6th Grade - Matter intro
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Matter
Anything that has mass and occupies space (volume).
Chemistry
The study of the properties of matter and how matter changes.
Substance
A single kind of matter that is pure and has a specific set of properties.
Physical property
A characteristic of a pure substance that can be observed without changing into another substance.
Chemical property
A characteristic of a pure substance that describes its ability to change into a different substance.
Element
A pure substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical or physical means. (ex. carbon (C), Oxygen (O))
Atom
The basic particle from which all elements are made.
Chemical bond
The force that holds two atoms together.
Molecule
A particle made of two or more atoms bonded together. The atoms can be the same (ex. two or more oxygen atoms) or different (ex. 1 water molecule combines 2 hydrogen atoms with 1 oxygen atom).
Compound
A pure substance made of two or more elements chemically combined. (ex. water, sugar, etc.)
Chemical formula
A formula that gives the elements in a compound and the ratio of atoms. (ex. water = H₂O)
Mixture
Two or more substances that are mixed together but not chemically combined. (for ex. a Dairy Queen blizzard with candy pieces mixed into the ice cream)
Heterogeneous mixture
A mixture in which pure substances are unevenly distributed throughout the mixture. (ex. chex mix)
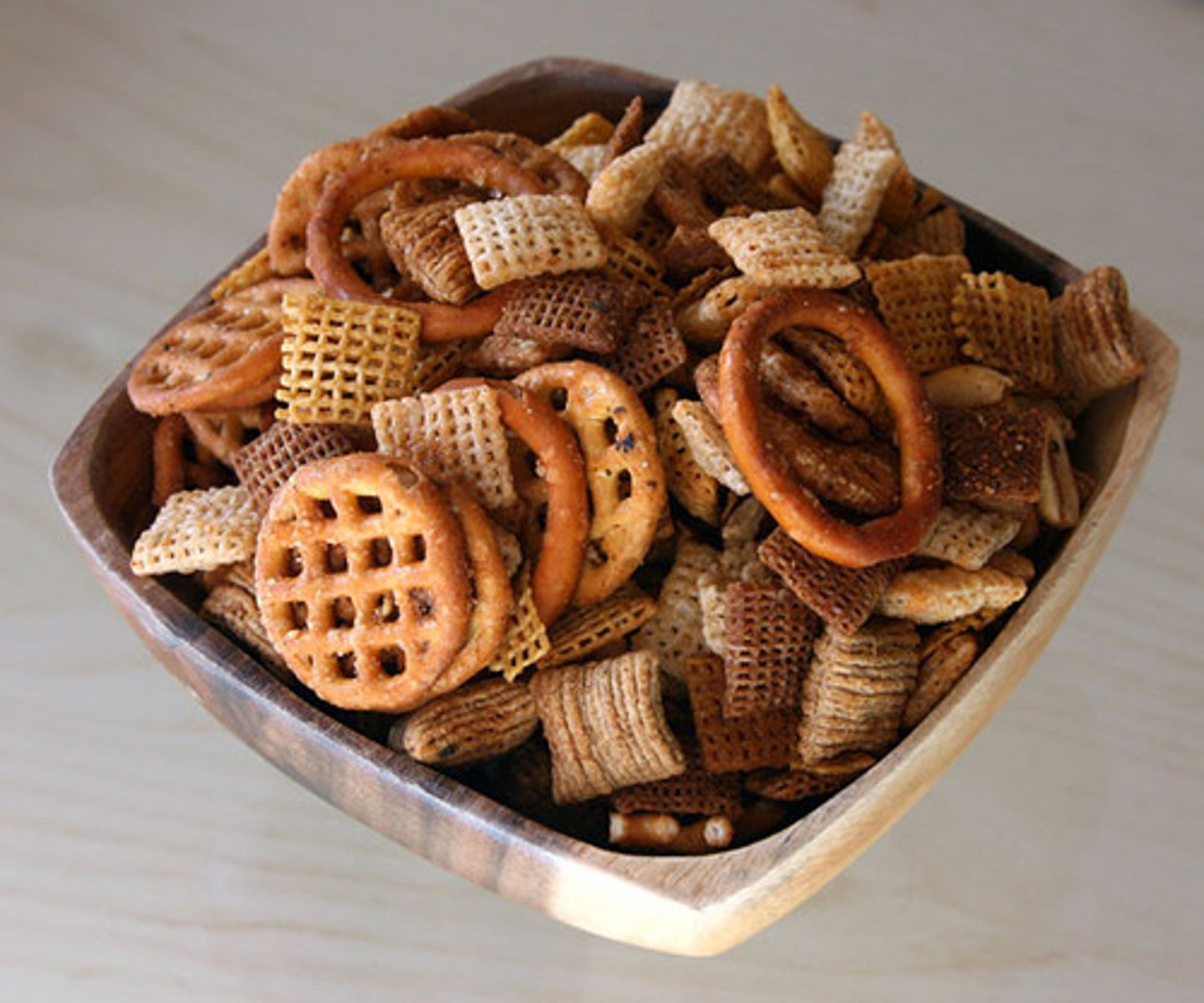

Homogeneous mixture
A mixture in which substances are evenly distributed throughout the mixture. (ex. solutions like sugar water)
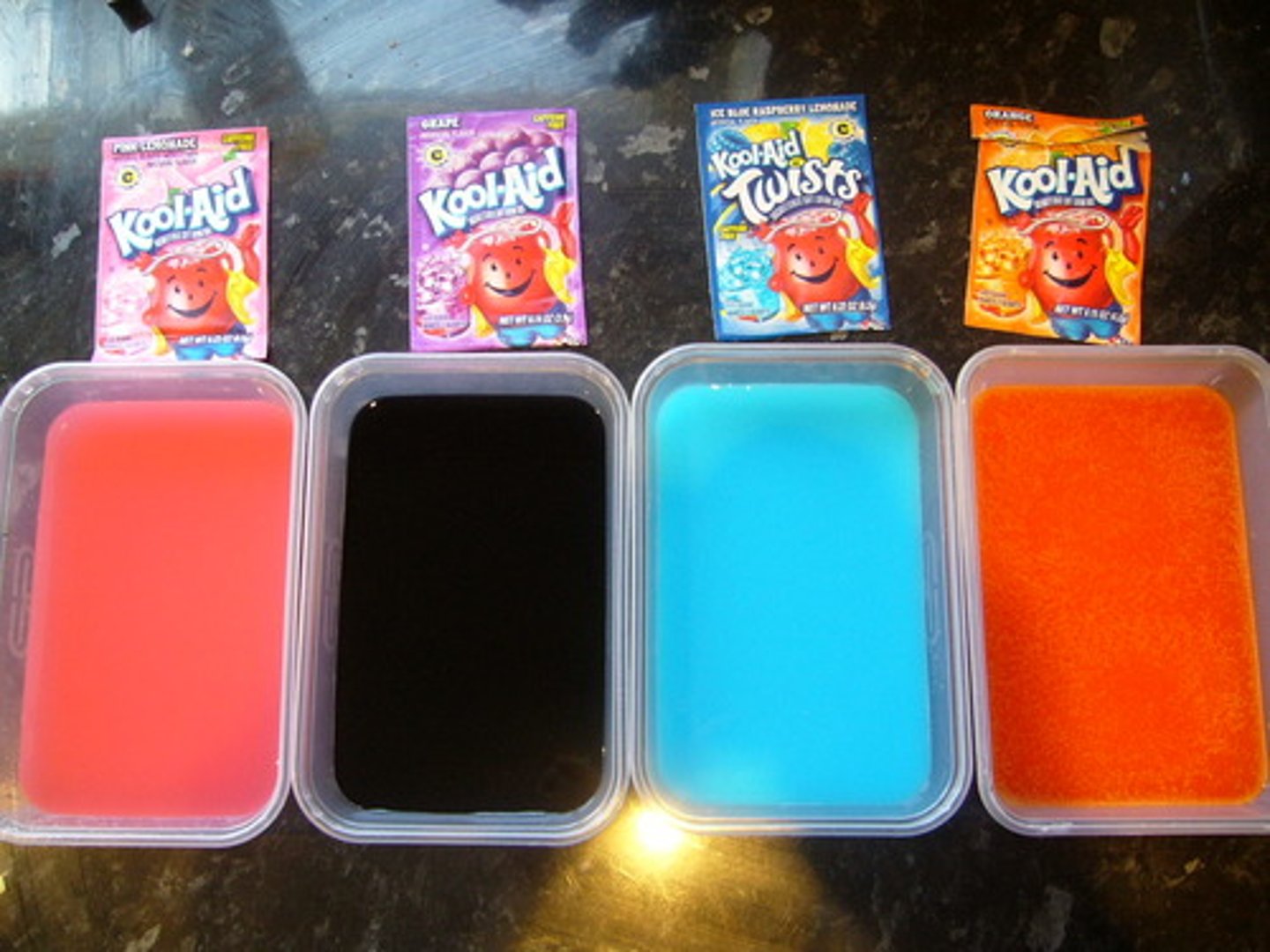

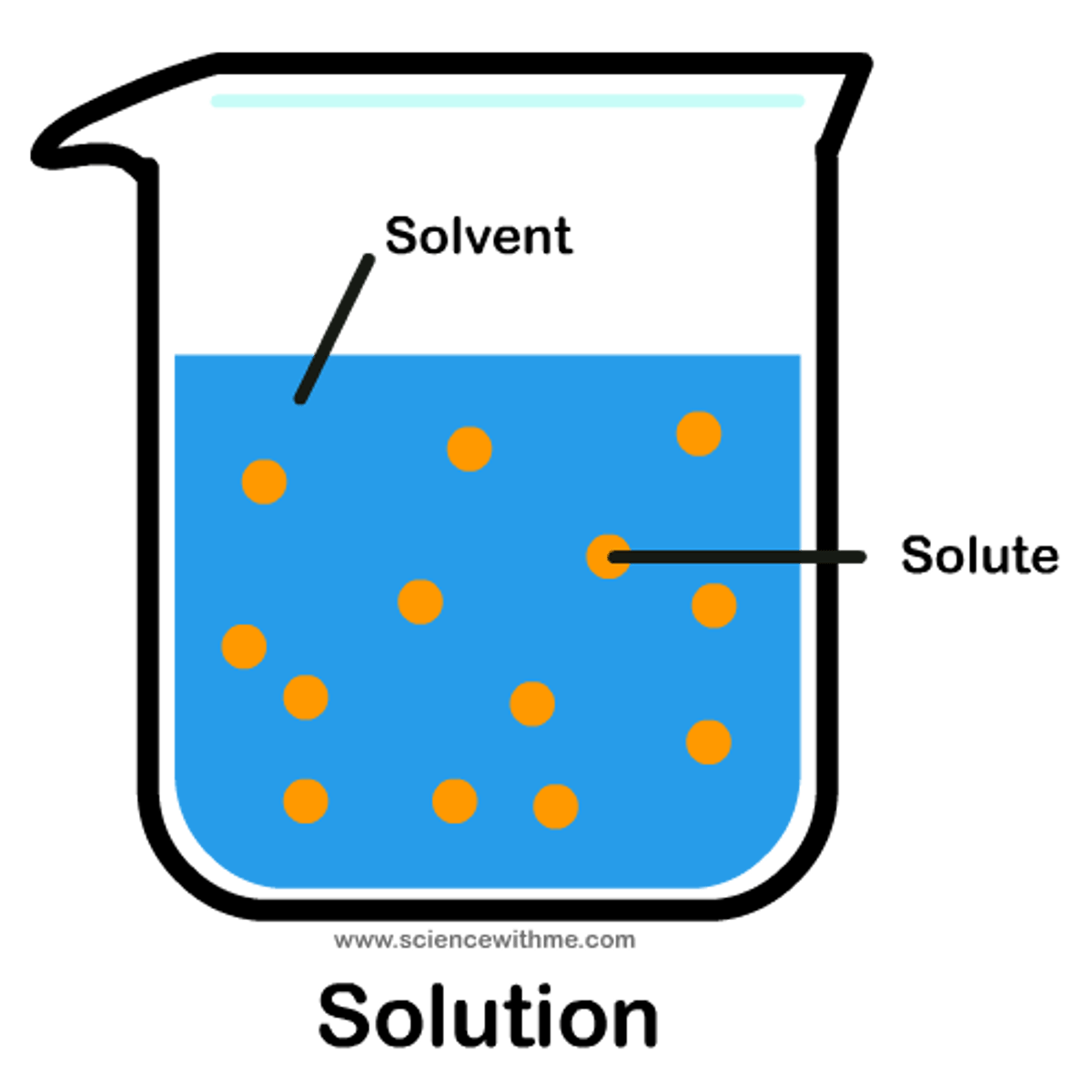
Solution
An example of a homogenous mixture; forms when substances dissolve.
Weight
A measure of the force of gravity on an object.
Mass
A measure of how much matter is in an object.
Density
The measurement of how much mass of a substance is contained in a given volume (space). density = mass/volume, m =d*v. We can use density to help identify elements, compounds, and substances.
Volume
The amount of space that matter occupies.
International System of Units
The system of units (SI) used by scientists to measure the properties of matter.
Observation
Information obtained through the senses and/or with the help of machines.
Inference
This is an educated guess using past experience and knowledge. One uses evidence and reasoning to make a conclusion.
Qualitative Observation
An observation that deals with characteristics that cannot be expressed in numbers. We use adjectives to note qualitative observations.
Quantitative observation
An observation that deals with a number or amount, for example measurements.