ASD Squeeze notes
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Stop Property
The property that the algorithm always stops for correct input data.
Partial Correctness
An algorithm is partially correct if it satisfies the condition: If the algorithm receiving correct input data stops, then its result is correct.
Total Correctness
An algorithm is totally correct for a given specification if and only if for any correct input data it stops and returns correct output.
Loop Invariant
A logical predicate such that if it is satisfied before entering any single iteration of the loop, then it is also satisfied after that iteration
Time Complexity
The number of dominating operations executed by the algorithm as a function of data size.
Pessimistic Time Complexity (W(n))
Expresses the number of dominating operations in the worst case of input data of size n:
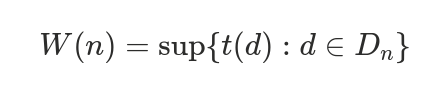
Average Time Complexity (A(n))
The expected value of the random variable representing the number of dominating operations
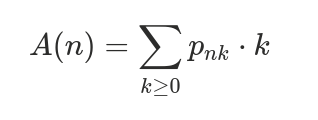
Space Complexity (S(n))
The number of units of memory used by the algorithm as a function of data size.
Big O Notation (O(g(n)))
Upper bound.
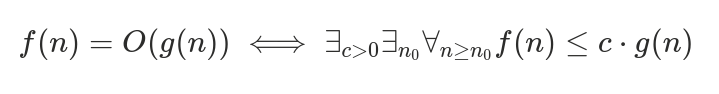
Big Theta Notation (Θ(g(n)))
Same rank of order.
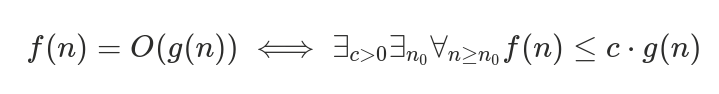
Divide and Conquer
A method where a problem is divided into smaller sub-problems such that it is easy to reconstruct the solution from the sub-solutions.
Positional Statistics
The k-th positional statistic in a sequence is the k-th smallest (or largest) element in the sequence.
Skipping search Algorithm Time complexity
W(len)=k1⋅Θ(len)
Skipping search average Time complexity
W(len)=k1⋅Θ(len)
Skipping search Algorithm Space complexity
O(1)
What is the optimal choice of K in Skipping search?
Optimal choice for k is square root of len.
Binary Search Time complexity
W(len)=Θ(log2(len))
Binary Search Average time complexity:
A(len)=Θ(log2(len))
Binary Search Space complexity:
S(len)=O(1)
What is the idea of Hoare’s positional statistics algorithm?
Running the partition procedure until the element in question won’t find its place
Hoare’s algorithm time complexity
O(n)
Hoare’s algorithm Average time complexity:
O(n)
Partition Procedure Time complexity:
W(n)=Θ(n)
Partition Procedure Average time complexity:
W(n)=Θ(n)
Partition Procedure Space complexity:
S(n)=O(1)
Selection Sort Time complexity:
W(len)=Θ(len^2)
Selection Sort Average time complexity:
A(len)=Θ(len^2)
Selection Sort Space complexity:
O(1)
Insertion Sort Time complexity:
W(n)=Θ(n2)
Insertion Sort Average Time complexity:
A(n)=Θ(n2)
Insertion Sort Space complexity:
O(1)
what is the worst case complexity of a search in an AVLHow much of acceleration can binary search give to the insertion sort algorithm?
It gives it acceleration by finding the right place for insertion in logarithmic time, but the complexity still is O(n2)
Merge Sort Time complexity:
W(len)=Θ(len⋅log(len))
Merge Sort Average time complexity:
A(len)=Θ(len⋅log(len))
Merge Sort Space complexity:
Using arrays: S(n)=Θ(n).
Using linked lists: S(n)=O(1) (neglecting recursion).
Stability of a sorting algorithm
A sorting algorithm is stable if it preserves the original order of ties (elements of the same value).
Linear-Logarithmic Bound
The best possible average time complexity for comparison-based sorting algorithms is Θ(nlogn).
QuickSort Time complexity:
W(n)=Θ(n2) (Pessimistic, e.g., already sorted data).
QuickSort Average time complexity:
A(n)=Θ(n⋅log(n)).
QuickSort Space complexity:
Pessimistic O(n) (linear) due to recursion.
Can be improved to Θ(log(n)) by implementing one recursive call iteratively.
CountSort Time complexity:
W(n,m)=Θ(2n+m)
CountSort Average time complexity:
W(n,m)=Θ(2n+m)
CountSort Space complexity:
S(n,m)=Θ(n+m)
What is the sense of master’s theorem?
It can represent time complexity of a recurrent algorithm that
divides a problem to a sub-problems, each of size n /b and then
merges the sub-solutions with the additional complexity
described by f (n )
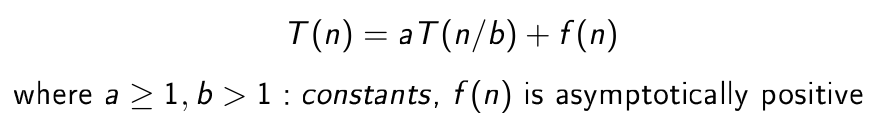
What are the 3 cases of the Master’s Theorem?
image
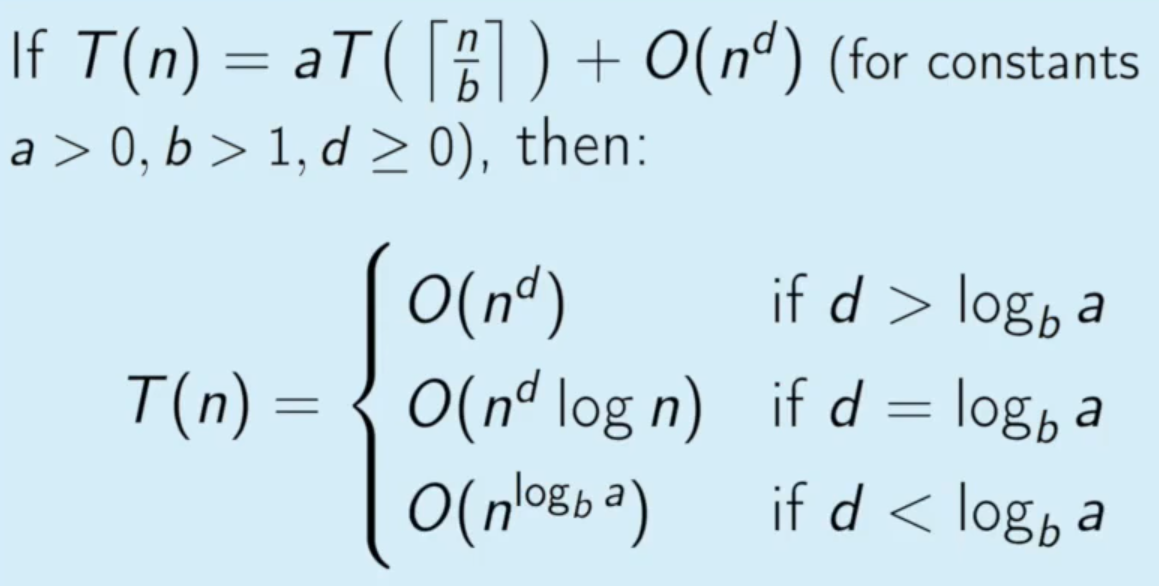
Abstract Data Type (ADT)
A mathematical model of a data structure that specifies the type of data stored, the operations supported, and the parameters/results of these operations. It separates the interface (what it does) from the implementation (how it does it).
Static Array
A fixed-size sequence of elements stored in contiguous memory.
Dynamic Array
An array that can resize itself when it becomes full.
Linked List:
A sequence of elements (nodes) where each node contains data and a reference (link) to the next node.
Stack
A LIFO (Last-In, First-Out) container.
Queue
A FIFO (First-In, First-Out) container.
Dequeue
a doubly-linked queue
What are the operations on a Singly-Linked List?
Access (at index): Θ(n)
Insert/Delete (at beginning): Θ(1)
Insert/Delete (after a known node): Θ(1)+search
Search: Θ(n)
isEmpty
first
last
insertAfter (insertBefore)
moveAfter (moveBefore)
removeAfter (removeBefore)
pushBack ( pushFront )
popBack ( popFront )
concat
splice
size
fi ndNext
What are the operations on a Doubly-Linked List?
Access (at index): Θ(n)
Insert/Delete (at beginning/end): Θ(1)
Insert/Delete (at known node): Θ(1)+search
Search: Θ(n)
What are the operations on a Stack?
Push: Θ(1)
Pop: Θ(1)
Top (Peek): Θ(1)
What are the operations on a Queue?
Enqueue: Θ(1)
Dequeue: Θ(1)
Priority Queue
An ADT where each element has a "priority". Elements with higher priority are served before elements with lower priority.
Binary Heap
A complete binary tree that satisfies the heap property:
Max-Heap Property: The key of every node is greater than or equal to the keys of its children.
Min-Heap Property: The key of every node is less than or equal to the keys of its children.
Complete Binary Tree
A binary tree where all levels are fully filled except possibly the last, which is filled from left to right.
What is the Up-Heap (Sift-Up) operation and what is its time complexity?
Restores heap property after insertion at the bottom. Swaps the node with its parent if the node is larger.
Time Complexity: Θ(log n)
What is the Down-Heap (Sift-Down) operation and what is its time complexity?
Restores heap property after replacing the root. Swaps the node with the lesser/larger (depending whether it is a min- or a max-heap) of its children if the node is smaller.
Time Complexity: Θ(log n)
how does Insert work in heaps and what is its time complexity?
Insert new node at the end and upheap
Time Complexity: Θ(log n)
how does Delete root (either DelMin or DelMax depending on whether it is a min- or a max-heap) work in heaps and what is its time complexity?
Move the last element of the heap to the root, delete the last element (‘cause it is redundantly in the end of the heap after assigning its value to the root) and downheap the new root
Time Complexity: Θ(log n)
What is a fast-construct procedure for a heap?(Floyd's Algorithm)
Constructs a heap from an unsorted array by calling
downHeapon all non-leaf nodes starting from the bottom.for(i = n/2; i > 0; i--) downHeap(i)
Dictionary (Map/Associative Array)
An ADT that stores Key-Value pairs and supports insert, delete, and search (find) operations by key.
Hash Function
A function that maps keys to indices in a hash table. Ideally, it distributes keys uniformly.
Collision
When two different keys hash to the same index.
Binary Search Tree (BST)
A binary tree where for every node, keys in the left subtree are smaller, and keys in the right subtree are larger.
Balanced BST/AVL:
A BST that automatically maintains height O(log n) (e.g., AVL, Red-Black Trees).
What is a BST (binary search tree)?
a tree, nodes of which have max of 2 children and left child is less than the parent and right child is bigger than the parent
what are BST operations and their complexities?
Search, Insert, Delete, Min, Max, Successor, Predecessor.
All operations depend on the height
hof the tree.Average Case (Random): Θ(log n)
Pessimistic Case (Skewed/Path): Θ(n)
what are the operations on a BALANCED BST?
The same that for BST:
Search, Insert, Delete, Min, Max, Successor, Predecessor.
But with pessimistic time complexity of O(log n)
How do we deal with collisions in a Hash Map?
Chaining: Each bucket contains a list of elements.
Open Addressing: Find another slot using a probe sequence (Linear, Quadratic, Double Hashing).
What is time complexity of operation on hash tables?
Search/Insert/Delete (Average): Θ(1)
Search/Insert/Delete (Pessimistic): Θ(n) (All keys collide)
Graph G = (V, E)
A set of vertices V and edges E.
Directed Graph (Digraph)
Edges have direction (ordered pairs).
Undirected Graph
Edges have no direction or both directions depending on the interpretation (unordered pairs).
Weighted Graph
Edges have associated values (weights).
Path
A sequence of vertices connected by edges.
Cycle
A path that starts and ends at the same vertex.
Connected Graph:
There is a path between every pair of vertices
A directed graph is weakly connected ⇔ for any pair of its vertices v,w there exists undirected path from v,w (i.e. the directions of arcs can be ignored)
A directed graph is stronlgy connected ⇔ for any pair of its vertices v,w there exists a directed path from v to w.
Tree
A connected acyclic undirected graph.
Degree (deg(v))
Number of edges incident to v. In directed graphs: in-degree and out-degree.
Simple graph:
a graph where there are no self-loops (edges or arcs of the form (v , v )).
Multi-graph:
a graph with multiple edges between the same pair of vertices
simple path:
no repeated edges (arcs)
elementary path:
no repeated vertices
reflexive relation:
self-loop on each vertex
symmetric relation
undirected graph or always mutual arcs
transitive relation
for any path there is a “short” arc
anti-symmetric relation
no mutual arcs, possible self-loops inverse of the relation: each arc is inversed
Strongly connected component:
a maximal subgraph that is strongly connected
Weakly connected component:
a maximal subgraph that is weakly connected
Forest
is a graph that does not contain cycles (but does not have to be connected). Basically a bunch of trees, hence the name
A rooted tree
is a tree with exactly one distinguished node called its root.
depth of a vertex
distance from the root.
empty graph
some vertices, no edges
full graph
a simple graph of n vertices and all possible edges
DAG
Directed Acyclic Graph
A sparse graph:
a graph with a number of edges that is significantly less than the maximum