Specular Reflection
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What symbol is used to identify angles?
Theta θ.
What are the three important angles that are important to us as sonogrpahers?
Angle of incidence (θi)
Angle of reflection (θr)
Angle if transmission (θt)
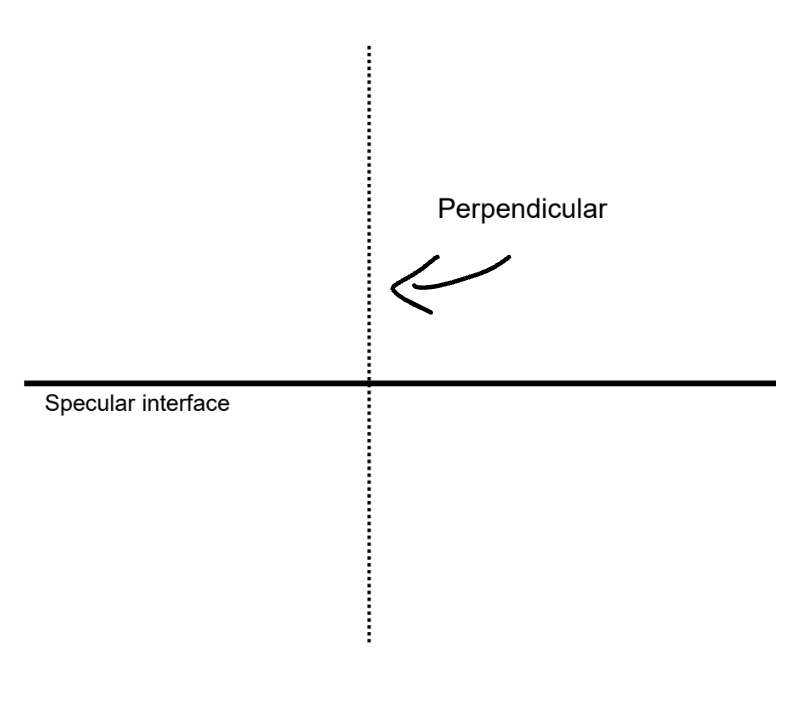
Where are all angles measured from?
The perpendicular.
True or False: The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are always different from a specular interface.
False. The angle of incidence and the angle of transmission are always the same from a specular interface.
On a specular interface, can the angle of transmission vary?
Yes.
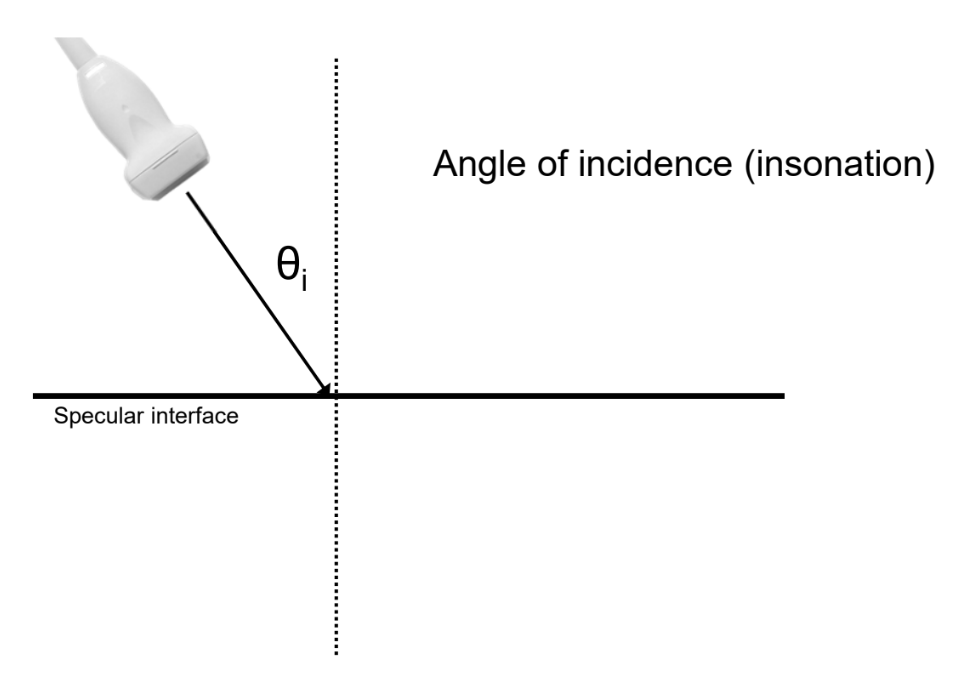
What is the angle of incidence?
See image
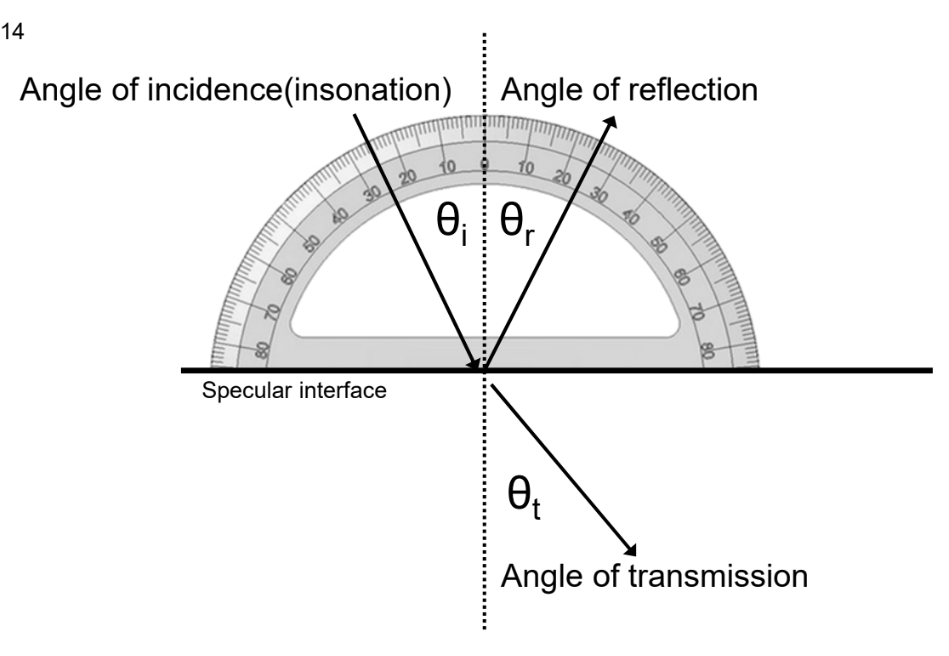
What is the angle of reflection?
See image
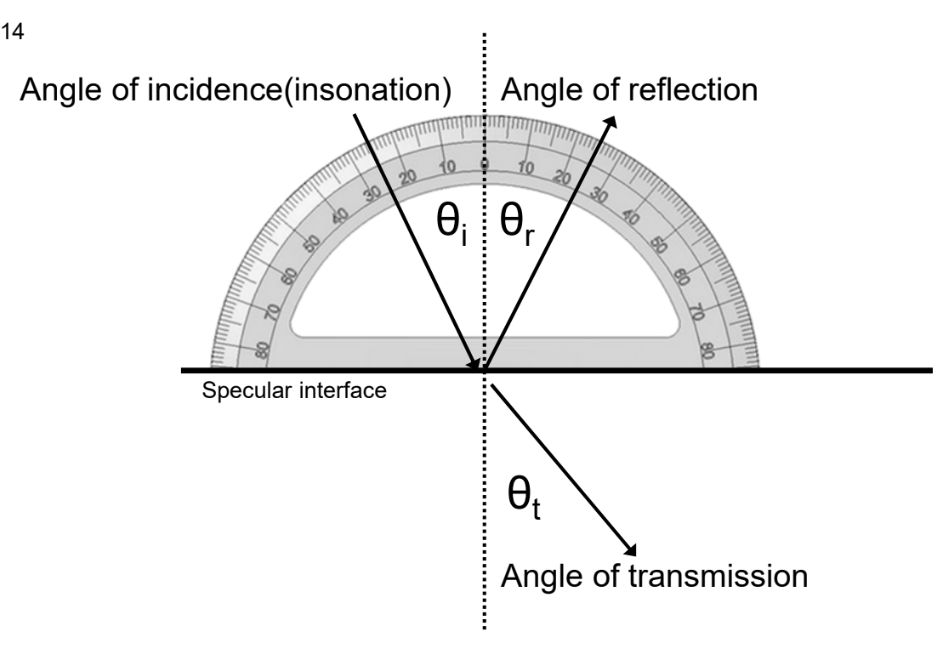
What is the angle of transmission?
See image
What is another name for the angle of incidence?
The angle of insonation.
What are the two types of angles of incidence?
Normal incidence
Oblique incidence
What is normal incidence?
When the beam of the sound (line) is perpendicular to the interface.
What is the angle of incidence when it is at normal?
0°
The perpendicular is also known as what?
The normal.
Are all angles measured from the interface or the normal?
The normal.
At normal incidence, all the angles (angle of incidence, angle of reflection, and angle of transmission) are all?
0°.
What is the best angle to image a specular interface?
At normal incidence.
Why is normal incidence the best angle to image a specular interface?
Because the echo will return to the transducer and refraction cannot occur.
Can refraction occur at normal incidence?
No.
Acoustic engineers use normal incidence to calculate what?
The percentage of sound reflected and transmitted at a specular interface.
What is IRC?
The percentage reflected of the incidence beam.
What does IRC stand for?
Intensity reflection coefficient.
What is ITC?
The percentage transmitted of the incidence beam.
What does ITC stand for?
Intensity transmission coefficient.
The IRC and the ITC add up to what?
100%.
The IRC and ITC depend of what?
The acoustic mismatch.
An increased acoustic mismatch does what to the IRC and ITC?
Increases IRC and decreases ITC.
A decreased mismatch acoustic mismatch does what to the IRC and ITC?
Decreases IRC and increases ITC.
A large impedance mismatch indicates that Z1 and Z2 are far from one another. This results in what three characteristics?
Large % reflected
Large IRC
Strong echo
A small impedance mismatch indicates that Z1 and Z2 are close to one another. This results in what three characteristics?
Small % reflected
Small IRC
Weak echo
Air has a low or high acoustic impedance?
Low.
Metal has a low or high acoustic impedance?
High.
The IRC of a soft tissue to soft tissue interface is what?
~ 1%
The IRC of an air to soft tissue interface (vice versa) is what?
~ 99.9%
The IRC of a bone to soft tissue interface (vice versa) is what?
~ 45%
What is the IRC equation? (Acoustic impedance mismatch equation)
IRC = [(Z2-Z1)/(Z2-Z1)]²
What are oblique incidences?
Where the beam is not perpendicular to the interface.
What angle is NOT going to be the angle of incidence it is oblique?
0°
With oblique incidences, does the angle of incidence equal the angle of reflection?
Yes.
With oblique incidences, does the angle of transmission equal the angle of incidence and transmission like in normal?
Not necessarily. It can vary.
What are two important points about oblique incidences?
Echo intensity is usually low since most of the incident intensity does not return to the transducer.
Refraction may occur.
What is refraction?
The change in direction of the wave as it crosses an interface due to change in speed.
Why is refraction a problem?
It breaks the design principle where sound should travel in a straight line. (Sound does not travel in a straight line when refraction occurs).
Refraction causes what?
Refractive artifacts.
What are the three artifacts that can be created by refraction?
Refractive mispositioning
Refractive duplication
Refractive edge shadowing
What two criteria MUST BOTH occur in order to have refraction occur?
An oblique incidence
A change in speed (wavelength)
Can refraction occur at normal incidence?
No.
Can refraction occur at oblique incidences?
No, unless there is ALSO a change in speed of sound.
What is Snell’s Law?
Sin θi/ Sin θt = C1/C2
In Snell’s Law, if C1 = C2, then what is Sin θi and Sin θt?
Sin θi = Sin θt
In Snell’s Law, if C1 < C2, then what is Sin θi and Sin θt?
Sin θi < Sin θt
In Snell’s Law, if C1 > C2, then what is Sin θi and Sin θt?
Sin θi > Sin θt
How can Snell’s Law be rearranged to solve for θt?
θt ≈ θi (C2/C1)
Refraction can be described in what two ways?
Toward or Away from Normal.
When refraction is described as TOWARD NORMAL, which is larger? θi or θt?
θi
When refraction is described as AWAY from NORMAL, which is larger? θi or θt?
θt
What is another way of identifying refraction in regards to the speeds of the mediums?
The beam of refraction is always bent towards the slower medium.
What is Total Internal Reflection?
When there is a refraction that bends back into the first medium that the incident beam originally penetrated through.
What is another name for Total Internal Reflection?
Critical Angle Reflection.
What two criteria MUST be MET to have Total Internal Reflection?
Oblique incidence
Change in speed where C2 > C1
With Total Internal Reflection, is there any transmission?
No, because the angle of transmission is greater than 90°, thus making it an angle of “reflection”.
Total Internal Reflection is most likely to occur where?
When there is a large angle of incidence (grazing angles).
Where can Total Internal Reflection occur?
When there is a large mismatch between the acoustic interfaces (C2 » C1) or when there is a large angle of incidence.
With total internal reflection, what percentage of sound in transmitted and what percentage is reflected?
0% is transmitted, 100% is reflected.
What is grazing incidence?
A very oblique incidence angle where the angle is ~ 80+°
True or False: When there is grazing incidence, only a slight increase in speed is needed for TIR to occur.
True.
Edge shadowing is due to what?
Reflection/refraction.
What is the clinical importance of edge shadowing?
It is most likely to happen in soft tissue to soft tissue interfaces at grazing incidence. It can also occur at soft tissue/bone interface.
How can you eliminate the possibility of TIR?
By getting perpendicular.