentiation changes
what genes are expressed
embryonic stem cells (ESCs)
Harvested from blastocysts; used to regenerate tissues and organs
Pluripotent—can generate most types of cells
blastocyst
the developing zygote, with cells surrounding a fluid-filled core, contains embryonic stem cells and the cells that will become the placenta
blastocyst parts
1. Inner cell mass/embryoblast
- where embryo develops from, embryonic stem cells
2. Trophoblast
- Outer layer of blastocyst
- Take part in placenta formation

totipotent
can give rise to all human cell types
-"all" & "powerful"
pluripotent
give rise to most human cell types but not all
-not placenta cells
fertilized eggs are...
totipotent
the blastocyst, specifically the inner mass cells are...
pluripotent
multipotent
can give rise to more than one cell type, but limited
(endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm)
unipotent
can only give rise to one cell type
-lung cell, heart cell, liver cell
cause of differentiation
-changes in gene expression, caused by transcription factors
you can take a differentiated cell and make it into a stem cell by adding...
-"pluripotency" factors
-master transcription factors: Oct4, Sox2, Nanog
-called "induced pluripotent stem cells" (iPS)
there are high levels of master transcription factors (Oct4, Sox2, Nanog) in embryonic stem cells
true, the inhibit differentiation, allowing the stems cells to stay stem cells and not specialize
master transcription factors induce differentiation
false!!
they repress it, allowing stem cells to stay stem cells
induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS)
-differentiated adult somatic cell + master transcription factors
-pluripotent
embryonic stem cells vs induced pluripotent stem cells
-ethical reasons
-immune rejection